Professional Documents
Culture Documents
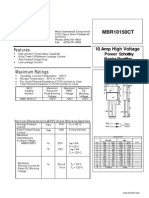
MBR20150CT
Uploaded by
josetantonioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MBR20150CT
Uploaded by
josetantonioCopyright:
Available Formats
w w w .mc c semi .
c om
MBR20150CT
20 Amp High Voltage
Features
High Junction Temperature Capability
Good Trade Off Between Leakage Cur-
rent And Forward Volage Drop
Low Leakage Current
MCC
Catalog
Number
Maximum
Recurrent
Peak Reverse
Voltage
Maximum
RMS
Voltage
Maximum
DC
Blocking
Voltage
MBR 20150 CT 150V 105V 150 V
Electrical Characteristics @ 25C Unless Otherwise Specified
Average Forward
Current
I
F(AV)
20 A T
C
= 155C
Peak Forward Surge
Current
I
FSM
180A 8.3ms, half
Maximum
Instantaneous
Forward Voltage
MBR20150CT
V
F
.92 V
M C C
*Pulse Test: Pulse Width380sec, Duty Cycle 2%
I
FM
= 10A
TJ = 25C
INCHES MM
DlM MlN MAX MlN MAX NOTE
A .600 .620 15.25 15.75
B .393 .409 10.00 10.40
N 0.102t y p. 2.6t yp .
PIN 1
PIN 3
PIN 2
CASE
A
B
C
K
J
I
H
G
F
E
D
N
M
L
H
150Volts
TO-220AB
PIN
1 3
Maximum Ratings
Operating Junction Temperature : 150C
Storage Temperature: - 50C to +150C
Per d iode Thermal Resistance 2.2C/W Junction to Case
Micro Commercial Components
21201 Itasca Street Chatsworth
CA 91311
Phone: (818) 701-4933
Fax: (818) 701-4939
C .104 .116 2.65 2.95
D .244 .259 6.20 6.60
E .356 .361 9.05 9.15
F .137 .154 3.50 3.93
G .511 .551 13.00 14.00
H .094 .106 2.40 2.70
I .024 .034 0.61 0.88
J .019 .027 0.49 0.70
K .147 .151 3.75 3.85
L .173 .181 4.40 4.60
M .048 .051 1.23 1.32
Total Thermal Resistance 1.3C/W Junction to Case
Barrier Rectifier
Power Schottky
Maximum
Reverse Current At
Rated DC Blocking
Voltage
I
R 25 A T
J
= 25C
5m A T
J
= 125C
V
F .75V I
FM
= 10A
T
J
= 125C
sine wave
w w w .mc c semi .c om
MBR20150CT
M C C
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
IF(av) (A)
PF(av)(W)
T
=tp/T tp
= 0.05
= 0.1
= 0.2
= 0.5
= 1
Fig. 1: Average forward power dissipation versus
average forward current (per diode).
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
Tamb(C)
IF(av)(A)
Rth(j-a)=Rth(j-c)
Rth(j-a)=15C/W
T
=tp/T tp
Fig. 2: Average forward current versus ambient
temperature ( = 0.5, per diode).
1E-3 1E-2 1E-1 1E+0
0
25
50
75
100
125
150
t(s)
IM(A)
Tc=50C
Tc=75C
Tc=125C IM
t
=0.5
Fig. 3: Non repetitive surge peak forward current
versus overload duration (maximum values, per
diode).
1E-3 1E-2 1E-1 1E+0
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
tp(s)
Zth(j-c)/Rth(j-c)
T
=tp/T tp
= 0.5
= 0.2
= 0.1
Single pulse
Fig. 4: Relative variation of thermal impedance
junction to case versus pulse duration (per diode).
0 25 50 75 100 125 150
1E-1
1E+0
1E+1
1E+2
1E+3
1E+4
1E+5
VR(V)
IR(A)
Tj=125C
Tj=25C
Tj=150C
Tj=100C
Tj=175C
Fig. 5: Reverse leakage current versus reverse
voltage applied (typical values, per diode).
