Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes MoreOnRedox
Notes MoreOnRedox
Uploaded by
Amy WuCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes MoreOnRedox
Notes MoreOnRedox
Uploaded by
Amy WuCopyright:
Available Formats
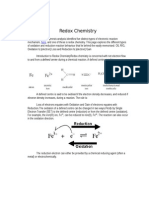
More on Redox: Lets look at some oxidation-reduction reactions 2 H2 + O2 2H2O In the above reaction hydrogen gained an oxygen atom,
m, therefore it as oxidi!ed" Oxygen lost and oxygen atom and gained a hydrogen atom, therefore it as reduced" Look at the oxidation state of the reactant and #roduct 2 H2$ + O2$ 2H2%+O2&otice that the oxidation state of Hydrogen changed from a neutral state to a #ositive oxidation state" It lost an electron" Oxygen changed from a neutral state to a negative oxidation state" It gained t o electrons" 'H( + 2O2 'O2 + 2H2O )ethane is oxidi!ed hen it gains an oxygen atom" Oxygen is reduced hen it gains hydrogen" Losing or gaining an oxygen atom as the first definition of redox reactions but once scientists determined that reactions ith other materials like chlorine and bromine had similar characteristics the definition of oxidation-reduction as broadened to the gain or loss of electrons" *+)+),+*- *eduction involves a gain of electron. /his is tricky. 01))2*3Oxidation%" 4ain of an oxygen atom 2" Loss of hydrogen atom 5" Loss of electrons (" Increase in oxidation state *eduction %" Loss of oxygen atom 2" 4ain of hydrogen atom 5" 4ain of electrons (" 6ecrease in oxidation state b. Oxidizing and Reducing Agents Oxidi!ing 2gent o *eactant that causes oxidation of another com#ound" o *eactant that is reduced" o *eactant that gains electrons o Oxygen is an oxidi!ing agent *educing 2gent o *eactant that causes reduction of another com#ound o *eactant that is oxidi!ed o *eactant that loses electrons o Hydrogen is a reducing agent
You might also like
- Chemical Bond Valence: Df8f7rf6f56d5dDocument91 pagesChemical Bond Valence: Df8f7rf6f56d5dfitradikojerdsswNo ratings yet
- REDOXDocument3 pagesREDOXJeianne Decerie MiguelNo ratings yet
- OxidationDocument5 pagesOxidationKudzanai MuchatoraNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions Grade 11Document69 pagesRedox Reactions Grade 11RahulNo ratings yet
- What Are Redox Reactions?: Chemical ReactionDocument8 pagesWhat Are Redox Reactions?: Chemical ReactionReal RuchitNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Handout 12 REF #: 012: Reduction and OxidationDocument5 pagesChemistry Handout 12 REF #: 012: Reduction and OxidationNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 19.1. Definition of Oxidation State For Carbon - Organic Chemistry IIDocument9 pages19.1. Definition of Oxidation State For Carbon - Organic Chemistry IIMirza Bilal MughalNo ratings yet
- Activity No 3 Procedure - Types of REDOX Reaction (Edit 2)Document5 pagesActivity No 3 Procedure - Types of REDOX Reaction (Edit 2)Claire DemayoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistryt 2 Week 5Document7 pagesGeneral Chemistryt 2 Week 5Charles David NavidadNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Reaction Mechanism: Prepared By: Ms - Sumina IbrahimDocument17 pagesInorganic Reaction Mechanism: Prepared By: Ms - Sumina IbrahimTuba AhmedNo ratings yet
- Redox MCQ Sheet For Jee MainDocument10 pagesRedox MCQ Sheet For Jee MainAbhay VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- (Week 5) - Module 5-Gen - Chem. 2Document14 pages(Week 5) - Module 5-Gen - Chem. 2Diana Joy Ancheta CldheiNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions: By: Fatimah Solihah Class: XI IPA 2 Sma Negeri 2 DepokDocument12 pagesRedox Reactions: By: Fatimah Solihah Class: XI IPA 2 Sma Negeri 2 Depokfatsol_No ratings yet
- Oxidizing and Reducing AgentDocument9 pagesOxidizing and Reducing Agentabuzar khalidNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument4 pagesRedox Reactionsmahika gaurNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XI CH 7 Chemistry Notes by AkDocument7 pagesHsslive XI CH 7 Chemistry Notes by AkappugmenonNo ratings yet
- Oxidation & Reduction: Redox ReactionsDocument5 pagesOxidation & Reduction: Redox ReactionsVenusCrazy 550No ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1679932480278 7046147521763878353Document13 pagesOrca Share Media1679932480278 7046147521763878353Endelyn Salva SajorgaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reduction Reactions PacketsDocument9 pagesOxidation Reduction Reactions Packetsrachana rupereeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsDocument43 pagesChapter 20 Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsTegar MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Expt 2 Oxidation Reduction ReactionsDocument32 pagesExpt 2 Oxidation Reduction Reactionstwinkledreampoppies100% (2)
