Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Turning The Car: How Car Steering Works
Uploaded by
Anonymous VWlCr439Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Turning The Car: How Car Steering Works
Uploaded by
Anonymous VWlCr439Copyright:
Available Formats
Turning the Car How Car Steering Works
Each front wheel must follow a different circle
Turning the Car
inside follow smaller radius that tighter turn than outside wheel line perpendicular to each wheel will intersect at center point of turn 2 most common types
rack-and-pinion recirculating ball
Rear wheel drive
Front wheel drive
geometry of the steering linkage
Ackermann Geometry
Ackermann Equations
R = (B/2) + [L / tan(�in)] �out= arctan{ 1/ [(B/L)+(1/Tan(�in))] }
R - Radius of Turn B - Distance between front and rear axle L - Distance to convergent point of steering linkages �in - Angle of inside wheel turn �out - Angle of outside wheel turn
Rack-and-pinion Steering
gearset enclosed in metal tube each end of rack protrude from tube tie rod connects to each end of rack tie rod connects to steering arm on spindle pinion gear attach to steering shaft When gear spins, the rack move
2 object of rack-and-pinion gearset
converts rotational motion into linear motion provides a gear reduction steering ratio
ratio of steering wheel turn to wheels turn
steering ratio
Example- 1 steering wheel revolution (360 degrees) results in 20 degrees of car wheels turning then steering ratio = 360/20 = 18:1 higher ratio = more turn steering wheel to get less wheels to turn but less effort lower ratio gives the steering a quicker response
Power Rack-and-pinion
Part of Power Rack
contains cylinder with piston in middle piston connect to rack with 2 ports of fluid Supply higher-pressure fluid to one side forces piston to move and also provide power to move rack
Recirculating-ball Steering
Power Steering
rotary-vane pump
How vane-pump work
pump is driven by the car's engine via a belt and pulley pull hydraulic fluid from return line at low pressure and force into outlet at high pressure amount of flow provided by the pump depends on engine speed
Rotary Valve
device that senses the force on the steering wheel torsion bar twists when apply torque top of the bar connect to steering wheel and bottom of bar connect to the pinion or worm gear amount of torque in torsion bar equal to torque of driver use to turn the wheel The more torque the driver uses to turn the wheels, the more the bar twists
As the bar twists, it rotates inside of spool valve relative to the outside. inner part of spool valve also connect to the steering shaft amount of rotation between inner and outer parts of spool valve depends on torque of driver applies to steering wheel
You might also like
- Gearboxes in AutomobilesDocument95 pagesGearboxes in AutomobilesAravind LakhanNo ratings yet
- Steering SystemDocument57 pagesSteering Systemsharad100% (2)
- Manual Transmission BasicsDocument90 pagesManual Transmission BasicsLeta SK100% (1)
- Torque Converter CDX,Alberta,Cengage CombinedDocument96 pagesTorque Converter CDX,Alberta,Cengage Combinedparkerroach21No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document96 pagesUnit 2David GaddalaNo ratings yet
- Function of Steering SystemDocument19 pagesFunction of Steering SystemTeju LoveNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Hydromatic Drive: Fluid Coupling ConverterDocument44 pagesUnit Iii Hydromatic Drive: Fluid Coupling ConverterGuruLakshmiNo ratings yet
- Steering System VinayDocument10 pagesSteering System VinayVinay YvNo ratings yet
- Auto TransmissionDocument32 pagesAuto TransmissionGthulasi78100% (1)
- Various Types of Steering System, Steering GeometryDocument32 pagesVarious Types of Steering System, Steering GeometrySumit Choudhary100% (1)
- Steering System Functions and Components ExplainedDocument20 pagesSteering System Functions and Components ExplainedMazheidy Mat DarusNo ratings yet
- Steering SystemDocument29 pagesSteering SystemJiju Joseph M100% (1)
- TM Unit 5Document16 pagesTM Unit 5eyobNo ratings yet
