Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Edit Air Density Lift Coefficient Temperature Altitude Density Altitude International Standard Atmosphere V-Speeds
Uploaded by
a2962109Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Edit Air Density Lift Coefficient Temperature Altitude Density Altitude International Standard Atmosphere V-Speeds
Uploaded by
a2962109Copyright:
Available Formats
Speed required[edit]
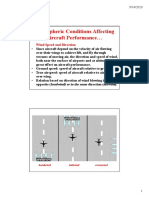
The takeoff speed required varies with air density, aircraft gross weight, lift coefficient,
and aircraft configuration (flap or slat position, as applicable) !ir density is affected by
factors such as field elevation and air te"perature This relationship between
te"perature,altitude, and air density can be e#pressed as a density altitude, or the
altitude in the $nternational Standard !t"osphere at which the air density would be
equal to the actual air density
%perations with transport category aircraft e"ploy the concept of the takeoff &'Speeds,
&(, &) and &* These speeds are deter"ined not only by the above factors affecting
takeoff perfor"ance, but also by the length and slope of the runway and any peculiar
conditions, such as obstacles off the end of the runway +elow &(, in case of critical
failures, the takeoff should be aborted, above &( the pilot continues the takeoff and
returns for landing !fter the co'pilot calls &(, he-she will call &) or .rotate,. "arking
speed at which to rotate the aircraft The &) for transport category aircraft is calculated
such as to allow the aircraft to reach the regulatory screen height at &* with one engine
failed Then, &* (the safe takeoff speed) is called This speed "ust be "aintained after an
engine failure to "eet perfor"ance targets for rate of cli"b and angle of cli"b
$n a single'engine or light twin'engine aircraft, the pilot calculates the length of runway
required to take off and clear any obstacles, to ensure sufficient runway to use for takeoff
! safety "argin can be added to provide the option to stop on the runway in case of
are/ected takeoff $n "ost such aircraft, any engine failure results in a re/ected takeoff as
a "atter of course, since even overrunning the end of the runway is preferable to lifting
off with insufficient power to "aintain flight
$f an obstacle needs to be cleared, the pilot cli"bs at the speed for "a#i"u" cli"b angle
(&#), which results in the greatest altitude gain per unit of hori0ontal distance travelled $f
no obstacle needs to be cleared, or after an obstacle is cleared, the pilot can accelerate to
the best rate of cli"b speed (&y), where the aircraft will gain the "ost altitude in the least
a"ount of ti"e 1enerally speaking, &# is a lower speed than &y, and requires a higher
pitch attitude to achieve
!ssisted takeoff[edit]
You might also like
- AP4ATCO - Factors AffectingDocument12 pagesAP4ATCO - Factors Affectingsamirsamira928No ratings yet
- Performance LandingDocument17 pagesPerformance LandingBFBGFD100% (2)
- ETOPS, Landing Distance Performance Et Al - Lecture #6Document48 pagesETOPS, Landing Distance Performance Et Al - Lecture #6BruceNo ratings yet
- Aviation DefinitionDocument22 pagesAviation DefinitionFahmi PrayogiNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Runway LengthDocument43 pagesAircraft Runway LengthLuiz AlvesNo ratings yet
- A/C Performance - GeneralDocument14 pagesA/C Performance - GeneralvivekNo ratings yet
- V-Speed Definitions and Takeoff Performance FactorsDocument2 pagesV-Speed Definitions and Takeoff Performance FactorsFaiza SaeedNo ratings yet
- 05takeoff Flight Path PerformanceDocument12 pages05takeoff Flight Path PerformanceAzlan Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Flight Planning ATP Chapter 1Document15 pagesFlight Planning ATP Chapter 1zest aviation100% (3)
- Aircraft PerformanceDocument54 pagesAircraft PerformanceManas Batra100% (1)
- PerformanceDocument140 pagesPerformanceOleacov SergiuNo ratings yet
- Learn Takeoff and Climbing ProceduresDocument6 pagesLearn Takeoff and Climbing ProceduresThar LattNo ratings yet
- Airplane Performance Courtesy BoeingDocument22 pagesAirplane Performance Courtesy Boeingr100% (1)