- RedoksDocument33 pagesRedokssanty_vanftowsNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Part 1Document10 pagesElectrochemistry Part 1Shofwa AnnisaaNo ratings yet
- Schneider - Chillers RangeDocument10 pagesSchneider - Chillers RangeerreagaaNo ratings yet
- MG + H So Mgso + H: Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel CellsDocument1 pageMG + H So Mgso + H: Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel CellsDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- REDOX Reaction: CombustionDocument13 pagesREDOX Reaction: Combustionanwar9602020No ratings yet
- ESM Inorganic Chemistry Group 5 - Oxidation and ReductionDocument29 pagesESM Inorganic Chemistry Group 5 - Oxidation and ReductionNurzamzam yuniarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 8.ABakshDocument10 pagesChemistry Chapter 8.ABakshNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument80 pagesRedox ReactionsShashwatNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 8. REDOX REACTIONSDocument6 pagesHsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 8. REDOX REACTIONSKrishnendu NairNo ratings yet
- Redox TitrationDocument24 pagesRedox TitrationNamrata patelNo ratings yet
- Redox Processes. Eh-pH RelationshipsDocument13 pagesRedox Processes. Eh-pH RelationshipsMozakkir AzadNo ratings yet
- MyDocument2 pagesMyShourya PratapNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa FauziahDocument28 pagesExplanation Text: By: Dwiyanti Octaviani Farrah Nabila F Malik Farhan Nazhara Ardhan Roikhan Azhari Syifa Fauziahsyifa fauziahNo ratings yet
- Oxidizing and Reducing AgentDocument3 pagesOxidizing and Reducing Agentmaryjoy cacaldoNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction EXTRA NOTE-1Document21 pagesOxidation and Reduction EXTRA NOTE-1sdrps8f95mNo ratings yet
- Redox PDFDocument7 pagesRedox PDFShaikh IradNo ratings yet
- OXIDATIONDocument8 pagesOXIDATIONAtif RanaNo ratings yet
- Army Public School Gopalpur: Redox ReactionDocument6 pagesArmy Public School Gopalpur: Redox ReactionAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Oxidizing and Reducing AgentsDocument2 pagesOxidizing and Reducing AgentsKenneth D. LigutomNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions - Lecture NotesDocument39 pagesRedox Reactions - Lecture NotespokeyballNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument2 pagesRedox Reactionschong56No ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument5 pagesRedox ReactionsAthulRKrishnanNo ratings yet
- H2 Chemistry (9729) Lecture Notes 2 Redox Reactions: Assessment ObjectivesDocument22 pagesH2 Chemistry (9729) Lecture Notes 2 Redox Reactions: Assessment ObjectivesArvin LiangdyNo ratings yet
- Oxidizing and Reducing AgentsDocument3 pagesOxidizing and Reducing Agentsvrindaa28No ratings yet
- Lidza - OxidationDocument3 pagesLidza - OxidationKudzanai MuchatoraNo ratings yet
- Oxidation-Reduction (Thory Solved Ex.) Module-1Document12 pagesOxidation-Reduction (Thory Solved Ex.) Module-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument41 pagesElectrochemistry Notesthomaspodo76No ratings yet
- Class XI Redox Reactions NotesDocument5 pagesClass XI Redox Reactions NoteseasaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and EquationDocument15 pagesChemical Reaction and Equationsanjayjoshi.jnvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Electron Transfer Reactions and Electrochem-IstryDocument31 pagesChapter 11 - Electron Transfer Reactions and Electrochem-IstryDeepraj VermaNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet in General Biology Week 10 Activity 1: Dig Out! ADocument4 pagesAnswer Sheet in General Biology Week 10 Activity 1: Dig Out! AMark Joedel MendezNo ratings yet
- Redox Titration KDBDocument45 pagesRedox Titration KDBKiranNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Oxidation and ReductionDocument2 pagesDefinitions of Oxidation and ReductionPunkajGuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CH 14 and 15Document14 pagesChemistry CH 14 and 15Bhavna RathodNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reduction ReactionDocument9 pagesOxidation Reduction ReactionJaxz DeepNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and ReductionDocument4 pagesOxidation and ReductionToniann JeffersonNo ratings yet