1 2 5 10 20 50 100 200
10
100
1000
VR(V)
C(pF)
F=1MHz
Tj=25C
Fig. 6: Junction capacitance versus reverse voltage
applied (typical values, per diode).
w w w .mc c semi .c om
M C C
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8
0.1
1.0
10.0
100.0
VFM(V)
IFM(A)
Tj=25C
Tj=125C
Typical values
Tj=125C
Fig. 7: Forward voltage drop versus forward
current (maximum values, per diode).
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
S(cm)
Rth(j-a) (C/W)
Fig. 8: Thermal resistance junction to ambient versus
copper surface under tab (Epoxy printed circuit board,
copper thickness: 35m) (STPS20150CGonly).
You might also like
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNo ratings yet
- 10 Amp High Voltage Schottky Barrier Rectifier FeaturesDocument3 pages10 Amp High Voltage Schottky Barrier Rectifier FeatureszubasuNo ratings yet
- BT10 600Document5 pagesBT10 600Buho FielNo ratings yet
- STTA1206D/DI/G: Turboswitch Ultra-Fast High Voltage DiodeDocument9 pagesSTTA1206D/DI/G: Turboswitch Ultra-Fast High Voltage DiodeMarcos AndréNo ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Tyn410 PDFDocument4 pagesTyn410 PDFIvan Ignacio Perez IbarraNo ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- DVM 1500 MDocument9 pagesDVM 1500 MHanif Rathore PrinceNo ratings yet
- Marine Electrical Practice: Marine Engineering SeriesFrom EverandMarine Electrical Practice: Marine Engineering SeriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Datasheet 2Document3 pagesDatasheet 2Michelle WalkerNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- 10 Amp Schottky Rectifier Features and SpecificationsDocument3 pages10 Amp Schottky Rectifier Features and SpecificationsDanijel Dacha RisticNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsFrom EverandA Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- 1.0A Schottky Barrier Rectifier: Lead Free Finish, Rohs Compliant (Note 5)Document3 pages1.0A Schottky Barrier Rectifier: Lead Free Finish, Rohs Compliant (Note 5)Jhon TitoNo ratings yet
- PC814 Series: AC Input PhotocouplerDocument6 pagesPC814 Series: AC Input PhotocouplerAngel David Barranco VergaraNo ratings yet
- Mosfet 100 VoltDocument9 pagesMosfet 100 Voltnithinmundackal3623No ratings yet
- BYW77P/PI-200: High Efficiency Fast Recovery Rectifier DiodesDocument6 pagesBYW77P/PI-200: High Efficiency Fast Recovery Rectifier DiodesGianmarco CastilloNo ratings yet
- Ixyh50N120C3D1: V 1200V I 50A V T 43Ns 1200V XPT Igbt Genx3 W/ DiodeDocument7 pagesIxyh50N120C3D1: V 1200V I 50A V T 43Ns 1200V XPT Igbt Genx3 W/ DiodeZxdIaminxXzlovewithzxXzyouzxNo ratings yet
- T1620-600W / 700W T1630-600W: Snubberless TriacDocument5 pagesT1620-600W / 700W T1630-600W: Snubberless TriacLaercio NasctoNo ratings yet
- Fast CoPack IGBT Features INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR WITH ULTRAFAST SOFT RECOVERY DIODEDocument11 pagesFast CoPack IGBT Features INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR WITH ULTRAFAST SOFT RECOVERY DIODEismifaizulNo ratings yet
- High density photocoupler for signal transmissionDocument4 pagesHigh density photocoupler for signal transmissionOlga PlohotnichenkoNo ratings yet
- B40 C1500R PDFDocument3 pagesB40 C1500R PDFDonovan NewtonNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument9 pagesDatasheetloisaomNo ratings yet
- Part Number: Acw-107: Electrical SpecificationsDocument2 pagesPart Number: Acw-107: Electrical SpecificationsgfshhdNo ratings yet
- G 4 BC 20 KDDocument11 pagesG 4 BC 20 KDJuan Carlos Terrones NuñezNo ratings yet
- Diodo Rectificador IDM FORDDocument6 pagesDiodo Rectificador IDM FORD801400No ratings yet
- STTH12003TV: High Frequency Secondary RectifierDocument5 pagesSTTH12003TV: High Frequency Secondary RectifierBruno NascimentoNo ratings yet
- CNY64/ CNY65/ CNY66: VishayDocument11 pagesCNY64/ CNY65/ CNY66: VishayadmirgaragicNo ratings yet
- Bta16 600BDocument5 pagesBta16 600BTio_louis32No ratings yet
- 5STR 03T2040Document8 pages5STR 03T2040Vikas PatelNo ratings yet
- Low Input Current Type PhotocouplerDocument5 pagesLow Input Current Type PhotocouplerqwertyuiNo ratings yet
- Byv52 200Document7 pagesByv52 200Fady HachemNo ratings yet
- Mccsemi: 1N746 Thru 1N759Document3 pagesMccsemi: 1N746 Thru 1N759Oscar Eduardo Ramirez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Irfb4020Pbf: Digital Audio MosfetDocument8 pagesIrfb4020Pbf: Digital Audio Mosfetto_netiksNo ratings yet
- IRG4BC20KD DatasheetDocument11 pagesIRG4BC20KD DatasheetjoaomimaNo ratings yet
- Huake-Mbr30100pt C570159Document3 pagesHuake-Mbr30100pt C570159cancey2No ratings yet
- 500mW 100 Volt Silicon Epitaxial Diode Features Low Current LeakageDocument4 pages500mW 100 Volt Silicon Epitaxial Diode Features Low Current LeakageVictoria KungNo ratings yet
- Pc817 DatasheetDocument5 pagesPc817 DatasheetprincebahariNo ratings yet
- 1.0SMB SeriesDocument6 pages1.0SMB SeriesPablo AllosiaNo ratings yet
- 5 M 0965 QT UDocument12 pages5 M 0965 QT UcesarlcaNo ratings yet
- mbrx0540 Schottky Barrier DiodeDocument5 pagesmbrx0540 Schottky Barrier DiodeMochammad SofyanNo ratings yet
- Irfp2907Pbf: Typical ApplicationsDocument9 pagesIrfp2907Pbf: Typical Applicationsrajeev_kumar_1231852No ratings yet
- 2N3903, 2N3904 General Purpose Transistors: NPN SiliconDocument7 pages2N3903, 2N3904 General Purpose Transistors: NPN SiliconGabrielRuedaDiazNo ratings yet
- CNY21Document10 pagesCNY21Leo KralNo ratings yet
- SINGLE PHASE BRIDGE Power Modules Spec SheetDocument6 pagesSINGLE PHASE BRIDGE Power Modules Spec SheetNalin Lochan GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1.225V Micropower Shunt Voltage Reference: DescriptionDocument9 pages1.225V Micropower Shunt Voltage Reference: DescriptionRicardo MosqueiraNo ratings yet
- New Product: Series Surface Mount T Z Transient Voltage SuppressorDocument3 pagesNew Product: Series Surface Mount T Z Transient Voltage Suppressormichaelliu123456No ratings yet
- IRG4PH40K: Features Features Features Features FeaturesDocument9 pagesIRG4PH40K: Features Features Features Features FeaturesJesus GuillermoNo ratings yet
- 20ETS12, 20ETS12S: SeriesDocument7 pages20ETS12, 20ETS12S: SeriesZe MiguelNo ratings yet
- KA5H0380R/KA5M0380R/KA5L0380R: Features DescriptionDocument14 pagesKA5H0380R/KA5M0380R/KA5L0380R: Features DescriptionVidal VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesDatasheet PDFAnonymous uFNLwiumyyNo ratings yet
- 20ETFDocument8 pages20ETFAbi TaufiqNo ratings yet
- IGBT with ultrafast soft recovery diodeDocument16 pagesIGBT with ultrafast soft recovery diodeCarlos BraiaNo ratings yet
- Zeners 1NDocument3 pagesZeners 1NGaby FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor With Ultrafast Soft Recovery DiodeDocument16 pagesInsulated Gate Bipolar Transistor With Ultrafast Soft Recovery DiodeCarlos BraiaNo ratings yet
- BUL903ED: High Voltage Fast-Switching NPN Power TransistorDocument6 pagesBUL903ED: High Voltage Fast-Switching NPN Power TransistorproctepNo ratings yet
- P4VM8Document35 pagesP4VM8Leandro MendesNo ratings yet
- ULN2004AC-inversor LvadoraDocument8 pagesULN2004AC-inversor Lvadoraarturo_hernandez_78No ratings yet
- TDA2822Document6 pagesTDA2822josetantonioNo ratings yet
- D D D D D D: ULN2001A, ULN2002A, ULN2003A, ULN2004A Darlington Transistor ArraysDocument11 pagesD D D D D D: ULN2001A, ULN2002A, ULN2003A, ULN2004A Darlington Transistor ArraysjosetantonioNo ratings yet
- Inchange 2SD2059 TO-220F NPN Power Transistor SpecDocument4 pagesInchange 2SD2059 TO-220F NPN Power Transistor SpecjosetantonioNo ratings yet
- Daewoo sw-351 Portable CD Radio Cassette SMDocument24 pagesDaewoo sw-351 Portable CD Radio Cassette SMjosetantonioNo ratings yet
- 45CMV Series Manual en v1.1Document77 pages45CMV Series Manual en v1.1Kamran CarayevNo ratings yet
- MT 1232usermanualDocument32 pagesMT 1232usermanualjosetantonio100% (1)
- Esquema Eletrico LG K8 K350DS - Manual de Servicio PDFDocument117 pagesEsquema Eletrico LG K8 K350DS - Manual de Servicio PDFHenry Tamayo43% (7)
- Modulador Am ToshibaDocument18 pagesModulador Am ToshibaMvz RalfNo ratings yet
- Daewoo Chasis CN-001Document50 pagesDaewoo Chasis CN-001Franco MolinaNo ratings yet
- Aoc 917sw Tsum1pfrDocument57 pagesAoc 917sw Tsum1pfrelectrocolorNo ratings yet
- 775i65g User Manual: Published June 2012Document43 pages775i65g User Manual: Published June 2012josetantonioNo ratings yet
- 45CMV Series Manual en v1.1Document77 pages45CMV Series Manual en v1.1Kamran CarayevNo ratings yet
- Descargar Manual Motherboard Foxconn n15235Document3 pagesDescargar Manual Motherboard Foxconn n15235Dumitrescu Mihai0% (5)
- 775i65g R3.0 - multiQIGDocument97 pages775i65g R3.0 - multiQIGjosetantonioNo ratings yet
- Modulador Am ToshibaDocument18 pagesModulador Am ToshibaMvz RalfNo ratings yet
- w25q64fw Revd 032513Document96 pagesw25q64fw Revd 032513Aldemir Fernando BattagliaNo ratings yet
- LM324 TiDocument36 pagesLM324 TiThanga rajNo ratings yet
- BT137 600e 353851Document14 pagesBT137 600e 353851josetantonioNo ratings yet
- 1n4735a PDFDocument2 pages1n4735a PDFjosetantonioNo ratings yet
- Aoc 2219v1 Users Manual 393031 PDFDocument1 pageAoc 2219v1 Users Manual 393031 PDFjosetantonioNo ratings yet
- Chassis CY-PH2529TOP-EW-21US Manual de ServicioDocument25 pagesChassis CY-PH2529TOP-EW-21US Manual de Servicioelectronico69No ratings yet
- Daewoo DLX-32D1SMSBDocument40 pagesDaewoo DLX-32D1SMSBMarco Antonio100% (4)
- Low RDS(ON) 20V N-Channel MOSFET for Load Switch and Battery ProtectionDocument6 pagesLow RDS(ON) 20V N-Channel MOSFET for Load Switch and Battery ProtectionjosetantonioNo ratings yet
- 42px4rvh MC RF 052cDocument37 pages42px4rvh MC RF 052cJorge RoccaNo ratings yet
- Aoc 2219v1 Users Manual 393031 PDFDocument1 pageAoc 2219v1 Users Manual 393031 PDFjosetantonioNo ratings yet
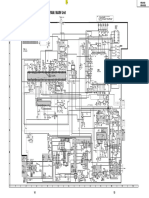
- SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMSDocument4 pagesSCHEMATIC DIAGRAMSjosetantonioNo ratings yet
- FDD5614PDocument6 pagesFDD5614PjosetantonioNo ratings yet
- Equipo Sony HCD-LX10000 PDFDocument86 pagesEquipo Sony HCD-LX10000 PDFjosetantonioNo ratings yet