Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cheatsheet 5
Cheatsheet 5
Uploaded by
Klins Tristan OliverOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cheatsheet 5
Cheatsheet 5
Uploaded by
Klins Tristan OliverCopyright:
Available Formats
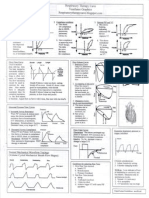
Emotional State: 1. Anxiety/ nervousness: watching every movement; asthma, respiratory failure, hypoxia 2. Depressed: quiet, denial 3.
Anger/ combative/ irritable: electrolyte imbalance 4. Euphoria: drugs, OD 5. Panic: hypoxia, tension pneumothorax, status asthmaticus. A-a Gradient: 1. If normal, hypoxia caused by hypoventilation, consider drug overdose, neuromuscular disorder. 2. If abnormal & SpO2 improves with increased FiO2. Consider PE, pneumothorax, asthma, emphysema, pneumonia, bronchitis, heart failure, congenital heart disease, aging. 3. If abnormal & refractory hypoxemia occurs, hypoxia caused by shunting problem onsider pneumonia, atelectasis, pulmonary edema or ARDS.
Interpreting EKGs: Left Bundle Branch Block: 1. 2 R waves in V5 and V6 2. Cannot diagnose infarct 3. Same as anterior Hemiblock = posterior hemiblock which is also same as biphasicular block Right Bundle Branch Block: 1. 2 R waves in V1 and V2 2. QRS is wide and looks like an M Anterior Hemiblock: 1. Q in lead I and S in III 2. QRS slightly widened 3. Occurs in left anterior descending of RCA with MI and heart disease 4. Causes Right Axis Deviation 5. May be associated with RBBB 6. 50% of posterior MIs Posterior Hemiblock: 1. S in 1 and Q in 3 2. Normal or slightly widened QRS 3. Occurs in Right anterior descending of RCA with MI or heart disease 4. Causes Right Axis Deviation 5. Rule out other causes of RAD 6. Rare, causes AV block, deadly Bifasicular Block: 1. A combination of blocks 2. Anterior Hemiblock + RBBB 3. Posterior Hemiblock + RBBB 4. Anterior Hemiblock + Posterior Hemiblock (also called LBBB) 5. May cause intermittent AV block Right Axis Deviation: 1. QRS negative in lead I 2. QRS positive in AVF 3. QRS negative in AVF and lead I if extreme RAD 4. QRS in V1, V2 isoelectric 5. Slender person with ventricular heart 6. Ventricular hypertrophy 7. Pulmonary disease 8. MI on left side of heart Left Axis Deviation: 1. QRS positive in lead I 2. QRS negative in AVF 3. QRS in V5 and V6 are isoelectric 4. Obese patients 5. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy 6. MI right side of heart
Respiratorytherapycave.blogspot.com 09/08/2009
Adjusting Flow Termination on Vision/Bipap: 1. Start: 25% for adults 1. Higher percentage desired (40%) a. In leak situation b. To reduce auto PEEP 2. Low Percentage desired (10%) a. To maximize tidal volume More EKG interpretations: Left Ventricular Hypertrophy: 1. QRS complexes with exaggerated amplitude both in height and depth 2. S wave in V1 is deep, large R in v5 3. Height of S in V1 + R in V5 =>35 mm 4. T wave inversion in V5 and V6 with a gradual downward slope Hyperkalemia: Flat p waves, wide QRS, peaked T Hypokalemia: Flat T waves, wide QRS, u waves Hypercalcemia: QT interval shortens Hypocalcemia: Prolonged QT interval Digitalis effect: a. PABS early sign 1. Gradual down-sloping of ST segment 2. Low K enhances Digitalis effect Quinidine Effects: (Anti-arrhythmic) 1. Widening of p waves and QRS 2. Often ST depression, prolonged QT 3. Maybe presence of U wave
You might also like
- Cardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med-Surg NUR4Document3 pagesCardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med-Surg NUR4ktfosterfd2095% (99)
- Cardiac DysrhythmiasDocument3 pagesCardiac DysrhythmiasKatherine Santiago92% (62)
- Kaplan & Sadock's Comprehensive Textbook of PsychiatryDocument2 pagesKaplan & Sadock's Comprehensive Textbook of PsychiatryMuhammad Abiyyu Farras0% (2)
- Ventilator Graphics Cheat Sheet (Part 1)Document1 pageVentilator Graphics Cheat Sheet (Part 1)Rick Frea100% (2)
- Ventilator Graphics Cheatsheet (Part 2)Document1 pageVentilator Graphics Cheatsheet (Part 2)Rick Frea100% (2)
- Cardiac Meds ChartDocument1 pageCardiac Meds ChartCharlotte Louise75% (4)
