Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Marine Phytoplankton
Uploaded by
Amabelle Anne BaduaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Marine Phytoplankton
Uploaded by
Amabelle Anne BaduaCopyright:
Available Formats
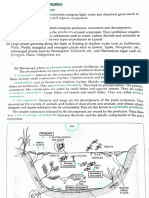
Marine Phytoplankton, also known as marine micro algae, is microscopic single-cell plants that are the most abundant
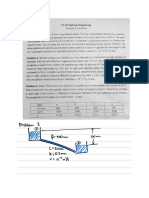
"vegetation" in the ocean. They are capable of turning water and light energy from the sun (phyto means light) into nutrients and oxygen, through a process called photosynthesis. According to NASA, marine algae are responsible for producing up to 90% of the Earth's oxygen supply. Scientists have found that their numbers have declined by about 40% since 1950 and are continuing to decline by about 1% per year. This trend could spell disaster for the entire marine ecosystem. Phytoplankton account for approximately 50% of global primary production, form the trophic base of nearly all marine ecosystems, are fundamental in trophic energy transfer and have key roles in climate regulation, carbon sequestration and oxygen production. (Mli, 2011) Because of their short life cycles, plankters respond quickly to environmental changes, and hence their standing crop and species composition are more likely to indicate thequality of the water mass in which they are found. They strongly influence certain non-biological aspects of water quality (such as pH, color, taste, and odor), and in a very practical sense, they are a part of water quality. Certain taxa often are useful in determining the origin or recent history of a given water mass. Because of their transient nature, and often patchy distribution, however, the utility of plankters as water quality indicators may be limited. PALMER, C.M. 1969. Planktons serve as food on the aquamarine life because of its size. But it will be better if these phytoplanktons will stock in a particular place so, marine creature will go there for food. This apparatus will help us to do these things and filtrates the wastes under the bodies of water.
You might also like
- Instruction ManualDocument3 pagesInstruction ManualAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Leaf Ash As Supplementary Cementitious Material PDFDocument1 pageBamboo Leaf Ash As Supplementary Cementitious Material PDFAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Leaf Ash As Supplementary Cementitious MaterialDocument8 pagesBamboo Leaf Ash As Supplementary Cementitious MaterialAJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Exer 3Document4 pagesExer 3Amabelle Anne Badua0% (1)
- Exer3 Summary and ConclusionDocument1 pageExer3 Summary and ConclusionAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- Gantt ChartDocument1 pageGantt ChartAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- Course Guide For Philippine Institutions 10 For Section C PDFDocument5 pagesCourse Guide For Philippine Institutions 10 For Section C PDFAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Surveying Field NotesDocument6 pages2 - Surveying Field NotesAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Surveying Field NotesDocument6 pages2 - Surveying Field NotesAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 FinalDocument3 pagesExercise 1 FinalAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation Tips 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.: Turn Off Unneeded Lights Use A Laptop Instead of A DesktopDocument1 pageEnergy Conservation Tips 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.: Turn Off Unneeded Lights Use A Laptop Instead of A DesktopAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- Transition: From Primitive Bony Fish To AmphibiansDocument2 pagesTransition: From Primitive Bony Fish To AmphibiansAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- Fact:: Albert Einstein's Brain Was AbnormalDocument3 pagesFact:: Albert Einstein's Brain Was AbnormalAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument8 pagesThe Calvin CycleAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Mohamad Amirul Afif Bin Abdul Majid - GisDocument33 pagesMohamad Amirul Afif Bin Abdul Majid - GisAkram ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Pond EcosystemDocument2 pagesPond Ecosystemskullbhai12No ratings yet
- Syllabus BFSC Centurion UniversityDocument19 pagesSyllabus BFSC Centurion UniversityLauda LessenNo ratings yet