- MIT 2.000 Class Understanding Engines & Transmissions: Kristin Schondorf Ford Motor Company Feb 21, 2002Document45 pagesMIT 2.000 Class Understanding Engines & Transmissions: Kristin Schondorf Ford Motor Company Feb 21, 2002Julio KinenNo ratings yet
- Automatic Transmission SystemDocument34 pagesAutomatic Transmission SystemGurpreet Singh AnttalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 - Propulsion Train & Shaft Line ComponentsDocument20 pagesLesson 11 - Propulsion Train & Shaft Line ComponentsMuhammad Kamran Malik100% (1)
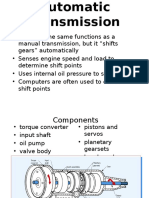
- Automotive Transmission SystemDocument65 pagesAutomotive Transmission SystemEngr Usman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Bma4723 Vehicle Dynamics Chap 8Document36 pagesBma4723 Vehicle Dynamics Chap 8Fu HongNo ratings yet
- Transmission SystemDocument85 pagesTransmission SystempavanmeNo ratings yet
- Automatict RansmissionDocument34 pagesAutomatict RansmissionGanapati HegdeNo ratings yet
- Automotive Transmission: Presented byDocument48 pagesAutomotive Transmission: Presented bySumit SharmaNo ratings yet
- BVA2124 Steering Systems (Lecture 1)Document31 pagesBVA2124 Steering Systems (Lecture 1)AdnannnNo ratings yet
- Automotive Transmission: Be Skilled Be SmartDocument55 pagesAutomotive Transmission: Be Skilled Be SmartgvnagamaniNo ratings yet
- Automatic Transmission GuideDocument34 pagesAutomatic Transmission GuideAsad Khan100% (3)
- Steering System PDFDocument27 pagesSteering System PDFwanawNo ratings yet
- Steering SystemDocument29 pagesSteering SystemNauman KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Transmission SystemDocument41 pagesLecture 5 - Transmission SystemengineeringdesignNo ratings yet
- Types of TransmissionDocument34 pagesTypes of Transmissionsrinuvasa raoNo ratings yet
- Automatic Transmission PDFDocument51 pagesAutomatic Transmission PDFwanaw100% (3)
- Steering GearDocument117 pagesSteering GearSamir Alshaar71% (7)
- Automatic TransmissionDocument97 pagesAutomatic Transmissionvarun55555No ratings yet
- Steering System PresentationDocument19 pagesSteering System PresentationSagar GhusalkarNo ratings yet
- Steering Gears Steering MechanismsDocument23 pagesSteering Gears Steering MechanismsthiagarajanNo ratings yet
- AUTOMATIC - TRANSMISSION (1) - Read-OnlyDocument16 pagesAUTOMATIC - TRANSMISSION (1) - Read-Only19MCE24 Poovendhan VNo ratings yet
- 4 ClutchDocument27 pages4 Clutchmelese EliasNo ratings yet
- Auto 5sem ATEDocument97 pagesAuto 5sem ATEatulsemiloNo ratings yet
- Steering Systems: by Kartheek Sunku 09761A03A1Document23 pagesSteering Systems: by Kartheek Sunku 09761A03A1Usha JyothiNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine / Diesel Engine CyclesDocument55 pagesInternal Combustion Engine / Diesel Engine CyclesAthul P PNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics PDFDocument49 pagesHydraulics PDFHasanul Hariz Jamil0% (1)
- Automatic TrasnmissionDocument57 pagesAutomatic Trasnmissionmohamed A.abdeltwabNo ratings yet
- 4 Drive Shaft and TransfercaseDocument43 pages4 Drive Shaft and Transfercasekidanemariam teseraNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering: TME-802 B. Tech Viii SemDocument33 pagesAutomobile Engineering: TME-802 B. Tech Viii SemAmit TewariNo ratings yet
- Httpss3.Us East 1.amazonaws - Comdocuments.scribd - Comdocs3fvpsvynb469g91s.pdfresponse Content Disposition Attachment3B20fDocument51 pagesHttpss3.Us East 1.amazonaws - Comdocuments.scribd - Comdocs3fvpsvynb469g91s.pdfresponse Content Disposition Attachment3B20fp.elpop56No ratings yet
- Principle of Power SteeringDocument62 pagesPrinciple of Power SteeringAtul Khanna80% (5)
- Automobile Engineering Unit IiDocument61 pagesAutomobile Engineering Unit IiRavindra_120267% (3)
- CH40 Automatic Transmissions and Transaxles STUDENT VERSIONDocument45 pagesCH40 Automatic Transmissions and Transaxles STUDENT VERSIONالأستاذ يوسف الخواجه للفيزياءNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO TRANSMISSION SYSTEM AdityaDocument20 pagesINTRODUCTION TO TRANSMISSION SYSTEM Adityavideo songNo ratings yet
