Professional Documents
Culture Documents
N ch3 08
Uploaded by
Mahfuz A. AzimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
N ch3 08
Uploaded by
Mahfuz A. AzimCopyright:
Available Formats
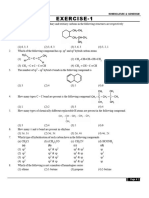
Haloalkanes: Physical Properties
The tables below show some physical data for a selection of haloalkanes. Haloalkane fluoromethane chloromethane chloroethane 1-chloropropane 2-chloropropane 2-chloro-2-methylpropane bromomethane bromoethane 1-bromopropane 2-bromopropane 2-bromo-2-methylpropane iodomethane iodoethane 1-iodopropane 2-iodopropane 2-iodo-2-methylpropane Formula CH3F CH3Cl CH3CH2Cl CH3CH2CH2Cl CH3CHClCH3 (CH3)2CClCH3 CH3Br CH3CH2Br CH3CH2CH2Br CH3CHBrCH3 (CH3)2CBrCH3 CH3I CH3CH2I CH3CH2CH2I CH3CHICH3 (CH3)2CICH3 Density (g cm3) 0.557 0.916 0.898 0.891 0.863 0.842 1.676 1.461 1.354 1.314 1.221 2.279 1.936 1.748 1.703 1.571 Tb (K) 194.7 248.9 285.4 319.7 308.8 323.8 276.7 311.5 344.1 332.5 346.4 315.5 345.4 375.5 362.5 373.1
Boiling point comparisons for various haloalkanes Haloalkane chloromethane dichloromethane trichloromethane tetrachloromethane Your task Study the data above carefully, then answer the following questions: 1. Make lists of the haloalkanes above to show which are liquids and which are gases at room temperature (assume it is 298K). What do you notice? 2. Describe and explain the effect on the densities and boiling points of haloalkanes in the following cases: a) the identity of the halogen present in the haloalkane is altered; and b) the number of carbon atoms in the haloalkane is increased. 3. What effect does increasing the number of halogen atoms present in a haloalkane have on the boiling point? Explain your answer. Copyright 2003 Nigel Saunders N-ch3-08 Formula CH3Cl CH2Cl2 CHCl3 CCl4 Tb (K) 248.9 313.1 334.8 349.6 Haloalkane fluoromethane chloromethane bromomethane iodomethane Tb (K) 194.7 248.9 276.7 315.5
You might also like
- CPP 20220411175711706233Document139 pagesCPP 20220411175711706233Ronit NigamNo ratings yet
- Alkyl HalideDocument112 pagesAlkyl HalideRaval sagarNo ratings yet
- MC HoDocument4 pagesMC HoMarcelo MagalhãesNo ratings yet
- Edit 1592206021 195648a81951e931 Alkyl Halide - TheoryDocument23 pagesEdit 1592206021 195648a81951e931 Alkyl Halide - Theorysultaneaditya.1No ratings yet
- Alkyl HalideDocument28 pagesAlkyl HalideManish RoyNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument14 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesKalpesh BishnoiNo ratings yet
- M Experiment 3 Hydrocarbon and Its DerivativesDocument3 pagesM Experiment 3 Hydrocarbon and Its DerivativesmchaleNo ratings yet
- I) Chalcones and Cinnamonyl Derivatives: Archo Piperidine, CHCL, RefluxDocument27 pagesI) Chalcones and Cinnamonyl Derivatives: Archo Piperidine, CHCL, RefluxUjjwal SharmaNo ratings yet
- IUPAC - Practice SheetDocument5 pagesIUPAC - Practice SheetRishi NairNo ratings yet
- Parishram (2024) : Alcohol, Phenol and EtherDocument3 pagesParishram (2024) : Alcohol, Phenol and Etherbiswajitttt8No ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument31 pagesOrganic ChemistrySameep Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- IsomerDocument30 pagesIsomerResy Maya18No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument14 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenesshreyansh tanwarNo ratings yet
