Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiration (Part 1)
Uploaded by
Jessie Clarinda JoyceOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Respiration (Part 1)
Uploaded by
Jessie Clarinda JoyceCopyright:
Available Formats
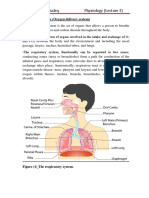
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
ANALYSING THE HUMAN BREATHING MECHANISM
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Analyzing the human breathing mechanism
Understanding the transport of oxygen in the human body.
Realising the importance of a healthy respiratory system
Structure of respiratory system
The structure of the lung
The process of inhalation and exhalation
Changes of air pressure in the thoracic cavity to inhalation, exhalation
The breathing mechanism
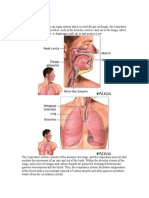
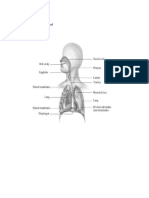
STRUCTURE OF HUMAN RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
ORGANS IN RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
NOSE
TRACHEA
LUNGS BRONCHUS ALVEOLI
Located in the center of the chest is a depression called a hilus. This is where the blood vessels connect the lungs to the heart, the main bronchi to the trachea, and where connective tissue holds everything in place. (LOCATION OF LUNGS)
The lungs are a pair of spongy, air-filled organs located on either side of the chest (thorax) The trachea (windpipe) conducts inhaled air into the lungs through its tubular branches, called bronchi The bronchioles eventually end in clusters of microscopic air sacs called alveoli. In the alveoli, oxygen from the air is absorbed into the blood
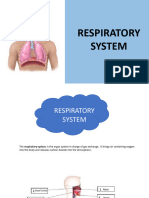
PROCESS OF INHALATION & EXHALATION
Breathing is a continuous process that involves both inhalation and exhalation. The process of taking in oxygen-rich air is known as inhalation. The process of releasing carbon dioxide-rich air into the atmosphere is known as exhalation.
During
inhalation, the diaphragm moves down and the ribs move upwards and outwards, thereby increasing the space in the chest cavity. This leads to the movement of air inside the lungs.
During
exhalation, the diaphragm moves to its former position and the ribs move downwards and inwards, thereby reducing the size of the chest cavity. This leads to the movement of air out of the lung.
NOSE
TRACHEA & BRONCHUS
ALVEOLI
IDENTIFY THE STRUCTURE OF LUNGS
You might also like
- Respiratory SystemDocument17 pagesRespiratory SystemMARVIN HILARIONo ratings yet
- Respiratory System OkDocument36 pagesRespiratory System Okakselerasi10No ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System Aniket DasDocument11 pagesHuman Respiratory System Aniket DasChep KepNo ratings yet
- The Human Breathing SystemDocument5 pagesThe Human Breathing SystemHarry Cianne Luther Sayon100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 8Document32 pagesRespiratory System 8Naanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Respiratory SystemKhrycys Olairez RNNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Document36 pagesTopic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Body Sistem Palmonary/Respiratori: Human Respiratory ProcessDocument5 pagesBody Sistem Palmonary/Respiratori: Human Respiratory ProcessPutri Revany ElvinNo ratings yet
- HBVHB B HBGVGHBDocument9 pagesHBVHB B HBGVGHBbaneNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System or Pulmonary SystemDocument53 pagesThe Respiratory System or Pulmonary Systemfharidaismail47No ratings yet
- Introduction To Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Respiratory Systemangel demonyoNo ratings yet
- Roses Are Red, Violets Are Blue, Without Your Lungs Your Blood Would Be, Too.Document249 pagesRoses Are Red, Violets Are Blue, Without Your Lungs Your Blood Would Be, Too.MabesNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Circulation: Secondary 2, Biology, Chapter 3Document10 pagesRespiration and Circulation: Secondary 2, Biology, Chapter 3Deddy KismanaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Anatomy Physiology and Dse DefinitionDocument4 pagesRespiratory Anatomy Physiology and Dse Definitionmiss RN100% (2)
- Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy & PhysiologyJohn Erlan LipataNo ratings yet
- Patho PneumoniaDocument26 pagesPatho PneumoniaRenz Ivan FuntilonNo ratings yet
- Chapter II - Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesChapter II - Respiratory SystemIndranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemJeffrey Costan100% (1)
- Chapter 1.1Document22 pagesChapter 1.1ieya_yNo ratings yet
- NCM 102 - Concept in OxygenationDocument173 pagesNCM 102 - Concept in OxygenationNess Korosu100% (1)