- Contents:: Oxidation and Reduction Oxidizing and Reducing Agent Process of OxidationDocument12 pagesContents:: Oxidation and Reduction Oxidizing and Reducing Agent Process of OxidationMUHAMMAD NABEEL ARIFNo ratings yet
- Advance Chem Q4module1.Oxidation-Reduction - ReactionDocument13 pagesAdvance Chem Q4module1.Oxidation-Reduction - ReactionAmelita TupazNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Hybridization TarakkyDocument36 pagesHybridization TarakkyKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Writing Ionic FormulaeDocument6 pagesWriting Ionic FormulaeKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- U04 Notes Part4 Intermolecular ForcesDocument66 pagesU04 Notes Part4 Intermolecular ForcesKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- U05 Notes Part4 Entropy SpontaneityDocument47 pagesU05 Notes Part4 Entropy SpontaneityKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- 9701 m17 QP 12Document16 pages9701 m17 QP 12Khondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Drying Agent and Dehydrating AgentDocument1 pageDrying Agent and Dehydrating AgentKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Naming WorksheetsDocument9 pagesNaming WorksheetsKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Q MsmplusDocument1 pageQ MsmplusKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Answer All The Questions in This Section in The Spaces Provided. The Total Mark For This Section Is 45Document20 pagesAnswer All The Questions in This Section in The Spaces Provided. The Total Mark For This Section Is 45Khondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Kinetic Theory and DiffusionDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Kinetic Theory and DiffusionKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Naming WorksheetsDocument9 pagesNaming WorksheetsKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- H-1 NMR: Low Resolution: Chemical ShiftsDocument1 pageH-1 NMR: Low Resolution: Chemical ShiftsKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Chemguide - Answers: Mass Spectra: The M+ LineDocument1 pageChemguide - Answers: Mass Spectra: The M+ LineKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- The Mass Spectrometer: Kms TarakkyDocument2 pagesThe Mass Spectrometer: Kms TarakkyKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- H-1 NMR: Introduction: Kms TarakkyDocument2 pagesH-1 NMR: Introduction: Kms TarakkyKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Q NmrH1highresDocument5 pagesQ NmrH1highresKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectra of Elements: Kms TarakkyDocument1 pageMass Spectra of Elements: Kms TarakkyKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Fragmentation Patterns: Kms TarakkyDocument2 pagesFragmentation Patterns: Kms TarakkyKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Finding Orders of Reaction Experimentally: Chemguide - AnswersDocument2 pagesFinding Orders of Reaction Experimentally: Chemguide - AnswersKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Chemguide - Answers: H-1 NMR: Low ResolutionDocument2 pagesChemguide - Answers: H-1 NMR: Low ResolutionKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Chemguide - Answers: H-1 NMR: IntroductionDocument2 pagesChemguide - Answers: H-1 NMR: IntroductionKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Chemguide - Answers: H-1 NMR: High ResolutionDocument2 pagesChemguide - Answers: H-1 NMR: High ResolutionKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Chemguide - Answers: Mass Spectra of ElementsDocument1 pageChemguide - Answers: Mass Spectra of ElementsKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Chemguide - Answers: The Mass SpectrometerDocument1 pageChemguide - Answers: The Mass SpectrometerKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Test For GR 9Document3 pagesTest For GR 9Khondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Studies: History and Culture of BangladeshDocument5 pagesBangladesh Studies: History and Culture of BangladeshKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Chemguide - Answers: Fragmentation PatternsDocument2 pagesChemguide - Answers: Fragmentation PatternsKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet