Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metabolisme Lipida
Uploaded by
Hilmia Fahma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views16 pagesFat Metabolism: Long Term Nutrient Storage in adipose cells in blood: HDL, LDL - FAAs, cholesterol - (plaque build up) Conversion in liver Excreted in bile used for energy and synthesis. "Fasted state" or Post-Absorptive Metabolism: Catabolic Pathways shift to maintain energy for metabolism.
Original Description:
Original Title
METABOLISME LIPIDA
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFat Metabolism: Long Term Nutrient Storage in adipose cells in blood: HDL, LDL - FAAs, cholesterol - (plaque build up) Conversion in liver Excreted in bile used for energy and synthesis. "Fasted state" or Post-Absorptive Metabolism: Catabolic Pathways shift to maintain energy for metabolism.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views16 pagesMetabolisme Lipida
Uploaded by
Hilmia FahmaFat Metabolism: Long Term Nutrient Storage in adipose cells in blood: HDL, LDL - FAAs, cholesterol - (plaque build up) Conversion in liver Excreted in bile used for energy and synthesis. "Fasted state" or Post-Absorptive Metabolism: Catabolic Pathways shift to maintain energy for metabolism.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
METABOLISME KARBOHIDRAT
AKMA
Fat Metabolism: Long Term Nutrient Storage
In adipose cells In blood: HDL, LDL
FAAs, cholesterol (plaque build up)
Conversion in liver Excreted in bile Used for energy & synthesis
Fat Metabolism: Long Term Nutrient Storage
Figure 22-5: Transport and fate of dietary fats
Fasted State or Post-Absorptive
Metabolism: Catabolic
Pathways shift to maintain energy for metabolism Storage glucose in blood organs in need
Fasted State or Post-Absorptive Metabolism: Catabolic
Figure 22-6: Fasted-state metabolism
Summary of Metabolic Conversions of Nutrients
Nutrients are used, or stored In general glucose, fats & AAs can be interconverted
Summary of Metabolic Conversions of Nutrients
Figure 22-2: Summary of metabolism
Metabolic Proscesses: Reversible Conversions
Glycogenesis (glucose to glycogen) Glycogenolysis (glycogen to glucose) Gluconeogenesis (amino acids to glucose) Lipogenesis (glucose or FAAs to fats) Lipolysis (fats to FAAs & glycerol)
Metabolic Energy Production: Review & Overview
Reactants: glucose
Glycogen, FAAs Amino acids
Phosphoylation Glycolysiscytoplasm
2 ATPs, anaerobic
Citric Acid Cycle-2 ATPs, mitochondria, aerobic Electron Transport system High energy e-, 32 ATPs
You might also like
- 2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2From Everand2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2No ratings yet
- Introduction To Metabolism: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran USUDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Metabolism: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran USUAnditha Namira RSNo ratings yet
- Tissue-Specific MetabolismDocument35 pagesTissue-Specific MetabolismLulu100% (2)
- Amino AcidDocument33 pagesAmino Acidlovelyc95100% (1)
- 1.4.5.4 - Hubungan Antar MetabolismeDocument32 pages1.4.5.4 - Hubungan Antar MetabolismeMulyanti YanthieNo ratings yet
- Integration of MetabolismDocument17 pagesIntegration of MetabolismSharif M Mizanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 1 HendersonDocument74 pages1 Hendersonbballchamp10No ratings yet
- B Topic 8 - Metabolism of CarbohydratesDocument62 pagesB Topic 8 - Metabolism of Carbohydratesfantasticedwin254No ratings yet
- 1.4.5.4 - Hubungan Antar MetabolismeDocument32 pages1.4.5.4 - Hubungan Antar MetabolismeAde Yosdi PutraNo ratings yet
- Review: - ACC RegulationDocument41 pagesReview: - ACC RegulationDiana ArwatiNo ratings yet
- Abetalipoproteinemia Powerpoint ReportDocument43 pagesAbetalipoproteinemia Powerpoint Reportpurpleflurp23No ratings yet
- Integration of MetabolismDocument40 pagesIntegration of MetabolismIrfanArifZulfikar100% (1)
- Metabolisme Lipid (2012)Document78 pagesMetabolisme Lipid (2012)fmdsNo ratings yet
- Fed State of MetabolismDocument40 pagesFed State of MetabolismBHARANIDHARAN M.VNo ratings yet
- Metabolism OverviewDocument43 pagesMetabolism OverviewWinnet MaruzaNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument74 pagesCARBOHYDRATESHaki TozakiNo ratings yet
- Narasi Presentasi Bagian Mekanisme Lipid (B11)Document4 pagesNarasi Presentasi Bagian Mekanisme Lipid (B11)Lana WintersNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Interrelationships Rev 2020-Lecture-StdsDocument79 pagesMetabolic Interrelationships Rev 2020-Lecture-StdsKavin AbdurrahiemNo ratings yet
- CH 19 Integration of MetabolismDocument63 pagesCH 19 Integration of Metabolismshee140802100% (1)
- Cholesterol SphingolipidsDocument31 pagesCholesterol SphingolipidsMaryam KNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of FatsDocument13 pagesMetabolism of FatsBaap ko Mat sikhaNo ratings yet
- Integration of MetabolismDocument40 pagesIntegration of MetabolismSofie Hanafiah NuruddhuhaNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol BiochemistryDocument17 pagesCholesterol BiochemistryKofi Fofie-AsieduNo ratings yet
