Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MSP430 Instruction Set Summary
Uploaded by
Somaraju DasamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MSP430 Instruction Set Summary
Uploaded by
Somaraju DasamCopyright:
Available Formats
MSP430 Family
Instruction Set Summary
Topics
5 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.4.1 5.4.2 5.4.3 5.4.4 Instruction Set Summary Symbols and Abbreviations Addressing Modes Instruction Set Summary Clock cycles, Length of Instruction Format I Instructions Format II Instructions Format III Instructions Miscellanous Instructions or Operators 5-3 5-4 5-5 5-6 5-8 5-8 5-9 5-9 5-9
Tables
Table 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Title Symbols and Abbreviations used in the Instruction Set Summary Addressing Modes MSP430 Family Instruction Set Summary Format I Instructions Format II Instructions Page 5-4 5-5 5-6 5-8 5-9
Notes
Title 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Page 5-5 5-7 5-8 5-9
Addressing Modes Emulated Instructions Cycle Time of the DADD Instruction Immediate mode in destination field
5-1
Instruction Set Summary
MSP430 Family
5-2
MSP430 Family
Instruction Set Summary
Instruction Set Summary
This chapter summarizes the MSP430 family instruction set.
5-3
Instruction Set Summary
MSP430 Family
5.1
Symbols and Abbreviations
The following table lists the instruction set symbols and abbreviations used throughout the rest of this chapter. Symbol Definition src As The source operand defined by As and S-reg The bits representing the addressing mode used for the source The used Working Register for the source src Register 2 or Status Register/Constant Generator 1 Working Register, general purpose Immediate Data Absolute address 16-bit label Carry Bit Overflow Bit The suffix .B at the instruction memonic will result in a byte operation Most significant Bit Symbol dst Ad Definition The destination operand defined by Ad and D-reg The bit representing the addressing mode used for the destination The used Working Register for the destination dst Register 1 or Stack Pointer Register 3 or Constant Generator 2 Working Register with n=4-15, general purpose Register indirect addressing Data transfer direction Top of Stack Negative Bit Zero Bit The suffix .W or no suffix at the instruction memonic will result in a word operation Least significant Bit
S-reg
D-reg R1 or SP R3 or CG2 Rn @ --> TOS N Z .W
R0 or PC Register 0 or Program Counter R2 or SR/CG1 R4 to R15 # & label C V .B
MSB
LSB
Table 5.1: Symbols and Abbreviations used in the Instruction Set Summary
5-4
MSP430 Family
Instruction Set Summary
5.2
Addressing Modes
All seven addressing modes for the source operand and all four addressing modes for the destination operand can address the complete address space. The bit numbers show the contents of the As resp. Ad mode bits. As 00 01 Ad 0 1 Addressing Mode Register Mode Indexed Mode Syntax Rn X(Rn) Description Register contents are operand (Rn + X) points to the operand. X is stored in the next word (PC + X) points to the operand. X is stored in the next word. Indexed Mode X(PC) is used The word following the instruction contains the absolute address. Rn is used as a pointer to the operand Rn is used as a pointer to the operand. Rn is incremented afterwards The word following the instruction contains the immediate constant N. Indirect Autoincrement Mode @PC+ is used
01
Symbolic Mode
ADDR
01
Absolute Mode
&ADDR
10 11
Indirect Register Mode Indirect Autoincrement Immediate Mode
@Rn @Rn+
11
#N
Table 5.2: Addressing Modes
Note:
Addressing Modes
The addressing modes using the PC as the working register use the normal effects of the addressing modes. The special addressing modes are caused by the pointing of the PC to the ROM word following the currently executed instruction.
5-5
Instruction Set Summary
MSP430 Family
5.3
Instruction Set Summary Status Bits dst + C dst src + dst dst src + dst + C dst src .and. dst dst .not.src .and. dst dst src .or. dst dst src .and. dst Branch to ....... PC+2 stack, dst PC Clear destination Clear carry bit Clear negative bit Clear zero bit dst - src dst + C dst (decimal) src + dst + C dst (decimal) dst - 1 dst dst - 2 dst Disable interrupt Enable interrupt Increment destination, dst +1 dst Double-Increment destination, dst+2dst Invert destination Jump to Label if Carry-bit is set Jump to Label if Zero-bit is set Jump to Label if (N .XOR. V) = 0 Jump to Label if (N .XOR. V) = 1 Jump to Label unconditionally Jump to Label if Negative-bit is set
1 Status bit always set Status bit not affected
* ADC(.B) ADD(.B) ADDC(.B) AND(.B) BIC(.B) BIS(.B) BIT(.B) * BR CALL * CLR(.B) * CLRC * CLRN * CLRZ CMP(.B) * DADC(.B) DADD(.B) * DEC(.B) * DECD(.B) * DINT * EINT * INC(.B) * INCD(.B) * INV(.B) JC/JHS JEQ/JZ JGE JL JMP JN
Legend: 0 x *
dst src,dst src,dst src,dst src,dst src,dst src,dst dst dst dst
src,dst dst src,dst dst dst
dst dst dst Label Label Label Label Label Label
V x x x 0 0 x x x x x x x x -
N x x x x x 0 x x x x x x x x -
Z x x x x x 0 x x x x x x x x -
C x x x x x 0 x x x x x x x x -
Status bit always cleared Status bit cleared or set on results Emulated Instructions
Table 5.3: MPS430 Family Instruction Set Summary
5-6
MSP430 Family
Instruction Set Summary
Status Bits V x N x Z x C x
JNC/JLO JNE/JNZ MOV(.B) * NOP * POP(.B) PUSH(.B) RETI
Label Label src,dst dst src
* RET * RLA(.B) * RLC(.B) RRA(.B) RRC(.B) * SBC(.B) * SETC * SETN * SETZ SUB(.B) SUBC(.B) SWPB SXT * TST(.B) XOR(.B)
Legend: 0 x *
dst dst dst dst dst
src,dst src,dst dst dst dst src,dst
Jump to Label if Carry-bit is reset Jump to Label if Zero-bit is reset src dst No operation Item from stack, SP+2 SP SP - 2 SP, src @SP Return from interrupt TOS SR, SP + 2 SP TOS PC, SP + 2 SZP Return from subroutine TOS PC, SP + 2 SP Rotate left arithmetically Rotate left through carry MSB MSB ....LSB C C MSB .........LSB C Subtract carry from destination Set carry bit Set negative bit Set zero bit dst + .not.src + 1 dst dst + .not.src + C dst swap bytes Bit7 Bit8 ........ Bit15 Test destination src .xor. dst dst
1 The Status Bit is set The Status Bit is not affected
x x 0 x x x x 0 x x
x x x x x 1 x x x x x
x x x x x 1 x x x x x
x x x x x 1 x x x x x
The Status Bit is cleared The Status Bit is affected Emulated Instructions
Table 5.3: MPS430 Family Instruction Set Summary (Concluded)
Note: Emulated Instructions All marked instructions ( * ) are emulated instructions. The emulated instructions use core instructions combined with the architecture and implementation of the CPU for higher code efficiency and faster execution.
5-7
Instruction Set Summary
MSP430 Family
5.4
Clock cycles, Length of Instruction
The operating speed of the CPU is independent from individual instructions. It depends on the instruction format and the addressing modes. The number of clock cycles refer to the internal oscillator frequency. 5.4.1 Format I Instructions #of cycles 1 2 4 Length of instruction 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 1 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 3 2 3 Example MOV R5,R8 BR R9 ADD R5,3(R6) XOR R8,EDE MOV R5,&EDE MOV 2(R5),R7 AND EDE,R6 MOV &EDE,R8 ADD 3(R4),6(R9) CMP EDE,TONI MOV 2(R5),&TONI ADD EDE,&TONI AND @R4,R5 XOR @R5,8(R6) MOV @R5,EDE XOR @R5,&EDE ADD @R5+,R6 BR @R9+ MOV #20,R9 BR #2AEh MOV @R9+,2(R4) ADD #33,EDE MOV @R9+,&EDE ADD #33,&EDE
Address Mode As Ad 00, Rn 0, Rm 0,PC 00, Rn 1, x(Rm) 1, EDE 1, &EDE 01, x(Rn) 0, Rm 01, EDE 01, &EDE 01, x(Rn) 1, x(Rm) 01, EDE 1, TONI 01, &EDE 1, &TONI 10, @Rn 10, @Rn 0, Rm 1, x(Rm) 1, EDE 1, &EDE 0, Rm 0, PC 0, Rm 0, PC 1, x(Rm) 1, EDE 1, &EDE
2 5
11, @Rn+ 11, #N 11, @Rn+ 11, #N 11, @Rn+ 11, #N
2 3 2 2 5
Table 5.4: Format I Instructions
Note:
Cycle Time of the DADD Instruction
The DADD instruction needs 1 extra cycle.
5-8
MSP430 Family
Instruction Set Summary
5.4.2
Format II Instructions Address Mode A(s/d) #of cycles RRC PUSH/ RRA CALL SWPB SXT 1 3/4 4 5 4 5 3 4 3 3 4/5 4/5 Length of instruction [words] Example
00, Rn 01, x(Rn) 01, EDE 10, @Rn 11, @Rn+ see Note 11, #N
1 2 2 1 1 2
SWPB R5 CALL 2(R7) PUSH EDE RRC @R9 SWPB @R10+ CALL #81h
Table 5.5: Format II Instructions
Note:
Immediate mode in destination field
Instructions should not use immediate mode in the destination field. This would result in unpredictable program operation.
5.4.3
Format III Instructions
Jxx - instructions need all the same #-of-cycles independent of a successfull Jump or not. Clock Cycle: 2 Cycle.
Length of Instruction: 1 word.
5.4.4 RETI Interrupt
Miscellanous Instructions or Operators Clock Cycle: Clock Cycle: 5 Cycle. 6 Cycle.
Length of instruction: 1 word.
5-9
Instruction Set Summary
MSP430 Family
5-10
You might also like
- MSP430 Instruction SetDocument9 pagesMSP430 Instruction Setnyana87No ratings yet
- 7 Segment DisplayDocument32 pages7 Segment DisplayGagah PrakosoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Mcu PDFDocument12 pagesUnit 2 Mcu PDFatulNo ratings yet
- MIPS Reference CardDocument2 pagesMIPS Reference CardJosé R. BecerraNo ratings yet
- DLX InfoDocument28 pagesDLX InforazaNo ratings yet
- Arm Instruction 2 - 001Document26 pagesArm Instruction 2 - 001Ankit SanghviNo ratings yet
- 03-Instruction Set ArchitectureDocument40 pages03-Instruction Set ArchitectureccoccoheadNo ratings yet
- Table 1a: The Complete MSP430 Instruction Set of 27 Core InstructionsDocument9 pagesTable 1a: The Complete MSP430 Instruction Set of 27 Core Instructionsmanjus46No ratings yet
- HJ1602A DatasheetDocument11 pagesHJ1602A DatasheetsunthomaNo ratings yet
- ARM Instruction SetDocument29 pagesARM Instruction SetNeeshank MahajanNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 7 Bahasa Rakitan: III: Matakuliah: T0324 / Arsitektur Dan Organisasi Komputer Tahun: 2005 Versi: 1Document30 pagesPertemuan 7 Bahasa Rakitan: III: Matakuliah: T0324 / Arsitektur Dan Organisasi Komputer Tahun: 2005 Versi: 1Ten Dian Novita SariNo ratings yet
