Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing - GD&T GD&T
Uploaded by
viswanadhvvsk0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views2 pagesBasic GD&T
Original Title
GD&T.pdf
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBasic GD&T
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views2 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing - GD&T GD&T
Uploaded by
viswanadhvvskBasic GD&T
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
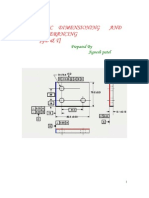
GD&T Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing - GD&T
The need to tolerance more then size led to a more precise system
GD&T
Allows for setting tolerance limits not just for size but for shape features as well. Dependant on function of part and relationship to mating parts. ASME Y14.5
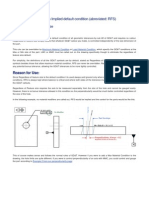
GD&T - Example
GD&T
GD&T described using feature control frame Need to understand:
Feature Control Frame
Note: Order is important
Geometric Characteristics Modifiers Datums
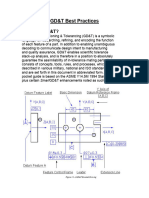
Geometric Characteristics
Modifiers
Symbols that help to define characteristics
Example: MMC Maximum Material Conditioncondition when most material exists
.75.02 MMC .77
External Feature
.75.02 Internal Feature MMC .73
Compare MMC to RFS
(Regardless of Feature Size)
Datums
Theoretically perfect points, lines and planes used for reference. Again function of part very important Classified as primary, secondary or tertiary.
.002 1.00.002
or
.002
Produced size 1.002 1.001 1.000 .999 .998
Tolerance RFS .002 .002 .002 .002 .002
Tolerance MMC .002 .003 .004 .005 .006
You might also like
- GD&T Seminar Agenda and ConceptsDocument69 pagesGD&T Seminar Agenda and ConceptsJayanthiANo ratings yet
- Dimensional Engineering Seminar: Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Variation Simulation ModelingDocument71 pagesDimensional Engineering Seminar: Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Variation Simulation Modelingprasungovindan100% (1)
- Dimensional Engineering SeminarDocument71 pagesDimensional Engineering Seminardramilt100% (4)
- GD&T - All Slides - Chapters 1-11 - Q&A - AnimatedDocument77 pagesGD&T - All Slides - Chapters 1-11 - Q&A - AnimatedOmar RiosNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Dimensioning & Tolerancing: Based On The ASME Y14.5M - 1994 Dimensioning and Tolerancing StandardDocument86 pagesGeometrical Dimensioning & Tolerancing: Based On The ASME Y14.5M - 1994 Dimensioning and Tolerancing Standardmohtram1037100% (4)
- GD&TDocument76 pagesGD&TVictoria Indira Gandhi100% (18)
- GDT TutorialDocument76 pagesGDT TutorialSrk ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- GDT TutorialDocument76 pagesGDT TutorialSivananthaa MurtheeNo ratings yet
- GD&T Fundamentals in 40 CharactersDocument76 pagesGD&T Fundamentals in 40 CharactersAnish PaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GD&T?Document11 pagesIntroduction To GD&T?AravindNo ratings yet
- 1.0 General: Drafting ManualDocument8 pages1.0 General: Drafting ManualMubashar Khalil Hashmi100% (1)
- The Basics of Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument9 pagesThe Basics of Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingKishanNo ratings yet
- GDT tutorialDocument76 pagesGDT tutorialscience ki DuniyaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Dimenstioning and ToleranceDocument82 pagesGeometrical Dimenstioning and ToleranceSreedhar PugalendhiNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GDTDocument83 pagesIntroduction to Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GDTabhijitmpatil3852No ratings yet
- GDT Day1Document119 pagesGDT Day1Narendrareddy RamireddyNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) : BackgroundDocument3 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) : BackgroundAkshayNo ratings yet
- GD&T Day 1 Part 1Document22 pagesGD&T Day 1 Part 1harshkallani100% (2)
- GD&T Fundamentals: Learn Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Symbols and BenefitsDocument11 pagesGD&T Fundamentals: Learn Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Symbols and BenefitsSURYA20051961No ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument4 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and TolerancingAshokNo ratings yet
- GD&T StdsDocument4 pagesGD&T StdsSri PupNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning AND Tolerancing (GD & T) : Prepared by Jignesh PatelDocument13 pagesGeometric Dimensioning AND Tolerancing (GD & T) : Prepared by Jignesh PatelunendratNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) : Part Production Communication ModelDocument76 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) : Part Production Communication ModelPedro SalinasNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Dimensioning and TolerenceDocument61 pagesGeometrical Dimensioning and TolerenceAd Man GeTigNo ratings yet
