Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Engineering Portal - Com Calculating Lightning Strike Distance
Uploaded by
vijaydev75Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Engineering Portal - Com Calculating Lightning Strike Distance
Uploaded by
vijaydev75Copyright:
Available Formats
elect rical-engineering-port al.com http://electrical-engineering-portal.
com/calculating-lightning-strike-distance
Calculating lightning strike distance
Return stroke current magnitude and strike distance (length of the last st epped leader) are interrelated. A number of equations have been proposed for determining the striking distance. The principal ones are as follows: 1. S = 2 x I + 30(1e I / 6.8) - Darveniza (1975) 2. S = 10 x I0.65 Love (1987; 1993) 3. S = 9.4 x I2/3 Whitehead (1974) 4. S = 8 x I0.65 IEEE (1985) 5. S = 3.3 x I0.78 Suzuki (1981) where: S is the strike distance in meters I is the return stroke current in kiloamperes It may be disconcerting to note that the above equations vary by as much as a factor of 2:1. However, light ning investigators now tend to favor the shorter strike distances given by Equation 4. Anderson, for example, who adopted Equation 2 in the 1975 edition of the Transmission Line
Reference Book (1987), now feels that Equation 4 is more accurate.
Mousa (1988) also supports this form of the equation. The equation may also be stated as follows: I = 0.041 x S1.54 SOURCE: Robert S. Nowell, Georgia Power Company
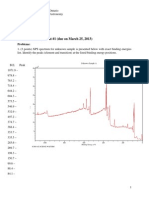
FIGURE 1 - Probability of stroke current exceeding abscissa f or strokes to f lat ground.
Recommended by others
You might also like
- Calculating Lightning Strike DistanceDocument2 pagesCalculating Lightning Strike DistanceTigrilloNo ratings yet
- Lightning-Induced Voltages: C.A. Nucci F. RachidiDocument63 pagesLightning-Induced Voltages: C.A. Nucci F. RachidiAbhishek Walter PaulNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ja (j-1) A (j+1) ADocument9 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ja (j-1) A (j+1) AcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Ans AssignDocument7 pagesAns AssignrohitpnNo ratings yet
- HRW Physics 1 Measurement PDFDocument12 pagesHRW Physics 1 Measurement PDFAntonio Marashi100% (1)
- P9826 HW2 2013Document5 pagesP9826 HW2 2013Muzamil ShahNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A-LEVEL PHY4 January 2002 QPDocument2 pagesEdexcel A-LEVEL PHY4 January 2002 QPapi-3726022No ratings yet
- Aero-Acoustic Modelling Using Large Eddy Simulation: Wzshen and J N SørensenDocument9 pagesAero-Acoustic Modelling Using Large Eddy Simulation: Wzshen and J N SørensenRio RobertöNo ratings yet
- Semiclassical Nonlinear Approach For Mesoscopic CircuitDocument4 pagesSemiclassical Nonlinear Approach For Mesoscopic CircuitIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Physics: Paper 2 As CoreDocument16 pagesPhysics: Paper 2 As CoreYaseenTamerNo ratings yet
- Bohrs Theory of The Hydrogen Atom 6Document16 pagesBohrs Theory of The Hydrogen Atom 6FerdiAhmadNo ratings yet
- 00104223Document12 pages00104223the_rag_4No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Measurement StandardsDocument12 pagesChapter 3 - Measurement StandardsYeevön LeeNo ratings yet
- Units and Measurements PDFDocument25 pagesUnits and Measurements PDFVirendra Gaur100% (1)
- A New Formulation of Electromagnetic Wave Scattering Using An On-Surface Radiation Boundary Condition ApproachDocument9 pagesA New Formulation of Electromagnetic Wave Scattering Using An On-Surface Radiation Boundary Condition ApproachSudantha Jayalal PereraNo ratings yet
- Ref - 17 - Part1Document10 pagesRef - 17 - Part1Grig GrigNo ratings yet
- Self-Study "Haynes - Shockley Experiment" Assignment 2022: C S E SDocument5 pagesSelf-Study "Haynes - Shockley Experiment" Assignment 2022: C S E SThulasizwe PhethaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Symmetry and Group Theory (Artigo)Document22 pagesApplications of Symmetry and Group Theory (Artigo)MoahVieiraNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Polluted High Voltage Insulators: IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering March 2014Document6 pagesModeling of Polluted High Voltage Insulators: IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering March 2014Romo BargowoNo ratings yet
