Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WH Questions
Uploaded by
Carlos Andrés Martínez SernaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WH Questions
Uploaded by
Carlos Andrés Martínez SernaCopyright:
Available Formats
Wh questions (Question Words)
Types of questions
There are two types of questions:
Yes or no questions Wh questions
Question words
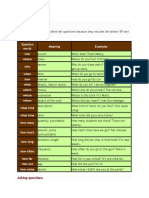
Question words are also called wh questions because they include the letters 'W' and 'H'. Question words who where why when how what which whose whom what kind person place reason Meaning Examples Who's that? That's Nancy. Where do you live? In Boston Why do you sleep early? Because I've got to get up early When do you go to work? At 7:00 How do you go? By car What do you do? I am an engineer Which one do you prefer? The red one. Whose is this book? It's Alan's. Whom did you meet? I met the manager. What kind of music do you like? I like quiet songs
time manner object, idea or action choice possession object of the verb description
what time how many
Time quantity (countable)
What time did you come home? How many students are there? There are twenty. How much time have we got? Ten minutes
how much
amount, price (uncountable) duration, length
how long
How long did you stay in that hotel? For two weeks. How often do you go to the gym? Twice a week. How far is your school? It's one mile far. How old are you? I'm 16. How come I didn't see at the party?
how often how far how old how come
frequency
distance Age reason
Asking questions
1.If you ask about the subject of the sentence, simply add the question word at the beginning: Example: James writes good poems. Who writes good pems?
2.If you ask about the predicate of the sentence (the part of a sentence which contains the verb and gives information about the subject), there are three options:
If there is a helping (auxilary) verb that precedes the main verb ( foe example, can, is, are, was, were, will, would...), add the question word and invert the subject and the helping (auxilary) verb. Examples: He can speak Chinese. What can he speak? They are leaving tonight. When are they leaving?
If you ask about the predicate and there is no helping (auxilary) verb and the verb is "to be", simply add the question verb and invert the subject and the verb. Example: The play was interesting. How was the play?
If there is no helping (auxilary) verb in the the predicate and the main verb is not "to be", add the auxilary "do" in the appropriate form. Examples: They go to the movies every Saturday. Where do they go to the movies? He wakes up early. When does he wake up? They sent a letter. What did they send?
You might also like
- Present Simple 04Document1 pagePresent Simple 04maestromiguelinglesNo ratings yet
- Intonation and Its ComponentsDocument2 pagesIntonation and Its ComponentsНастя КононNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice ExerciseDocument3 pagesActive and Passive Voice ExerciseKathy KhooNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Grade X Adjective in SeriesDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Grade X Adjective in SeriesLlyanne DeeNo ratings yet
- Giao An Tieng Anh Lop 8 Moi Thi Diem Tron Bo PDFDocument379 pagesGiao An Tieng Anh Lop 8 Moi Thi Diem Tron Bo PDFThành ĐạtNo ratings yet
- First Second Conditional Board Game PDFDocument2 pagesFirst Second Conditional Board Game PDFMaricel Potot RiveroNo ratings yet
- Teaching Listening and SpeakingDocument23 pagesTeaching Listening and SpeakingMa. Andrea MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Adjectives: Adjective OrderDocument6 pagesAdjectives: Adjective Ordersnapy shutNo ratings yet
- Talking About The Future Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesTalking About The Future Lesson PlanAdriana Neagoe100% (2)
- ConditionalsDocument2 pagesConditionalsunutulmazNo ratings yet
- Form and Comparison of AdverbsDocument4 pagesForm and Comparison of AdverbsCriss CristinaNo ratings yet
- Language Differentiated Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLanguage Differentiated Lesson Planapi-280553324No ratings yet
- English Grammar Summary: Omission of Information, Reported Speech, Expressing Facts, Hypotheses and Neutral StatementsDocument4 pagesEnglish Grammar Summary: Omission of Information, Reported Speech, Expressing Facts, Hypotheses and Neutral StatementsGabbey Mendoza100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Entertainment 10th GradeDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Entertainment 10th Gradeandreivanesa100% (2)