- Asm AsmblerDocument93 pagesAsm AsmblerstormviruxNo ratings yet
- Assembly ProgrammingDocument6 pagesAssembly ProgrammingASKKSANo ratings yet
- Mips Isa Eecc550Document28 pagesMips Isa Eecc550liuylNo ratings yet
- Te3004 HW3 A01168632 A01163133Document10 pagesTe3004 HW3 A01168632 A01163133MiauskiNo ratings yet
- Week 04Document68 pagesWeek 04aroosa naheedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Machine Languages and Digital LogicDocument76 pagesChapter 2: Machine Languages and Digital LogicSiddhartha BitlaNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting The DSP On NM HDV For Cisco 2600/3600/3700/VG200 Series RoutersDocument5 pagesTroubleshooting The DSP On NM HDV For Cisco 2600/3600/3700/VG200 Series RoutersChoubane LamineNo ratings yet
- ARM InstructionsDocument6 pagesARM InstructionsSteven AstorgaNo ratings yet
- 2162 Term Project: The Tomasulo Algorithm ImplementationDocument5 pages2162 Term Project: The Tomasulo Algorithm ImplementationThomas BoyerNo ratings yet
- Chapter04 ProcessorDesign PDFDocument39 pagesChapter04 ProcessorDesign PDFTrần Thảo NguyênNo ratings yet
- St7 ASM Quick ReferenceDocument2 pagesSt7 ASM Quick ReferenceДиана Ангелова-АтанасоваNo ratings yet
- ARM Teaching MaterialDocument33 pagesARM Teaching MaterialbalaNo ratings yet
- ARM Teaching MaterialDocument33 pagesARM Teaching MaterialVishal NairNo ratings yet
- AS400 Iseries Tips Tricks Guides Revision Notes LearningsDocument34 pagesAS400 Iseries Tips Tricks Guides Revision Notes LearningsVISHNU400No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 AssemblerDocument44 pagesChapter 2 Assemblertabassum100% (2)
- ARM Teaching MaterialDocument33 pagesARM Teaching MaterialViswa PraveenNo ratings yet
- C_LOW_LEVELDocument53 pagesC_LOW_LEVELphanduy1310No ratings yet
- Lec378au05 05Document13 pagesLec378au05 05LaxmanPrajapatNo ratings yet
- Opcode AsmDocument72 pagesOpcode AsmbingbanglaNo ratings yet
- Ca Lec4Document20 pagesCa Lec4Sana IftikharNo ratings yet
- JN0 661Document53 pagesJN0 661viatr0nic100% (1)
- ARM Introduction & Instruction Set ArchitectureDocument71 pagesARM Introduction & Instruction Set ArchitecturebalaNo ratings yet
- Ebook - Atmel Avr AssemblerDocument20 pagesEbook - Atmel Avr AssemblerelfrichNo ratings yet
- LMC-SSC2E16-01 Serial: User ManualDocument12 pagesLMC-SSC2E16-01 Serial: User ManualFred ShihNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document86 pagesChapter 5Muhammad OmerNo ratings yet
- PD 667 Profibus - Slave Configuration Guide.: IndexDocument7 pagesPD 667 Profibus - Slave Configuration Guide.: Indexwer974No ratings yet
- MOSHELL COMMANDS TO BE USED IN ERICSSON OSSDocument18 pagesMOSHELL COMMANDS TO BE USED IN ERICSSON OSSWUSHUNo ratings yet
- Module-2 Notes PDFDocument12 pagesModule-2 Notes PDFChandra shekara mnNo ratings yet
- ES Module 2 NotesDocument39 pagesES Module 2 NotesBhavana H NNo ratings yet
- Char CommDocument8 pagesChar CommfhidipNo ratings yet
- Lab Workbook of Microprocessor For StudentsDocument43 pagesLab Workbook of Microprocessor For StudentsHarris Baig100% (1)
- Unit 5 NotesDocument25 pagesUnit 5 NoteskaustubhNo ratings yet
- Assembler Functions and Machine Dependent FeaturesDocument62 pagesAssembler Functions and Machine Dependent FeaturesdeivanayagamNo ratings yet
- Low Level C ProgrammingDocument49 pagesLow Level C Programmingmspereira100% (1)