- Physics Papers SolutionsDocument30 pagesPhysics Papers SolutionsKavya BhattNo ratings yet
- Transfer Matrix Method For Dual Chamber by MihaiDocument7 pagesTransfer Matrix Method For Dual Chamber by MihaiaruatscribdNo ratings yet
- Aipmt 2010 ScreeningDocument55 pagesAipmt 2010 ScreeningManjunath@116No ratings yet
- Lecture12 EDMDocument13 pagesLecture12 EDMOmar Adnan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Load Factors 5Document14 pagesDynamic Load Factors 5Solomon MiNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2014 Answer Key Online 11-04-2014Document11 pagesJEE Main 2014 Answer Key Online 11-04-2014anushrikocher1450% (2)
- UNIT-2 Structure of AtomDocument6 pagesUNIT-2 Structure of Atomranjit sahaNo ratings yet
- 9702 w02 QP 2Document16 pages9702 w02 QP 2Farhad AliNo ratings yet
- RingResonators TheoryandModelingDocument11 pagesRingResonators TheoryandModelingDaniel GrigoriNo ratings yet
- Unit and Dimension and Error Anylysis ArihantDocument25 pagesUnit and Dimension and Error Anylysis ArihantBrahmanand Tiwari100% (6)
- Vibrations Eoliennes IntroDocument26 pagesVibrations Eoliennes Intromacjosmanuel5453No ratings yet
- 2 3 1 A Stressstraincalculations 1 1Document5 pages2 3 1 A Stressstraincalculations 1 1api-308131962No ratings yet
- (A. Goldmann (Auth.), A. Goldmann (Eds.) ) Noble Me PDFDocument343 pages(A. Goldmann (Auth.), A. Goldmann (Eds.) ) Noble Me PDFFulanito de TalNo ratings yet
- L1-Introduction To SpectrosDocument9 pagesL1-Introduction To Spectrosken adamsNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM)Document29 pagesUnit 6: Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM)farie ahmadNo ratings yet
- Measure CHDocument28 pagesMeasure CHBhargavi KmNo ratings yet
- Practical Magnetic DesignDocument20 pagesPractical Magnetic DesignvmsaNo ratings yet
- Travish 1997 0174Document7 pagesTravish 1997 0174Particle Beam Physics LabNo ratings yet
- Walker4 ISM Ch32Document31 pagesWalker4 ISM Ch32Alejandro Romero Mejia100% (1)
- Plucked String Models FromtheKarplus StrongAlgorithmtoDigitalWG&BeyondDocument15 pagesPlucked String Models FromtheKarplus StrongAlgorithmtoDigitalWG&BeyondboboNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods of Physics - Fall 2010 - Dr. E.J. ZitaDocument6 pagesMathematical Methods of Physics - Fall 2010 - Dr. E.J. ZitaabiyyuNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Slip-Ring Induction Motor: Effects of Rotor AsymmetryDocument4 pagesThree-Phase Slip-Ring Induction Motor: Effects of Rotor AsymmetryMahmoud ElsayedNo ratings yet
- 21 (14 Files Merged)Document19 pages21 (14 Files Merged)onurkagan.yigitNo ratings yet
- Equ Mount PDFDocument23 pagesEqu Mount PDFaa ssNo ratings yet
- Fernando Dıaz Alonso Et Al - Characteristic Overpressure-Impulse-Distance Curves For Vapour Cloud Explosions Using The TNO Multi-Energy ModelDocument8 pagesFernando Dıaz Alonso Et Al - Characteristic Overpressure-Impulse-Distance Curves For Vapour Cloud Explosions Using The TNO Multi-Energy ModelSodaMoussezNo ratings yet
- HasegawaDocument3 pagesHasegawaMay VargasNo ratings yet
- Beam Bending Lab ReportDocument9 pagesBeam Bending Lab Reportapi-3105192830% (1)
- 2009 RI Prelims Physics H2 P2lDocument14 pages2009 RI Prelims Physics H2 P2lcjcsucksNo ratings yet
- WWW - Thinkiit.in: Current ElectricityDocument13 pagesWWW - Thinkiit.in: Current ElectricitythinkiitNo ratings yet
- ZCA101 Chapter 01Document56 pagesZCA101 Chapter 01Ren Liew Jia QingNo ratings yet
- Analytical Results For Nonlinear Compton Scattering in Short Intense Laser PulsesDocument16 pagesAnalytical Results For Nonlinear Compton Scattering in Short Intense Laser PulsesJulio Balbin AriasNo ratings yet
- Midterm 01 Physics 2 UTDocument8 pagesMidterm 01 Physics 2 UTJonathan OrNo ratings yet
- Vibrations Eoliennes Intro PDFDocument26 pagesVibrations Eoliennes Intro PDFkolombo1776No ratings yet
- Jurong Junior College: Physics 9646/2Document22 pagesJurong Junior College: Physics 9646/2Chen ZhihaoNo ratings yet
- Practical Magnetic Design: Inductors and Coupled Inductors: Power Supply Design SeminarDocument23 pagesPractical Magnetic Design: Inductors and Coupled Inductors: Power Supply Design Seminarbookreader1968No ratings yet
- Experiment: 2 Skills: O/R/R and A/IDocument10 pagesExperiment: 2 Skills: O/R/R and A/IKayenNo ratings yet
- Lance Nielson-Konzen NENG 605 HW1Document5 pagesLance Nielson-Konzen NENG 605 HW1Lance Nielson-KonzenNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11From EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11No ratings yet
- Ancient India by Krishnaswamy Iyengar PDFDocument488 pagesAncient India by Krishnaswamy Iyengar PDFRavichandran KpNo ratings yet
- Electrical Thumb Rules You MUST Follow (Part 2)Document2 pagesElectrical Thumb Rules You MUST Follow (Part 2)vijaydev75100% (1)
- Ancient India by Krishnaswamy Iyengar PDFDocument488 pagesAncient India by Krishnaswamy Iyengar PDFRavichandran KpNo ratings yet
- Fuel - Consumption - Chart - Standard Diesel EngineDocument1 pageFuel - Consumption - Chart - Standard Diesel EngineCaptIsqanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Thumb Rules You MUST Follow (Part 3) : Size of Capacitor For Power Factor CorrectionDocument4 pagesElectrical Thumb Rules You MUST Follow (Part 3) : Size of Capacitor For Power Factor Correctionvijaydev75No ratings yet
- Electrical Thumb Rules You MUST Follow (Part 1)Document4 pagesElectrical Thumb Rules You MUST Follow (Part 1)vijaydev75100% (2)
- TCM HandbookDocument109 pagesTCM Handbookvijaydev75No ratings yet
- Electrical Thumb Rules You MUST Follow (Part 4)Document4 pagesElectrical Thumb Rules You MUST Follow (Part 4)vijaydev75No ratings yet
- Calculation of Ventilation Requirements For Indoor Pools Based On Moisture EvaporationDocument12 pagesCalculation of Ventilation Requirements For Indoor Pools Based On Moisture Evaporationibrahim68No ratings yet
- CCTVDocument22 pagesCCTVvijaydev75No ratings yet
- Basics of 3-Phase Induction Motor (Part 3)Document10 pagesBasics of 3-Phase Induction Motor (Part 3)vijaydev75No ratings yet
- Ecodial enDocument3 pagesEcodial envijaydev75No ratings yet
- ABB XLPE Cable Systems Users Guide Rev 3Document28 pagesABB XLPE Cable Systems Users Guide Rev 3vijaypshindeNo ratings yet
- Principles and Characteristics of Distance ProtectionDocument6 pagesPrinciples and Characteristics of Distance Protectionvijaydev75No ratings yet
- Testing and Commissioning of MetalClad SwitchgearDocument4 pagesTesting and Commissioning of MetalClad Switchgearvijaydev75100% (1)
- SIEMENS WholeHouse Protection StrategyDocument3 pagesSIEMENS WholeHouse Protection Strategyvijaydev75No ratings yet
- UK Electrical Industry British Standards BSDocument19 pagesUK Electrical Industry British Standards BSvijaydev75100% (1)
- Guidelines To Visual Inspection of Electrical Installations - EEPDocument5 pagesGuidelines To Visual Inspection of Electrical Installations - EEPvijaydev75No ratings yet
- Guideline To Design Electrical Network For Building (Small Area) - EEPDocument4 pagesGuideline To Design Electrical Network For Building (Small Area) - EEPvijaydev75No ratings yet
- The Role of Circuit Breakers in LVMV Power SystemsDocument5 pagesThe Role of Circuit Breakers in LVMV Power Systemsvijaydev75No ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Portal - Com Price of A TransformerDocument3 pagesElectrical Engineering Portal - Com Price of A Transformervijaydev75No ratings yet
- Safety Clearance Recommendations For TransformerDocument6 pagesSafety Clearance Recommendations For Transformervijaydev75No ratings yet
- Principles and Characteristics of Distance ProtectionDocument6 pagesPrinciples and Characteristics of Distance Protectionvijaydev75No ratings yet
- Power Supply of Luminaires With Magnetic BallastsDocument4 pagesPower Supply of Luminaires With Magnetic Ballastsvijaydev75No ratings yet
- Functions Performed by Electrical SwitchgearDocument3 pagesFunctions Performed by Electrical Switchgearvijaydev75No ratings yet
- Inspection of Electrical Installations in Home Part 2Document7 pagesInspection of Electrical Installations in Home Part 2vijaydev75No ratings yet
- Inspection of Voltage Drop in ConductorsDocument2 pagesInspection of Voltage Drop in Conductorsvijaydev75No ratings yet
- Overview of Electrical Loads in BuildingDocument3 pagesOverview of Electrical Loads in Buildingvijaydev75No ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Standards For LVMVHV Part2Document13 pagesElectrical Safety Standards For LVMVHV Part2vijaydev75No ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Standards For LVMVHV Part1Document12 pagesElectrical Safety Standards For LVMVHV Part1vijaydev75No ratings yet