- English Lesson Plan Phrasal VerbsDocument2 pagesEnglish Lesson Plan Phrasal VerbsSarah EttaNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs in The Past Simple Tense (Gap-Fill)Document1 pageIrregular Verbs in The Past Simple Tense (Gap-Fill)Derry RiccardoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: GETTING STARTED - My Favourite Salad: Unit 7: Recipes and Eating HabitsDocument36 pagesLesson 1: GETTING STARTED - My Favourite Salad: Unit 7: Recipes and Eating HabitsNguyệt HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Vobulary Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesVobulary Lesson Planapi-274517519No ratings yet
- History of The English Language: Inflectional Simplicity QuestionsDocument2 pagesHistory of The English Language: Inflectional Simplicity QuestionsJR VideosNo ratings yet
- Superlative and Comperative DegreeDocument4 pagesSuperlative and Comperative DegreeAyu WulandariNo ratings yet
- Articles & DeterminersDocument29 pagesArticles & DeterminersAsep Deris AriantoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Unit 1 (Week 1 - MC4) : Flashcard: Picture Flashcards of Family Tree 1 &2Document36 pagesLesson Plan Unit 1 (Week 1 - MC4) : Flashcard: Picture Flashcards of Family Tree 1 &2khanhNo ratings yet
- Adjectives Ending in ED and INGDocument6 pagesAdjectives Ending in ED and INGRis NaryantoNo ratings yet
- (Ngoại Ngữ) Đề CươngDocument41 pages(Ngoại Ngữ) Đề CươngSammy VõNo ratings yet
- Listening A2 All DocumentsDocument12 pagesListening A2 All DocumentsBhavin Patel0% (1)
- Teaching Language ConstructionDocument5 pagesTeaching Language ConstructionManyu RadjabliNo ratings yet
- Meaning & Use: When Do We Use The Tense? We Use TheDocument13 pagesMeaning & Use: When Do We Use The Tense? We Use TheKynnel JuliettNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan QuatifiersDocument4 pagesLesson Plan QuatifiersLatifah RimaNo ratings yet
- English Final EditDocument112 pagesEnglish Final EditSanathNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Defining and Non Relative Clauses XII IDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Defining and Non Relative Clauses XII IDina PopoviciNo ratings yet
- Preposition Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesPreposition Lesson Planapi-248341220No ratings yet
- ADA 3. Guía Educativa.Document16 pagesADA 3. Guía Educativa.Angel Jafet Us TecNo ratings yet
- Nouns PresentationDocument44 pagesNouns PresentationIvan Jr100% (1)
- Going To Will Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesGoing To Will Lesson PlanIflazi Art100% (1)
- Determiners in EnglishDocument27 pagesDeterminers in EnglishSajadAbdaliNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech ExerciseDocument3 pagesReported Speech ExerciseGema HanaNo ratings yet
- Example Lesson Plan 1Document13 pagesExample Lesson Plan 1EKA RUSMAWATY BINTI SUJAKNo ratings yet
- The Present Simple Tense: Zion LanguagesDocument23 pagesThe Present Simple Tense: Zion LanguagesZion Languages100% (1)
- A Lesson Plan On Present TenseDocument2 pagesA Lesson Plan On Present TenseSharmaine MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Lexicology. Lesson 2. The WordDocument23 pagesLexicology. Lesson 2. The WordStella GuțuNo ratings yet
- SPEAKING - Ur-Harmer-ScrivenerDocument20 pagesSPEAKING - Ur-Harmer-ScrivenerMiss Abril0% (1)
- Auxiliary VerbDocument18 pagesAuxiliary VerbKinkin MatJinNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Noun Possessive CaseDocument10 pages2.1. Noun Possessive CaseAna DerilNo ratings yet
- There Isthere Are Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesThere Isthere Are Lesson PlanMadalina AndronacheNo ratings yet
- Presentation (Count, Noncount)Document33 pagesPresentation (Count, Noncount)kuanzc100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson PlansamiraNo ratings yet
- PassivesDocument7 pagesPassivesredhornNo ratings yet
- 7 Future TensesDocument2 pages7 Future TensesFikru0No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English - FinalDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in English - FinalRONEL GALELANo ratings yet
- Adverbs of FrequencyDocument2 pagesAdverbs of Frequencyinmacarmonam1700100% (10)
- CPD Reading and ListeningDocument37 pagesCPD Reading and ListeningNadia KniftonNo ratings yet
- Simple Present StructureDocument9 pagesSimple Present StructureCarlos Esteban Alvarez LandaNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument7 pagesModal VerbsAna Angeleska-SpiroskaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Relative Clause Junior Secondary1Document6 pagesLesson Plan Relative Clause Junior Secondary1Omar BelazriNo ratings yet