- Rack and Pinion Steering System ExplainedDocument20 pagesRack and Pinion Steering System ExplainedYogeshGargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.1 Transmission System ClutchDocument33 pagesChapter 6.1 Transmission System ClutchdoomraNo ratings yet
- Automotive Drivetrains: ClutchesDocument44 pagesAutomotive Drivetrains: ClutchespapagunzNo ratings yet
- Car Steering Systems: PresenterDocument14 pagesCar Steering Systems: Presenterankur402No ratings yet
- ClutchesDocument76 pagesClutchesAravind Lakhan90% (10)
- FM Pump in Ic EngineDocument10 pagesFM Pump in Ic EngineKarthik RajanNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Donny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume Iv: Performancing the EvolutionFrom EverandDonny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume Iv: Performancing the EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Construction and Manufacture of AutomobilesFrom EverandConstruction and Manufacture of AutomobilesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- UntitledDocument39 pagesUntitledJoao Paulo PachecoNo ratings yet
- HTMLDocument68 pagesHTMLnasticaNo ratings yet
- Aoc 715g2892-2-3 Power Supply PDFDocument1 pageAoc 715g2892-2-3 Power Supply PDFAnonymous VWlCr439100% (1)
- The Windows 7 Boot ProcessDocument2 pagesThe Windows 7 Boot ProcessGerard DijkstraNo ratings yet
- General Installation ManualDocument64 pagesGeneral Installation ManualAnonymous VWlCr439No ratings yet
- Lenovo G Z 50 Series Hardware Mmaintanence ManualDocument96 pagesLenovo G Z 50 Series Hardware Mmaintanence ManualOnur KarNo ratings yet
- The Great Book of Best Quotes of All Time. - OriginalDocument204 pagesThe Great Book of Best Quotes of All Time. - OriginalAbhi Sharma100% (3)
- Understanding TFT-LCD TechnologyDocument11 pagesUnderstanding TFT-LCD TechnologyAnonymous VWlCr439No ratings yet
- User's Manual: GB NL F E D IDocument21 pagesUser's Manual: GB NL F E D IFlorea NicolaeNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines5.14Document46 pagesSimple Machines5.14Anonymous VWlCr439No ratings yet
- Book 4Document318 pagesBook 4Екатерина Рачкова100% (1)
- Refrigerant Temperature-Pressure Chart with over 100 TypesDocument1 pageRefrigerant Temperature-Pressure Chart with over 100 TypescristiangodeanuNo ratings yet
- Inspect & Service Braking SystemsDocument42 pagesInspect & Service Braking SystemsAnonymous VWlCr439No ratings yet
- Inspect & Service Braking SystemsDocument42 pagesInspect & Service Braking SystemsAnonymous VWlCr439No ratings yet
- The Complete Guide To Home CarpentryDocument255 pagesThe Complete Guide To Home Carpentrylandog100% (8)
- Category: Process Control Question: How Does A Pressure Regulator Work? AnswerDocument1 pageCategory: Process Control Question: How Does A Pressure Regulator Work? AnswerAnonymous VWlCr439No ratings yet
- First TimeDocument33 pagesFirst TimeAnonymous VWlCr439No ratings yet
- Understanding TFT-LCD TechnologyDocument11 pagesUnderstanding TFT-LCD TechnologyAnonymous VWlCr439No ratings yet
- Structures and MechanismsDocument12 pagesStructures and MechanismsAnonymous VWlCr439No ratings yet
- Manuale Mynute Csi - IngDocument56 pagesManuale Mynute Csi - IngAnonymous VWlCr439No ratings yet
- 04 - Foundry Work For The AmateurDocument49 pages04 - Foundry Work For The AmateurGaveUpOnTV100% (4)
- How to Hack Wireless Internet ConnectionsDocument10 pagesHow to Hack Wireless Internet ConnectionsSamibloodNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines5.14Document46 pagesSimple Machines5.14Anonymous VWlCr439No ratings yet
- Curs 8 - 3 POO in PHPDocument3 pagesCurs 8 - 3 POO in PHPMirela MarinescuNo ratings yet
- DOM QuickrefDocument1 pageDOM QuickrefMirela MarinescuNo ratings yet
- How to Hack Wireless Internet ConnectionsDocument10 pagesHow to Hack Wireless Internet ConnectionsSamibloodNo ratings yet
- E426 1 Mynute JDocument12 pagesE426 1 Mynute JAnonymous VWlCr439No ratings yet
- Case of A Wireless HackDocument8 pagesCase of A Wireless HackDudi AbdurachmanNo ratings yet
- Case of A Wireless HackDocument8 pagesCase of A Wireless HackDudi AbdurachmanNo ratings yet