- SCES3123: W1 - Tutorial 1Document2 pagesSCES3123: W1 - Tutorial 1Muhammad NajmiNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM TEST 3 BEAT THE NEET (@ark - Neet)Document27 pagesBIOCHEM TEST 3 BEAT THE NEET (@ark - Neet)Manisha Senthil velNo ratings yet
- Iupac MCQ-2Document5 pagesIupac MCQ-2BhimaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision DPP 2Document8 pagesChemistry Revision DPP 2Praphul Pulkit GiriNo ratings yet
- DPP NomenclatureDocument7 pagesDPP Nomenclaturegamishtag18No ratings yet
- University of Windsor Chemistry and Biochemistry Chemistry 59-235 Apr. 17, 2012 Final Exam Time: 3 HoursDocument7 pagesUniversity of Windsor Chemistry and Biochemistry Chemistry 59-235 Apr. 17, 2012 Final Exam Time: 3 HoursmohammedNo ratings yet
- Halogen+Compound+ +PYQ+by+PC+SirDocument4 pagesHalogen+Compound+ +PYQ+by+PC+SirSuraj SinghNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE SHEET - 01 (Chemistry) : Basic Concept of Organic (IUPAC, Isomerism)Document6 pagesPRACTICE SHEET - 01 (Chemistry) : Basic Concept of Organic (IUPAC, Isomerism)ABD 17No ratings yet
- 62c2d57c17f4c30011d5e108 - ## - Alcohol, Phenol & Ether - DPP 01Document3 pages62c2d57c17f4c30011d5e108 - ## - Alcohol, Phenol & Ether - DPP 01Prarabdh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab 2Document5 pagesChem Lab 2Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- Organic Structures From Spectra-Edition 4-Solutions Manual-LibreDocument39 pagesOrganic Structures From Spectra-Edition 4-Solutions Manual-LibreBill Odette100% (5)
- StereochemistryDocument57 pagesStereochemistrycisna ambarwatiNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols & EthersDocument12 pagesAlcohols, Phenols & EtherssiddharthchillapwarNo ratings yet
- 15 Naming and Drawing Functional Groups Practice WorksheetDocument4 pages15 Naming and Drawing Functional Groups Practice WorksheetCorey Becker33% (6)
- Fenetil KromonDocument20 pagesFenetil Kromonelda merruNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument18 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Etherssaksham05060% (1)
- Haloalkanes & Haloarenes - 15-11-2020Document45 pagesHaloalkanes & Haloarenes - 15-11-2020Class 11aNo ratings yet
- Flavonoids From Flower of Linum Capitatum Kit: Facta UniversitatisDocument5 pagesFlavonoids From Flower of Linum Capitatum Kit: Facta Universitatiskontiki500No ratings yet
- 25-28 - Alcohol - EtherDocument8 pages25-28 - Alcohol - EtherkomalsdhakebNo ratings yet
- ALCOLDocument21 pagesALCOLthidaithanhNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature & IsomerismDocument19 pagesNomenclature & Isomerismkoli1417789No ratings yet
- DPC 2011 3 4 195 200Document6 pagesDPC 2011 3 4 195 200atifbhattNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Hydroxyl CompoundsDocument60 pagesChapter 6-Hydroxyl CompoundsNur Ayu Nadhirah Bt YahyaNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesIshita GuptaNo ratings yet
- 8 Formyl 7 Hydroxy 4 MethylcoumarinDocument8 pages8 Formyl 7 Hydroxy 4 Methylcoumarinrakeshtalele007No ratings yet
- Water Quality Gaza MapsDocument10 pagesWater Quality Gaza MapsReemALMousawiNo ratings yet
- Ozone Depleting SubstancesDocument7 pagesOzone Depleting SubstancesWellfroNo ratings yet
- Iitian'S Hub: Assignment # 1 General Organic Chemistry ChemistryDocument11 pagesIitian'S Hub: Assignment # 1 General Organic Chemistry ChemistrySAHILI RANENo ratings yet
- Chemcad Unifac GroupsDocument6 pagesChemcad Unifac Groupssnikt7863443No ratings yet
