Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Session 2
Session 2
Uploaded by
theresa.painterOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Session 2
Session 2
Uploaded by
theresa.painterCopyright:
Available Formats
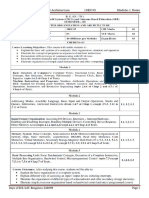
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION
This module provides an overview of computer organization and architecture. It is assumed that the reader has some basic knowledge of hardware such as logic gates, flip-flops, registers etc. This module is divided into 5 units each emphasizing on the need, organization, and architecture. Examples and block diagrams are provided in each unit to make the reader comfortable. Unit 1 gives an overview structure. Unit 2 describes the addressing methods and instruction execution methods. It includes various instructions, its formats, addressing methods and execution of a computer instructions. Unit 3 describes the organization of hardware which enables a #$% to perform its main function & instruction fetch and instruction execution. This unit shall also introduce the possibilit! of generating control signals in the #$% b! micro -programmed control and an alternative approach called hardwired control. Unit 4 explains different t!pes of memories, its organization and working, also the various techni'ues used to increase the effective speed, reduce the cost and size of main memor!. Unit 5 discusses the various wa!s in which input(output can take place between the #$% and the peripheral devices. The I() methods like $rogrammed I() , *irect emor! +ccess, Interrupt I() , I() channels and I() processors are discussed. This module concentrates on general design and architecture of a computer. ,ith this background the user can go in for an! specific design and architecture and also appreciate the different computer organizations and architectures such as -educed Instruction .et #omputer/-I.#0 #omputer/#I.#0. and #omplex Instruction .et of basic computer organization, which includes emor! - processor interaction and "us
functional components of a computer,
You might also like
- Computer PackagesDocument82 pagesComputer PackagesPETER KAMAU100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Modern Computer Architecture: From Logic Gates to Parallel ProcessingFrom EverandFundamentals of Modern Computer Architecture: From Logic Gates to Parallel ProcessingNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument111 pagesComputer Organization and ArchitectureKarthik P67% (3)
- Advanced Computer Architecture: CSE-401 EDocument71 pagesAdvanced Computer Architecture: CSE-401 EJitender GargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction: 1.1 Organization and Architecture 1.2 Structure and FunctionDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction: 1.1 Organization and Architecture 1.2 Structure and FunctionChu Quang HuyNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Architecture Q&A 2018 - It Exams-Quick UnderstandingDocument17 pagesMicroprocessor Architecture Q&A 2018 - It Exams-Quick UnderstandingAkhs SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Module 1Document36 pages1 - Module 1sammy CNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Organisation and ArchitectureDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Computer Organisation and ArchitectureJohn KaranjaNo ratings yet
- AcaDocument3 pagesAcasweetunannuNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Computer and Programming in C: (CSE - 101 F)Document339 pagesFundamentals of Computer and Programming in C: (CSE - 101 F)Himanshu SukhejaNo ratings yet
- NAND 2 TetrisDocument13 pagesNAND 2 TetrisADITYA MOHAN GUPTA 18BCE1017No ratings yet
- 1.1the Computer SystemsDocument65 pages1.1the Computer Systems00.wonderer.00No ratings yet
- AcaDocument71 pagesAcaRishabh PurwarNo ratings yet
- Nuevo Documento de TextoDocument3 pagesNuevo Documento de TextoJUAN ANTONIO MILIANO SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Comp Arc)Document24 pagesChapter 1 (Comp Arc)gualnegusNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Havard N VonDocument4 pagesCOMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Havard N Vonv5kbkrmdfpNo ratings yet
- 5.6 Basic Computer Structure: Basic Maintenance Training Manual Module 5 Digital Technology / EISDocument26 pages5.6 Basic Computer Structure: Basic Maintenance Training Manual Module 5 Digital Technology / EISIvomadnessNo ratings yet
- Complete CO Notes 5UNITSDocument218 pagesComplete CO Notes 5UNITS560 KarthikNo ratings yet
- KCS-302 CaoDocument155 pagesKCS-302 CaoDeepesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Management and Business Technology.Document13 pagesFaculty of Management and Business Technology.victorjeffry24No ratings yet
- Computer Architecture and Organization Learning Module 1Document31 pagesComputer Architecture and Organization Learning Module 1Maoi ReyesNo ratings yet
- COA Mod 1Document41 pagesCOA Mod 1diwewe9515No ratings yet
- Basic 1Document51 pagesBasic 1ys013330No ratings yet
- Architecture of Computers: Vistula UniversityDocument34 pagesArchitecture of Computers: Vistula Universityq5nfvkbyyrNo ratings yet
- Computer OrganizocessorsDocument109 pagesComputer Organizocessors716 Rashika.RNo ratings yet
- Kalinga University Department of Computer ScienceDocument29 pagesKalinga University Department of Computer SciencevivekkumarsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1comDocument38 pagesChapter 1comaregawi weleabezgiNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Components Part II: LessonDocument14 pagesEmbedded Systems Components Part II: LessonSayan Kumar KhanNo ratings yet
- Programming in C Mccs 2022Document218 pagesProgramming in C Mccs 2022224akiNo ratings yet
- Co Unit 1Document42 pagesCo Unit 1Lokesh TALAGATLANo ratings yet
- Com Org Unit IvDocument17 pagesCom Org Unit Iveugeniogabriel15No ratings yet
- Unit IDocument15 pagesUnit IPraisy Sunaina PendyalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part IIIDocument36 pagesChapter 1 Part IIIParas Chand ThaqureeNo ratings yet
- CAE101: Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument31 pagesCAE101: Computer Organization and ArchitectureGuru BalanNo ratings yet
- CO&A 18EC35 Module-1 Notes Dileep Kumar K SDocument32 pagesCO&A 18EC35 Module-1 Notes Dileep Kumar K SThanushree RMNo ratings yet
- Prelim Text Copyright 2001 DGMDocument174 pagesPrelim Text Copyright 2001 DGMTiruchengode VinothNo ratings yet
- Module Part1Document21 pagesModule Part1Charan ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: The Components of The System UnitDocument9 pagesChapter 4: The Components of The System UnitTinashe BareNo ratings yet
- Computer SystemDocument141 pagesComputer Systemmhammadnjmaden45No ratings yet
- OVERVIEW OF OPERATING SYSTEM UpdatedDocument9 pagesOVERVIEW OF OPERATING SYSTEM UpdatedLloyd VegafriaNo ratings yet
- Computer Org - L3Document29 pagesComputer Org - L3محمد العموديNo ratings yet
- Itc 102 Module 1Document7 pagesItc 102 Module 1Lehd OnlaoNo ratings yet
- Winter Semester 2021-2022Document3 pagesWinter Semester 2021-2022batmanNo ratings yet
- Computer Applications in ManagmentDocument43 pagesComputer Applications in ManagmentssskcollegeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument5 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Computer Organization and ArchitectureSteffany Roque100% (1)
- Capítulo 1 Con 1.1 y 1.2 Con ImagenDocument3 pagesCapítulo 1 Con 1.1 y 1.2 Con ImagenSebastián RamírezNo ratings yet
- Programming in C Unit 1Document22 pagesProgramming in C Unit 1Manda VaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Components of A Computer: Input UnitDocument11 pagesComponents of A Computer: Input UnitsnzNo ratings yet
- CSE 259 Lecture1 2Document9 pagesCSE 259 Lecture1 2robin haqueNo ratings yet
- CSA - Chapter 1Document39 pagesCSA - Chapter 1Nikita vermaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1 ArchitectureDocument129 pagesLecture - 1 ArchitectureFitsum AyeleNo ratings yet
- 5EC3-01: Computer Architecture: Unit-I What Are Digital Computers?Document19 pages5EC3-01: Computer Architecture: Unit-I What Are Digital Computers?Himanshi SainiNo ratings yet
- M Raza 2205-BH-PS-19, I2, Final Course ReviewDocument9 pagesM Raza 2205-BH-PS-19, I2, Final Course ReviewMuhammad razaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Plan With Solution: 1. Classification: 2Document10 pagesAssignment Plan With Solution: 1. Classification: 2Sumit JainNo ratings yet
- MCS-012 Block 3Document94 pagesMCS-012 Block 3Abhishek VeerkarNo ratings yet
- (PPT) Digital Electronics 2 For StudentsDocument6 pages(PPT) Digital Electronics 2 For StudentsJONNA ACABONo ratings yet
- Computer System ArchitectureDocument25 pagesComputer System ArchitecturethelodieNo ratings yet
- CAO Unit 1Document13 pagesCAO Unit 1mdmomin7517No ratings yet
- RBI BulletinDocument118 pagesRBI Bulletintheresa.painter100% (1)
- 2014 EventsDocument16 pages2014 Eventstheresa.painterNo ratings yet
- Qiv PDFDocument350 pagesQiv PDFtheresa.painterNo ratings yet
- Biconnected ComponentsDocument3 pagesBiconnected Componentstheresa.painterNo ratings yet
- Answer Pattern Analysis Sheet: Test Performance Performance AnalysisDocument4 pagesAnswer Pattern Analysis Sheet: Test Performance Performance Analysistheresa.painterNo ratings yet
- Single Source Shortest Paths DijkstraDocument4 pagesSingle Source Shortest Paths Dijkstratheresa.painterNo ratings yet
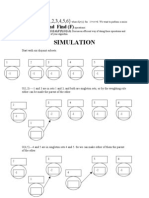
- Simulation: Union (U) and Find (F)Document3 pagesSimulation: Union (U) and Find (F)theresa.painterNo ratings yet
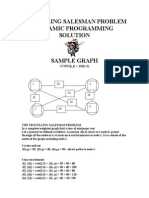
- Travelling Salesman Problem Dynamic ProgrammingDocument2 pagesTravelling Salesman Problem Dynamic Programmingtheresa.painterNo ratings yet
- Some Notes On Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata by Frank PfenningDocument5 pagesSome Notes On Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata by Frank Pfenningtheresa.painterNo ratings yet
- Equivalence of Fas: Minimize MinimizeDocument20 pagesEquivalence of Fas: Minimize Minimizetheresa.painterNo ratings yet
- Informal Proof of Correctness: 2014/2/3 CSC 3130 Formal Languages and Automata Theory 1Document29 pagesInformal Proof of Correctness: 2014/2/3 CSC 3130 Formal Languages and Automata Theory 1theresa.painterNo ratings yet
- Class Discussion: Can You Draw A DFA That Accepts The Language (A B - K 0,1,2, ) Over The Alphabet (A, B) ?Document10 pagesClass Discussion: Can You Draw A DFA That Accepts The Language (A B - K 0,1,2, ) Over The Alphabet (A, B) ?theresa.painterNo ratings yet
- Church's ThesisDocument8 pagesChurch's Thesistheresa.painterNo ratings yet
- AutomataDocument4 pagesAutomataHitender DalalNo ratings yet