Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP 1-Hemo
Uploaded by
Maria MandidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP 1-Hemo
Uploaded by
Maria MandidCopyright:
Available Formats
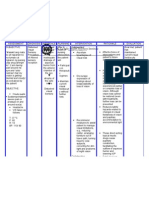
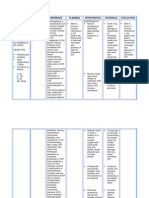
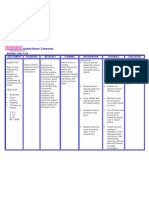
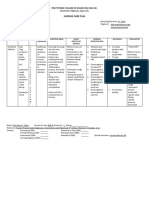
Assessment Subjective: Hindi ako masyadong nakaka inum ng tubig, kaya nanuyot ang balat ko.
Objective: -Dry skin -Chopped Lips -Restlessness V/S taken: Temp: 36.3C PR: 88bpm RR:17cpm BP:110/80mmhg
Diagnosis Deficient fluid volume may be related to active fluid loss (hemorrhage, vomiting, gastric intubation, diarrhea, burns, wounds, fistulas).
Inference Inadequate water intake, loss through vomiting, diarrhea, gastrointestinal obstruction, fever or sweating, hemorrhage, burns, third space fluid shifting.
Planning After 4 hours of nursing interventions, the Patient will maintain fluid volume at a functional level as evidenced by individually adequate urinary output with normal specific gravity, stable vital signs, moist mucous membranes, good skin turgor, and prompt capillary refill.
Intervention Independent Monitor urinary output.
Weigh daily and compare with 4hour fluid balance. Evaluate clients ability to manage own hydration.
Ascertain clients beverage preferences, and set up a 24-hour schedule for fluid intake. Turn frequently, gently
Rationale Fluid replacement needs are based on correction of current deficits and ongoing losses. Measureme nt provides useful data for comparison. Impaired gag and swallow reflexes and change in level of consciousness are among the factors that affect clients ability to replace fluids orally. Relieves thirst and discomfort of dry mucous membranes and augments parenteral replacement. Tissues are susceptible to breakdown because of vasoconstriction and increased fragility. Skin and
Evaluation After 4 hours of nursing interventions, the Patient was able to maintain fluid volume at a functional level as evidenced by individually adequate urinary output with normal specific gravity, stable vital signs, moist mucous membranes, good skin turgor, and prompt capillary refill
massage skin, and protect bony prominences.
Provide skin and mouth care.
mucous membranes are dry with decreased elasticity because of vasoconstriction and reduced intracellular water. Decreased cerebral tissue perfusion frequently results in changes in mentation.
Provide safety precautions.
You might also like
- EVD PosterDocument1 pageEVD PosterDwie 'keonk' UnisaspalaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Short Term: Independent: Independent: Short TermDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Short Term: Independent: Independent: Short TermSittie Sobaidah D. DimakutaNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Physical Mobility Acute PainDocument8 pagesNCP Impaired Physical Mobility Acute PainAi RouNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis DKA Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis DKA Care Planعبدالله خليل العسل100% (1)
- NCP OsteoarthritisDocument4 pagesNCP OsteoarthritisKyle Margaret Flores100% (1)
- Gcic NCP Seizure PICUOSMUNDocument2 pagesGcic NCP Seizure PICUOSMUNhanyaklein100% (3)
- The Perfect Exercise - Ba Gua Circle Walking Nei GungDocument6 pagesThe Perfect Exercise - Ba Gua Circle Walking Nei GungLaron ClarkNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis: AdvertisementsDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis: AdvertisementsJamea TumbagaNo ratings yet
- NCP Disturbed Visual Sensory Perception Related To Chemotherapy Evidenced by Visual DistortionDocument2 pagesNCP Disturbed Visual Sensory Perception Related To Chemotherapy Evidenced by Visual DistortionCamille Grace100% (2)
- NCP - Risk For InjuryDocument3 pagesNCP - Risk For InjuryRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Natural History of DiseaseDocument31 pagesNatural History of Diseasegabo dasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationpopoy03100% (3)
- Cleft Lip Palate NCPDocument2 pagesCleft Lip Palate NCPLerma PagcaliwanganNo ratings yet
- NCP FractureDocument2 pagesNCP FractureAi Rou100% (1)
- N C PDocument3 pagesN C PTrixia Diaz100% (1)