- Downloads PDF Arm ARM Instruction SetDocument64 pagesDownloads PDF Arm ARM Instruction SetPramod NNo ratings yet
- LCD 2x16 SpecDocument13 pagesLCD 2x16 SpecArnoldA100% (1)
- Instruction Sequencing and Processor ArchitectureDocument25 pagesInstruction Sequencing and Processor Architecturesamueljamespeter100% (4)
- ARM Instruction Set ArchitectureDocument71 pagesARM Instruction Set ArchitectureVamsi SomisettyNo ratings yet
- ARM Introduction & Instruction Set Architecture: Aleksandar MilenkovicDocument31 pagesARM Introduction & Instruction Set Architecture: Aleksandar Milenkovicavireddy1No ratings yet
- Arc Instruction Sets P 10Document9 pagesArc Instruction Sets P 10Cao HuyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ISADocument4 pagesChapter 3 ISAshahzadktk133No ratings yet
- Lecture 6b: MSP430 Assembly Language Tutorial: MSP430 CPUDocument64 pagesLecture 6b: MSP430 Assembly Language Tutorial: MSP430 CPUSufyan NikaninNo ratings yet
- Lab 6.2.2 Configuring OSPF Authentication: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The EnterpriseDocument4 pagesLab 6.2.2 Configuring OSPF Authentication: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The Enterprisemohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- 020 AsmDocument31 pages020 AsmFrang JabardNo ratings yet
- Practical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationFrom EverandPractical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- Assembly Programming:Simple, Short, And Straightforward Way Of Learning Assembly LanguageFrom EverandAssembly Programming:Simple, Short, And Straightforward Way Of Learning Assembly LanguageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- RPM Measurement and Calculations Using Tsop Ir Receiver: I J A R E E I EDocument6 pagesRPM Measurement and Calculations Using Tsop Ir Receiver: I J A R E E I ESomaraju DasamNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2013 14 CP0705 SYB MAT 516 Computational TechniquesDocument2 pagesFALLSEM2013 14 CP0705 SYB MAT 516 Computational TechniquesSomaraju DasamNo ratings yet
- Msp430 InstDocument9 pagesMsp430 InstSomaraju DasamNo ratings yet
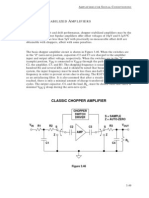
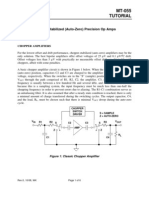
- Chop AmpDocument3 pagesChop AmpNiaz ManikNo ratings yet
- MTDocument6 pagesMTSomaraju DasamNo ratings yet
- I2c EEPROM MSP430Document8 pagesI2c EEPROM MSP430Julian Andres Gomez GomezNo ratings yet
- MSP430 Instruction Set SummaryDocument10 pagesMSP430 Instruction Set SummarySomaraju DasamNo ratings yet
- MSP430 Instruction Set SummaryDocument10 pagesMSP430 Instruction Set SummarySomaraju DasamNo ratings yet
- Msp430 InstDocument9 pagesMsp430 InstSomaraju DasamNo ratings yet
- VHDL Module2 Rev BDocument22 pagesVHDL Module2 Rev BSomaraju DasamNo ratings yet
- LPC2292 2294Document54 pagesLPC2292 2294Somaraju DasamNo ratings yet
- 03 Assembly Language ProgrammingDocument33 pages03 Assembly Language ProgrammingJaideep Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- VHDL BasicsDocument20 pagesVHDL BasicsSomaraju DasamNo ratings yet
- VHDLPRGDocument64 pagesVHDLPRGanmol123454No ratings yet
- Spatial Averaging of Time-Frequency Distributions For Signal Recovery in Uniform Linear ArraysDocument11 pagesSpatial Averaging of Time-Frequency Distributions For Signal Recovery in Uniform Linear ArraysSomaraju DasamNo ratings yet