Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmasheet Amlodipine Besylate
Pharmasheet Amlodipine Besylate
Uploaded by
Sherlyn KirisakiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmasheet Amlodipine Besylate
Pharmasheet Amlodipine Besylate
Uploaded by
Sherlyn KirisakiCopyright:
Available Formats
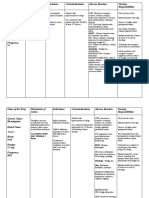
Name of the Drug AMLODIPINE BESYLATE
General Action
Specific Action
Indication Angina pectoris due to coronary artery spasm (Prinzmetals variant angina) Chronic stable angina, alone or in combination with other drugs Essential hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensives
Contraindications
Adverse Reaction
Nursing Responsibilities
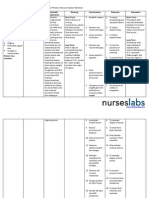
Antianginal Inhibits the movement Antihyperte of calcium ions across the membranes of nsive cardiac and arterial Calcium muscle cells; inhibits channel Norvasc transmembrane blocker calcium flow, which Dosage: 1 tab results in the 10mg OD depression of impulse formation in specialized cardiac pacemaker cells, Pregnancy slowing of the category C velocity of conduction of the cardiac impulse, depression of myocardial contractility, and dilation of coronary arteries and arterioles and peripheral arterioles; these effects lead to decreased cardiac work, decreased cardiac oxygen consumption, and in patients with vasospatic angina, increased delivery of oxygen to cardiac cells.
Contraindicated with allergy to CNS: Dizziness, ASSESMENT: amlodipine, impaired lightheadedness, headache, History: Allergy to amlodipine, impaired hepatic or renal hepatic or renal asthenia, fatigue, lethargy function, sick sinus syndrome, heart block, lactation, heart function, sick sinus failure, syndrome, heart Physical: Skin lesions, color, edema; P, BP, baseline ECG; CV: Peripheral edema, block (second or peripheral perfusion, auscultation; R, adventitious sounds; arrhymias third degree), and liver evaluation, GI normal output; LFTs, renal function lactation. tests, urinalysis Dermatologic: Flushing, Use cautiously withrash jaundice (yellowing of INTERVENTIONS: the skin or eyes). heart failure, pregnancy. Warning: Monitor patient carefully (BP, cardiac rhythm, and GI: Nausea, abdominal output) while adjusting drug to therapeutic dose; use special discomfort caution if patient has heart failure. Urinating more or less than Monitor BP carefully if patient is also on nitrates. Monitor cardiac rhythm regularly during stabilization of usual, or not at all; dosage and periodically during long term therapy. Administer drug without regard to meals. Fever, chills, body aches, flu symptoms; Always remember and follow the 10 Rs of drug administration. Tired feeling, muscle weakness, and pounding or TEACHING POINTS: uneven heartbeats; Take with meals if upset stomach occurs. You may experienced these side effects: Nausea, vomiting chest pain; (eat frequent small meals); headache (adjust lightning, noise, and temperature; medication may ordered) swelling, rapid weight gain; Report irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, swelling of the hands or feet, pronounced dizziness, constipation. Vomiting, diarrhea, or heavy sweating can cause you to become dehydrated. This can lead to very low blood pressure, electrolyte disorders, or kidney failure while you are taking amlodipine and benazepril. Drink 6 to 8 full glasses of water daily while you are taking this medication.
Name of the Drug MEFENAMIC ACID ApoMefenamic, ponstel 500 mg 1 cap 3x/day Pregnancy category C
General Action NSAID
Specific Action
Indication
Contraindications
Adverse Reaction
Nursing Responsibilities
CNS: Headache, dizziness, BEFORE: AntiRelief of moderateContraindicated somnolence, insomnia, inflammatory, pain when therapy with Assess for history of allergies, renal, hepatic, CV,GI analgesic and will not exceed 1 hypersensitivity to fatigue, tiredness, tinnitus, conditions; pregnancy; lactation mefenamic acid, ophthalmic effects antipyretic week. Assess the physical for skin color and lesions; orientation, aspirin allergy, and Dermatologic: Rash, activities related Treatment of reflexes, opthalmolgic, and andiometric evaluation, as treatment of prurotus, sweating, dry to inhibition of primary peripheral sensation; P, edema R, adventitious sounds,; renal preoperative pain mucous prostaglandin dysmenorrhea. function tests, serum electrolytes, stool guaiac with coronary artery membranes,stomatitis synthesis; exact bypass grafting. mechanisms of DURING: GI: nausea, dyspepsia, GI action are not Be aware that patient may be at increase risk for CV events, Use cautiously with pain, diarrhea, vomiting, known. GI bleeding, monitor accordingly. asthma, renal or constipation, flatulence Give the milk or food to decrease GI upset. hepatic impairment, Arrange for periodic ophthalmologic examinations during peptic ulcer disease, GU: Dysuria, renal long-term therapy. GI bleeding, impairment If overdose occurs, institute emergence procedureshypertension heart supportive therapy and induced emesis, activated charcoal, failure, pregnancy Hematologic: bleeding, and/or an osmotic cathartic lactation. platelet inhibition wiyh Do not exceed 1 