- Capnography Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCapnography Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (1)
- Cheat Sheet 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet 1Rick Frea100% (10)
- Cheetsheet 6Document1 pageCheetsheet 6Rick Frea92% (12)
- ABG Made EasyDocument10 pagesABG Made EasyMayer Rosenberg100% (38)
- Lab ValuesDocument3 pagesLab Valuessurviving nursing school100% (1)
- Cheetsheet 6Document1 pageCheetsheet 6Rick Frea92% (12)
- Cheat Sheet 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet 1Rick Frea100% (10)
- Cheatsheet 3Document1 pageCheatsheet 3Rick Frea100% (1)
- Lab CheatsheetDocument1 pageLab CheatsheetRick Frea86% (7)
- Vent Modes ChartDocument1 pageVent Modes Chartladyhavocinc100% (1)
- Cheatsheet 3Document1 pageCheatsheet 3Rick Frea100% (1)
- Lab CheatsheetDocument1 pageLab CheatsheetRick Frea86% (7)
- Lab CheatsheetDocument1 pageLab CheatsheetRick Frea86% (7)
- Haemodynamic Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesHaemodynamic Pocket GuideDarryl Betts85% (13)
- Basic Arrhythmia RulesDocument3 pagesBasic Arrhythmia Rulesgreenflames0997% (30)
- Schaum's Outline of Emergency Nursing: 242 Review QuestionsFrom EverandSchaum's Outline of Emergency Nursing: 242 Review QuestionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- All Obgyn Osce (2) Good Book For OsceDocument75 pagesAll Obgyn Osce (2) Good Book For OsceMohamed Hassan91% (47)
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsFrom EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Cheatsheet 2Document1 pageCheatsheet 2Rick Frea86% (7)
- Acid-Base WorksheetDocument2 pagesAcid-Base WorksheetMayer Rosenberg100% (18)
- Cardiac Study GuideDocument11 pagesCardiac Study Guidejenwiley318096% (74)
- Cardiac Med ChartsDocument6 pagesCardiac Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotes100% (15)
- Critical Care NoteDocument10 pagesCritical Care NoteHanis Rozib99% (70)
- Lab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Document9 pagesLab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Linsey Bowen75% (8)
- Cheatsheet 2Document1 pageCheatsheet 2Rick Frea86% (7)
- Cheatsheet 4Document1 pageCheatsheet 4Rick FreaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Diseases Cheat SheetDocument1 pageRisk For Diseases Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (5)
- Types of Assisted VentilationDocument1 pageTypes of Assisted VentilationJerry G100% (3)
- (SVR) Measures Systemic Resistance and Reflects Afterload of Left Ventricle Average Perfusion of A Cardiac CycleDocument1 page(SVR) Measures Systemic Resistance and Reflects Afterload of Left Ventricle Average Perfusion of A Cardiac Cyclesarah_stover_1100% (4)
- Ventilation Cheat SheetDocument1 pageVentilation Cheat Sheetlizzy59683% (6)
- RT ConsultDocument5 pagesRT ConsultRick Frea100% (2)
- Ventilation For DummiesDocument39 pagesVentilation For Dummiessuyalamit100% (6)
- Respiratory DysfunctionDocument1 pageRespiratory Dysfunctionoxidalaj100% (3)
- RT Consult Form Side #2Document1 pageRT Consult Form Side #2Rick Frea100% (1)
- Emergency Room Aerosolized Medication ProtocolDocument3 pagesEmergency Room Aerosolized Medication ProtocolRick Frea67% (3)
- Neo-Peds Intubation Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNeo-Peds Intubation Cheat SheetRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Calculations Study GuideDocument6 pagesCritical Care Calculations Study GuideAja Blue100% (2)
- Respiratory Care Review: An Intense Look at Respiratory Care Through Case StudiesFrom EverandRespiratory Care Review: An Intense Look at Respiratory Care Through Case StudiesNo ratings yet
- Risk For Diseases Cheat SheetDocument1 pageRisk For Diseases Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (5)
- RT Consult Form Side #2Document1 pageRT Consult Form Side #2Rick Frea100% (1)
- RT Consult Form Side #1Document2 pagesRT Consult Form Side #1Rick Frea100% (2)
- RT ConsultDocument5 pagesRT ConsultRick Frea100% (2)
