Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Copar Notes
Copar Notes
Uploaded by
upuanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Copar Notes
Copar Notes
Uploaded by
upuanCopyright:
Available Formats
COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING
CO-PAR Community Organizing Participatory Action Research Community Organizing Process by which health services, agencies, and people and of the people of the community brought together to: o Identify/learn their own problem o Plan activities o Act on this basis o Evaluate COMMUNITY ORGANIZING EMPHASIZE Strengthening the community members capability in: o Problem solving skills And Necessary for self-reliant development o Decision making skills Community Organizing process has someone plays the role of a Community Organizer Roles and Responsibilities of a Community Health Nurse Manager Guide Advocate Coordinator, Counselor, Change Agent Health Care Provider Nurse Trainer Researcher Organizer Leader Educator Primary role, Primary responsibilities promotion of health and prevention of illness Supervisor Community Organizer Person who mobilize: Individual Family Sick or Well Community To come together in unity and collectively address given: Issues Needs Problem * assess by way of research PARTICIPATORY ACTION RESEARCH
Is an investigation on problems and issues of the community by way of research. Representatives of community participates in the actual research. Local Researcher Outside Researcher = Community Health Nurse Act as researchers themselves, doing research of their own problem. The essential element of Participatory Action Research is participation Participatory Action Research Objectives: o To encourage consciousness of the suffering o To empower people to determine the cause of their own problem o To analyze these problem o To develop competence for changing their own situation o To act by themselves in responding to their own problems Ideal participatory research process involves the community in all research aspect 1. Identification of research problem 2. Formulation of research design 3. Data gathering 4. Validation of research 5. Data presentation 6. Recommendations 7. Action of activities COPAR Phase/Process According to (Sister Jimenez) PRE ENTRY PHASE At the NGO level o Formulation of institutional goals, objectives and targets for the program o Revision of curriculum o Training of faculty if CO-PAR o Coordinate participation of other departments within the institution At the community level o Community consultations/dialogues o Setting of issues related to site selection o Development of criteria for site selection Criteria in selecting community Site must be Depressed and underserved Oppressed Poor Exploited Struggling Area must not have a serious peace and order problem
o Site selection o Preliminary Social Investigation (PSI) Identify contact person Gather overview of the demographic characteristics, health services and facilities of the community o Networking with LGUs, NGOs and other departments ENTRY PHASE Integration with the community main objective: Gain Trust First task courtesy call to the Brgy. Captain Establish rapport * house calls * joining to social activities Imbibe their lifestyle Immerse yourself Live with them Reside on the area * live in the center/modest dwelling Sensitization of the community social preparation Information campaign on health services Continuing/deep social investigation Process of collecting, collating, analyzing data to draw the clear picture of the community Core Group formation (CG) o Consist of identified potential leaders Characteristics of a potential leaders 1. Respected community members 2. Responsible/committed 3. Willing to work for a desired change 4. Has good communication skills 5. Has wide influence to elite/poor community members Self-awareness and leadership training (SALT) Coordination with other community organization o Representing different sectors of the community
Willingness to be organized Community needing health assistance o Check vital health statistic can determine general health status o Malnutrition rate o Lack of health facility/health care providers Counter-part of the community (support, commitment, resources) Accessible to transport and communication
