Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GSM Network Optimization
Uploaded by
DavidDavidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GSM Network Optimization
Uploaded by
DavidDavidCopyright:
Available Formats
GSM network optimization dropped calls, congestion causes and solutions
GSM network optimization dropped calls, congestion causes and solutions
1. Call drop in mobile communications, dropped calls is in the allocation of a voice channel (TCH), due to some reason, so that the call is lost or interrupted, the normal calls can not be a phenomenon. Call drop not only affects the network targets, but the user will cause a lot of inconvenience is a user complaint hot spots.
1.1 The causes call drop 1, dropped calls caused by the interference: Interference include the same frequency, adjacent channel and crosstalk. When the cell phone in the service receive a strong signal the same frequency or adjacent-channel interference, it will cause deterioration of bit error rate, so that cell phones near impossible to accurately demodulate the BSIC code or can not correctly receive mobile station measurement report. Base stations for mobile phones through the allocation of SDCCH good voice channels to be used after the absence of nearby residential BSIC code can not be used to determine which cell of the voice channels, resulting in dropped calls. Crosstalk mainly from external disturbances, such as the CDMA base station uplink frequency will interfere with me. 2, due to dropped calls caused by switching: (1) MS in the call, the phone list to calculate the best six neighboring cells to prepare for the switch, but when the network coverage is bad, will have to switch frequently, resulting in non-host cell, resulting in dropped calls. (2) The number of residential traffic due to busy traffic will push to the neighboring cells, but adjacent cell signal poor or non-idle channel will be generated when the dropped calls. (3) island effect. If the service district A because of the terrain causes produce the coverage of the field strength of the island C, and C around the island again for the coverage of cell B, as in A, the list of neighboring cells not add cell B, then when the user C create a call out of the island after a C, because of switching will have nowhere to dropped calls. 3, parameter setting unreasonable due to dropped calls: The main parameters affecting call drop switching parameters and the parameters of neighboring cells. Such as: PMRG is set too high or the adjacent cell parameters of a mistake can lead to dropped calls. 4, base station hardware, dropped calls caused by: BTS hardware failure can also cause dropped calls, NOKIA device 7745 (CHANNEL FAILURE RATE ABOVE DEFINED THRESHOLD)
, 7949 (DIFFERENCE IN RX LEVELS OF MAIN AND DIVERSITY ANTENNA / TRX) is a particular attention, since these alarms accompanied by dropped calls. 5, Abis interface failure resulting from dropped calls Abis interface, including the BSC has not received a survey report from the BTS, more than TA limits, switching process, a number of signaling failures and a number of internal factors, in addition to Abis interface bit error rates. 6, covering poor dropped calls caused by: Some district due to the excessive coverage of cell coverage resulted in the periphery of the signal is not good, the value of low-level mobile phones in the list measured values of the adjacent cell levels also fail to access requirements (eg RXLEV ACCESS MIN = -95dBm) caused dropped calls, in remote areas, where poor network coverage occurs frequently dropped calls.
1.2 call drop solution to dropped calls if a district is high, you can first check dropped calls by the report (such as the 163 Report), first determine where caused due to dropped calls. (1) for dropped calls caused due to switching solution can first carry out a wide range of road tests, passed the road test is to determine adjacent cell to switch and which is not normal. For some with the cell has to switch between the relatively high rate of cell congestion should be the focus of testing and the need to check whether there are blind spots around the district exists, if it is for this reason should be revised because the relevant frequency and add a new base station or the expansion of the original a base station coverage. For the switch to set unreasonable because of dropped calls caused by the situation in accordance with the measured switching parameters with appropriate modifications. For those who do not balance because of traffic, resulting in busy due to target base station without switching channels arising from dropped calls, the solution is to carry out traffic adjustments or expansion. (2) The interference caused due to dropped calls, should first determine whether or external interference with adjacent channel interference. If it is found tampering with the adjacent residential district have the same frequency, can be resolved by modifying the frequency. If upon inspection did not find the same frequency can be used Agilent test equipment to the field, through the spectral analysis, if my net is higher than the uplink of the background noise down, then there may be due to CDMA base stations, base station I have not put filters on the resulting interference. (3) For the parameter setting unreasonable due to dropped calls, regular inspection by the adjacent cell parameter settings, set the error to make timely adjustments to resolve. (4) for base station hardware, and dropped calls caused by Abis mouth can be by looking to understand the specific reasons for alarm at the same time and also a base station personnel, transport personnel complement
each other to resolve. (5) Increase RXP (Rxlev Access Min) to reduce the coverage, to avoid the cell phone because of dropped calls caused by poor signal. (6) For Open DR (Directed Retry) of the cell, you can at the same time DRM (Directed Retry Improvement) set to 1, and properly set DRT (DrThreshold), to avoid the traffic signal onto a bad cell caused dropped calls.