- Cheatsheet 4Document1 pageCheatsheet 4Rick FreaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Room Aerosolized Medication ProtocolDocument3 pagesEmergency Room Aerosolized Medication ProtocolRick Frea67% (3)
- Neo-Peds Intubation Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNeo-Peds Intubation Cheat SheetRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Normal Pediatric RR and HRDocument1 pageNormal Pediatric RR and HRRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument5 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-218813072No ratings yet
- SC Health and Welfare FormDocument4 pagesSC Health and Welfare FormLeandro Tamayo14% (7)
- Fluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsFrom EverandFluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Bonehead Electrocardiography: The Easiest and Best Way to Learn How to Read Electrocardiograms—No Bones About It!From EverandBonehead Electrocardiography: The Easiest and Best Way to Learn How to Read Electrocardiograms—No Bones About It!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- CO2 Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesCO2 Pocket GuideDarryl Betts100% (7)
- Tidal Volumes Cheat SheetDocument1 pageTidal Volumes Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (1)
- ABG InterpretationDocument1 pageABG Interpretationnulall100% (18)
- Critical Care Survival GuideDocument2 pagesCritical Care Survival Guidetringalama100% (4)
- Mechanical Ventilator Management ProtocolDocument3 pagesMechanical Ventilator Management ProtocolRick Frea100% (2)
- Respiratory PathophysDocument1 pageRespiratory PathophysTori IkeharaNo ratings yet
- Inhaler LexiconDocument4 pagesInhaler LexiconRick Frea100% (2)
- Electrolyte CompleteDocument6 pagesElectrolyte CompleteTofan Ana100% (2)
- A Simplified ECG GuideDocument4 pagesA Simplified ECG Guidejalan_z96% (27)
- 100 Essential Drugs1Document8 pages100 Essential Drugs1Matt McGlothlin85% (13)
- FLASH CardsDocument3 pagesFLASH Cardsclarheena100% (2)
- Name That EKG: D:/My Documents/Documents/AIME/Handouts/EKG PracticeDocument5 pagesName That EKG: D:/My Documents/Documents/AIME/Handouts/EKG PracticelcascolanNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Respiratory Distress GuidelinesDocument1 pagePediatric Respiratory Distress GuidelinesRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Static Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetDocument1 pageStatic Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument9 pagesPulmonary Function TestsRick Frea0% (1)
- EKG Rhythms2 PDFDocument7 pagesEKG Rhythms2 PDFAya KamajayaNo ratings yet
- Adjusting Ventilator SettingsDocument7 pagesAdjusting Ventilator SettingsSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Therapy: 66 Test Questions Student Respiratory Therapists Get Wrong Every Time: (Volume 1 of 2): Now You Don't Have Too!: Respiratory Therapy Board Exam Preparation, #1From EverandRespiratory Therapy: 66 Test Questions Student Respiratory Therapists Get Wrong Every Time: (Volume 1 of 2): Now You Don't Have Too!: Respiratory Therapy Board Exam Preparation, #1No ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesFrom EverandAdvanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- RT!: Reflections on a Career in Respiratory TherapyFrom EverandRT!: Reflections on a Career in Respiratory TherapyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Inhaler LexiconDocument4 pagesInhaler LexiconRick Frea100% (2)
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument9 pagesPulmonary Function TestsRick Frea0% (1)
- Mechanical Ventilator Management ProtocolDocument3 pagesMechanical Ventilator Management ProtocolRick Frea100% (2)
- Tidal Volumes Cheat SheetDocument1 pageTidal Volumes Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (1)
- RsbiDocument1 pageRsbiRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Respiratory Distress GuidelinesDocument1 pagePediatric Respiratory Distress GuidelinesRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Static Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetDocument1 pageStatic Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Resuscitation ProgramDocument6 pagesNeonatal Resuscitation ProgramRick Frea100% (5)