- 737 Performance Reference Handbook - EASA EditionFrom Everand737 Performance Reference Handbook - EASA EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- AerodynamicsDocument26 pagesAerodynamics5gk9scnnx9No ratings yet
- Lecture Note 5Document69 pagesLecture Note 5Tolga Burak UysalNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Design Module Wing Loading and Take-Off Weight CalculationDocument34 pagesAircraft Design Module Wing Loading and Take-Off Weight CalculationNavya nayakNo ratings yet
- Ce415 Lec 2 4Document61 pagesCe415 Lec 2 4Jackie ArulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Composition of Aircraft WeightDocument25 pagesLecture 2-Composition of Aircraft WeightLevent Önder0% (2)
- Take Off and LandingDocument24 pagesTake Off and LandingKhairul Hasan100% (1)
- FD RT 4 - Basic Performance HandbookDocument51 pagesFD RT 4 - Basic Performance Handbooksidsharma31No ratings yet
- Aircraft Performance Factors Affecting Runway LengthDocument14 pagesAircraft Performance Factors Affecting Runway LengthMaged SalemNo ratings yet
- PerformanceDocument60 pagesPerformanceRAPALLY ABHILASHNo ratings yet
- B737 Use of Take Off ChartsDocument11 pagesB737 Use of Take Off ChartsmohammedredhadjoudiNo ratings yet
- FAA P 8740 02 DensityAltitude (Hi Res) BrandedDocument8 pagesFAA P 8740 02 DensityAltitude (Hi Res) BrandedrayduxNo ratings yet
- Aircraft DesignDocument35 pagesAircraft Designsamarthshetty283No ratings yet
- AIRFIELD: It Is An Area Where An Aircraft Can Land and Take Off, Which May or M A y Not Be Equipped With Any Navigational Aids or MarkingsDocument8 pagesAIRFIELD: It Is An Area Where An Aircraft Can Land and Take Off, Which May or M A y Not Be Equipped With Any Navigational Aids or MarkingsmrudulaNo ratings yet
- Takeoff ResumenDocument10 pagesTakeoff ResumenoibNo ratings yet
- Perf DES LDG GADocument2 pagesPerf DES LDG GAskynorthNo ratings yet
- Airport EngineeringDocument21 pagesAirport EngineeringSri Kanth100% (1)
- One Engine Out Missed Approaches DesignDocument3 pagesOne Engine Out Missed Approaches Designchhetribharat08No ratings yet
- Effect Temperature and AltDocument4 pagesEffect Temperature and AltFaiza SaeedNo ratings yet
- ABC SummaryDocument65 pagesABC SummaryIslam AbdelshafyNo ratings yet
- V SpeedsDocument7 pagesV SpeedsRick du PreezNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Performance IntroductionDocument75 pagesAircraft Performance IntroductionFreddie FoxxNo ratings yet
- Civil Aviation Amendment Order 2004 Performance RequirementsDocument5 pagesCivil Aviation Amendment Order 2004 Performance Requirementsgreg mNo ratings yet
- FMG3104Document20 pagesFMG3104Mohammad SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Take-Off Field LengthDocument4 pagesTake-Off Field LengthErvina Ahyudanari100% (1)
- Aircraft Weight and Balance Handbook: FAA-H-8083-1AFrom EverandAircraft Weight and Balance Handbook: FAA-H-8083-1ARating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chpter 1 Introduction To Airport EngineeringDocument30 pagesChpter 1 Introduction To Airport Engineeringmkpatel007100% (2)
- StallDocument14 pagesStallskhogtapurNo ratings yet
- Gate Flight Mechanics by VayushastraDocument36 pagesGate Flight Mechanics by Vayushastraudaykumar100% (4)
- Alar Bn8 3 DistancesDocument6 pagesAlar Bn8 3 DistancesgabitosgNo ratings yet
- Cive 461 Transportation Engineering Introduction To Planning and Design of Airport FacilitiesDocument29 pagesCive 461 Transportation Engineering Introduction To Planning and Design of Airport Facilitiessamir el-khodariNo ratings yet
- NASA Information Summaries Wind-Up TurnDocument10 pagesNASA Information Summaries Wind-Up TurnBob Andrepont100% (1)
- Ultimate Perfo-LAMHADERDocument10 pagesUltimate Perfo-LAMHADERhananeNo ratings yet
- Scheduled Performance of Multi-Engine Transport AircraftDocument30 pagesScheduled Performance of Multi-Engine Transport AircraftAyush KmaNo ratings yet
- Descent and Landing Procedures for Piston, Turboprop and Jet AircraftDocument24 pagesDescent and Landing Procedures for Piston, Turboprop and Jet AircraftVlad Bogdan100% (1)
- Airport Eng 2Document72 pagesAirport Eng 2Furqan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Runway Design: Prepared By:-Dr. Vaibhav SharmaDocument34 pagesRunway Design: Prepared By:-Dr. Vaibhav SharmajohnNo ratings yet