- Respiratory-System 1Document12 pagesRespiratory-System 1xavier patacsilNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesThe Respiratory SystemAditya PrasadNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesRespiratory SystemMark Jhosua Austria GalinatoNo ratings yet
- Meri Bing Tugas RespiratoryDocument4 pagesMeri Bing Tugas RespiratoryNona MeyNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument17 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesArjun ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemUzumaki Naruto (NARUTADIKS)No ratings yet
- "Assessing Respirations": Prepared By: Marie Cecille Liberty S. VarillaDocument11 pages"Assessing Respirations": Prepared By: Marie Cecille Liberty S. VarillaMarie Cecille Soliven VarillaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System in Human BeingsDocument11 pagesRespiratory System in Human BeingsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemSamson SeiduNo ratings yet
- Gray's Anatomy of The Human BodyDocument18 pagesGray's Anatomy of The Human BodyShinigami AmnerrorNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Grade 9 - Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesPpt-Grade 9 - Respiratory SystemEdralyn Panes VillacrucisNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AssessmentDocument12 pagesRespiratory AssessmentAmanda ScarletNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Group 5Document16 pagesRespiratory System: Group 5Rashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: Carolina Rancier Horacio Vicioso Patricia Otero Dessirée Reyes Ana CarolinaDocument8 pagesThe Respiratory System: Carolina Rancier Horacio Vicioso Patricia Otero Dessirée Reyes Ana CarolinapattsoteroNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- LEC - Week 9 (Respiratory)Document42 pagesLEC - Week 9 (Respiratory)Al SerenosoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Agatha Babyet A. Alabata, Bsn-Iii StemDocument31 pagesRespiratory System: Agatha Babyet A. Alabata, Bsn-Iii StemJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology - MelaneeDocument5 pagesAnatomy Physiology - MelaneeNikkoBacasonNo ratings yet
- Funda LecDocument5 pagesFunda LecJoannalyn FlordelizNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologymalindaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory TractsDocument2 pagesRespiratory TractsMervis ChandaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - Bio 2 ADocument31 pagesRespiratory System - Bio 2 A20181539No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument54 pagesRespiratory SystemALYZZA JANE BUNANo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory Systemcharamina13No ratings yet
- Topic 2.3 - Human Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesTopic 2.3 - Human Respiratory Systembienfrancis.reyes.jhsNo ratings yet
- Breathing and RespirationDocument30 pagesBreathing and Respirationhamzahazard527No ratings yet
- Respiratory System The Body System Responsible For Gas Exchange Between The Body and The External EnvironmentDocument3 pagesRespiratory System The Body System Responsible For Gas Exchange Between The Body and The External EnvironmentJona ThanNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Metric 1rst ChapterDocument13 pages1.3 Metric 1rst ChapterDr. Mariam SahitoNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Human Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesDiffusion and Human Respiratory SystemPriscilla AshwiniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Respiratory PhysiologyDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Respiratory PhysiologyKingsley UdeajaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture - 5 PDFDavid JokerNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument249 pagesRespiratoryBulborea MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Theory of LungDocument7 pagesTheory of LungAndres Dario R LozNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: PHYSIOLOGY-the Branch of Biology That Deals With The Internal Workings ofDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: PHYSIOLOGY-the Branch of Biology That Deals With The Internal Workings ofshonievin100% (2)
- Respiratory2 0Document26 pagesRespiratory2 0api-258400031No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemVin EighteenthNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesRespiratory SystemxoxogeloNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is A Chemical Reaction That Happens in All Living CellsDocument3 pagesRespiration Is A Chemical Reaction That Happens in All Living CellsKani KurmanbekovaNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet