Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ةرضاحم 3: Alkyne: ةيويحلا ءايميكلا مسق - ةعارزلا ةيلك ةرهاقلا ةعماج 2 semester 2011/2012
Uploaded by
Samar MagdyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ةرضاحم 3: Alkyne: ةيويحلا ءايميكلا مسق - ةعارزلا ةيلك ةرهاقلا ةعماج 2 semester 2011/2012
Uploaded by
Samar MagdyCopyright:
Available Formats
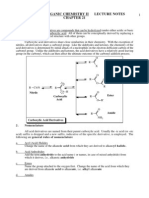
3: Alkyne / - 2102/1102 2nd semester
Stability :
extra" bond in an alkyne is weaker than the alkene bond: As with hydrocarbons in general, alkynes are non-polar and are insoluble in water but soluble in non-polar organic solvents The bonds are a region of high electron density so alkynes are typically nucleophiles. Alkynes typically undergo addition reactions in which one or both of the -bonds are converted to new s bonds. Terminal alkynes, R-CC-H, are quite acidic for hydrocarbons, pKa = 26 Deprotonation of a terminal acetylene gives an acetylide ion.
1 - Acidity of Terminal Alkynes
This carbanion can be used as a C centered nucleophile. These are important systems because the reaction of a carbanion with a C centered electrophile (such as alkyl halides) allows for the formation of new C-C bonds and hence larger more complex molecules.
2- Reaction with Grignard reagents:
CH3MgBr HC Acytelene CH HC CMgBr + CH4
CH3-Br
HC Propyne
C- CH3
MgBr2
3 - Alkylation of Alkynes
NaNH2 , NH3 HC Acetylene NaNH2 , NH3 CH3-C CH3- CH2Br 2-Pentyne CH HC C Na
CH3-Br CH3-C Propyne CH
C-CH2-CH3
CH3-CH2-CH2 CH3-CH2-CH2-C 1-Pentyne CH + RX C H C
CH3
H Cis-2-Hexene
Solution NaNH2 , NH3 CH3-CH2-CH2-C CH + CH3-CH2-CH2-C C Na
CH3I CH3-CH2-CH2 C H Cis-2-hexene C H CH3 H2 , Lindler Catalyst CH3-CH2-CH2-C C - CH3
4 - Preparation of Alkynes via Elimination reactions
5-Addition Reactions of Alkynes 1 - Hydrogenation of Alkynes
CH3-CH2-CH2 - CH2 Octane H H2 / Pd C CH3-CH2-CH2 - C 4-Octyne Na / NH3 C - CH2 - CH2- CH3 Lindler catalyst CH3-CH2-CH2
CH2 - CH2 - CH2- CH3
H C CH2-CH2 - CH3
Cis - 4 - Octene H C CH3-CH2-CH2 Trans - 4 - Octene CH2-CH2 - CH3 C H
6 - Hydration of Alkynes
7 - Ozonolysis of Alkynes
You might also like
- Reasoning Questions in Organic Chemistry Text ExerciseDocument14 pagesReasoning Questions in Organic Chemistry Text ExerciseEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Alkynes: Properties, Reactions and UsesDocument33 pagesAlkynes: Properties, Reactions and UsesAlvis MwangiNo ratings yet
- Alkynes: Properties, Reactions and UsesDocument3 pagesAlkynes: Properties, Reactions and UsesCamille AdleNo ratings yet
- Alkynes: State University of New York at AlbanyDocument28 pagesAlkynes: State University of New York at AlbanyStephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Chemistry Department FST Uin SGD BandungDocument25 pagesOrganic Chemistry Chemistry Department FST Uin SGD BandungSudrajatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Alkynes, From Carey Organic ChemsitryDocument50 pagesChapter 9: Alkynes, From Carey Organic ChemsitryHani ShamsedeenNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Questions in Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesReasoning Questions in Organic ChemistryAasthaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6 (Hydrocarbons)Document6 pagesExercise 6 (Hydrocarbons)Wendell Kim Llaneta0% (2)
- Ve 3. Hafta Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument11 pagesVe 3. Hafta Alkanes and CycloalkanesMevra TuranNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of AlkynesDocument31 pagesSynthesis of AlkynesttinbddinNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocument11 pagesHand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesLuisgarciaBerlangaNo ratings yet
- AlkeneDocument12 pagesAlkeneAditya NandaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 Reactions of Carbonyl CompoundsDocument18 pagesLesson 9 Reactions of Carbonyl Compoundsdela2No ratings yet
- LECTURE-6C-The-Chemistry-of-Alkenes-and-Alkynes-CME-2023Document37 pagesLECTURE-6C-The-Chemistry-of-Alkenes-and-Alkynes-CME-2023LinearNo ratings yet
- Alkyne Chemistry EEEDocument42 pagesAlkyne Chemistry EEEVictor MutugiNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: Sources, Classification and PropertiesDocument22 pagesHydrocarbons: Sources, Classification and PropertiesManan TyagiNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and AlkynesDocument22 pagesAlkenes and AlkynesAyodele AdeyonuNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Ques in Organic ChemistryDocument14 pagesReasoning Ques in Organic ChemistryRIHINBHATNAGAR50% (2)
- Alkynes: Reactions To KnowDocument10 pagesAlkynes: Reactions To KnowyeateshwarriorNo ratings yet
- Vollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 13Document47 pagesVollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 13superfr3shmNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ABCT2423: AlkynesDocument31 pagesOrganic Chemistry ABCT2423: AlkynesDyrus WongNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Class NotesDocument19 pagesORGANIC CHEMISTRY Class NotesWolam guyNo ratings yet
- Al KynesDocument19 pagesAl KynesAnkit JaipuriaNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Organic ChemDocument12 pagesReasoning Organic ChemUtkarsh BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Alkane and CycloalkaneDocument24 pagesAlkane and CycloalkaneMike EzioNo ratings yet
- Summary::, R' RNC) Cp2Zr, X &,C-R' H30+ Cp2Zr, X + R'ChoDocument4 pagesSummary::, R' RNC) Cp2Zr, X &,C-R' H30+ Cp2Zr, X + R'ChoNguyễn TấnNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes. Set 1Document7 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes. Set 1Achyuta GajurelNo ratings yet
- The Stabilization of Allylic Systems in Conjugated DienesDocument22 pagesThe Stabilization of Allylic Systems in Conjugated DienesKarim El KhatibNo ratings yet
- Alkynes: Unsaturated Hydrocarbon: Jully Tan School of EngineeringDocument25 pagesAlkynes: Unsaturated Hydrocarbon: Jully Tan School of EngineeringSàtz ÑÖÑïtNo ratings yet
- Revised Organic ChemistryDocument90 pagesRevised Organic ChemistryMinh TieuNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and AldehydeDocument21 pagesAlcohol and AldehydehmtlionNo ratings yet
- (Chem 31) LE2 Samplex + AnsKey (1-1920)Document10 pages(Chem 31) LE2 Samplex + AnsKey (1-1920)Glyzen GaleonNo ratings yet
- UNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument50 pagesUNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acidssukaina fatima100% (1)
- Halogenoalkanes and Haloarenes: Nucleophilic Substitution ReactionsDocument30 pagesHalogenoalkanes and Haloarenes: Nucleophilic Substitution ReactionsEarNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Reactions and MechanismsDocument120 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Reactions and MechanismsLoveena Steadman100% (8)
- Alkenes 2Document45 pagesAlkenes 2cikgu_amin100% (1)
- HydrocarbonsDocument30 pagesHydrocarbonsSneha AunttyNo ratings yet
- Alkynes - Problem SolutionsDocument21 pagesAlkynes - Problem SolutionsfrankjenNo ratings yet
- McMurry 7e Ch19-23 Notes 5-29-07Document55 pagesMcMurry 7e Ch19-23 Notes 5-29-07Kay BradyNo ratings yet
- Types of Organic ReactionsDocument31 pagesTypes of Organic ReactionsNurulMAprilia80% (5)
- Complete Organic Chemistry (Brahmastra) Part 2Document763 pagesComplete Organic Chemistry (Brahmastra) Part 2mohdamaankhan74No ratings yet
- Alkene Preparation and ReactionsDocument46 pagesAlkene Preparation and Reactionsnlprofessional07No ratings yet
- Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition ReactionsDocument64 pagesChapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactionsaggelisgeorge8546No ratings yet
- General Information OF Organic Chemistry: Jan 10, 2016 Usamvb Timisoara Facultatea de Medicină Veterinară 1Document23 pagesGeneral Information OF Organic Chemistry: Jan 10, 2016 Usamvb Timisoara Facultatea de Medicină Veterinară 1Flaviu TomuțaNo ratings yet
- 13 HydrocarbonDocument114 pages13 HydrocarbonCharviNo ratings yet
- Addition Reactions of AlkynesDocument5 pagesAddition Reactions of AlkynesJaya Chitra Degala RamaluNo ratings yet
- Alkene Alkyne PDFDocument45 pagesAlkene Alkyne PDFKartikeya AryaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones TheoryDocument28 pagesAldehydes, Ketones Theoryshilpa sakhareNo ratings yet
- 31 CH203 Fall 2014 Lecture 31 PDFDocument22 pages31 CH203 Fall 2014 Lecture 31 PDFBUCH203No ratings yet
- Reasoning Questions in Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesReasoning Questions in Organic ChemistryPavankumar SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1-ALKENE PDFDocument51 pagesChapter 3.1-ALKENE PDFYasserAbyNo ratings yet
- Learn: Chapter-10 Haloalkanes & Haloarenes Class-XII Subject-ChemistryDocument32 pagesLearn: Chapter-10 Haloalkanes & Haloarenes Class-XII Subject-Chemistryprajaktac506No ratings yet
- Preparations of Alkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesDocument71 pagesPreparations of Alkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesRavi100% (1)
- NCERT Unit 12 Hydrocarbon by Manoj YadavDocument19 pagesNCERT Unit 12 Hydrocarbon by Manoj YadavKunaL VrmaNo ratings yet
- A Green Method For Synthesis of Cyclohexanone Oxidation of Cyclohexanol Using Sodium HypochloriteDocument6 pagesA Green Method For Synthesis of Cyclohexanone Oxidation of Cyclohexanol Using Sodium Hypochloritefleetfoxes886% (7)
- Physical & Chemical Properties of AlkanesDocument18 pagesPhysical & Chemical Properties of AlkaneskjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- SN and E 2019 PDFDocument108 pagesSN and E 2019 PDFDwi ShabrinaNo ratings yet
- Advances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookFrom EverandAdvances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookArmando J. L. PombeiroRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- HivDocument16 pagesHivSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Logistics Department Leadership ApplicationDocument3 pagesLogistics Department Leadership ApplicationSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Events Department Leadership ApplicationDocument3 pagesEvents Department Leadership ApplicationSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Imbaba Program Recruitment CriterionDocument3 pagesImbaba Program Recruitment CriterionSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- HIV Anime FinalDocument14 pagesHIV Anime FinalSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- 8 Groups, Teams, Power and ConflictDocument3 pages8 Groups, Teams, Power and ConflictSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Schedule Team 6Document2 pagesSchedule Team 6Samar MagdyNo ratings yet
- HIV Anime FinalDocument14 pagesHIV Anime FinalSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Attitudes: Attitude Is The Willingness To Act in A Specific Way Under A Specific Conditions and Situations, WhichDocument5 pagesAttitudes: Attitude Is The Willingness To Act in A Specific Way Under A Specific Conditions and Situations, WhichSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- CEIOSS ReportDocument10 pagesCEIOSS ReportSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- 2 CommunicationDocument3 pages2 CommunicationSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- L.1 Marketing 425Document43 pagesL.1 Marketing 425Samar MagdyNo ratings yet
- 3 Personality 2Document3 pages3 Personality 2Samar MagdyNo ratings yet
- 6 LeadershipDocument5 pages6 LeadershipSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- 7 Organizational DesignDocument4 pages7 Organizational DesignSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) The Stages of Project Feasibility StudyDocument17 pagesChapter (2) The Stages of Project Feasibility StudySamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Evaluationl English 1Document18 pagesEvaluationl English 1Samar MagdyNo ratings yet
- L.3. Monopolistic Competition - OligopolyDocument12 pagesL.3. Monopolistic Competition - OligopolySamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Secure DownloadDocument10 pagesSecure DownloadSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Evaluationl English 1Document18 pagesEvaluationl English 1Samar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Fungi & Fungal-Like OrganismsDocument47 pagesFungi & Fungal-Like OrganismsSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 ProtectionDocument25 pagesSec 3 ProtectionSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- AlcoholsDocument11 pagesAlcoholsSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Evaluationl English 1Document18 pagesEvaluationl English 1Samar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Plant Protection: Cairo University Faculty of Agriculture Department of Plant PathologyDocument44 pagesPrinciples of Plant Protection: Cairo University Faculty of Agriculture Department of Plant PathologySamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Fungi & Fungal-Like OrganismsDocument47 pagesFungi & Fungal-Like OrganismsSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & MitosisDocument31 pagesCell Cycle & MitosisSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal AbrerationsDocument34 pagesChromosomal AbrerationsSamar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 ProtectionDocument25 pagesSec 3 ProtectionSamar MagdyNo ratings yet