- Carp Polyculture in Central and Eastern Europe, The Caucasus and Central AsiaDocument84 pagesCarp Polyculture in Central and Eastern Europe, The Caucasus and Central Asiatheremfarmer2020No ratings yet
- Cell Biovolume and Surface Area in Phytoplankton of Mediterranean Transitional Water Ecosystems: Methodological AspectsDocument24 pagesCell Biovolume and Surface Area in Phytoplankton of Mediterranean Transitional Water Ecosystems: Methodological Aspectsoanaoana2427No ratings yet
- Diatoms of JaipurDocument12 pagesDiatoms of JaipurAshish DesaiNo ratings yet
- APUNTES Biologia Marina PDFDocument143 pagesAPUNTES Biologia Marina PDFLucía BarberaNo ratings yet
- Red TideDocument9 pagesRed TideKhang KhangNo ratings yet
- PlanktonologyDocument2 pagesPlanktonologyIzzahLina100% (1)
- Zooplankton As Live Food For Fry and Fingerlings of NileDocument14 pagesZooplankton As Live Food For Fry and Fingerlings of NilethehealingartistNo ratings yet
- Plankton Notes PDFDocument14 pagesPlankton Notes PDFArzoo NaazNo ratings yet
- Plankton Blooms in Vortices: The Role of Biological and Hydrodynamic Time ScalesDocument12 pagesPlankton Blooms in Vortices: The Role of Biological and Hydrodynamic Time ScalesEmilio Hernandez-GarciaNo ratings yet
- Investigatory ProjectsDocument15 pagesInvestigatory ProjectsTushar Kush50% (2)
- Broeckerglobalwarming75 PDFDocument5 pagesBroeckerglobalwarming75 PDFDavid AppellNo ratings yet
- Barnes & Clarke 2011 Antarctic Marine Biology PDFDocument7 pagesBarnes & Clarke 2011 Antarctic Marine Biology PDFValentina Sandoval ParraNo ratings yet
- Kualitas Air Rawa Jombor Klaten, Jawa Tengah Berdasarkan Komunitas FitoplanktonDocument14 pagesKualitas Air Rawa Jombor Klaten, Jawa Tengah Berdasarkan Komunitas FitoplanktonFidela Alfrieda ASNo ratings yet
- Submitted by Gyamar Kenni Bcom P, 1 Year: Global Decline of Phytoplankton and Its RamificationsDocument11 pagesSubmitted by Gyamar Kenni Bcom P, 1 Year: Global Decline of Phytoplankton and Its RamificationsKenniNo ratings yet
- Fish Farming PresentationDocument11 pagesFish Farming PresentationRahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Phytoplankton Dynamics in Aquaculture Ponds: ProductionDocument2 pagesPhytoplankton Dynamics in Aquaculture Ponds: ProductionAsa Étudier La-DienNo ratings yet
- Scribd.materials.archiv of Environmental and Life Sciences,2012. Vol.1, No.1 (January), 04 29 2011 - 01 12 2012.ecology, biology, environmental sciences, water quality, hydrobiology, biogeochemistry, environmental education: papers, books, reviews, evaluations, bibliography, abstractsDocument350 pagesScribd.materials.archiv of Environmental and Life Sciences,2012. Vol.1, No.1 (January), 04 29 2011 - 01 12 2012.ecology, biology, environmental sciences, water quality, hydrobiology, biogeochemistry, environmental education: papers, books, reviews, evaluations, bibliography, abstractsSergei OstroumovNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Global-Scale Physical-Biological Interaction ProcessesDocument13 pagesLecture 5: Global-Scale Physical-Biological Interaction ProcessesMaraschino1993No ratings yet
- Journey To The End of The EarthDocument5 pagesJourney To The End of The EarthVridhi AroraNo ratings yet
- Pigment Composition of Freshwater Charophyceae: Michael Schagerl, Clemens PichlerDocument13 pagesPigment Composition of Freshwater Charophyceae: Michael Schagerl, Clemens PichlerNadin AriaNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument14 pagesMICROBIOLOGYPrakashNo ratings yet
- Jeffrey 1975Document4 pagesJeffrey 1975abbasalisu1234No ratings yet
- Bi308 Scenario Based AssignmentDocument7 pagesBi308 Scenario Based AssignmentArshika DeoNo ratings yet
- Crossm: Fungi in The Marine Environment: Open Questions and Unsolved ProblemsDocument15 pagesCrossm: Fungi in The Marine Environment: Open Questions and Unsolved ProblemsBintang Rapshodio TaneNo ratings yet
- Effect of Stocking Density On Survival and Growth of Endangered Bata, Labeo Bata (Hamilton-Buchanan) in Nursery PondsDocument9 pagesEffect of Stocking Density On Survival and Growth of Endangered Bata, Labeo Bata (Hamilton-Buchanan) in Nursery PondsNguyễn LamNo ratings yet
- Bioindicators The Natural Indicator of Environmental PollutionDocument10 pagesBioindicators The Natural Indicator of Environmental PollutionAngie GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Environmental Drivers of Population Variability in Colony-Forming Marine DiatomsDocument14 pagesEnvironmental Drivers of Population Variability in Colony-Forming Marine DiatomsFranciscoNo ratings yet