- Lipid MetabolismDocument17 pagesLipid MetabolismMiran El-MaghrabiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Distribution, Metabolism, and ExcretionDocument93 pagesCarbohydrate Distribution, Metabolism, and ExcretionPSPD - Hana Athaya NNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate 1Document60 pagesCarbohydrate 1jahahn.t.sullivanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7.4 Lipid MetabolismDocument9 pagesLecture 7.4 Lipid MetabolismHuzaifa MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Metabolism: Lipid Metabolism: Inge HolsbeeksDocument35 pagesMetabolism: Lipid Metabolism: Inge Holsbeekssabasaktir4142No ratings yet
- Cardiac MetabolismDocument35 pagesCardiac Metabolismwaqas_xsNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Metabolism: (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein)Document37 pagesNutrition and Metabolism: (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein)Trishia BonNo ratings yet
- Bms2 Integration of MetabolismDocument42 pagesBms2 Integration of MetabolismhohoylandNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument72 pagesCarbohydratesRAMA ABO SAMRANo ratings yet
- I. Specific Catabolic PathwaysDocument17 pagesI. Specific Catabolic PathwaysMary Rose Bobis VicenteNo ratings yet
- LIPDocument28 pagesLIPsamar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy (Post.) Lipid Metabolism DR - Amal BadrDocument35 pagesPhysiotherapy (Post.) Lipid Metabolism DR - Amal BadrthestaffforpediatricptNo ratings yet
- 4 Lipoprotein MetabolismDocument35 pages4 Lipoprotein Metabolismazouz jaboobiNo ratings yet
- Lipid MetabolismDocument68 pagesLipid Metabolismcpagente01No ratings yet
- Lipoproteins: SummaryDocument3 pagesLipoproteins: SummaryEzekiel Morena RiveraNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument16 pagesCarbohydratessabreen hiresNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of LipidsDocument21 pagesMetabolism of LipidsViragNo ratings yet
- 8 Carbohydrate Metabolism PDFDocument36 pages8 Carbohydrate Metabolism PDFDayne Ocampo-SolimanNo ratings yet
- VK Intermediary MetabolismDocument3 pagesVK Intermediary MetabolismPuri Wulandari RahayuNo ratings yet
- Lipidis2 L8 MBC 110Document27 pagesLipidis2 L8 MBC 110Russian LimongaNo ratings yet
- BCH 2212 - For Anatomy and Physiology - 084524Document63 pagesBCH 2212 - For Anatomy and Physiology - 084524Aminu IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and The LiverDocument72 pagesNutrition and The LiveranggiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ix - Mechanism of Lipids MetabolismDocument33 pagesChapter Ix - Mechanism of Lipids MetabolismAngelo AngelesNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Interrelationships Rev 07-11-2014Document82 pagesMetabolic Interrelationships Rev 07-11-2014algutNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D. E. A. B. C. D. E.: Answer A: The Primary Mechanism by Which Answer B: Desmosterolosis Is An Extremely RareDocument18 pagesA. B. C. D. E. A. B. C. D. E.: Answer A: The Primary Mechanism by Which Answer B: Desmosterolosis Is An Extremely RareHoanNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Makronutrien FixDocument132 pagesMetabolisme Makronutrien FixbelaariyantiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Final - Integrated - Metabolism-16Document113 pagesBiochemistry Final - Integrated - Metabolism-16keisha jonesNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol: Qasim Jawad AL-DaamiDocument31 pagesCholesterol: Qasim Jawad AL-Daamiraafat mohammedNo ratings yet
- BIO 202 Biochemistry II by Seyhun YURDUGÜL: Carbohydrate Metabolism I GlycolysisDocument59 pagesBIO 202 Biochemistry II by Seyhun YURDUGÜL: Carbohydrate Metabolism I GlycolysisYasin Çağrı KılıçerNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol Metabolism 2021Document43 pagesCholesterol Metabolism 2021Eniola abdullahi AduagbaNo ratings yet
- Lipids and Its Metabolism ProjectDocument51 pagesLipids and Its Metabolism ProjectJopeter Alicer TinayaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument62 pagesLesson 7 - Carbohydrate MetabolismMary Mae DequiñaNo ratings yet
- 09 Metabolism Part 1 For StudentsDocument32 pages09 Metabolism Part 1 For StudentsKlieden LobrigasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 TAG Metabolism + Adipose + Fatty LiverDocument38 pagesLecture 5 TAG Metabolism + Adipose + Fatty Livernironkushbhuyan2002No ratings yet
- Metabolisme Makronutrien FixDocument132 pagesMetabolisme Makronutrien FixKadek RiskaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and The LiverDocument66 pagesNutrition and The LiverAzizRakhaNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS AS METAB-WPS OfficehhDocument5 pagesLIPIDS AS METAB-WPS OfficehhBethNo ratings yet
- 3LUDocument2 pages3LUabukasyahNo ratings yet
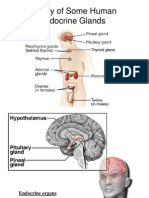
- How To Read A Chest X RayDocument11 pagesHow To Read A Chest X RayHilmia Fahma100% (2)
- 3.kuliah Endokrin I UWKDocument32 pages3.kuliah Endokrin I UWKHilmia FahmaNo ratings yet
- 1 AnIntroductiontoEndocrinologyDocument37 pages1 AnIntroductiontoEndocrinologyHilmia FahmaNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme ProteinDocument14 pagesMetabolisme ProteinTajul PatasNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme ProteinDocument14 pagesMetabolisme ProteinTajul PatasNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme LipidaDocument16 pagesMetabolisme LipidaHilmia FahmaNo ratings yet
- Hosts UmbrellaDocument1 pageHosts UmbrellaFabsor SoralNo ratings yet
- Adiposity in CVDDocument11 pagesAdiposity in CVDHilmia FahmaNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Chest X-RayDocument10 pagesPaediatric Chest X-Raypheeplukz100% (1)