Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analysis Slope Stability
Uploaded by
iangbeyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analysis Slope Stability
Uploaded by
iangbeyCopyright:
Available Formats
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.
ANALYSIS SLOPE STABILITY Site ID : Site Name : I. Data Boring LOG
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 1
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
II.
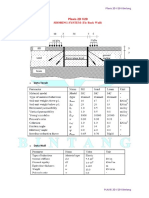
Nilai- Nilai Parameter Tanah
Parameter Material Model Type of Material Dry soil weight Wet soil weight Permeability in hor. direction Permeability in ver. direction Youngs modulus Poissons ratio Cohesion (constant) Friction Angel Dilatancy angel III. Analisis Pembebanan Tower Beban Tower = 50 kN
d s Kx Ky E v C
Humus Berpasir Mohr-coulomb Undrained 16 18 1 1 9000 0.3 1 30 0
Lempung Mohr-coulomb drained 16 20 1 1 15000 0.3 10 30 0
IV. Analisis Kelongsoran dengan Aplikasi Plaxis v.8.2 A. Plaxis Input
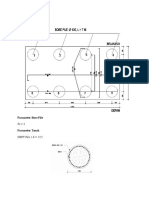
Gambar 1. Geometri Lereng
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 2
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
IV.1.
Tahap Gravity Loading Tahap awal dari analysis digunakan untuk menghitung tegangantegangan awal akibat berat sendiri massa tanah dan tegangan horosontal. Fase 1: Gravity Loading Calculation type: plascic Start from phase: 0 initial phase Parameter: - Additional step = 100 - Ignore undrained behaviour - Delete intermediate steps - Loading input: total multipliers Multipliers: Mweight_= 1 (maksudnya tegangan tanah terjadi dari berat sendiri tanah sendiri sehingga factor pengali beratnya = 1).
IV.2.
Tahap Safety Factor akibat Gravity Loading Untuk mencari factor aman sebelum ada beban pondasi. Fase 2: SF gravity loading Calculation type: Phi-c reduction Start from phase: 1 Gravity Loading Parameter: - Additional step = 100 - Loading input: increment multipliers Multipliers: MSF_= 0.1
IV.3.
IV.4.
Tahap Beban Pondasi Fase 3: beban pondasi Calculation type: Plastic Start from phase: 2 Safety Factor akibat Gravity Loading Parameter: Additional step = 100 Loading input: staged construction Reset displacement to Zero Delete intermediate steps Tahap Beban Luar Fase 4: beban luar Calculation type: Plastic Start from phase: 3 beban pondasi Parameter: Additional step = 100 Delete intermediate steps Loading input: total multipliers Multipliers: Mload A_= 50 kN
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 3
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
IV.5.
Tahap SF Pondasi dan Beban Tower Fase 5: SF Pondasi dan Beban Tower Calculation type: Phi-c reduction Start from phase: 4 beban luar Parameter: Additional step = 100 Loading input: increment multipliers Multipliers: MSF_= 0.1
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 4
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
B. Plaxis Input 1. Tahap Gravity Loading Pada tahap ini menunjukkan hasil bahwa dengan berat sendiri tanah, pada lereng mengalami pergerakan sebesar 165.07E10-3 m.
Gambar 2. Lereng terdeformasi akibat Gravity Loading
Gambar 3. arah gerakan tanah dan penurunan akibat gravity Loading
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 5
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
2. Tahap Vertical Loading Pada tahap ini tanah menerima beban yang dimodelkan sebagai beban merata (tractions). Tanah mengalami deformasi yaitu sebesar 285.57E10-3m.
Gambar 4. Lereng terdeformasi akibat Vertical Loading
Gambar 5. arah gerakan tanah dan penurunan akibat Vertical Loading
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 6
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
Gambar 6. arah gerakan tanah dan penurunan akibat Vertical Loading (shading model)
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 7
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
PLAXIS CURVE V.8 Angka keamanan akibat Beban Pondasi dan Tower:
Dari Kurva diketahui bahwa SF akibat gravity loading dan beban Pondasi dan tower adalah1.352. Angka ini lebih kecil dibandingkan dengan SF minimal untuk keruntuhan yaitu 1.5 Sehingga disimpulkan bahwa lereng tidak aman jika gravity dan Beban pondasi dan tower bekerja maksimal. V. Kesimpulan
Lereng tidak aman dan dibutuhkan retaining wall untuk stabilitas lereng.
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 8
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
displacement vector (u) Mstage the Mstage parameter is associated with the Staged construction option in PLAXIS (see Staged construction). This total multiplier gives the proportion of a construction stage that has been completed. Without input from the user, the value of Mstage is always zero at the start of a staged construction analysis and at the end it will generally be 1.0. It is possible to specify a lower ultimate level of Mstage using the Advanced option of the Parameters tab sheet. However, care should be taken with this option. In calculations where the loading input is not specified as Staged construction, the value of Mstage remains zero. Marea The Marea parameter is also associated with the Staged construction option. This parameter gives the proportion of the total volume of soil clusters in the geometry model that is currently active. If all soil clusters are active then Marea has a value of 1.0. Stiffness As a structure is loaded and plasticity develops then the overall stiffness of the structure will decrease. The Stiffness parameter gives an indication of the loss of stiffness that occurs due to material plasticity. The parameter is a single number that is 1.0 when the structure is fully elastic and reduces in magnitude as plasticity develops. At failure the value is approximately zero. It is possible for this parameter to have negative values if softening occurs. Pmax The Pmax parameter is associated with undrained material behaviour and represents the maximum absolute excess pore pressure in the mesh, expressed in the unit of stress. During undrained loading in a plastic calculation Pmax generally increases, whereas Pmax generally decreases during a consolidation analysis. Stresses 'xx 'yy 'zz xy '1 '2 '3 p' q p excess
effective horizontal stress (x-direction) effective vertical stress (y-direction) effective stress in the out-of-plane direction (z-direction) shear stress in absolute sense the largest effective principal stress the intermediate effective principal stress in absolute sense the smallest effective principal stress isotropic effective stress (mean effective stress) deviatoric stress (equivalent shear stress) excess pore pressure
See the Scientific Manual for a definition of the stress and strain components. The phrase 'in absolute sense' in the description of the principal components is added because, in general, the normal stress and strain components are negative (compression is negative). Note that the deviatoric stress and strain components are always positive. Stress components are expressed in the units of stress; strains are dimensionless.
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 9
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
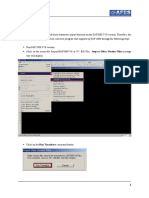
Memulai Plaxis 8.x Program > Plaxis 8.x > 1. Plaxis Input
Pilih New Project > OK
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 10
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
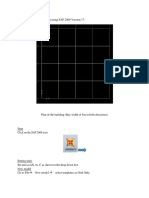
General Setting
Isi Title, Contoh: Slope Stability
Setting Units, Geometry Dimensions atau ukuran lembar kerja dan Grid, Pilih OK
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 11
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
Pemodelan
Pilih Geometry line, (tool yang diberi kotak)
Gambarkan Geometrynya sesuai dengan kondisi lapangan.
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 12
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
Jika lereng masih dalam kondisi existing. Setelah pemodelan, Pilih Loads > Standard Fixities
Maka akan seperti gambar dibawah ini:
Kemudian Pilih Material Sets
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 13
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
Pilih Contoh tanah yang mendekati keadaan sebenarnya Pindahkan Kekotak sebelah kiri Pilih Edit
Isi Data Tanah sesuai dengan data hasil pengujian tanah.
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 14
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 15
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
Setelah selesai Klik sambil ditahan lalu pindahkan ke gambar tempat tanah tersebut,
Klik sambil ditahan
Lepas disini
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 16
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
Langkah selanjutnya adalah Pilih Generete Mest seperti gambar dibawah ini:
Hasilnya akan seperti gambar dibawah ini:
Pilih Update
Pilih Initial condition
Isi berat jenis air > OK
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 17
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
Langkah selanjutnya adalah: Pilih Calculate
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 18
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
Tahap Gravity Loading Tahap awal dari analysis digunakan untuk menghitung tegangantegangan awal akibat berat sendiri massa tanah dan tegangan horosontal. Fase 1: Gravity Loading Calculation type: plascic Start from phase: 0 initial phase Parameter: - Additional step = 100 - Ignore undrained behaviour - Delete intermediate steps - Loading input: total multipliers Multipliers: Mweight_= 1 (maksudnya tegangan tanah terjadi dari berat sendiri tanah sendiri sehingga factor pengali beratnya = 1).
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 19
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 20
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
Tahap Safety Factor akibat Gravity Loading Untuk mencari factor aman sebelum ada beban pondasi. Fase 2: SF gravity loading Calculation type: Phi-c reduction Start from phase: 1 Gravity Loading Parameter: - Additional step = 100 - Loading input: increment multipliers Multipliers: MSF_= 0.1
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 21
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 22
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
Pilih Project yang akan dibuka, *.DTA > Open
Hasilnya adalah sebagai berikut:
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 23
Analysis Slope Stability dengan Plaxis 8.x
Untuk melihat model tampilannya. Pilih Deformations > Total displacements Atau yang lainnya.
By: dedy trianda
Hal. 24
You might also like
- Sikadur®-42 MP SlowDocument6 pagesSikadur®-42 MP SlowGihasAbdNo ratings yet
- SIKA Sikadur 42 MP Normal HCDocument5 pagesSIKA Sikadur 42 MP Normal HCKang Mas WiralodraNo ratings yet
- Parameter 1Document63 pagesParameter 1eka nur fitriyanaNo ratings yet
- Perbaikan Tanah Kelompok 9 - 26112-21Document16 pagesPerbaikan Tanah Kelompok 9 - 26112-21Zalfa Aidah5No ratings yet
- FileDocument140 pagesFilebetahita_80174No ratings yet
- Template Foundation BorepileDocument1 pageTemplate Foundation BorepileMuhammad AmarNo ratings yet
- Manual SACS - SeastateDocument7 pagesManual SACS - SeastatevenacavainferiorNo ratings yet
- Road Condition Monitoring SystemDocument17 pagesRoad Condition Monitoring SystemAndrei ItemNo ratings yet
- Calculation Jembatan CastelatedDocument18 pagesCalculation Jembatan CastelatedrifkynetNo ratings yet
- Lateral Pile Capacity Caculation Using Broms's Method (Free Head Type)Document8 pagesLateral Pile Capacity Caculation Using Broms's Method (Free Head Type)Mohammad Tawfiq WaraNo ratings yet
- Daftar Korelasi Parameter TanahDocument18 pagesDaftar Korelasi Parameter Tanahadrian100% (1)
- Perhitungan Pondasi Sumuran: Input Data Disain AwalDocument1 pagePerhitungan Pondasi Sumuran: Input Data Disain AwaldeddiiskandarNo ratings yet
- 1.b.PILE SLAB-5m (69+625 - 69+775) - OkDocument24 pages1.b.PILE SLAB-5m (69+625 - 69+775) - OkAkmal SyarifNo ratings yet
- CCAA Salinity T56Document22 pagesCCAA Salinity T56HTC1111No ratings yet
- MTDF-CV-300-SPE-1011-R3A - Specification For PilingDocument22 pagesMTDF-CV-300-SPE-1011-R3A - Specification For PilingDidi Hadi RiantoNo ratings yet
- Design Report of Pedestrian Bridge 2 (Jl. Tb. Simatupang) 18122017Document81 pagesDesign Report of Pedestrian Bridge 2 (Jl. Tb. Simatupang) 18122017Andrew LimbongNo ratings yet
- Analysis Report - Tower 62 Tbi 3Document72 pagesAnalysis Report - Tower 62 Tbi 3Muhammad AmarNo ratings yet
- 52 - Interface With SAP2000 - DocDocument12 pages52 - Interface With SAP2000 - DocFauzankalibataNo ratings yet
- Pondasi Tang Pancang Spun PileDocument22 pagesPondasi Tang Pancang Spun PileMochammad ShokehNo ratings yet
- Analisis Stabilitas Lereng Menggunakan Model Numerik 3 Dimensi Studi Kasus Lereng Sekolah Terpadu (Jurnal)Document13 pagesAnalisis Stabilitas Lereng Menggunakan Model Numerik 3 Dimensi Studi Kasus Lereng Sekolah Terpadu (Jurnal)I'anatul FarikhahNo ratings yet
- Bagh Ring Road Project: Calculation of Soil SpringsDocument1 pageBagh Ring Road Project: Calculation of Soil Springsazam1uNo ratings yet
- Pondasi Conveyor C-1 - Rev A (02!12!2011)Document40 pagesPondasi Conveyor C-1 - Rev A (02!12!2011)Barita JonBos SilalahiNo ratings yet
- As 1742.6-2004 Manual of Uniform Traffic Control Devices Tourist and Services SignsDocument9 pagesAs 1742.6-2004 Manual of Uniform Traffic Control Devices Tourist and Services SignsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- General Specification For Road WorksDocument19 pagesGeneral Specification For Road WorksNaveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Shoring System (Tie Back Wall) 2DDocument10 pagesShoring System (Tie Back Wall) 2DAndiNo ratings yet
- Hitung Flexibel Pavement No.5Document8 pagesHitung Flexibel Pavement No.5Syaiful RahmanNo ratings yet
- CR2151 BPK PRO CIV 001 - Civil Work ProcedureDocument8 pagesCR2151 BPK PRO CIV 001 - Civil Work ProcedureIda Bagus Gede Roma Harsana PutraNo ratings yet
- Foundation (Spread Footing) : 11215 1 UD F5 Inftr 1 SlabDocument24 pagesFoundation (Spread Footing) : 11215 1 UD F5 Inftr 1 SlabDhimas Surya NegaraNo ratings yet
