Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fourth Ventricle
Uploaded by
mumun_shidaeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fourth Ventricle
Uploaded by
mumun_shidaeCopyright:
Available Formats
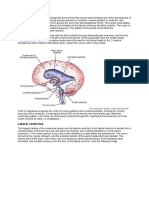
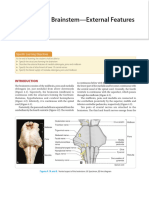
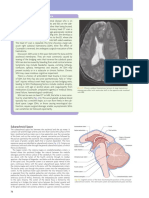
Fourth ventricle.
It is the cavity of the hindbrain, lying between the cerebellum posteriorly and the pons and medulla oblongata anteriorly. The fourth ventricle is a tent shaped cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid. It is lined with ependyma and continuous above with cerebral aqueduct and below with central canal of medulla oblongata. On each size, a narrow prolongation, the lateral recess, projects around the brainstem; its lateral aperture (forame of Luschka) lies below the cerebellar flocculus (small lobe of
the cerebellum at the posterior border of the middle cerebellar peduncle).
Boundaries. Floor Called rhomboid fossa. It is formed by the dorsal surface of the pons and upper part of the medulla. Thus, the floor of the fourth ventricle is divided into pontine and medullary parts separated by the stria medullaris. A. Pontine part. This part presents a depression called superior fovea that separates the medial eminence from the upper vestibular area. The lower part of the medial eminence present a prominent elevation called facial colliculus. This colliculus is produced by the abducent nucleus surrounded by the facial nerve fibers. The upper vestibular area is produced by the lateral and superior vestibular nuclei. B. Medullary part. This area presents an inverted V - shaped depression called inferior fovea which divides into three trigones from medial to lateral. Hypoglossal trigone that overlies the hypoglossal nucleus. Vagal trigone that overlies the dorsal nucleus of the vagus Vestibular trigone ( inferior vestibular area ) that overlies the inferior and medial vestibular nuclei
Lateral wall i. ii. Roof i. ii. iii. Upper part : superior medullary velum between the two superior cerebellar peduncles. Middle part : part of the cerebellum Lower part L inferior medullary velum between the two inferior cerebellar peduncles. Upper part : superior cerebellar peduncles. Lower part : inferior cerebellar peduncles as well as gracile and cuneate tubercles.
Recesses of the 4th ventricle i. ii. Two lateral recesses Dorsal or cerebellar recess
Communication of the 4th ventricle i. ii. iii. With the 3rd ventricle through the aqueduct of sylvius With central canal of the spinal cord With the two subarachnoid space through a. Two lateral foramina of Luschka b. One median foramen of Magendie.
You might also like
- The Fourth VentricleDocument16 pagesThe Fourth VentricleHiraNo ratings yet
- The Fourth VentricleDocument4 pagesThe Fourth Ventriclemanojchouhan2014No ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy of Fourth VentricleDocument16 pagesGross Anatomy of Fourth VentricleRafique AhmedNo ratings yet
- Brain Ventricles: (Rabbia Yousaf) Pharm-D Rashid Latif College of PharmacyDocument29 pagesBrain Ventricles: (Rabbia Yousaf) Pharm-D Rashid Latif College of PharmacyShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- The Ventricular SystemDocument6 pagesThe Ventricular SystemM Arsalan TariqNo ratings yet
- Brain VentriclesDocument23 pagesBrain VentriclesAndrei Scripcaru100% (1)
- Neuroanatomy 11: Brain Ventricles: The Anterior HornDocument3 pagesNeuroanatomy 11: Brain Ventricles: The Anterior HornstuffNo ratings yet
- Ant 325materialDocument13 pagesAnt 325materialDestiny BlissNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomia Part 2Document35 pagesNeuroanatomia Part 2farzana25No ratings yet
- Lateral Ventricles: The Ventricular System of The Human BrainDocument4 pagesLateral Ventricles: The Ventricular System of The Human BrainMarNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Gross Features of HindbrainDocument26 pagesNervous System: Gross Features of HindbrainShere Almansuori100% (1)
- 48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoDocument28 pages48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoRichelle IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Medulla Oblongata: Mohsen Alenezi Fawaz AlreshedyDocument22 pagesMedulla Oblongata: Mohsen Alenezi Fawaz AlreshedyMhsnNo ratings yet
- Ventricles: Dr. Katharina Kian R. Demerre - Bacolod PT 21Document70 pagesVentricles: Dr. Katharina Kian R. Demerre - Bacolod PT 21Cyril Jay G. OrtegaNo ratings yet