week therapy higher doses, neutropenia, Always remember and practice the 10 Rs eosinophilia, leukopenia, pancytopenia, AFTER: thrombocytopenia, Take drug with food; take only the prescribed dosage and agranulocytosis, teach not to take the drug longer than 1 week granulocytopenia, aplastic Discontinue drug and consult health care provider if rash, anemia, decrease Hgb or Hct, diarrhea, or digestive problems occur. bone marrow depression, Dizziness or drowsiness can occur ( so avoid driving and menorrhagia using dangerous machinery ) Respiratory: Dyspnea, Report sore throat, fever, rash, itching, weight gain, swelling hemoptysis, pharyngitis, in the ankles or fingers, changes in vision; cephalexin. bronchospasm, rhinitis Other: Peripheral edema, anaphylactoid reactions to anaphylactic shock
You might also like
- Risk For Injury NCP SeizuresDocument2 pagesRisk For Injury NCP Seizurestimie_reyes88% (8)
- Survey Questionnaire - Health CareDocument2 pagesSurvey Questionnaire - Health Careapi-194241825100% (4)
- Diploma in Geriatric Medicine - Sample Questions: Clostridium Difficile ToxinDocument7 pagesDiploma in Geriatric Medicine - Sample Questions: Clostridium Difficile ToxinakstergNo ratings yet
- Sleep 50 QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesSleep 50 QuestionnaireSónia Alves100% (1)
- Salient Features DO 13Document27 pagesSalient Features DO 13Robin Rubina100% (4)
- Comlex Ii & Usmle Ii Cram Sheets - Gastroenterology Vitamins ObesityDocument31 pagesComlex Ii & Usmle Ii Cram Sheets - Gastroenterology Vitamins ObesitySolomon Seth Sallfors100% (1)
- GerdDocument69 pagesGerdopkhfdegNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyArnel MacabalitaoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AMIODARONE & PROPOFOLDocument3 pagesDrug Study AMIODARONE & PROPOFOLNIKKI CARYL ZAFRANo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Colleen S. de La Rosa BSN IiiDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Colleen S. de La Rosa BSN IiiColleen De la RosaNo ratings yet
- MS Drug Study 1Document6 pagesMS Drug Study 1Elijah MarfilNo ratings yet
- Dolan Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDolan Drug StudyLian Robbie BautistaNo ratings yet
- Note: Dosage May Be Gradually Increased Over: AmlodipineDocument4 pagesNote: Dosage May Be Gradually Increased Over: Amlodipineanette katrinNo ratings yet
- Laranang, Mica Joy R. Drug Study: BSN 123 Group 90Document5 pagesLaranang, Mica Joy R. Drug Study: BSN 123 Group 90Gerard Louise Esmao RNNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Document11 pagesDRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- EnalaprilDocument2 pagesEnalaprilpinksapphire929100% (2)
- Name of Drug Dosage/ Frequency / Timing/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesName of Drug Dosage/ Frequency / Timing/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesphoebeNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmlodipine Drug StudyJoseph Dann Enero Jr.100% (3)
- Cholinesterase Inhibitors - AlzheimersDocument1 pageCholinesterase Inhibitors - AlzheimerscpboilergirlNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyJenniferValmocenaNo ratings yet
- ARCHEDERA (Drug Study #10&11)Document2 pagesARCHEDERA (Drug Study #10&11)SHIELA MAE ARCHEDERANo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Med Ward Week 2)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Med Ward Week 2)Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AlzheimersDocument12 pagesDrug Study Alzheimersella retizaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument12 pagesDrugsJean RamosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Atenolol, Cefuroxime, SimvastatinDocument4 pagesDrug Study Atenolol, Cefuroxime, Simvastatinpaupaulala100% (4)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyAnne Marie BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- Catapres (Clonidine)Document2 pagesCatapres (Clonidine)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study orDocument5 pagesDrug Study orRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OrthoDocument12 pagesDrug Study OrthoSienaNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsMarie Kris Chua AbelleraNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive - ABCDDocument5 pagesAntihypertensive - ABCDTingCheung100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNicole Rachelyn MartinNo ratings yet
- Print MeDocument4 pagesPrint MeDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Tolleno Drug Study LONGDocument9 pagesTolleno Drug Study LONGHannah TollenoNo ratings yet
- Case Study: RLE DutyDocument12 pagesCase Study: RLE DutyEsther Ellise AbundoNo ratings yet
- AMLODIPINEDocument2 pagesAMLODIPINEMary Reigns BuhatNo ratings yet
- Captopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyDocument4 pagesCaptopril Is An ACE Inhibitor and Works by Relaxing Blood Vessels So That Blood Can Flow More EasilyKsksksksNo ratings yet
- B. Drug Study: Diarrhea, Ulceration, Vomiting, Abdominal CrampsDocument12 pagesB. Drug Study: Diarrhea, Ulceration, Vomiting, Abdominal CrampsSienaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteDocument10 pagesCollege of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteMa. Sheenadel ZamudioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study D InsipidusDocument7 pagesDrug Study D InsipidusAisha MarieNo ratings yet
- Diclofenalac Sodium (Fenac)Document3 pagesDiclofenalac Sodium (Fenac)karenmichellelecarozNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyizzieliciousNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyZek ComidoyNo ratings yet
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteDocument1 pageCollege of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study StaDocument3 pagesDrug Study StaarjeighNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLester Paul SivilaNo ratings yet
- CNS: Headache, InsomniaDocument5 pagesCNS: Headache, InsomniaDave FagaritaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideMark ToxNo ratings yet
- HF and CAD Case ScenarioDocument17 pagesHF and CAD Case ScenarioElla Neiza AngelesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AhhhahahhaDocument11 pagesDrug Study AhhhahahhaShiela Mae Llarenas LoretoNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs - Cardiac DrugsDocument14 pagesEmergency Drugs - Cardiac DrugsKookie JunNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug Study NaproxenparacetamolDocument3 pagesPedia Drug Study NaproxenparacetamolKuro HanabusaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studydana100% (2)
- Final Drug StudyDocument4 pagesFinal Drug StudyBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Brand Name:: VasopressinDocument3 pagesBrand Name:: VasopressinHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument13 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitieskev mondaNo ratings yet
- Amplodipine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmplodipine Drug StudyRai HanahNo ratings yet
- De Jesus, Lovelle Grace E. (Drug Study)Document7 pagesDe Jesus, Lovelle Grace E. (Drug Study)LOVELLE GRACE DE JESUSNo ratings yet
- Syncope, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandSyncope, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- PFCCS Instructor Director Consultant CriteriaDocument3 pagesPFCCS Instructor Director Consultant CriteriaImam RahmadiNo ratings yet
- Master Sheet RamshaDocument9 pagesMaster Sheet RamshaArisha NusratNo ratings yet
- Systematic Review of Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors Among Police OfficersDocument20 pagesSystematic Review of Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors Among Police OfficersBarbara SousaNo ratings yet
- Annexure A Subcontractor PrequalificationDocument11 pagesAnnexure A Subcontractor Prequalificationshazeb aliNo ratings yet
- Cancer Industry, The Classic Expose of The - Moss, Ralph WDocument546 pagesCancer Industry, The Classic Expose of The - Moss, Ralph Wpdf ebook free download80% (5)
- Role of Sports in Managing StressDocument33 pagesRole of Sports in Managing StressReyanne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Dapus PDFDocument9 pagesDapus PDFSaskiaaNo ratings yet
- Beriso Drug StudyDocument5 pagesBeriso Drug StudyKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing QuizDocument3 pagesCommunity Health Nursing QuizhemihemaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Excess CRFDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Excess CRFDana Fajardo RezanoNo ratings yet
- Leishmaniasis: Key FactsDocument6 pagesLeishmaniasis: Key FactsNurul Hikmah PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Design Manual For Low Volume Roads Part CDocument32 pagesDesign Manual For Low Volume Roads Part CHannaNo ratings yet
- University of Cape Town Division of Occupational Therapy - Ahs3107W ArthritisDocument7 pagesUniversity of Cape Town Division of Occupational Therapy - Ahs3107W ArthritisAlexaNo ratings yet
- Remote Health Atlas Resuscitation Trolley: 1. General InformationDocument3 pagesRemote Health Atlas Resuscitation Trolley: 1. General InformationSusanti ShantyNo ratings yet
- Zapanta, Harry John FCM2 Assignment 1Document2 pagesZapanta, Harry John FCM2 Assignment 1Harry John ZapantaNo ratings yet
- WPA Educational Programme On Depressive Disorders PDFDocument98 pagesWPA Educational Programme On Depressive Disorders PDFGe NomNo ratings yet
- Desk Research P&SDocument8 pagesDesk Research P&SAnkit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Primark Chemical Commitment Meeting - Dhaka - Sep - 2016Document31 pagesPrimark Chemical Commitment Meeting - Dhaka - Sep - 2016Dyeing DyeingNo ratings yet
- Dolor PlaquetasDocument5 pagesDolor PlaquetasmoisesNo ratings yet
- Personal Care ProductsDocument39 pagesPersonal Care ProductsRachel Taburda100% (1)
- Situation Analysis of Children With Disabilities For The Development of An Inclusive Society in The Republic of KazakhstanDocument100 pagesSituation Analysis of Children With Disabilities For The Development of An Inclusive Society in The Republic of KazakhstanUNU-MERITNo ratings yet
- Agung HidayatullahDocument58 pagesAgung HidayatullahIta Aprilia SaktiNo ratings yet
- Zeiss Octa Ux Ebook en 31-20-0144ii Cir10959Document48 pagesZeiss Octa Ux Ebook en 31-20-0144ii Cir10959EugeniaNo ratings yet