COMMUNITY DIAGNOSIS/STUDY PHASE (research phase) Selection of the research team Training on data collection Planning for the actual gathering of data Data gathering Training on data validation Community validation Presentation of the community study/diagnosis and recommendations Prioritization of community needs/problems for action COMMUNITY ORGANIZATION/CAPABILITY BUILDING PHASE Community meetings to draw-up guidelines for the organization Election of officer Development of management systems: (Delineation of the Roles, Function, and Task of Officers) Training of leaders Team building exercises to enhance cohesiveness Action-Reflection-Action-Session COMMUNITY ACTION PHASE Organization and training of BHWs Village or Grassroot Workers PIME of health services Project Implementation/Monitoring and Evaluation (Project Management) Resource mobilization 5 MS MANPOWER MACHINE MATERIAL METHOD MONEY SPACE Setting up of linkages/network/referral system SUSTENANCE AND STRENGTHENING PHASE Formulation and ratification of constitution and by-laws Identification and development of secondary leaders Setting up a financing scheme Continuing education and training of BHWs Development of long term community health development plans Formalizing linkages, networks and referral system TURNOVER/PHASE OUT Transfer of community organizer roles and responsibilities and documents subsequent follow-up
CO-PAR main goal is to attain COMMUNITY DEVELOPMENT better quality life * Basic needs are met * Equal rights * Self-reliance * Active participation COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING Definition: WHO Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well being Modern Concept Health refers to optimum level of functioning of individual, family, community OLOF is influence by the Eco System Eco System Factors Socio-economic status Education Employment Housing Hereditary factor genetic Health care delivery system Activities and Behavior mag HL tayo Manage Stress Regular Exercise Do not Smoke Priority Message Regular health check-up Eat healthy foods Weight loss Political factors Environmental factors WHO special field of nursing that combines: o Skills of nursing o Public health o Social assistance and functions Dr. C. E. Winslow public health is a science and art of 3 Ps o Promotion of health o Prevention of illness/hazards through organize community efforts o Prolonging life Statement: every citizens has his BIRTHRIGHT of good health and longevity CHN according to Dr. Ruth Freeman A service rendered by a professional nurse o To individuals, family, community and population groups o At home o Clinics o Schools o And workplace
CHN subspecialty School Health Nursing Occupational Health Nursing CHN according to Dr. Maglaya The utilization of the nursing process in the different levels of clientele, individual, family, community and population groups concerned with the Promotion of health Prevention of disease And Disability and Rehabiliation CHN as Field Of Nursing Practice Hallmark of CHN is that it is Population or Aggregate-Focused Emphasis on the importance of the Greatest Good for the Greatest Number Goal of improving Community Health is realized through interdisciplinary/multi effort Philosophy of CHN Dr. Shetland CHN is based on the Worth and Dignity of Man Ultimate Goal of CHN To raise the level of health of the citizenry Principles of CHN Based on recognized needs of the community Understand the objectives and policies of the agency Family is the basic unit of service Always available to all regardless of Race, Creed and Socio-economic status Use available community health resource - Indigenous resource o Dried proteins Pounded Dilis Pounded Shrimp Pounded Monggo Record and report data accurately research/legal Health teaching is primary responsibility Evaluation of programs Continuous professional growth CONCEPTS OF COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING Health promotion primary responsibility Generalist never Specialist Population is the main focus Individual, Family, Community including Population Group Pregnant, Newborn, Elderly, Youth
Population Group those who share a common characteristics, developmental stages and common exposure to health problems Community health nursing process is implicit in the practice of CHN Essence of nursing Dynamic and cyclic process Systemic approach CHN PROCESS 1. Assessment o Establishing rapport Greetings Introduce self o Collection of data/facts/information METHODS TO COLLECT DATA Interview Records review Family Health Record Physical assessment Observation Diagnostic exam o Diagnosis identification of the client, families and community needs based on the gathered data 2. Planning o Prioritizing needs Ranking and Scaling Nature of problem Preventive potential Modifiability of the problem Salience perception o Stating goals and objective o Goal setting o Expected outcome o Developing parameters evaluation process THE PLANNING CYCLE/PROCESS
Evalutaion
Situational analysis
Strategy setting
Goal/Objective setting
1. Situational Analysis Where are we now? o Gather, tabulate, analyze and interpret data o Identify the problems/issues/needs 2. Goal and Objective Setting Where do you want to go? o Define program goals and objectives o Assign priorites among objectives 3. Strategy and Activity Settings How do we get there? o Design CHN programs o Ascertain resources o Analyze constraints and limitations 4. Evaluation How do we know we are there? o Specify criteria and standards o Determine outcomes HOME VISIT (should always have: PURPOSE and OBJECTIVE) Is a professional face to face contact done by the nurse to the family Factors Affecting Frequency of Home Visits o Physical/psychological and educational needs o Acceptance of the family (PRIORITY NEEDS) o Policy of a given agency Steps during Home Visit 1. Greetings/Introduce Self 2. Stating purpose and objective Priorities during Home Visit 1. Newborn (FIRST) 2. Post-Partum 3. Pregnant mother 4. Morbid individual (LAST) PUBLIC HEALTH BAG Is an essential and indispensable equipment of the Public Health Nurse used during home visit BAG TECHNIQUE A tool making use of a Public Health Bag and which the Public Nurse can perform procedures during home visits Rationale in the use of PHN BAG o Technique during Home Visit:
It help render effective nursing care Principle of Bag Technique 1. Minimize if not totally prevent the spread of infection 2. Save time and effort 3. Not to overshadow the concern of the client and family BP apparatus, stethoscope and umbrella are carried separately SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS Bag and its contents must be free from any contamination Always do hand washing Gather necessary equipments to render Nursing Care Place waste bag, paper lining outside SOLUTION 1. Benedict solution for sugar detection 2. Acetic acid solution for albumin detection 3. Zephiram solution soaking solution 4. Alcohol, Betadine 5. Ammonia LEVELs of CLIENTELE Individual, Family, Community, Population Group Sick or Well LEVELS OF PRIMARY HEALTH FACILITY PRIMARY Client in Fair health and with early symptoms of illness o Barangay Health Center (BHC), City Health Office (CHO), Municipal Health Office (MHO), Lying-in Clinics, Puericulture Center, Community Hospitals SECONDARY Patient in symptomatic stage of an illness and requires moderately specialized knowledge/facilities o Provincial Hospitals, District Hospitals, Municipal Hospitals, Emergency Hospitals TERTIARY Patients seriously threaten and requires highly technical facilities and knowledge o National Hospitals, Teaching/Training Hospitals, Regional Hospitals (SPECIALTY HOSPITALS) 2 TYPES OF PRIMARY HEALTH CARE WORKERS 1. Village/Grassroot workers Trained hilots o Trained individuals BHW, TBA, Trained hilot, Trained Dentist, Trained Nutritionist 2. Intermediate Health Care Workers o Professional Groups RH Physicians, RH Nurse, RH Midwife, RH Dentist, Medtech, Nutritionist, Sanitary Inspector Ratio to Population o 1 Physician = 20,000 o 1 Nurse = 20,000
o o o o
1 Med Tech = 20,000 1 Sanitary Inspector = 20,000 1 Dentist = 50,000 1 Midwife = 5,000
QUALIFICATIONS OF A COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSE BASIC REQUIREMENT o BSN Public Health Nurse 2 o RN o MAN with Positions Positions 1. Chief Nurse o BSN, RN, MAN o 5yrs experience as Community Health Nurse o 3yrs experience as Supervisor 2. Assistance Chief Nurse o 5yrs experience as Community Health Nurse o 2yrs experience as Supervisor 3. Regional Training Nurse o BSN, RN, MAN o 6yrs experience as Community Health Nurse o 3yrs experience as Trainor /Educator 4. Regional Supervisor o BSN, RN, MAN o 5yrs experience as Community Health Nurse o 2yrs experience as Supervisor 5. Provincial Supervisor o BSN, RN, MAN o 5yrs experience as Community Health Nurse 6. Nurse Instructor o BSN, RN, MAN o 3yrs experience as Community Health Nurse with teaching abilities 7. Nursing Program Supervisor o BSN, RN, MAN o 7yrs experience as Community Health Nurse with Training to DOH programs PRIMARY HEALTH CARE Is an essential Health Care based on practical and socially acceptable methods and technology Made universally accessible to Individual, Family, Community History of Public Health Care WHAT: Alma Ata Conference WHEN: September 6-12, 1978 WHERE: Alma Ata,USSR/Russia WHO: WHO/Unicef WHO: Dr. Dizon/Dr. Villar
Legal Basis: LOI 949 Signed by: Pres. Ferdinand Marcos on October 1979 GOAL OF PUBLIC HEALTH CARE Health for all Filipinos and health in the hands of the people by year 2020 MISSION Strengthening the health system wherein people will manage their own health care KEY/CORE STRATEGY PARTNERSHIP PILLARS/CORNERSTONE OF PUBLIC HEALTH CARE Support Mechanism mad available Community Participation Active Appropriate technology Multi-Sectoral linkages CHARACTERISTIC OF PUBLIC HEALTH CARE Accessible/Available Community Bases Affordable Sustainable Integral/Important Acceptable VITAL HEALTH STATISTIC Is the study on vital events such as Birth-Fertility Deaths Mortality Morbidity Main Objective: to determine general health status of the community
You might also like
- PALMAR ReviewerDocument24 pagesPALMAR ReviewerRizza Ayala88% (8)
- Community Health Nursing: I - Definition of TermsDocument25 pagesCommunity Health Nursing: I - Definition of TermsRichard Ines Valino97% (29)
- PALMER Reviewer NursingDocument20 pagesPALMER Reviewer NursingJennilyn Salas100% (12)
- Pentagon Notes PALMERDocument27 pagesPentagon Notes PALMERPaula100% (3)
- 300 Items NLE ReviewerDocument33 pages300 Items NLE ReviewerJenneth Baguilat Bay-ed100% (8)
- PalmarDocument5 pagesPalmarshenric1667% (3)
- COPAR ReviewerDocument6 pagesCOPAR ReviewerRichard Ines Valino94% (16)
- Community Health Nursing Notes SummaryDocument9 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Notes Summarysorryandreosayanisalreadytaken100% (28)
- Palmer Complete Edited Royal PentagonDocument26 pagesPalmer Complete Edited Royal PentagonRichard Ines Valino98% (42)
- Pentagon Review Royal PentagonDocument33 pagesPentagon Review Royal PentagonRichard Ines Valino99% (70)
- Overall CHN Handout 1Document54 pagesOverall CHN Handout 1Tifanny Shaine Tomas86% (7)
- Community Health Nursing - HandoutDocument27 pagesCommunity Health Nursing - Handoutisaac_dre100% (8)
- Professional Adjustment Leadership Management and ResearchDocument10 pagesProfessional Adjustment Leadership Management and Researchshenric16100% (1)
- NLE ReviewerDocument246 pagesNLE Reviewerblazegomez99% (69)
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewDocument16 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Reviewɹǝʍdןnos97% (63)
- COPARDocument21 pagesCOPAREdra VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- CHN ReviewerDocument12 pagesCHN ReviewerArvi GayeNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Reviewer PDFDocument12 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Reviewer PDFChristine Joy MuñozNo ratings yet
- CHN in House Module 1Document7 pagesCHN in House Module 1Catherine AteradoNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Copar MswordDocument12 pages1st Sem Copar MswordAisha MamentaNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Reviewer: - 1 Twitter: @nursehoomanDocument13 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Reviewer: - 1 Twitter: @nursehoomanNezel Anne B. DOROMALNo ratings yet
- The Community - Chn2 1Document56 pagesThe Community - Chn2 1Andree GalloNo ratings yet
- Community Health 1 2Document80 pagesCommunity Health 1 2gloriamaoreNo ratings yet
- BSRT Rotation Notes A5 FormatDocument54 pagesBSRT Rotation Notes A5 FormatJade Louise FkshmNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument9 pagesCommunity Health NursingtheglobalnursingNo ratings yet
- Munity Empowerment Program in Health - SMTR 6 2014 - DFDocument46 pagesMunity Empowerment Program in Health - SMTR 6 2014 - DFAlivia SoerayaNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Reviewer: - 1 Twitter: @nursehoomanDocument12 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Reviewer: - 1 Twitter: @nursehoomanVIKTORIA SARAH DIZONNo ratings yet
- CHN - JoyDocument3 pagesCHN - JoyJoy VelascoNo ratings yet
- Community Organizing Participatory Action ResearchDocument11 pagesCommunity Organizing Participatory Action Researchlanie_jecielNo ratings yet
- Planning On Community Health Nursing InterventionsDocument47 pagesPlanning On Community Health Nursing InterventionsNicole Audrey JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Key Points To Remember Qualities of A ChnurseDocument15 pagesKey Points To Remember Qualities of A Chnursekaren mae alcantaraNo ratings yet
- Community Assessment: Prepper by Nariman NOUHDocument25 pagesCommunity Assessment: Prepper by Nariman NOUHN N100% (1)
- What Is Copar?: COPAR Stands For Community Organizing Participatory Action ResearchDocument4 pagesWhat Is Copar?: COPAR Stands For Community Organizing Participatory Action ResearchRAMIL GOPEZNo ratings yet
- Maglaya Community Health Nursing NotesDocument2 pagesMaglaya Community Health Nursing NotesMaria Bernadette Manumbas60% (5)
- CHN Notes For Boards PDFDocument25 pagesCHN Notes For Boards PDFKish Gabriel GanadoNo ratings yet
- Copar - Ust-ConDocument5 pagesCopar - Ust-ConEdgarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document17 pagesUnit 2Shini SimonNo ratings yet
- CHN LecDocument3 pagesCHN Lecyasmingapaz30No ratings yet
- Handout COPARDocument10 pagesHandout COPARkrissyNo ratings yet
- CoparDocument6 pagesCoparJesikah EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Community Health 2 Power PointDocument31 pagesCommunity Health 2 Power Pointmuhirwa SamuelNo ratings yet
- COPARDocument12 pagesCOPARcandiaangeltherese1318238No ratings yet
- W3 - Community Diagnosis LectureDocument46 pagesW3 - Community Diagnosis LectureKeziah Mary AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Community CHP 7Document20 pagesNursing Care of The Community CHP 7Patricia Mag-akatNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument10 pagesCommunity Health NursingBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- CHN MergedDocument261 pagesCHN MergedRej h100% (1)
- Unit 1 C H N: A O: What Is A Community ?Document43 pagesUnit 1 C H N: A O: What Is A Community ?Marcus, RN96% (49)
- The Nursing Process in The Care of The CommunityDocument96 pagesThe Nursing Process in The Care of The CommunityCzarina Aeri RollorataNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing 2:: Population Groups and Community As ClientsDocument20 pagesCommunity Health Nursing 2:: Population Groups and Community As ClientsRamzen Raphael DomingoNo ratings yet
- CoparDocument7 pagesCoparMa Christina RovillosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process in The Care of Population Groups and Community MIDTERMDocument6 pagesNursing Process in The Care of Population Groups and Community MIDTERMjillmonicadaquipil7No ratings yet
- Community Organizing Through Paticipatory Action Researchco ParDocument35 pagesCommunity Organizing Through Paticipatory Action Researchco ParZanesville Lymont L. SubidoNo ratings yet
- Nle Test Plan: Nursing Practice IDocument14 pagesNle Test Plan: Nursing Practice IericNo ratings yet
- Copar: Community Organizing Participatory Action ResearchDocument57 pagesCopar: Community Organizing Participatory Action ResearchSophia WongNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Community CHP 7Document20 pagesNursing Care of The Community CHP 7marissaNo ratings yet
- Capp Activity 2 (Operaña)Document6 pagesCapp Activity 2 (Operaña)Ellayza OperanaNo ratings yet
- CHN Task 1Document6 pagesCHN Task 1paolo cominguezNo ratings yet
- COPAR or Community Organizing Participatory Action Research Is A Vital Part ofDocument5 pagesCOPAR or Community Organizing Participatory Action Research Is A Vital Part ofPrei BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Week 1 CoparDocument9 pagesWeek 1 CoparSansaiNo ratings yet
- Copar HandoutDocument4 pagesCopar Handoutjillmonicadaquipil7No ratings yet
- Drugs That Affect The Hematological SystemDocument4 pagesDrugs That Affect The Hematological Systemoxidalaj100% (2)
- ANSAP IVT Accomplished Requirements Form 3+3+2Document1 pageANSAP IVT Accomplished Requirements Form 3+3+2PhilippineNursingDirectory.comNo ratings yet
- Growth and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesGrowth and Developmentoxidalaj100% (1)
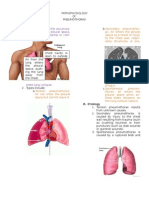
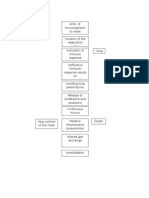
- Pathophysiology of EmphysemaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Emphysemaoxidalaj100% (2)
- Lung AbscessDocument2 pagesLung Abscessoxidalaj100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of COPDDocument1 pagePathophysiology of COPDoxidalaj100% (1)
- Diabetic Nephropathy Case StudyDocument61 pagesDiabetic Nephropathy Case Studyoxidalaj98% (63)
- Pathophysiology of PneumothoraxDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Pneumothoraxoxidalaj84% (19)
- Respiratory DysfunctionDocument1 pageRespiratory Dysfunctionoxidalaj100% (3)
- Skin PreparationDocument2 pagesSkin Preparationoxidalaj100% (24)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Pneumoniaoxidalaj97% (32)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Pneumoniaoxidalaj97% (31)
- Nursing Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument14 pagesNursing Fluids and Electrolytesaga1028100% (18)
- Human Fertilization Is The Union of A Human Egg and SpermDocument7 pagesHuman Fertilization Is The Union of A Human Egg and Spermoxidalaj100% (1)
- ENEMADocument16 pagesENEMAoxidalaj100% (8)
- Gastric GavageDocument8 pagesGastric Gavageoxidalaj100% (15)
- Perineal CareDocument10 pagesPerineal Careoxidalaj100% (11)
- Oxygen TherapyDocument46 pagesOxygen Therapyoxidalaj100% (4)
- N100 Rle Back MassageDocument24 pagesN100 Rle Back Massageoxidalaj100% (1)
- The Nursing ProcessDocument44 pagesThe Nursing Processoxidalaj100% (9)
- A Wealth of Untapped HeritageDocument29 pagesA Wealth of Untapped HeritageLokesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Naked LunchDocument18 pagesNaked LunchNikhita Mendis100% (1)
- Enver Hoxha The TitoitesDocument264 pagesEnver Hoxha The TitoitesΠορφυρογήςNo ratings yet
- Organ DonationDocument9 pagesOrgan DonationKeeranmayeeishraNo ratings yet
- PSY-201 Cognition - New Course OutlineDocument3 pagesPSY-201 Cognition - New Course OutlineEmaanNo ratings yet
- 2.human Rights in BangladeshDocument9 pages2.human Rights in BangladeshSaimum HasanNo ratings yet
- Amigurumi Animal PatternsDocument147 pagesAmigurumi Animal PatternsMarie-Colette Robillard100% (6)
- Basic Elements of The Christian Witness Lee - Watchman NeeDocument25 pagesBasic Elements of The Christian Witness Lee - Watchman NeeBeverly SowahNo ratings yet
- Meeting Dating Seducing PDFDocument39 pagesMeeting Dating Seducing PDFwhitepaladin50% (2)
- Material Apoyo 1 Ingles Dot WorksDocument10 pagesMaterial Apoyo 1 Ingles Dot WorksElvira Figueroa RomeroNo ratings yet
- Dev't PPA I (Chap-3)Document35 pagesDev't PPA I (Chap-3)ferewe tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Elestomeric BearingsDocument152 pagesElestomeric BearingsvaibhavNo ratings yet
- Volume 47, Issue 24, June 10, 2016Document113 pagesVolume 47, Issue 24, June 10, 2016BladeNo ratings yet
- NBE3U-Literary Essay & Rubric-Nov-23.docx-2Document3 pagesNBE3U-Literary Essay & Rubric-Nov-23.docx-2731728No ratings yet
- Jainism - Tirthankaras, Vardhaman Mahavira & TriratnaDocument5 pagesJainism - Tirthankaras, Vardhaman Mahavira & TriratnaAishwaryaNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Chaudhary Kushagra RajNo ratings yet
- November 2022Document3 pagesNovember 2022pkumuhammadiyah banjarNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Design-Cua: S s2 S s2 y S SDocument9 pagesReinforced Concrete Design-Cua: S s2 S s2 y S SRegine Ignacio SobremonteNo ratings yet
- The Infinite Miracles of MindfulnessDocument11 pagesThe Infinite Miracles of MindfulnessSreeja SujithNo ratings yet
- ZI Publications SDN BHD & Anor V Jabatan Agama Islam Selangor & OrsDocument17 pagesZI Publications SDN BHD & Anor V Jabatan Agama Islam Selangor & OrsShasmeethaa NairNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2 Badminton With NotesDocument7 pagesLesson Plan 2 Badminton With Notesapi-309735553100% (1)
- Answer KeyDocument14 pagesAnswer Keypancho_andresNo ratings yet
- CV Project Manager-M.Ammar PDFDocument6 pagesCV Project Manager-M.Ammar PDFMoaatazz NouisriNo ratings yet
- Manual Dawn of Magic 2Document24 pagesManual Dawn of Magic 2William CruzNo ratings yet
- Presentation Hearsay Evidence MalaysiaDocument9 pagesPresentation Hearsay Evidence MalaysiaN Farhana Abdul Halim0% (1)
- 10 Tips For Indica Vape CartjrgbwDocument2 pages10 Tips For Indica Vape Cartjrgbwmanxpaint65No ratings yet
- Smith 1992 Annals of Tourism ResearchDocument17 pagesSmith 1992 Annals of Tourism ResearchCacá Pitrez100% (3)
- Research Methodology 3Document12 pagesResearch Methodology 3Ushna ShahNo ratings yet
- Creation - The World Building GameDocument17 pagesCreation - The World Building Gamecameronhyndman100% (1)
- Alcatel IPTouchSIPphonesinstallationDocument17 pagesAlcatel IPTouchSIPphonesinstallationAnonymous IVK8YRNo ratings yet