2. Congestion 2.1, resulting in congestion of the reasons: 1, SDCCH congestion: We must be clear what the event through SDCCH to complete: a, location update, b, call setup, c, SMS and so on. SDCCH congestion occurred in the LAC area over the border and the railway Highway. In the LAC zone boundaries, cell phone location update needs to be done; rail road next to the cell phone to do the re-election, which will result in SDCCH congestion, we often can find very little traffic in those areas, but the SDCCH congestion is very serious. Holidays came, overwhelming message is also that certain quarters of the SDCCH congestion, and thus there is no idle SDCCH for the call setup services, affecting the wireless termination rates. 2, TCH Congestion: TCH Traffic Channel, is designed for call service, when the SDCCH connection for the call setup, you will find no extra slot can be allocated to the user, resulting in traffic congestion will also affect the wireless termination rates. If the base station carrier frequency allocation is not enough, or hot spots in the traffic congestion occurs TCH.
2.2, solve the congestion of the method: 1, SDCCH congestion solution: (1) increasing the SDCCH channel configuration: Channel configuration in two ways: Combined Configuration: BCCH/SDCCH/4/PCH/AGCH sharing TS0, TS1 can also be used to configure SDCCH, such a carrier frequency can be configured up to 12 SDCCH channels. This configuration is for single-carrier frequency of the cases, in remote areas where traffic can be low in this configuration. Separated Configuration: BCCH / PCH / AGCH shared TS0, TS1, TS2 can be used to configure the SDCCH, of course, two slots are available, you can use only one, so that a carrier frequency can be configured up to 16 SDCCH channels.
Based on the number of signaling, select the number of SDCCH configuration. (2) modify the parameters of HYS The mobile station for cell reselection, if the original cell and target cell belong to a different location area, then the mobile station re-election in the district must initiate a location update process. Due to the decline of radio channel characteristics, usually in the LAC region at the junction of the measured values of C2-2 district are subject to larger fluctuations, so that frequent mobile station cell reselection. Although the mobile station cell reselection of the interval of the two will not take less than 15 seconds, but 15 seconds in terms of location update time is extremely short-lived. It not only greatly increase the network signaling traffic, the wireless resources are not fully utilized, and because the mobile station in the location update process can not respond to paging, thus allowing the system to reduce the termination rates. GSM requirements adjacent area (location area and this area different) signal level must be compared with large signal level in this area, and their difference must be greater than HYS (cell reselection delay) provides that the value of the mobile station was to start cell re-election. HYS value can be increased, reducing the flow of re-election for the district. 2, TCH congestion solution: (1) Open the DR, so that idle channel adjacent cell sharing the district's traffic. At the same time should be set up DRM and DRT, to avoid dropped calls, as has been described. (2) Select two or three traffic idle neighboring cells, modify PMRG. Meanwhile, we should note that the district should be selected with the switch between cell are more to be effective. (3) by reducing PMAX (msTxPwrMaxCell), Rxp reduce the coverage to reduce traffic. (4) The traffic hot spots is available through micro-cellular and indoor coverage to absorb the traffic.
In short, dealing with dropped calls and congestion is a daily focus of network optimization is directly related to the assessment of the network targets. Practical work in a variety of problems that may arise, which we need constantly to explore and gain experience. Only solve the problems arising in the network, optimizing network resources, improve the network's operating environment and improve the network operation quality, in order to enable the network to run in the best condition for the rapid development of mobile communications services to provide strong technical support and Network Support.
GSM network optimization theory and operational methods
Principle and operation of GSM network optimization method
GSM network from China began in 1995 as a commercial use, it has been there for six years. In six years, has achieved a spectacular growth rate, at present, China's GSM network has more than 100 million users, the network scale and capacity has leapt to second in the world. As the network continues to expand and improve the network quality has also been rising, but with the intensity of competition and the ever-increasing demands of users, how to run the network to achieve relatively good running condition, has become the most important network operators. Here's to focus on models to explore the Ericsson GSM network optimization theory and methods. First, the concept of network optimization GSM network optimization work is officially put into operation refers to the GSM network, data acquisition, data analysis, identify the issues affecting the quality of the reasons for network operations, and through parameter adjustment and the adoption of certain technical means to enable the network to achieve the best operating condition, so that the existing have the best benefits of network resources, but also on the GSM network planning and construction of future maintenance and reasonable proposals put forward. GSM network optimization include the exchange of wireless network optimization and network optimization two aspects.
2, the following description of the exchange network optimization.
Inductive network performance problems
By analyzing the statistical data, and switches the user's declaration records can be a problem to optimize the network to have a general understanding.
