Professional Documents
Culture Documents
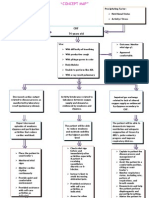
Impaired Tissue Perfusion
Uploaded by
Lyka Mae Imbat - PacnisCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Impaired Tissue Perfusion
Uploaded by
Lyka Mae Imbat - PacnisCopyright:
Available Formats
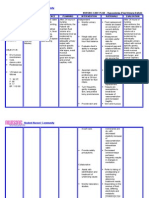
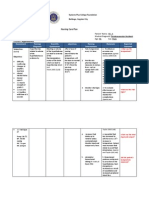
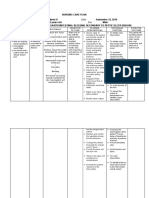
Nursing Problem: Impaired Tissue Perfusion Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired tissue perfusion related to decrease hemoglobin concentration in the
blood as manifested by low RBC count of 3.82, low hemoglobin count of 107, decrease paO2 level of 72.2, cyanosis and coolness of distal extremities, capillary refill of 4 seconds, dyspnea and restlessness. Nursing Goal: After 4 hours of rendering series of nursing interventions, the client will be able to demonstrate increased perfusion as will be manifested by normal RBC and hemoglobin count, normal paO2 level, normal skin color and normal temperature of distal extremities, capillary refill of 2 seconds, absence of dyspnea and absence of restlessness Nursing Interventions: Nursing Intervention/Responsibility
Rationale
Independent 1. Determine vital signs/hemodynamic Provide baseline data for comparison to follow parameters including cognitive status trends and evaluate response to interventions 2. Keep client semi Fowlers position and To decrease oxygen consumption and raise legs 20-30 degrees promotes lung expansion 3. Provide a quiet environment To promote adequate rest because stimuli and stress stimulate catecholamines and increases oxygen consumption 4. Provide psychological support by Honesty can be reassuring when so much maintaining a calm attitude, but admit activity and worry are apparent concerns if questioned 5. Provide adequate rest and positioning To achieve maximum comfort 6. Encourage relaxation techniques To reduce anxiety 7. Elevate legs when in sitting position To enhance venous return 8. Advise to move slowly, dangling legs To prevent orthostatic hypotension before standing 9. Elevate edematous legs and avoid To enhance venous return and restrictive restrictive clothing clothing worsen edema 10. Give information about positive signs or To provide emotional support and improvement encouragement 11. Monitor for changes in sensorium May indicate poor cerebral perfusion and deterioration so it must be addressed immediately 12. Instruct to perform deep breathing Improves breathing and oxygen intake exercises 13. Provide frequent small meals Reduces pressure on diaphragm and enhances chest expansion Dependent 14. Administer high flow oxygen To increase oxygen available for cardiac function and tissue perfusion 15. Administer inotropics as prescribed Increases cardiac output by increasing cardiac contractility
16. Administer diuretics as prescribed 17. Administer stool softeners if necessary as prescribed 18. Provide law salt food
To decrease fluid in the vascular compartment thus decreasing the workload of the heart To limit valsalva effect To decrease salt concentration in the blood that attracts water and increases fluid in the vascular compartment
Nursing Goal: After 4 hours of rendering series of nursing interventions, the client was able to demonstrate increased perfusion as manifested by normal RBC and hemoglobin count, normal paO2 level, normal skin color and normal temperature of distal extremities, capillary refill of 2 seconds, absence of dyspnea and absence of restlessness.
You might also like
- Housestaff Manual 2023-2024 - MeadeDocument267 pagesHousestaff Manual 2023-2024 - MeadeMelchor Alcántara Barrera100% (2)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Science Quiz for Elementary StudentsDocument26 pagesScience Quiz for Elementary StudentsCatherine Joy Dela Cruz92% (13)
- Electric Alex 519171918 GernDocument950 pagesElectric Alex 519171918 GernShyamSoniNo ratings yet
- Garlic: Blood Pressure Lowering HerbsDocument4 pagesGarlic: Blood Pressure Lowering HerbsJane TuazonNo ratings yet
- ACCUVIX XG Reference Manual E PDFDocument274 pagesACCUVIX XG Reference Manual E PDFMonica FajardoNo ratings yet
- Bulacan State University: College of NursingDocument29 pagesBulacan State University: College of NursingJohn Philip M. Lacas RN100% (3)
- CiticholineDocument1 pageCiticholineLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- CiticholineDocument1 pageCiticholineLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument34 pagesCase StudyBSNNursing101No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Guest SpeakerDocument1 pageIntroduction To The Guest SpeakerLyka Mae Imbat - Pacnis92% (12)
- Introduction To The Guest SpeakerDocument1 pageIntroduction To The Guest SpeakerLyka Mae Imbat - Pacnis92% (12)
- Introduction To The Guest SpeakerDocument1 pageIntroduction To The Guest SpeakerLyka Mae Imbat - Pacnis92% (12)
- ABCDE Emergency Scenarios - OSCE RevisionDocument10 pagesABCDE Emergency Scenarios - OSCE RevisionJesús AmadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing care for viral hepatitis patientDocument2 pagesNursing care for viral hepatitis patientLyka Mae Imbat - Pacnis90% (10)
- Answer KeyDocument24 pagesAnswer KeyLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Fistula NCPDocument1 pageFistula NCPHasna LisnaNo ratings yet
- Nurse InterviewDocument1 pageNurse InterviewTiarnida NababanNo ratings yet
- MRCP Notes 2006Document117 pagesMRCP Notes 2006Walaa Ismail HidirbiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plan FinalErickson OcialNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputAdnan Khan100% (1)
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- Case CHFDocument10 pagesCase CHFAgnes Erlita Distriani Patade50% (2)
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thDocument2 pagesNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Emj Cases : Questions For Case 1Document8 pagesEmj Cases : Questions For Case 1Azmyza Azmy100% (1)
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument6 pagesDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarNo ratings yet
- Concept Map - Abby !Document2 pagesConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- NCP PlanningDecreased in Cardiac Output Related To Low Hemoglobin and Hematocrit CountDocument6 pagesNCP PlanningDecreased in Cardiac Output Related To Low Hemoglobin and Hematocrit CountMabelle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing CareDocument6 pagesIncomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing CareTherese MargaretNo ratings yet
- TAHBSO ReportDocument4 pagesTAHBSO ReportsachiiMeNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument2 pagesNCP PainApril_Ivy_Raga_3835No ratings yet
- NCP On DyspneaDocument5 pagesNCP On DyspneaDizzy BualanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.Document6 pagesIneffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.SAROL, RYAN CHRISTIAN B.No ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LDocument2 pagesSt. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LAirme Raz AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Case Study RespiDocument3 pagesCase Study RespiMark Jheran AlvarezNo ratings yet
- NCP CKDDocument3 pagesNCP CKDRiel TumandaNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemia Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypovolemia Nursing Care PlanLyn Reyes100% (1)
- Nursing Care of Uremic SyndromeDocument11 pagesNursing Care of Uremic Syndromeyoedha_banditozz50% (2)
- Subjective: "Sumikip Ang Dibdib Ko at Hindi Ako Makahinga NG Maayos" As IndependentDocument2 pagesSubjective: "Sumikip Ang Dibdib Ko at Hindi Ako Makahinga NG Maayos" As IndependentCorinneNo ratings yet
- NCP AgnDocument2 pagesNCP Agnj3nann3No ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac Output FinalDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output FinalSandraDeeNo ratings yet
- Example of Drug StudyDocument2 pagesExample of Drug Studydonna mae junioNo ratings yet
- NCP CvaDocument4 pagesNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitYesha Mae MartinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HF FinalDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan HF FinalCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDocument5 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDavid CalaloNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsDocument4 pagesAngiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsPutri Mulia HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Nursing of The Childbearing FamilyDocument3 pagesNursing of The Childbearing Familyroby sorianoNo ratings yet
- Case 1 - Pneumonia (Final)Document4 pagesCase 1 - Pneumonia (Final)Joegie ArioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudydjanindNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPEduard C. TaganapNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaNo ratings yet
- Addison's DiseaseDocument14 pagesAddison's Diseasedivya4nirmalaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety R:T Death ThreatDocument8 pagesAnxiety R:T Death ThreatAlfredo BaulaNo ratings yet
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureLeng Royo BrionesNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument3 pagesCardiogenic Shockmerin sunilNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPRose AnnNo ratings yet
- Manage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesManage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusNo ratings yet
- NCP Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid Volume DeficitNecheal BaayNo ratings yet
- Retinopathy of PrematurityDocument15 pagesRetinopathy of Prematuritymarissa ulkhairNo ratings yet
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 pagesNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- CHF Concept MapDocument4 pagesCHF Concept MapLisaSanders99No ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument26 pagesQuestionsLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced NutritionDocument1 pageImbalanced NutritionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Unang YakapDocument1 pageUnang YakapLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageImpaired Gas ExchangeLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Bibliography Books: .HTML Accessed On September 3, 2012Document3 pagesBibliography Books: .HTML Accessed On September 3, 2012Lyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Chronic PainDocument1 pageChronic PainLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- SimvastatinDocument1 pageSimvastatinLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Zantac Generic Name: Ranitidine Dosage, Route, Frequency: 50 MG IV Every 8 Hours ClassificationDocument1 pageBrand Name: Zantac Generic Name: Ranitidine Dosage, Route, Frequency: 50 MG IV Every 8 Hours ClassificationLyka Mae Imbat - Pacnis100% (1)
- Parent and Child NSGDocument1 pageParent and Child NSGLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Going DeeperDocument2 pagesGoing DeeperLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Parent and Child NSGDocument1 pageParent and Child NSGLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Utilization Focused TheoryDocument1 pageUtilization Focused TheoryLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- The Liberal Medical DilemmaDocument2 pagesThe Liberal Medical DilemmaLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Risk FactorsDocument11 pagesRisk FactorsLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- HNPDocument7 pagesHNPLyka Mae Imbat - Pacnis100% (1)
- (Legprof) CPR - Memory JoggerDocument1 page(Legprof) CPR - Memory JoggerLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Drawing The LineDocument3 pagesDrawing The LineLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument2 pagesHypertensionRodel Yacas0% (1)
- LO's Tom W2Document3 pagesLO's Tom W2tomvandantzigNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for PreeclampsiaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for PreeclampsiaTsu Wei Chua0% (1)
- Kasus Acute Alcohol Poisoning ForensikDocument8 pagesKasus Acute Alcohol Poisoning ForensikSheila Sesary JNo ratings yet
- Situs Inversus Totalis in A 72-Year-Old Man WestAfrJRadiolDocument4 pagesSitus Inversus Totalis in A 72-Year-Old Man WestAfrJRadiolAnonymous 9QxPDpNo ratings yet
- Uwrt 1103 - Family Tree EssayDocument6 pagesUwrt 1103 - Family Tree Essayapi-301005929No ratings yet
- The Importance of Badminton Sports in Forming A Healthy LifestyleDocument8 pagesThe Importance of Badminton Sports in Forming A Healthy LifestyleAcademic JournalNo ratings yet
- Circulation 2006 Boyle 339 52 PDFDocument21 pagesCirculation 2006 Boyle 339 52 PDFSherlocknovNo ratings yet
- Nr. Crt. CNP Lipide COL LDL HDL TG Mediu (R/U) Imagist Ica: Arges 05/18/2021 Pg. 1/10Document10 pagesNr. Crt. CNP Lipide COL LDL HDL TG Mediu (R/U) Imagist Ica: Arges 05/18/2021 Pg. 1/10marinescu danNo ratings yet
- Worry more, live longer: How stress may benefit your healthDocument7 pagesWorry more, live longer: How stress may benefit your healthdiogofffNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Instruction ManualDocument19 pagesInstruction Manual Instruction ManualIshmael WoolooNo ratings yet
- 5 Cardiac Cycle & Heart SoundsDocument32 pages5 Cardiac Cycle & Heart SoundsDisha SuvarnaNo ratings yet
- Arritmias Guia EscDocument36 pagesArritmias Guia EscKenny CantonNo ratings yet
- Sgarbossa'S Criteria 1: Running HeadDocument5 pagesSgarbossa'S Criteria 1: Running HeadDavid RobertsonNo ratings yet
- 6 1 1 Response ChartDocument2 pages6 1 1 Response Chartapi-25585932750% (2)
- Human Body WebQuestDocument6 pagesHuman Body WebQuestjennyferchoNo ratings yet
- Cvs Mbbs PDFDocument57 pagesCvs Mbbs PDFAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Original PDF Pathophysiology of Heart Disease A Collaborative 6th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesOriginal PDF Pathophysiology of Heart Disease A Collaborative 6th Edition PDFwilliams.allen717100% (37)
- Edan Im8 Specs SheetDocument15 pagesEdan Im8 Specs SheetGoutham RevuruNo ratings yet
- TCI Regiment - Candidate Medical FormDocument2 pagesTCI Regiment - Candidate Medical FormRichard Inoa JimenezNo ratings yet
- HDFC Life Critical Illness Plus RiderDocument8 pagesHDFC Life Critical Illness Plus RiderranbirrathiNo ratings yet
- Heart Sounds GuideDocument2 pagesHeart Sounds GuideShmuel BarshalomNo ratings yet
- Compact ECG Arrhythmia SimulatorDocument2 pagesCompact ECG Arrhythmia SimulatorismailshajjiNo ratings yet