- TS10 Earthworks Drainage Bitument WorksDocument75 pagesTS10 Earthworks Drainage Bitument WorksmojgfdNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Bore PileDocument5 pagesPerhitungan Bore PileFitri Yani100% (1)
- List of ContentsDocument53 pagesList of ContentstiniNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Tiang PancangDocument64 pagesPerhitungan Tiang PancangibnuNo ratings yet
- Bharat Heavy Plate & Vessels Limited - VisakhapatnamDocument8 pagesBharat Heavy Plate & Vessels Limited - VisakhapatnamRama Subramanyam ManepalliNo ratings yet
- Afes Calc. of Found. Diesel Oil TankDocument52 pagesAfes Calc. of Found. Diesel Oil TankIman RahmatullahNo ratings yet
- Gouw 2014Document23 pagesGouw 2014Lissa ChooNo ratings yet
- Shear CentreDocument2 pagesShear CentreSooraj SivanNo ratings yet
- Peru NDTDocument50 pagesPeru NDTGabrielNo ratings yet
- Footings - Rectangular Spread Footing AnalysisDocument8 pagesFootings - Rectangular Spread Footing Analysisdicktracy11No ratings yet
- CivilFEM GeotechnicalDocument107 pagesCivilFEM GeotechnicalJose Antonio Paredes VeraNo ratings yet
- Example Foundation Calculation by AfesDocument25 pagesExample Foundation Calculation by AfesPanithi Brahmasâkhâ100% (1)
- SK 1400 Calculation Structure Report - Lifting Analysis RBDocument32 pagesSK 1400 Calculation Structure Report - Lifting Analysis RBRustam RiyadiNo ratings yet
- Diketahui:: Arah MemanjangDocument14 pagesDiketahui:: Arah Memanjangskipy_nutNo ratings yet
- Calculation Note Rev.0Document8 pagesCalculation Note Rev.0Riandi HartartoNo ratings yet
- EX02. 2D Beam Analysis (Simply Supported Beam)Document6 pagesEX02. 2D Beam Analysis (Simply Supported Beam)Lisa DiasNo ratings yet
- Bentley Q&ADocument35 pagesBentley Q&AinnovativekarthiNo ratings yet
- Dsain Pelat Lantai JembatanDocument35 pagesDsain Pelat Lantai JembatanRismansyah Rizqian SundawaNo ratings yet
- MJPN PGAS 3514 CV CA 009 - Calculation For Guard HouseDocument735 pagesMJPN PGAS 3514 CV CA 009 - Calculation For Guard Houseabduh81No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Section DesignDocument8 pagesChapter 11 - Section DesignDavid SinambelaNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications For Earthworks, Geosynthetics Rev.CDocument121 pagesTechnical Specifications For Earthworks, Geosynthetics Rev.Cvisnupada100% (1)
- Calculation 40 VF 3540ABDocument382 pagesCalculation 40 VF 3540ABPeja JusohNo ratings yet
- SAP - Non Linear Analysis - AzadDocument20 pagesSAP - Non Linear Analysis - AzadHemant SonawadekarNo ratings yet
- SAP2000 PushoverDocument20 pagesSAP2000 PushoverHemant Sonawadekar100% (1)
- GTL S08 Ex 03 Elasto Plastic Analysis of Drained FootingDocument0 pagesGTL S08 Ex 03 Elasto Plastic Analysis of Drained FootinglinoficNo ratings yet
- Create Composite Material in PatranDocument20 pagesCreate Composite Material in PatranlowCLNo ratings yet
- PHYS 101 Experiment 2. Static and Kinetic Friction On An Inclined PlaneDocument2 pagesPHYS 101 Experiment 2. Static and Kinetic Friction On An Inclined Planemirsad türkerNo ratings yet
- RCC Rectangular Overhead Water TankDocument19 pagesRCC Rectangular Overhead Water TankSRINIVAS DNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 17 Rapid DrawdownDocument17 pagesTutorial 17 Rapid DrawdownJustoArteagaHuacchaNo ratings yet
- Converting Static To Equivalent Earthquake MethodDocument12 pagesConverting Static To Equivalent Earthquake MethodV.m. RajanNo ratings yet
- Potprocedureinstructions: (Swl-Amplus Project)Document18 pagesPotprocedureinstructions: (Swl-Amplus Project)Priyanka GuleriaNo ratings yet
- Verification of A Gravity Wall: AssignmentDocument11 pagesVerification of A Gravity Wall: AssignmentJeronimo FatimaNo ratings yet