- Risk For InjuryDocument4 pagesRisk For InjuryJanina Patricia BuddleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For "Glaucoma"Document7 pagesNursing Care Plan For "Glaucoma"jhonroks100% (7)
- NCP Visual SensoryDocument2 pagesNCP Visual SensoryEugene UCNo ratings yet
- Potts Disease NCPDocument6 pagesPotts Disease NCPDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- NCP - GlaucomaDocument1 pageNCP - GlaucomaKath CuevasNo ratings yet
- NCP - Blurred VisionDocument3 pagesNCP - Blurred VisionJohn Cenas45% (22)
- NCP - LeprosyDocument3 pagesNCP - LeprosyKevin DareNo ratings yet
- Cataract NCPDocument1 pageCataract NCPMhegz Halcon75% (8)
- NCP 8fDocument2 pagesNCP 8fRaiel B. Buenviaje RN0% (1)
- Disturbed SleepDocument1 pageDisturbed Sleepmawel100% (1)
- (NCPS) Impaired Physical Mobility 2Document2 pages(NCPS) Impaired Physical Mobility 2roren100% (1)
- NCP - BipolarDocument2 pagesNCP - BipolarSasha FongNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN SeizureDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN SeizureOscar Villados Jr.100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- NCP CataractDocument2 pagesNCP CataractMaureen Gay Acierto Tegui67% (3)
- Cataract NCP: Submitted To: Mrs. Ashdel Artes Submitted By: Fajardo, Nicole Francis YDocument5 pagesCataract NCP: Submitted To: Mrs. Ashdel Artes Submitted By: Fajardo, Nicole Francis YNicole Francis Fajardo67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan GlaucomaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Glaucomasephirus77750% (4)
- NCP CataractDocument3 pagesNCP CataractKate ChavezNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocument3 pagesDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJashtine JingcoNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationDocument2 pagesAnxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationmonaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: General: Goals Met GenreralDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: General: Goals Met GenreralRomzy BasañesNo ratings yet
- NCP Cataract SurgeryDocument5 pagesNCP Cataract SurgeryKristaJaneCelmarBagcatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Subconjunctival Hemorrhage OSDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For Subconjunctival Hemorrhage OSRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPLornz E. Cantos100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationria_soriano_2No ratings yet
- NXCP Disturbed Sensory Perception3Document2 pagesNXCP Disturbed Sensory Perception3marielle_dellaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Johndelle Banlasan Hernan100% (1)
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesImpaired Skin IntegrityBesael BaccolNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorNo ratings yet
- Ncp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDDocument4 pagesNcp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Impaired Verbal CommDocument3 pagesImpaired Verbal CommKM100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanNeza AgdalesNo ratings yet
- NCP LaminectomyDocument4 pagesNCP LaminectomyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Navidas-Hearing Impairnent Act.Document2 pagesNavidas-Hearing Impairnent Act.Fran Lan100% (1)
- Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1Document8 pagesRisk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1kint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan SeizureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Seizuretimie_reyes100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNo ratings yet
- Gout N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageGout N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCP FVDDocument2 pagesNCP FVDMarlon AnryNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesHepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan SeizureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan SeizureTeresa JunioNo ratings yet
- Self Care DeficitDocument1 pageSelf Care DeficitWilly EstacionNo ratings yet
- NCP PryllDocument6 pagesNCP PryllpjcolitaNo ratings yet
- Javier, Darryl O. BSN311-Group 42Document3 pagesJavier, Darryl O. BSN311-Group 42karthi karthiNo ratings yet
- NCP Blurred VisionDocument3 pagesNCP Blurred VisionRM MoralesNo ratings yet