- The Ethnography of Speaking and Structure of ConversationDocument12 pagesThe Ethnography of Speaking and Structure of ConversationAna Maria Garcia Rodriguez100% (1)
- Example Lesson Plan Name Student Profile: Topic: Aims::: Hercules Chipps TravelDocument5 pagesExample Lesson Plan Name Student Profile: Topic: Aims::: Hercules Chipps TravelLiz BiggsNo ratings yet
- 0 Eating Out Lesson PlanDocument4 pages0 Eating Out Lesson PlanManastirea ContNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect Tense 111Document3 pagesPast Perfect Tense 111Nur HafezaNo ratings yet
- Asking QuestionsDocument2 pagesAsking QuestionsAndraa AndraNo ratings yet
- WH QuestionsDocument2 pagesWH QuestionscarmenNo ratings yet
- A Review of Verb Tense: Simple FormsDocument9 pagesA Review of Verb Tense: Simple FormsCarlos Andrés Martínez SernaNo ratings yet
- Forming Comparative and Superlative AdjectivesDocument10 pagesForming Comparative and Superlative AdjectivesJaime CaroNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument3 pagesSimple Present TenseCarlos Andrés Martínez SernaNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Los Andes: Simple Present VS Present Progressive (GUIDE)Document3 pagesLiceo de Los Andes: Simple Present VS Present Progressive (GUIDE)Carlos Andrés Martínez SernaNo ratings yet
- Guide - Grade 9thDocument2 pagesGuide - Grade 9thCarlos Andrés Martínez SernaNo ratings yet
- Q&A FractureDocument13 pagesQ&A FractureRed JimenoNo ratings yet
- Mico - Hydraulic Power Brake Systems For ForkliftsDocument4 pagesMico - Hydraulic Power Brake Systems For ForkliftsJenner Volnney Quispe Chata100% (1)
- ReportDocument6 pagesReportLâmViênNo ratings yet
- Melo V PeopleDocument1 pageMelo V PeoplejjangNo ratings yet
- 1 SAP HCM Overview - IntroductionDocument32 pages1 SAP HCM Overview - IntroductionashwiniNo ratings yet
- INSTRUCTIONS FOR USOL PRIVATE REAPPEAR DE January 2022Document4 pagesINSTRUCTIONS FOR USOL PRIVATE REAPPEAR DE January 2022RaghavNo ratings yet
- Onechanbara - Bikini Samurai Squad Game GuideDocument83 pagesOnechanbara - Bikini Samurai Squad Game GuideStefan RoscaNo ratings yet
- CALDER New Research On Low-Frequency Membrane AbsorbersDocument11 pagesCALDER New Research On Low-Frequency Membrane AbsorbersAndre VareNo ratings yet
- Optical CamouflageDocument27 pagesOptical CamouflageAlliluddin ShaikNo ratings yet
- Criminal InvestigationDocument11 pagesCriminal Investigationjohn martin urbinaNo ratings yet
- South WestDocument1 pageSouth WestDarren RadonsNo ratings yet
- UNIX Introduction 1Document18 pagesUNIX Introduction 1Akash SavaliyaNo ratings yet
- Dossier 015 enDocument5 pagesDossier 015 enAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- The Spokesman Weekly Vol. 32 No. 39 May 30, 1983Document12 pagesThe Spokesman Weekly Vol. 32 No. 39 May 30, 1983SikhDigitalLibraryNo ratings yet
- Alcatel 9400 PDFDocument4 pagesAlcatel 9400 PDFNdambuki DicksonNo ratings yet
- E9d30c8 4837smartDocument1 pageE9d30c8 4837smartSantoshNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research Chapter 1-5Document16 pagesQualitative Research Chapter 1-5Mikhaela Centeno100% (1)
- Class 11 Assignment 10 (Prac)Document3 pagesClass 11 Assignment 10 (Prac)9crollno14bhewensagarsahuNo ratings yet
- Students List - All SectionsDocument8 pagesStudents List - All SectionsChristian RiveraNo ratings yet
- Resume For Singapore Spass Civil EngineerDocument8 pagesResume For Singapore Spass Civil EngineerArul SD100% (1)
- The Lion and The Boar Story EnglishDocument2 pagesThe Lion and The Boar Story EnglishKemal AmarullahNo ratings yet
- Determining The Value of The Acceleration Due To Gravity: President Ramon Magsaysay State UniversityDocument12 pagesDetermining The Value of The Acceleration Due To Gravity: President Ramon Magsaysay State UniversityKristian Anthony BautistaNo ratings yet
- RagragsakanDocument6 pagesRagragsakanRazel Hijastro86% (7)
- Moatiz Riaz - Area Sales ManagerDocument1 pageMoatiz Riaz - Area Sales ManagerMoatiz RiazNo ratings yet
- Ef3 Englisch 04 14 08052014Document20 pagesEf3 Englisch 04 14 08052014PiPradoNo ratings yet
- Case Digest 2 S.C. MEGAWORLD CONSTRUCTIONDocument3 pagesCase Digest 2 S.C. MEGAWORLD CONSTRUCTIONRomualdo CabanesasNo ratings yet
- A Feasibility/Project Study OnDocument14 pagesA Feasibility/Project Study OnWilson Domingo LazarteNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Waskaye nicolasNo ratings yet
- West Bengal State University Department of EnglishDocument33 pagesWest Bengal State University Department of Englishnandan yadavNo ratings yet
- Arizona History and Social Science StandardsDocument57 pagesArizona History and Social Science StandardsKJZZ PhoenixNo ratings yet