- Neonatal Ventilator Vent Set-Up CheatsheetDocument1 pageNeonatal Ventilator Vent Set-Up CheatsheetRick Frea50% (2)
- Neonatal Ventilator Vent Set-Up CheatsheetDocument1 pageNeonatal Ventilator Vent Set-Up CheatsheetRick Frea50% (2)
- Medicine: Congenital Chloride Losing DiarrheaDocument9 pagesMedicine: Congenital Chloride Losing DiarrheaGabriela PopescuNo ratings yet
- EpistaxisDocument2 pagesEpistaxisScutelnicLiliaNo ratings yet
- Joint Commission International's Essentials of Health Care Quality and Patient SafetyDocument28 pagesJoint Commission International's Essentials of Health Care Quality and Patient Safetyedi100% (2)
- Lesson Plan Genito UrinaryDocument26 pagesLesson Plan Genito UrinaryEllen AngelNo ratings yet
- Final Pharmacology MCQDocument12 pagesFinal Pharmacology MCQSiraj Choudhari0% (1)
- The Digital Journey To Wellness Hospital Selection - Research Studies PDFDocument39 pagesThe Digital Journey To Wellness Hospital Selection - Research Studies PDFAna Paula MargaridoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing: Jessie Daclis, RN, Usrn, MbacDocument110 pagesFundamentals of Nursing: Jessie Daclis, RN, Usrn, MbacAllyza Jane SartigaNo ratings yet
- Patient Monitoring Systems: Suneetha.G Synergy Business SchoolDocument23 pagesPatient Monitoring Systems: Suneetha.G Synergy Business SchoolUsman NaeemNo ratings yet
- Ulkus2Document11 pagesUlkus2Stefanie SuwitaNo ratings yet
- Clinical: GuidelinesDocument58 pagesClinical: Guidelinesdonovandube8235No ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting of PregnancyDocument1 pageNausea and Vomiting of Pregnancypuskesmas ciapusNo ratings yet
- The Hospital Is Dead, Long Live The Hospital! - McKinseyDocument22 pagesThe Hospital Is Dead, Long Live The Hospital! - McKinseyYanto Sandy TjangNo ratings yet
- Entroso Shane Mtlbe Activity#1Document5 pagesEntroso Shane Mtlbe Activity#1Shane EntrosoNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Reactions: Within 24 Hours of TransfusionDocument6 pagesTransfusion Reactions: Within 24 Hours of TransfusionClaudette Jane SoNo ratings yet
- Menopause Daftar PustakaDocument3 pagesMenopause Daftar PustakaMuhammad Izzuddin Abdul JalilNo ratings yet
- Meniere's DiseaseDocument32 pagesMeniere's DiseaseMOISED MOisedm100% (1)
- WORKSHOP No 4Document22 pagesWORKSHOP No 4Yainel RomeroNo ratings yet
- Spanish ACLS Provider Manual ErrataDocument2 pagesSpanish ACLS Provider Manual ErrataurbanincultureNo ratings yet
- Policies and Progressive Programmes of Health, Waterworks and Sanitation Provide A Moral Base and Legitimacy To British Administration in Colonial Ferozepore (Punjab) - A Historical REVIEW, 1895-1947Document10 pagesPolicies and Progressive Programmes of Health, Waterworks and Sanitation Provide A Moral Base and Legitimacy To British Administration in Colonial Ferozepore (Punjab) - A Historical REVIEW, 1895-1947TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Value of MRI-PDFF For Hepatic Steatosis in Patients With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-AnalysisDocument10 pagesDiagnostic Value of MRI-PDFF For Hepatic Steatosis in Patients With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-AnalysisNada Utami PrahastiwiNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Guided Regional Nerve BlocksDocument32 pagesUltrasound Guided Regional Nerve BlocksSiva SankarNo ratings yet
- Psychosexual Service BookletDocument28 pagesPsychosexual Service Bookletgrtbags2302No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Clinical Nursing Skills 8 e 8th Edition 013511473xDocument4 pagesSolution Manual For Clinical Nursing Skills 8 e 8th Edition 013511473xGregoryRussellajwd100% (46)
- CertificateDocument1 pageCertificatemahesh yadavNo ratings yet
- African Horse Sickness GuidelinesDocument6 pagesAfrican Horse Sickness GuidelinesFajarAriefSumarnoNo ratings yet
- Huntingtons Disease BrochureDocument2 pagesHuntingtons Disease Brochureapi-455212625No ratings yet