- G D & TDocument40 pagesG D & TjohnNo ratings yet
- GD&T NotesDocument24 pagesGD&T NotesDarshan Sn100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Geometric Dimensioning & TolerancingDocument109 pagesFundamentals of Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancingkiran.katsNo ratings yet
- 1 Exercises Product Quatity Control Geometrical TolerancingDocument66 pages1 Exercises Product Quatity Control Geometrical TolerancingHasan Can MuratNo ratings yet
- GD&T 1Document41 pagesGD&T 1Sai CharanNo ratings yet
- Training MaterialDocument151 pagesTraining MaterialNarendrareddy RamireddyNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing: Navigation Search Citations Reliable and Independent SourcesDocument8 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing: Navigation Search Citations Reliable and Independent SourcesDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GDDocument8 pagesIntroduction To GDCatalin FinkelsteinNo ratings yet
- GD&T Dimensioning and Tolerancing GuideDocument3 pagesGD&T Dimensioning and Tolerancing Guidedesign12No ratings yet
- Symbol: None - Always Implied Default Condition (Abreviated: RFS) Category: Feature of Size DefinitionDocument2 pagesSymbol: None - Always Implied Default Condition (Abreviated: RFS) Category: Feature of Size Definitionvin_ckNo ratings yet
- Chap 1-1Document53 pagesChap 1-1hudarusliNo ratings yet
- GD&T12Document136 pagesGD&T12Roshan KhedkarNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning ModuleDocument46 pagesDimensioning ModulekpklavNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GD&TDocument81 pagesIntroduction To GD&Tmanchorus100% (1)
- Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument40 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and TolerancingK T SathishNo ratings yet
- G D & TDocument40 pagesG D & TGanyer LopezNo ratings yet
- G D & TDocument40 pagesG D & Tmaruti mishraNo ratings yet
- GT&DDocument17 pagesGT&DMicha VardyNo ratings yet
- GD&T Symbols and Tolerance Zones ExplainedDocument6 pagesGD&T Symbols and Tolerance Zones Explainedchethan048100% (1)
- 04 GD&T IntroTutorialDocument73 pages04 GD&T IntroTutorialrust_02No ratings yet
- GD&T Best Practices and TrainingDocument4 pagesGD&T Best Practices and TrainingtrandangbkNo ratings yet
- GD&T Course Covers Essential Concepts Like Rules 1 and 2Document4 pagesGD&T Course Covers Essential Concepts Like Rules 1 and 2yuvarajaNo ratings yet
- GD&T Machine Drawing GuideDocument22 pagesGD&T Machine Drawing GuideY006 -HonochNo ratings yet
- Uses of Geometrical Dimensional and Tolerance: IntroductionDocument11 pagesUses of Geometrical Dimensional and Tolerance: IntroductionJuicYm mNo ratings yet
- Solidworks 2018 Learn by Doing - Part 3: DimXpert and RenderingFrom EverandSolidworks 2018 Learn by Doing - Part 3: DimXpert and RenderingNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 3 (DimXpert and Rendering)From EverandSolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 3 (DimXpert and Rendering)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- SolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3From EverandSolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Geometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing for Design, Manufacturing and Inspection: A Handbook for Geometrical Product Specification Using ISO and ASME StandardsFrom EverandGeometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing for Design, Manufacturing and Inspection: A Handbook for Geometrical Product Specification Using ISO and ASME StandardsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Sheet Metal Exam PreparationFrom EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Sheet Metal Exam PreparationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Successful Service Design for Telecommunications: A comprehensive guide to design and implementationFrom EverandSuccessful Service Design for Telecommunications: A comprehensive guide to design and implementationNo ratings yet
- Useful Decimal Chart2Document1 pageUseful Decimal Chart2viswanadhvvskNo ratings yet
- UsefulchartsDocument1 pageUsefulchartsviswanadhvvskNo ratings yet
- Paneer Tikka Masaala RecipeDocument1 pagePaneer Tikka Masaala RecipeviswanadhvvskNo ratings yet
- Basic Components of Pneumatic CircuitsDocument3 pagesBasic Components of Pneumatic CircuitsviswanadhvvskNo ratings yet
- Bubbles ShooterDocument2 pagesBubbles ShooterviswanadhvvskNo ratings yet
- Golf 1Document2 pagesGolf 1viswanadhvvskNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Lesson 2 - Export A 2D Drawing As An IGES: FILE Menu: #Open, Name:, #OpenDocument3 pagesTutorial Lesson 2 - Export A 2D Drawing As An IGES: FILE Menu: #Open, Name:, #OpenviswanadhvvskNo ratings yet
- Golf 1Document2 pagesGolf 1viswanadhvvskNo ratings yet