- 72 HR ReviewerDocument8 pages72 HR ReviewerAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Brain StemDocument19 pagesBrain StemSajid HussainNo ratings yet
- Ventricles of BrainDocument30 pagesVentricles of BrainbegeerizikNo ratings yet
- BRAINSTEMDocument17 pagesBRAINSTEMaroosadilbar27No ratings yet
- Ventricles of The Brain and CSF CirculationDocument14 pagesVentricles of The Brain and CSF Circulationmhr27112002No ratings yet
- Brainstem: Medulla OblongataDocument130 pagesBrainstem: Medulla OblongataBhawana BhatodiyaNo ratings yet
- Brainstem - Activity SheetDocument12 pagesBrainstem - Activity SheetlindaNo ratings yet
- Brain Stem: Rabbia Yousaf (Pharm-D) Rashid Latif College of PharmacyDocument30 pagesBrain Stem: Rabbia Yousaf (Pharm-D) Rashid Latif College of PharmacyShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy Draft For PBLDocument10 pagesGross Anatomy Draft For PBLadaumedNo ratings yet
- Embryology Course V - Body Cavities, Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesEmbryology Course V - Body Cavities, Respiratory SystemRawa MuhsinNo ratings yet
- Brain Stem Part 1Document6 pagesBrain Stem Part 1ZED AlanaziNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The BrainDocument32 pagesBlood Supply of The BrainShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Thoracic cavity & contents: Thorax Unit Lecture 3 & 4 مسعلأا ليلج رديح .دDocument18 pagesThoracic cavity & contents: Thorax Unit Lecture 3 & 4 مسعلأا ليلج رديح .دMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Brain StemDocument47 pagesBrain StemSorina IspasNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument12 pagesUntitled DocumentambiliNo ratings yet
- Brainstem (Pons, Medulla, Midbrain) : Dr. MariaDocument23 pagesBrainstem (Pons, Medulla, Midbrain) : Dr. MariaMuhammad Mustaqeem100% (1)
- DR Sakher Al-Khaderi Consultant Radiologist AmcDocument85 pagesDR Sakher Al-Khaderi Consultant Radiologist AmcionululNo ratings yet
- Brain Stem FullDocument25 pagesBrain Stem FullCosplay AccountNo ratings yet
- ThoraxDocument40 pagesThoraxapi-324160601100% (1)
- Neuroanatomy 2Document10 pagesNeuroanatomy 2ahmdalhthrh10No ratings yet
- Var 29 - 30Document4 pagesVar 29 - 30Honey BabaNo ratings yet
- Neuro Anatomy of BrainDocument79 pagesNeuro Anatomy of BrainSruthi SruthiNo ratings yet
- 48-Hour Chick ReviewerDocument5 pages48-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatrice100% (1)
- Middle Cranial FossaDocument5 pagesMiddle Cranial Fossaalexandra663No ratings yet
- Meninges PPT NPDocument21 pagesMeninges PPT NPEmshellr RomeNo ratings yet
- Aa AnatomyDocument109 pagesAa AnatomyshailendraNo ratings yet
- Aprimaion Angulo PontocerebelosoDocument64 pagesAprimaion Angulo PontocerebelosoLuis Carlos Avellaneda CurchoNo ratings yet
- LAB EXERCISE 4 - 4 MM Frog EmbryoDocument7 pagesLAB EXERCISE 4 - 4 MM Frog EmbryoGerald Angelo DeguinioNo ratings yet
- Attachment 1Document39 pagesAttachment 1wingakira5No ratings yet
- Brainstem (Old Testament)Document19 pagesBrainstem (Old Testament)marizamoraNo ratings yet
- ThoraxDocument29 pagesThoraxapi-249972919No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Meninges Ventricles CerebrospinalfluidDocument120 pagesAnatomy of Meninges Ventricles CerebrospinalfluidSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Ns1 Assignment 2 Meninges Group 1Document4 pagesNs1 Assignment 2 Meninges Group 1Roselle AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Embryology, Gross Anatomy and Histology of Lungs and Pleura: For PC-II Medicine Students By: Zelalem ADocument58 pagesEmbryology, Gross Anatomy and Histology of Lungs and Pleura: For PC-II Medicine Students By: Zelalem AAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Embryology of Body Cavities, Mesenteries and DiaphragmDocument35 pagesEmbryology of Body Cavities, Mesenteries and DiaphragmKankomba MuleyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Personal NoteDocument7 pagesAnatomy Personal NoteShereen Al-ObinayNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument11 pagesBrainBilal MashagebahNo ratings yet
- Nose and Nasal Cavity - 1Document39 pagesNose and Nasal Cavity - 1Sonali SudhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The Respiratory System: The Respiratory Tract Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Principal BronchiDocument47 pagesChapter 3 The Respiratory System: The Respiratory Tract Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Principal Bronchisomebody_maNo ratings yet
- Overview of Visceral Thorax - PleuraDocument33 pagesOverview of Visceral Thorax - PleuraHrishikesh BirjeNo ratings yet
- Case 3 S H: Ubdural AematomaDocument9 pagesCase 3 S H: Ubdural AematomaAndreea LăzăroiuNo ratings yet
- Null 4Document47 pagesNull 4Kenyan MillanNo ratings yet
- Medulla 7Document37 pagesMedulla 7siddharth.roy26587No ratings yet
- Brain StemDocument4 pagesBrain StemHeart Of Ayurveda Beatrice DNo ratings yet
- Ventricles Sub ArachnoidspaceDocument41 pagesVentricles Sub ArachnoidspaceShivaranjani sakthivelNo ratings yet
- Case Study Ucmed 6TH FloorDocument44 pagesCase Study Ucmed 6TH FloorPasay Trisha Faye Y.No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Death and Postmortem ChangesDocument72 pagesChapter 2 Death and Postmortem ChangesdebbytenriNo ratings yet
- Brain AnatomyDocument57 pagesBrain AnatomyCarlo BelazaNo ratings yet
- LMNL Vs UmnlDocument49 pagesLMNL Vs UmnlLohshini ManickavasagamNo ratings yet
- Memory PhysiologyDocument40 pagesMemory PhysiologyAttiqaQureshiNo ratings yet
- ALL Chapter Instructor Guide Fot Therapeutic Communications in Nursing PsychologyDocument237 pagesALL Chapter Instructor Guide Fot Therapeutic Communications in Nursing PsychologyLaurie RNtobe100% (1)
- Brain Thesis StatementDocument5 pagesBrain Thesis Statementzyxnlmikd100% (2)
- Neural Control and Co OrdinationDocument16 pagesNeural Control and Co OrdinationDARSHAN KUMAR TNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Brain Stem: ANA 313 Neuro-Anatomy LectureDocument41 pagesAnatomy of Brain Stem: ANA 313 Neuro-Anatomy LectureSaidu TanimuNo ratings yet
- (MicroB) 3.6 Brainstem LesionsDocument6 pages(MicroB) 3.6 Brainstem Lesionsnelson lopezNo ratings yet
- Function of The BrainDocument16 pagesFunction of The BrainJohn Matthew CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Auditory Brainstem ResponseDocument18 pagesAuditory Brainstem ResponseFree dataNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument21 pagesStrokedalida pekkanNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Practical NeurophysiotherapyDocument379 pagesHandbook of Practical NeurophysiotherapyAlbert Manimtim100% (2)
- What Are The Different Parts of The Brain?: CerebrumDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Different Parts of The Brain?: CerebrumDhez Bertudaso-Morales ManansalaNo ratings yet
- Nerve Tract in Spinal CordDocument30 pagesNerve Tract in Spinal CordirfanzukriNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Extrapyramidal SyndromeDocument50 pagesKuliah Extrapyramidal SyndromePutri Azka RinandaNo ratings yet
- Horner'S Syndrome - : Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationDocument3 pagesHorner'S Syndrome - : Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationVictorija Evania Lucille DeldioNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Testing - PPT 2012Document19 pagesCranial Nerve Testing - PPT 2012ifer_018No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document15 pagesChapter 7Bea SeloterioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of BrainstemDocument66 pagesAnatomy of BrainstemFitria OctavianiNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Circulation DimalNPM Final 051221Document80 pagesCerebral Circulation DimalNPM Final 051221Chok ArgoniaNo ratings yet
- 1to7.2.2020 Discussion QUESTIONS PDFDocument63 pages1to7.2.2020 Discussion QUESTIONS PDFJulyhathul KuraishiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology (Chapter 2)Document8 pagesAbnormal Psychology (Chapter 2)Mavy QueenNo ratings yet
- Tap Ghi Chep 1Document85 pagesTap Ghi Chep 1vutuyen519No ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy and How The Brain WorksDocument1 pageBrain Anatomy and How The Brain Worksdudong borjaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy SemifinalsDocument5 pagesAnaphy SemifinalsRej CosainNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology LectureDocument105 pagesNervous System Anatomy and Physiology LectureButch Dumdum75% (12)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BraineriannajNo ratings yet
- Challenged Child SeminarDocument101 pagesChallenged Child SeminarEr Shah Rukh Qadri100% (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingFrom EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1138)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)