- LKPD TATA NAMA KimiaDocument9 pagesLKPD TATA NAMA Kimiagabriel.dominggo 192010013No ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenol EtherDocument5 pagesAlcohol Phenol Etherhareharanbt22No ratings yet
- InsekDocument26 pagesInsekDicky alfiansyah PutraNo ratings yet
- Tutor 1 Kimia PDFDocument3 pagesTutor 1 Kimia PDFFaris 2806No ratings yet
- Addition of Hydrohalogenic Acids To Alkenes in Aqueous-Organic, Two-Phase Systems in The Presence of Catalytic Amounts of Onium Salts PDFDocument3 pagesAddition of Hydrohalogenic Acids To Alkenes in Aqueous-Organic, Two-Phase Systems in The Presence of Catalytic Amounts of Onium Salts PDFatomoscoNo ratings yet
- 4 June 2022 ChemistryDocument68 pages4 June 2022 Chemistryadsaks2528No ratings yet
- Erna Fitriana AlfantiDocument6 pagesErna Fitriana AlfantiIzam M. FalahNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenol S SolutionsDocument11 pagesAlcohols Phenol S SolutionsagNo ratings yet
- Halogen DerivativesDocument10 pagesHalogen DerivativesharshitsharmasportsNo ratings yet
- NMR Controlled TitrationDocument162 pagesNMR Controlled TitrationSamuel AguiarNo ratings yet
- Alkoholi: OH C C OH OH CDocument53 pagesAlkoholi: OH C C OH OH CElvir MNo ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanisms-II APSP PDFDocument20 pagesOrganic Reaction Mechanisms-II APSP PDFGOURISH AGRAWAL100% (1)
- Organic II Final Exam Practice QuestionsDocument14 pagesOrganic II Final Exam Practice Questionstru99_nl100% (1)
- JR & ER - Eng. PC PDFDocument33 pagesJR & ER - Eng. PC PDFmarmaduke32No ratings yet
- Halogenated Benzenes, Toluenes and Phenols with Water: Solubility Data SeriesFrom EverandHalogenated Benzenes, Toluenes and Phenols with Water: Solubility Data SeriesAri L. HorvathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Registered Student List - EEE 4345 - Measurement and Instrumentation Sheet1 PDFDocument1 pageRegistered Student List - EEE 4345 - Measurement and Instrumentation Sheet1 PDFMahfuz A. AzimNo ratings yet
- (Mohammed Mahfuz Azim)Document13 pages(Mohammed Mahfuz Azim)Mahfuz A. AzimNo ratings yet
- Nonimmigrant Visa - Print Application IDDocument1 pageNonimmigrant Visa - Print Application IDMahfuz A. AzimNo ratings yet
- Explain The Different Types of Innovation?Document2 pagesExplain The Different Types of Innovation?Mahfuz A. AzimNo ratings yet
- BE Experiment 3 Lab ReportDocument2 pagesBE Experiment 3 Lab ReportMahfuz A. AzimNo ratings yet
- Bhaiya BioDocument1 pageBhaiya BioMahfuz A. AzimNo ratings yet
- Welqt-Fvovk Z Evmv (3Q ZJV) Qvovi Awmög Bvwuk Cöms MDocument2 pagesWelqt-Fvovk Z Evmv (3Q ZJV) Qvovi Awmög Bvwuk Cöms MMahfuz A. AzimNo ratings yet
- Undergraduate Admission ApplicationDocument3 pagesUndergraduate Admission ApplicationMahfuz A. AzimNo ratings yet
- 8 01x Fall 2002 Problem Expt CFDocument2 pages8 01x Fall 2002 Problem Expt CFMahfuz A. AzimNo ratings yet
- Mohammed Mahfuz AzimDocument1 pageMohammed Mahfuz AzimMahfuz A. AzimNo ratings yet
- National Earth Olympiad 2012: The Participants Will Be Expected To Have Knowledge in The Following TopicsDocument1 pageNational Earth Olympiad 2012: The Participants Will Be Expected To Have Knowledge in The Following TopicsMahfuz A. AzimNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics DepartmentDocument1 pageMassachusetts Institute of Technology Physics DepartmentMahfuz A. AzimNo ratings yet
- N ch3 06 PDFDocument1 pageN ch3 06 PDFMahfuz A. AzimNo ratings yet