Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EDSC 304 - Graphic Organizer
EDSC 304 - Graphic Organizer
Uploaded by
bobonkaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EDSC 304 - Graphic Organizer
EDSC 304 - Graphic Organizer
Uploaded by
bobonkaCopyright:
Available Formats
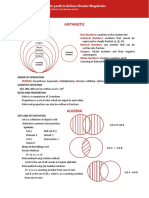
Word Categorization Chart [Parts of an Equation]
Word
Conjugates
Definition
The result of writing the sum of two terms as a difference or vice-versa. (Typically known as using the opposite sign)
Facts/Properties
It only applies in binomials which mean two values.
When you multiply conjugates, you are doing something similar to what happens with a difference of squares: 2 2 a b = (a + b)(a b)
Examples
1.) x+2 2.)6- 6+ x-2
Non-Examples (Incorrect)
1.) 1-2 1-2
2.) 5- 5-
3.)-4+3 -4-3 4.) 3 3+ 1.) 2 -1 -1 is the coefficient. 2.) 5x is a coefficient itself.
Coefficient
A number or symbol multiplied with a variable or an unknown quantity in an algebraic term.
A coefficient tells you how many variables the number has.
http://www.youtube.com /Watch?v=T9vz755kd20
1.) 3x 3 is the coefficient. 2.) 4 +2x-7 4 and 2 are coefficients. 3.) 6x-5 6 is the coefficient.
Polynomial
A polynomial can have constants, variables and exponents, but never division by a variable.
There are special names for polynomials with 1, 2 or 3 terms:
1.) 2x 2.) 5xy+4x-2
1.) 3 2.)
Monomial (1 term) Binomial (2 terms) Trinomial (3 terms)
3.) x-3 4.) 7
Exponent(s)
A quantity representing the power to which a given number or expression is to be raised, usually expressed as a raised symbol beside the number or expression.
The exponent of a number says how many times to use the number in a multiplication. Exponents are also called Powers or Indices.
1.) =555=125 2.) = 3.) = =
1.)
2.) 2 = (2y)(2y)(2y) 3.) = 55
= 0.0625 = 64
Radical(s)
The radical symbol , is used to represent the square root of a number.
The number under the root symbol is called radicand. The expression is read as a radical n or the n th root of a. The expression is read as ath root of b raised to the c power. is also written as
1.) 2.) 3.) 4.)
1.) 2.)
You might also like
- GRE - Quantitative Reasoning: QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandGRE - Quantitative Reasoning: QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Perfect Square Trinomial: Algebraic FractionsDocument7 pagesPerfect Square Trinomial: Algebraic FractionsSagaeHarukiNo ratings yet
- Precal m2Document9 pagesPrecal m2RechelleNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Tr. JennDocument40 pagesPrepared By: Tr. JennMa. Jennifer MapanooNo ratings yet
- Algebraic ExpressionsDocument32 pagesAlgebraic ExpressionsGelvie LagosNo ratings yet
- When You Multiply by A Negative Number The Inequality Sign Changes DirectionDocument16 pagesWhen You Multiply by A Negative Number The Inequality Sign Changes Directionaly jacksonNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Expressions 2.1 Definition and Terminologies: X X X XDocument10 pagesAlgebraic Expressions 2.1 Definition and Terminologies: X X X Xadu_ce105No ratings yet
- Math Reviewer - AlgebraDocument9 pagesMath Reviewer - AlgebraCristina Aquino-SajoniaNo ratings yet
- 1 MathDocument7 pages1 MathAlexandra EscalonaNo ratings yet
- CHAP2Document11 pagesCHAP2Remington SalayaNo ratings yet
- Factorisation 8thDocument5 pagesFactorisation 8thMeenakshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Exponents and Powers: by Abigail SantiagoDocument16 pages1.2 Exponents and Powers: by Abigail SantiagogailmerksNo ratings yet
- Aljebra ReviewerDocument15 pagesAljebra ReviewerDaniel S. MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Polynomials Objectives:: element, is used. Thus, if a is an element of set A, we indicate this by writing "a ϵDocument11 pagesPolynomials Objectives:: element, is used. Thus, if a is an element of set A, we indicate this by writing "a ϵAlfredNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1.-Algebraic Nomenclature:: TermDocument102 pagesAlgebra 1.-Algebraic Nomenclature:: TermNéstor CamarilloNo ratings yet
- Algebra AaaaaDocument10 pagesAlgebra Aaaaavcunanan20ur0411No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document21 pagesChapter 3wagapak111No ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 Mathematics As LanguageDocument19 pagesChapter 2.1 Mathematics As LanguageKlebhyella Cherie BajeNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering (Coe) Freshmen Tutorial Week 2019: Al - JebrDocument6 pagesCollege of Engineering (Coe) Freshmen Tutorial Week 2019: Al - JebrCayle OlaNo ratings yet