- NCP Blurred VisionDocument3 pagesNCP Blurred Visionناديه المعمريNo ratings yet
- Compartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)Document2 pagesCompartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)eunica16No ratings yet
- CaseDocument2 pagesCaseDash DacalNo ratings yet
- BoilDocument4 pagesBoilPipipopoNo ratings yet
- Khorana AA - Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Neutropenic Cancer PatientsDocument8 pagesKhorana AA - Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Neutropenic Cancer PatientsFarid RakhmanNo ratings yet
- NCLEX PreparatioNNDocument2 pagesNCLEX PreparatioNNgeng gengNo ratings yet
- Cortes I 2007Document2 pagesCortes I 2007KamalPatelNo ratings yet
- Ductal Carcinoma in SituDocument7 pagesDuctal Carcinoma in SituLittle DevNo ratings yet
- A Case Report On Wound Healing Activity of Cow GheeDocument4 pagesA Case Report On Wound Healing Activity of Cow GheeKishan PatelNo ratings yet
- Kumri in GoatDocument11 pagesKumri in GoatDr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis in PregnancyDocument18 pagesTuberculosis in PregnancyNitesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- C. HPCT File Week 1 Introduction To General Pathology and HistoTechniquesDocument32 pagesC. HPCT File Week 1 Introduction To General Pathology and HistoTechniquesAliah Anne MagnoNo ratings yet
- Pain Management, The Veterinary Technicians PerspectyveDocument14 pagesPain Management, The Veterinary Technicians PerspectyveClínica Veterinaria TODOVETNo ratings yet
- Методологическая Разработка По Английскому Языку На Тему «Case Study. Respiratory: Chronic Cough»Document1 pageМетодологическая Разработка По Английскому Языку На Тему «Case Study. Respiratory: Chronic Cough»AleBldNo ratings yet
- Introductory LetterDocument2 pagesIntroductory Letterapi-239073517No ratings yet
- Evidence Base For Shaken Baby SyndromeDocument30 pagesEvidence Base For Shaken Baby Syndromecicleo74No ratings yet
- Management and Outcome of Testicular Torsion: Background ConclusionDocument4 pagesManagement and Outcome of Testicular Torsion: Background Conclusionabdullahi husseinNo ratings yet
- Appendix 2: List of High Alert MedicationDocument7 pagesAppendix 2: List of High Alert MedicationhanselMDNo ratings yet
- Neurocritical Care in The General Intensive Care UnitDocument17 pagesNeurocritical Care in The General Intensive Care UnitdanielNo ratings yet
- Amyloid Vaccine For Alzheimer's Disease - Is It Feasible by Supreet Khare, Deeksha Seth, Shrayash KhareDocument4 pagesAmyloid Vaccine For Alzheimer's Disease - Is It Feasible by Supreet Khare, Deeksha Seth, Shrayash Khareijr_journalNo ratings yet
- Charlie Gard Ethics, Conflict and Medical Treatment For ChildrenDocument15 pagesCharlie Gard Ethics, Conflict and Medical Treatment For ChildrenNurudeen AdesinaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Sensitivity of Most Commonly Isolated Bacteria From Feline Upper Respiratory Infection (URI)Document3 pagesAntimicrobial Sensitivity of Most Commonly Isolated Bacteria From Feline Upper Respiratory Infection (URI)KAREN LEE MEI FONGNo ratings yet
- GrieDocument410 pagesGrieamravati_hospital8No ratings yet
- Efficacy of Dialectical Behavior Therapy For Adolescents at High Risk For Suicide: A Randomized Clinical TrialDocument11 pagesEfficacy of Dialectical Behavior Therapy For Adolescents at High Risk For Suicide: A Randomized Clinical TrialLia Marcela Rivera HernandezNo ratings yet
- Food ImpactionDocument21 pagesFood ImpactionKarina SabriatiNo ratings yet
- 100 Diseases Treated by Single Point of Acupuncture (001 070)Document70 pages100 Diseases Treated by Single Point of Acupuncture (001 070)Domingo Garcia Gonzalez0% (1)
- Adrenal Gland Disease in Ferrets: Elisabeth Simone-Freilicher, DVM, DABVP-AvianDocument13 pagesAdrenal Gland Disease in Ferrets: Elisabeth Simone-Freilicher, DVM, DABVP-AvianGabriel MendesNo ratings yet
- Class-Xii-Biology Project-2023-24Document14 pagesClass-Xii-Biology Project-2023-24Shraddha MajhiNo ratings yet
- Hormone Therapy: The Basics: What Are Hormones and How Are They Used As Therapy?Document4 pagesHormone Therapy: The Basics: What Are Hormones and How Are They Used As Therapy?Ubaidillah Romadlon AlfairuziNo ratings yet
- Diasquisis Rev - NeurologiaDocument5 pagesDiasquisis Rev - NeurologiaEva Sala RenauNo ratings yet