1, switches the main working parameters of the collection collection from the following aspects: 1) The Board received the current data collection of data, such as switch B NUMBER ANALYSE, D tables, ES analysis table, the routing analysis table, SAE definition, a variety of signaling SIZE alarm monitoring data and the definition of data to switch between adjacent Bureau Definition. Data Analysis and the Bureau whether
there is a mistake. 2) The switch of statistical data collection using the MSC's statistical functions, mainly TRAFFIC ROUTE MEASUREMENT, TRAFFIC TYPE MEASUREMENT, TRAFFIC DISPERSION MEASUREMENT, get busy (non-holidays 10:00-11:00 am) switch relay circuits and systems statistical data, focusing on relay circuit termination rates, congestion rate, traffic, equipment, good rates, exchange system in all directions of traffic, termination rates and other information. Function through the STS appears to be the switch to switch between EOS and the Bureau tables. In addition the system should also be alert for collection and analysis, especially SIZE alarms, equipment, occupancy alarm information. 3) TUP signaling layer of the collection using the C7MTI low uptake rates for some relay relay track to achieve TUP layer of data, analysis successive failure.
2, data analysis 1) MSC Bureau analysis of the data in Table B Check if there are B NUMBER points to an invalid route, so that all calls were against the number of blocking, for routing incoming into the source of the corresponding B NUMBER carefully analyze whether the definition of complete, whether the gaps; Check the accuracy of ES table definition, focus on examination of audio recording to inform or obstructive (COS) whether the definition is reasonable, so as not to mislead as to inform sound, allowing users to Behavior Through Rate; Check the temporary roaming number and the switching of the provisional number of definitions; Check the relay to a Board to whether there is obstruction, if any, can be indirect through other routes Check the various boards of the relay to the put-through rate, if the put-through rate is too low, should check with the VMSC signaling, as well as to consider other routes with the adapter; Check whether the definition of D form is reasonable, because the D table definition is not accurate, will lead to the switch TRAFFIC TYPE statistics does not make sense; the same time, uptake rates calculated by the switch will also affect the definition principle is: in a number of B-table analysis chain should only occur once in D value; Check whether the definition of data roaming Bureau complete and accurate; Check the accuracy of the definition of signaling points; Inspection Agency to switch between the definition of the relevant parameters are accurately check switch alarm situation. Statistical data analysis in the switch, we need to be optimized for the overall operation of the system have an understanding of, for example switches, loading, etc., so that does not impinge on the work of carrying out the specific optimization of the system have a negative impact, such as to enable certain functions cause the
system due to excessive load higher. TRAFFIC ROUTE analysis: focus on analysis of uptake rates, equipment, good rates, congestion rate, each road traffic. If the relay circuit occurs every road traffic congestion more than 0.6ERL, should consider expansion of the relay system, such as the system is not the case of congestion with low uptake rates respond to the signaling relay ends with the inspection TRAFFIC TYPE Analysis: The traffic in all directions, the number of test calls, put-through rate analysis, impact analysis of the cause of the system put-through rate, and arrive at solutions. It should be noted that the definition of the value of the switch D to be accurate, otherwise TRAFFIC TYPE may not make sense. TRAFFIC DISPERSION analysis: the adoption of the statistics, be able to grasp the various boards to the traffic situation, for the trunk configuration and to improve the switch Through Rate of great significance. SERVICE QUALITY Analysis: the adoption of the analysis, we can TRAFFIC TYPE or ROUTE of the EOS statistics, identify the issues affecting the specific reasons for termination rates. SERVICE QUALITY reality is that the EOS value TRAFFIC TYPE for link to find out the specific reasons for the call failure. SERVICE QUALITY statistical objects can be TRAFFIC TYPE, or one or more ROUTE. EOS analysis: the use of MSC's STS features can be collected END OF SELECTION (EOS) statistical data through the analysis of these data, the system can be affecting the main reason for termination rates in order to take concrete measures to be optimized. 3) an analysis of alarm messages 3, MSC specific optimization measures 1) Check the definition of B in Table D parameters are reasonable because of B in the table D parameters affecting TRAFFIC TYPE statistical results, so if the D value is defined unreasonable termination rates will affect the calculation of the value of the switch, but also the result of different TRAFFIC TYPE generate errors, misleading optimization analysis. D parameter defines the principle that: D value should be matched with the call type; a call number in the sequence analysis of D parameters can only be used once. 2) The statistical analysis of busy EOS The continuation during the call, there are many factors that lead to call failure, and each call will be a failure in the switch internally generated a failure code-EOS yards. EOS by examining the statistical data can be found in a number of hidden problems, such as B table definition errors. Listed below are several common EOS disproportionate solutions: ES33: LS or TS-side called Busy (C7 LINK, SLB), no solution; ES90: B in the table RC points to an invalid routing; ES100: the user dialed the number is not defined in Table B, Table B should check whether the definition of integrity; Ericsson, China Mobile, Nokia (Ty].) 3m6? N e
ES114: routing congestion, you can check TRAFFIC ON ROUTE statistical data to check which routes are congested; ES400: Paging mobile phone users do not response, should check the MSC and the BSC of BTDM the T3212 parameters are reasonable, appropriate to shorten cycle time of registration; ES758: LS or TS called terminal is busy (C7 LINK, STB), no solution; ES858: call failed, wireless systems tend to show that there is congestion. ES3377: called being PAGE BUSY or paging mobile phone users do not response, should check the MSC and the BSC of BTDM the T3212 parameters are reasonable, appropriate to shorten cycle time of registration.
3) notify the inspection record for the correct guidance to inform recording user behavior, to reduce the number of invalid test call has a big role. Should make full use of the recording with notification, a higher proportion of the EOS to make use of recording the user, such as the called party is busy and so on. Under normal circumstances a switch box with two recording machines notice, one of which can be used as the other alternate routes, or load sharing, if they only opened a machine frame, you tend to notice because of busy recording arising from a large number of ES114, namely, software routing congestion. Network optimization should be carried out on each section of PHRACE monitor to see if there are recording errors and the ability to emit notification sound, used in instruction: TCTDI 4) SAE check switch handling the call during a series of functions involved in the transmission of information between blocks, and each time the call to use these function blocks some of the data records, which reflect the quantity of data records is the SIZE. When these function blocks the capacity of the definition of SIZE is not enough, they will lead the call failed. To note the following points: Activate "SOFTWARE FILE CONGESTION" monitoring function, and often the software checks whether there is congestion. This feature is occupied by continuous monitoring of dynamic SAE, such as dealing with the traffic associated with the SAE, the command for the DBTSP: TAB = SAACTIONS; CP30 of the SAE automatically monitor activation command to: SAOCS; SAE definition of some important automatic alarm function, when these SAE's usage exceeds a certain threshold, the switch will produce a corresponding warning. This feature is mainly used to monitor static SAE, such as the user associated with the SAE, and is not continuous monitoring, sampling time is 40 minutes, the command is: AFTSP through the TRAFFIC MEASUREMENTS ON ROUTE function to indirectly check the SAE related to the use of, for example in the case of hardware there is enough to block, you can suspect that the definition of the relevant SAE is not enough; (s) F.db2T K \ 'i STS by checking the relevant counters to monitor the use of SAE. OBJECT TYPE used as a SAE.
Regular checks of the use of a number of SAE and found that not enough time should be expanded; SAE attention to the inter-relations, and modify the definition of a SAE should take into account their associated SAE; expansion project to increase the MALT, BT and other hardware equipment, in addition to increasing their own SAE, special attention should also increase the number of relevant functional blocks of the SAE. 5) increase the success rate of the switch to switch between 6) The Council on the 7th Inter-signaling trace 7) The software version verification, check whether Youlou patch, feel free to contact Ericsson 8) The use of TEST SYSTEM, you can get some signals from within the information needed. For example, a user can be tracked for the EOS, for some particular failure is easy to find excluded. For a user to recover EOS (Caller ID: 13,600,000,001) TEST SYSTEM; ON IN RE IANRANDINFO; ON IN DO: IF DR4 = 1; IF DR5 = 3; i: _ V a hy & IF DR6 = 6; www.mscbsc.comj b: W @ U D'g zp) D | IF DR7 = 0; & U * VD m T6m9TIF DR8 = 0; www.mscbsc.com s) n1mf V ((z Q4U $ z IF DR9 = 0; IF DR10 = 0; IF DR11 = 0; IF DR12 = 0; IF DR13 = 0; IF DR14 = 1; CODE H'28; CODE H'182; CODE 1;
ON VAR DO: IF PR0 = H'FF; PV; ON VAR RE 20; INIT
Against an income of route-tracing EOS:
TEST SYSTEM; PRINT STRVAR TRAN 0 -: 60; ON IN RA ANEOSC1; ON IN DO: IF DR1 = H'XX; (H'XX is the name of the corresponding pointer into the route) DO R0; DO:; INIT; 3, the following is a description of the wireless network. Relative to the exchange of network optimization, radio network optimization in the network optimization is even more important and more complex than the exchange of network optimization, which is caused due to the wireless environment, complex, and therefore to improve the wireless on, often to give the whole network access greatly improved pass rate Effects the quality of wireless networks are generally the following areas: wireless network congestion, district, or the carrier frequency is not working properly, the signal is too weak and the poor quality caused by dropped calls, switching. 1, data acquisition. BSC wireless part of the network optimization parameters generally include cell collection, cell data collection (STS) and road test combination. Data were collected on the following aspects: 1) SDCCH channel: There are mainly assigned frequency, success rate, congestion rate, call drop rate of 4 Indicators 2) TCH: There are facilities in good order, assignment success rate, congestion, dropped calls, total traffic, traffic per channel. 3) HANDOVER: a switch requests, the success rate, switch did not receive the rate, HANDOVER LOST and other indicators. 4) wireless parameter acquisition: in the district has made the switch parameters 5) The road test is also very important 2, the data analysis: 1) Cell parameter analysis: The cell parameters of the entire Board has been treated LOG down compared to some of the definitions can be found unreasonably parameters, cell parameters on the impact of wireless networks is a direct and effective. 2) STS analysis: with statistical reports, we can find equipment, good rates, congestion, and various wireless channel frequency assignment, assignment success rate, the wireless PAGING success rate, switching the success rate. SDCCH channels: mainly assigned frequency, success rate, congestion rate, call drop rate of 4 Indicators. Such
as call drop rate, generally because of high TCH congestion, SDCCH carrier frequency signal is too weak, or base station hardware. If congestion is low but the success rate is low, it may be the carrier frequency transceiver system problems TCH: There are facilities in good order, assignment success rate, congestion, dropped calls, total traffic, traffic per channel. , Such as equipment intact but there is no traffic, it may hang the plot, such as the TCH assigned to the low success rate and the cell traffic is not high, there may be the problem feeder carrier frequency of days. If there is congested traffic is not high, then the plot is not working properly.
HANDOVER: a switch requests, the success rate, switch did not receive the rate, HANDOVER LOST and other indicators. Switch the success rate is greater than 95%, loss rate of less than 1%, such as the success rate of switching is too small and the number of small switches can switch between the view that the unreasonable. Such as the switching frequency through the high, may wish to consider whether there is the same frequency interference, since such switching may be caused by poor quality.
PAGING: mainly depends on the success rate of the wireless PAGING indicator of the success of the two PAGING sum divided by the total number of PAGING number should be higher than 90%, if lower than this, they have wireless coverage, frequency interference aspects.
3) Road test: crossing test can find the following issues: the definition of an error caused by the same frequency band or adjacent channel interference, the antenna pick wrong, irrational relationship between neighboring cells, base stations, hardware failure, GSM wireless signal coverage, the wireless signal quality, as well as intra - BSC and inter-BSC handover situation, has passed the road test to discover and solve problems, thereby enhancing network quality, while road test information obtained by the network for future expansion and construction provide a valuable basis.
3, specific optimization measures: STS statistics combined with road tests, in general these issues can be found. The following brief discussion about the causes of the issues and software solutions 1) TCH congestion. However, if the district traffic congestion or a low-TCH assigned to the low success rate, which may be a hardware failure can be improved to exclude hardware troubleshooting. If it is caused due to lack of channel congestion, should generally be by increasing the carrier frequency or a base station solution, but within a certain range can be resolved by adjusting the cell parameters. adjust base station power, the parameters include BSPWRB, BSPWRT, BSPWR, BSTXPWR, should pay attention to its corresponding adjustment of the relationship, BSPWRB and BSPWR, BSPWRT and
BSTXPWR counterparts. Otherwise, the base station hardware will occur can not be solved. Although the district to reduce power can reduce the coverage, reduce traffic, thereby reducing congestion, but may also signal the resulting blind spot of some. changes to switch between cell phone only from the high traffic to low traffic cell to switch adjusted ACCMIN, ACCMIN refers to mobile phone access to the threshold level, an appropriate increase ACCMIN, to reduce the effective range of residential, ACCMIN generally not less than -- 90db. But this is also creating new blind spot problem. Open the Assign to Worse cell function, a reasonable set AWOFFEST parameters. This feature means that when the call to establish the SDCCH after the assignment of TCH, the permit assigned to the wireless quality than the current cell is worse on the plot of the TCH. Parameters can be adjusted in the 3-15db, but this may have caused due to poor quality of the call drop. adjust the cell switching boundary parameters KOFFSET, raising switching to reduce traffic. In addition, there are other methods such as cell load sharing, cell layer and so on.
2) call drop. signal is weak, weak signals can increase the power and check the adjustment of the base station to resolve the relationship between neighboring cells. poor quality, mainly in the same frequency or adjacent-channel interference. Source of interference may be an external source of interference or neighboring cell. Interference can improve road test and the BSC within a "channel event record", the designated cell interference monitoring, command: RACEI: CELL =, DTIME =; open frequency hopping to reduce interference and reduce dropped calls class rate, with the FM-related parameters: HOP, HSN, FHOP, COMB. switch, switch should check whether the data is reasonable, complete, check the district BSIC parameter, BSIC error will cause switch failure. Others, such as base stations, hardware failure, transmission instability, from top to bottom-line power does not match the other. 3) PAGING success rate is low. coverage is poor, increase base station coverage, reducing the ACCMIN, taking into account the impact of dropped calls, ACCMIN recommended to take 104. T3212 is set too large, a reasonable T3212 time settings can reduce the number of invalid PAGING, set T3212 time to combine the capacity of BSC and MSC, is set too small will affect the switch from overload. According to experience, medium-sized network T3212 desirable for 30 minutes, a large network to take 1 hour.
frequency interference serious, due to frequency interference, could result in mobile phones PAGING no response, the success rate is low. Available from OBJTYPEwww.mscbsc.com y Q: S "Z UD ? P RANDAMACC statistics and the base station frequency interference statistics to identify problem areas, reduce frequency interference and improve PAGING success rate. BSC switches properly set properties, such as opening GLOBALPAGING so. 4) Road side to take the road test result analysis found some problem areas, such as the coverage is not good, poor voice quality. coverage analysis: the signal intensity-85DBM can achieve a better outdoor coverage,-75DBM above can achieve a better indoor coverage. Voice quality problem: the signal intensity-85DBM above and poor voice quality (voice quality in 3 above), may be a preliminary determination is due to interference caused by the base station through the sweptreceiver combination of the database to identify sources of interference. Frame loss rate of problem: in general due to hardware failure caused by interference and the base station. 5) The search for the whole network frequency interference radio frequency interference affecting the call quality of the most important factor, usually frequency interference check method: ANT drive test analysis, swept receiver swept analysis, Ericsson provided by the BSC FAS (frequency interference test) analysis of the specific command: RARII, RABDC, RARCI, RARRI, RARRP, RARTI, through the above method of checking the frequency interference sources, using pitch angle adjustment of base station antennas, base station transmit power, frequency adjustment solution to the frequency interference problem. 6) relative to collar the whole network to find the definition of residential district relative to collar ties, generally from the base station to be relative to the map collar district relations, but because of the base station height, geographical environment, the use of high-gain antennas and other causes collar complex relationship relative to the actual Some phase but did not define the relationship between T cell, which will easily lead to decline in voice quality, dropped calls. Through the use of NCS (relative to collar district to find) function to solve this problem. Specific orders: RABII, RABDC, RABRI, RABRP, RABTI.
Fourth, the process of Attention GSM system optimization is a constant of the system parameters and hardware devices for dynamic adjustment process, while optimizing the system performance is also a work of a balanced process, and modify a parameter may be increased in a performance, but also other properties associated with reducing the consequences of , which require us to carefully balanced. For the optimization of process parameters of amendments should only be 11 for each record, so that problems can be promptly restored the old post-
operating parameters. Therefore, in the optimization process should be a lot of statistical work in order to change the system performance have a clear understanding.
You might also like
- Radio Network Planning and Optimisation for UMTSFrom EverandRadio Network Planning and Optimisation for UMTSJaana LaihoRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Workshop On Teletalk Network Modernization and 3G ExpansionDocument33 pagesWorkshop On Teletalk Network Modernization and 3G ExpansionClaudia Dombroski100% (1)
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionFrom EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionNo ratings yet
- CAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkFrom EverandCAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- What Is Difference Between Congestion and BlockingDocument17 pagesWhat Is Difference Between Congestion and Blockingappu_mailNo ratings yet
- Understanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandUnderstanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeMaciej NawrockiNo ratings yet
- CSSR AnalysisDocument14 pagesCSSR AnalysisAhmed OmerNo ratings yet
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkFrom EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkNo ratings yet
- GUL Inter-Working Strategy-Mobifone LTE 530 Project PDFDocument17 pagesGUL Inter-Working Strategy-Mobifone LTE 530 Project PDFHomQuaNo ratings yet
- 2G Cluster Optimization Acceptance Report Revised - 20171225pmDocument17 pages2G Cluster Optimization Acceptance Report Revised - 20171225pmForu MophiliaNo ratings yet
- Genex Cloud ACP GuidelineDocument10 pagesGenex Cloud ACP GuidelineMohammad RidwanNo ratings yet
- HUAWEI E392u-12 User Manual (V100R001 01)Document2 pagesHUAWEI E392u-12 User Manual (V100R001 01)sam2976No ratings yet
- Frequency Assignment To Cellular Mobile Operators in AJK & GBDocument1 pageFrequency Assignment To Cellular Mobile Operators in AJK & GBAzam KhanNo ratings yet
- Backhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsFrom EverandBackhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsKazi Mohammed Saidul HuqNo ratings yet
- Mobile Handset Testing A Report For Ofcom, The Uk Communication Regula TorDocument38 pagesMobile Handset Testing A Report For Ofcom, The Uk Communication Regula Toranahh ramakNo ratings yet
- Optimization Procedures LteDocument12 pagesOptimization Procedures LteMARCUS SANCHEZNo ratings yet
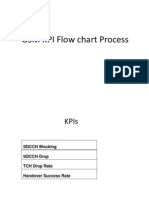
- GSM KPI Flow Chart ProcessDocument12 pagesGSM KPI Flow Chart ProcessMohammed Al MandhariNo ratings yet
- GSM Frequency Planning-Presentation PDFDocument22 pagesGSM Frequency Planning-Presentation PDFسعید خزاییNo ratings yet
- Airtel Site Acceptance PAT Document: Nigeria Airtel MC 2G Phase 1 ProjectDocument20 pagesAirtel Site Acceptance PAT Document: Nigeria Airtel MC 2G Phase 1 ProjectAdetayo OnanugaNo ratings yet
- Poor CSSRDocument2 pagesPoor CSSRIdowu OjoNo ratings yet
- Optimization Process PDFDocument79 pagesOptimization Process PDFtadjouaminaNo ratings yet
- GSM Call Drop Problem AnalysisDocument66 pagesGSM Call Drop Problem AnalysisMesfin TibebeNo ratings yet
- RTWP IssueDocument4 pagesRTWP Issueekoyudip1No ratings yet
- 2G Huawei Performance MonitoringDocument70 pages2G Huawei Performance MonitoringBatool FatimaNo ratings yet
- Double BCCH AllocationDocument17 pagesDouble BCCH AllocationUmarFarooqNo ratings yet
- (RF) Call Drops On Traffic Channel HuaweiDocument4 pages(RF) Call Drops On Traffic Channel Huaweikarthir26No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cellular Network Planning and Optimisation: 2G/2.5G/3G... Evolution to 4GFrom EverandFundamentals of Cellular Network Planning and Optimisation: 2G/2.5G/3G... Evolution to 4GNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Selective PagingDocument9 pagesIntelligent Selective PagingRao DheeruNo ratings yet
- 3g Inteference Test and Solution ReportDocument10 pages3g Inteference Test and Solution ReportRussell OsiNo ratings yet
- KPIs in Actix Guide Book 0118Document73 pagesKPIs in Actix Guide Book 0118dtvt40No ratings yet
- 2G Call Drop CountersDocument316 pages2G Call Drop Counterskarthikeyan_dhandapaNo ratings yet
- KPI Trouble Shooting: Security LevelDocument13 pagesKPI Trouble Shooting: Security LevelIslam AdamNo ratings yet
- Concentric Cell Main ParameterDocument15 pagesConcentric Cell Main ParameterMahdi Khansari100% (1)
- GU 900 MHZ Non-Standard Frequency Spacing (SRAN7.0 - 01)Document56 pagesGU 900 MHZ Non-Standard Frequency Spacing (SRAN7.0 - 01)gopizizou50% (2)
- TE 484: Network PlanningDocument65 pagesTE 484: Network PlanningopareaduboahenNo ratings yet
- Orange CI: ABIDJAN Cocody Cluster2Document17 pagesOrange CI: ABIDJAN Cocody Cluster2Opeyemi DadaNo ratings yet
- BTS Power ControlDocument31 pagesBTS Power ControlLee NghiaNo ratings yet
- Report FinalDocument55 pagesReport Finalkacel marzoukNo ratings yet
- TEC Guidelines On EMF TestingDocument40 pagesTEC Guidelines On EMF TestingSrinivas RajuNo ratings yet
- Alcatel BSS Parameter DictionaryDocument1,278 pagesAlcatel BSS Parameter DictionaryrajasapramNo ratings yet
- Radio Link TimeoutDocument1 pageRadio Link TimeoutharinjakaNo ratings yet
- Problem Analysis Flow Charts For GSM KPIsDocument21 pagesProblem Analysis Flow Charts For GSM KPIsAnonymous D9ShNMfVNo ratings yet
- Checking Points of BTSDocument2 pagesChecking Points of BTSErangaNo ratings yet
- UMTS Network Expansion Solution V2 0Document6 pagesUMTS Network Expansion Solution V2 0Umar PervaizNo ratings yet
- Nokia Siemens Networks Flexi MR 10 BTS Datasheet 19022013Document5 pagesNokia Siemens Networks Flexi MR 10 BTS Datasheet 19022013Joao SilvaNo ratings yet
- D2hanjar Hourly Running HourlyDocument55 pagesD2hanjar Hourly Running HourlyHanjar PrakasiwiNo ratings yet
- HUAWEI - Statistics Data Analysis and Optimization V 4.0Document154 pagesHUAWEI - Statistics Data Analysis and Optimization V 4.0Abdel SbeitiNo ratings yet
- Metricell General PresentationDocument39 pagesMetricell General PresentationkarimbandariNo ratings yet
- GSM-To-UMTS Training Series 02 - WCDMA Radio Network Coverage Planning - V1.0Document86 pagesGSM-To-UMTS Training Series 02 - WCDMA Radio Network Coverage Planning - V1.0AliKaiserNo ratings yet
- TRX and RF Cable TroubleshootingDocument7 pagesTRX and RF Cable TroubleshootingAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Common BCCH For GSM 900 - 1800 Dual Band OperationDocument15 pagesCommon BCCH For GSM 900 - 1800 Dual Band Operationridon mbayi100% (1)
- NXP CatalogDocument30 pagesNXP CatalogAnshul Srivastava100% (2)
- Critical Success Factors For 4G LTE Launching in Taiwan: A Study On Customers' ExpectationsDocument44 pagesCritical Success Factors For 4G LTE Launching in Taiwan: A Study On Customers' ExpectationsAnshul SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Class Diagram: 5.2.1 Attributes and RelationshipsDocument8 pages5.2 Class Diagram: 5.2.1 Attributes and RelationshipsAnshul SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Distance CalculatorDocument15 pagesDistance CalculatorAnshul SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- PDF Id 1SLK01NxPU0sTcEllCu5N2T2LcgNsFAF q7OHCk2VIoI&pageid P&attachment FalseDocument1 pagePDF Id 1SLK01NxPU0sTcEllCu5N2T2LcgNsFAF q7OHCk2VIoI&pageid P&attachment FalseAnshul SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Wcdma Call FlowDocument15 pagesWcdma Call FlowShantanu MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- NPO - Rec - Parameters - For - Radio - RU20Document26 pagesNPO - Rec - Parameters - For - Radio - RU20djemai cherguiNo ratings yet
- Technik: RefraDocument54 pagesTechnik: Reframustaf100% (1)
- Alma Matter SpeechDocument1 pageAlma Matter Speechlariza gallegoNo ratings yet
- Waste SM4500-NH3Document10 pagesWaste SM4500-NH3Sara ÖZGENNo ratings yet
- TTD Accommodation ReceiptDocument2 pagesTTD Accommodation ReceiptDharani KumarNo ratings yet
- Frankenstein ExtractDocument1 pageFrankenstein ExtractAnneNo ratings yet
- Sears Canada: Electric DryerDocument10 pagesSears Canada: Electric Dryerquarz11100% (1)
- Effect of Spent Engine Oil On The Internal Structure of Corchorus OlitoriusDocument55 pagesEffect of Spent Engine Oil On The Internal Structure of Corchorus Olitoriusanon_568621284No ratings yet
- Intern JanataDocument59 pagesIntern JanataKhairul IslamNo ratings yet
- Coca-Cola BeverageDocument17 pagesCoca-Cola BeverageMahmood SadiqNo ratings yet
- Banking Adbl EnglishDocument74 pagesBanking Adbl Englishdevi ghimireNo ratings yet
- Board of DirectorsDocument2 pagesBoard of DirectorsjonahsalvadorNo ratings yet
- Book2Chapter10 and 11 EvaluationDocument55 pagesBook2Chapter10 and 11 EvaluationEmmanuel larbiNo ratings yet
- Libra Office Question Answer EnglishDocument11 pagesLibra Office Question Answer EnglishAndrew ParkarNo ratings yet
- Action Research Intervention in English 9Document6 pagesAction Research Intervention in English 9Rey Kris Joy ApatanNo ratings yet
- Angles - of - Elevation - and - Depression Lesson STEMDocument18 pagesAngles - of - Elevation - and - Depression Lesson STEMmheojhun0% (1)
- A Cultura-Mundo - Resposta A Uma SociedDocument7 pagesA Cultura-Mundo - Resposta A Uma SociedSevero UlissesNo ratings yet
- Alburg-Caldwell Manor 1784-1826 Draft by Fay YoungDocument3 pagesAlburg-Caldwell Manor 1784-1826 Draft by Fay YoungNancy Cunningham100% (1)
- G5 Series User ManualDocument22 pagesG5 Series User ManualDaniel MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Data Mining With Apriori AlgorithmDocument12 pagesData Mining With Apriori AlgorithmMAYANK JAINNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 6GK5213-3BB00-2TB2: Transfer RateDocument6 pagesData Sheet 6GK5213-3BB00-2TB2: Transfer RateClaudiu VlasceanuNo ratings yet
- Math912 2Document7 pagesMath912 2Mbq ManbriquaNo ratings yet
- GSM Rtu Controller Rtu5011 v2 PDFDocument27 pagesGSM Rtu Controller Rtu5011 v2 PDFAbdul GhaniNo ratings yet
- Battle Group Builder + Commonwealth Infantry Roster - Wargames DesignDocument12 pagesBattle Group Builder + Commonwealth Infantry Roster - Wargames DesignPete PoliNo ratings yet
- 2018-2021 VUMC Nursing Strategic Plan: Vision Core ValuesDocument1 page2018-2021 VUMC Nursing Strategic Plan: Vision Core ValuesAmeng GosimNo ratings yet
- Automatic Drive Positioner: SectionDocument207 pagesAutomatic Drive Positioner: SectionHakob AdamyanNo ratings yet
- 17 Samss 518Document20 pages17 Samss 518Mohamed H. ShedidNo ratings yet
- Kalsi P S - Organic Reactions and Their Mechanisms 5eDocument26 pagesKalsi P S - Organic Reactions and Their Mechanisms 5eeasy BooksNo ratings yet
- Beg 2018 XXDocument42 pagesBeg 2018 XXFranz Gustavo Vargas MamaniNo ratings yet
- Slides 5 - Disposal and AppraisalDocument77 pagesSlides 5 - Disposal and AppraisalRave OcampoNo ratings yet
- Demand Management in Global Supply Chain - Disertasi S3Document166 pagesDemand Management in Global Supply Chain - Disertasi S3Ahmad BuchoriNo ratings yet