- Bizmath Lecture7Document36 pagesBizmath Lecture7Wahab AftabNo ratings yet
- Gmat MathDocument7 pagesGmat MathRamya KsamyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document27 pagesLesson 2Ivy Rose PanganodNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument18 pagesAlgebraJhana Kimberly S. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Expressions For ClassDocument25 pagesAlgebraic Expressions For ClassRonald Abrasaldo SatoNo ratings yet
- Algebra: Block Diagram of The Number SystemDocument18 pagesAlgebra: Block Diagram of The Number SystemMichelle Corpuz IballaNo ratings yet
- Basic Math Review GuideDocument1 pageBasic Math Review GuideMark Lloyd Cabahug LibronNo ratings yet
- Integer Exponents: A A A A ADocument5 pagesInteger Exponents: A A A A Achloe NavarroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Blank Lessons PDFDocument11 pagesChapter 2 Blank Lessons PDFUthman BadmusNo ratings yet
- Algebra: Rational NumbersDocument31 pagesAlgebra: Rational NumbersMark John Paul CablingNo ratings yet
- Jocelyn G. Tamares Teacher IDocument33 pagesJocelyn G. Tamares Teacher IJocelyn Garces-TamaresNo ratings yet
- Maths Assignment GRP 2Document3 pagesMaths Assignment GRP 2Treashana McdonaldNo ratings yet
- Exponentsexponents The Mathematicians ShorthandDocument29 pagesExponentsexponents The Mathematicians ShorthandJhon Ryan AlmendarezNo ratings yet
- Math6 Q3 Module2 Week2Document4 pagesMath6 Q3 Module2 Week2ALLYSSA MAE PELONIA100% (1)
- Unit 2Document36 pagesUnit 2HazemNo ratings yet
- ExpressionsDocument20 pagesExpressionsLưu ThảoNo ratings yet
- 7u (Grade 7) AlgebraDocument21 pages7u (Grade 7) AlgebraMJ :[No ratings yet
- Updated BCA Maths Complete ContentDocument72 pagesUpdated BCA Maths Complete ContentPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Polynomials - 1Document3 pagesPolynomials - 1devanshu sharmaNo ratings yet
- 9th STD Polynomials Text .Book - 2021 Vol 1Document19 pages9th STD Polynomials Text .Book - 2021 Vol 1maheshprasadNo ratings yet
- Algebra: Algebraic ExpressionDocument4 pagesAlgebra: Algebraic ExpressionTherese CuetoNo ratings yet
- The Student Will Be Able To:: ObjectiveDocument20 pagesThe Student Will Be Able To:: ObjectiveShemeka Durant BurtonNo ratings yet
- The Student Will Be Able To:: ObjectiveDocument22 pagesThe Student Will Be Able To:: ObjectiveEdwin LopezNo ratings yet
- Student Notes IndiciesDocument8 pagesStudent Notes IndiciesAshley GomezNo ratings yet
- Student Notes - Indicies PDFDocument8 pagesStudent Notes - Indicies PDFAshley GomezNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Maths WS 06Document10 pagesClass 6 Maths WS 06dikshasrivastava9911No ratings yet
- 1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions 20-21Document29 pages1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions 20-21Salim AbdurrohmanNo ratings yet
- PolynomialsDocument24 pagesPolynomialssmartyshubh choreographyNo ratings yet
- CSC 112 - Lecture 8Document6 pagesCSC 112 - Lecture 8olumideemmanuel940No ratings yet
- Math ReviewerDocument6 pagesMath ReviewerMaria MendozaNo ratings yet
- Math - Reviewer For Grade 7Document6 pagesMath - Reviewer For Grade 7Maria MendozaNo ratings yet
- (BASIC MATH) Algebraic Expressions PDFDocument7 pages(BASIC MATH) Algebraic Expressions PDFJan Mae EstaresNo ratings yet
- 7 Maths NCERT Exemplar Chapter 10Document27 pages7 Maths NCERT Exemplar Chapter 10swaleha samreen jamadarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 3 Math 8Document10 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 3 Math 8Jhon PayatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - AlgebraDocument28 pagesChapter 1 - AlgebraAnna MethyldaNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer MathDocument10 pagesLET Reviewer MathJohn Carlo Telan Panganiban80% (5)
- Algebra Secret RevealedComplete Guide to Mastering Solutions to Algebraic EquationsFrom EverandAlgebra Secret RevealedComplete Guide to Mastering Solutions to Algebraic EquationsNo ratings yet
- The Nuts and Bolts of Proofs: An Introduction to Mathematical ProofsFrom EverandThe Nuts and Bolts of Proofs: An Introduction to Mathematical ProofsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)