- Calculate Optimal Runway LengthsDocument4 pagesCalculate Optimal Runway Lengthshanoo akNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Runway LengthDocument43 pagesAircraft Runway LengthAgung TrianshariNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Characteristics: (B-Section) Instructor: SATISH SajjaDocument44 pagesAircraft Characteristics: (B-Section) Instructor: SATISH SajjaPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- FPP Cat 1Document9 pagesFPP Cat 1ay9 antarNo ratings yet
- Boeing 737-800 Flight NotesDocument3 pagesBoeing 737-800 Flight NotesAnish Shakya100% (1)
- Stall Angle Critical For Aircraft LiftDocument14 pagesStall Angle Critical For Aircraft LiftLu MengaoNo ratings yet
- Engine PerformanceDocument12 pagesEngine PerformanceJuly TadeNo ratings yet
- Phases of A FlightDocument3 pagesPhases of A FlightGani PateelNo ratings yet
- AIRCRAFT WEIGHT BALANCEDocument20 pagesAIRCRAFT WEIGHT BALANCEjesty0% (1)
- The Samora Machel and Helderberg Conspiracies and Other South African Air AccidentsFrom EverandThe Samora Machel and Helderberg Conspiracies and Other South African Air AccidentsNo ratings yet
- Christ the Redeemer atop Corcovado mountain in Rio de JaneiroDocument3 pagesChrist the Redeemer atop Corcovado mountain in Rio de Janeiroa2962109No ratings yet
- Volatile memory types like DRAM and SRAM explainedDocument3 pagesVolatile memory types like DRAM and SRAM explaineda2962109No ratings yet
- Data Storage: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument6 pagesData Storage: Jump To Navigation Jump To Searcha2962109No ratings yet
- Cd-Rom: Optical DiscsDocument14 pagesCd-Rom: Optical Discsa2962109No ratings yet
- Sega CDDocument11 pagesSega CDa2962109No ratings yet
- Corcovado Rack RailwayDocument4 pagesCorcovado Rack Railwaya2962109No ratings yet
- Rack Railway: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument13 pagesRack Railway: Jump To Navigation Jump To Searcha2962109No ratings yet
- Compact disc holds up to 700 MB of dataDocument15 pagesCompact disc holds up to 700 MB of dataa2962109No ratings yet
- New7Wonders of The WorldDocument7 pagesNew7Wonders of The Worlda2962109No ratings yet
- The Biggest Problem With Wealth InequalityDocument2 pagesThe Biggest Problem With Wealth Inequalitya2962109No ratings yet
- Rail adhesion issues caused by fallen leavesDocument7 pagesRail adhesion issues caused by fallen leavesa2962109No ratings yet
- New7Wonders of The WorldDocument7 pagesNew7Wonders of The Worlda2962109No ratings yet
- Corcovado Rack RailwayDocument4 pagesCorcovado Rack Railwaya2962109No ratings yet
- Rail adhesion issues caused by fallen leavesDocument7 pagesRail adhesion issues caused by fallen leavesa2962109No ratings yet
- Christ the Redeemer atop Corcovado mountain in Rio de JaneiroDocument3 pagesChrist the Redeemer atop Corcovado mountain in Rio de Janeiroa2962109No ratings yet
- Rack Railway: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument13 pagesRack Railway: Jump To Navigation Jump To Searcha2962109No ratings yet
- What Is A Jet Engine Hot StartDocument1 pageWhat Is A Jet Engine Hot Starta2962109No ratings yet
- Tupac ShakurDocument5 pagesTupac Shakura2962109No ratings yet
- Map ProjectionsDocument12 pagesMap Projectionsa2962109No ratings yet
- Sap ErpDocument6 pagesSap Erpa2962109No ratings yet
- Cupressus SempervirensDocument1 pageCupressus Sempervirensa2962109No ratings yet
- CartographyDocument12 pagesCartographya2962109No ratings yet
- New Taipei City - Taiwan's Largest CityDocument3 pagesNew Taipei City - Taiwan's Largest Citya2962109No ratings yet
- History: Qing DynastyDocument2 pagesHistory: Qing Dynastya2962109No ratings yet
- New Taipei City - Taiwan's Largest CityDocument3 pagesNew Taipei City - Taiwan's Largest Citya2962109No ratings yet
- The Musical MomentDocument3 pagesThe Musical Momenta2962109No ratings yet
- New Taipei City - Taiwan's Largest CityDocument3 pagesNew Taipei City - Taiwan's Largest Citya2962109No ratings yet
- Gestalt Therapy - 1Document3 pagesGestalt Therapy - 1a2962109No ratings yet
- The Terra Nova Expedition 1910-13Document1 pageThe Terra Nova Expedition 1910-13a2962109No ratings yet
- The Terra Nova Expedition 1910Document1 pageThe Terra Nova Expedition 1910a2962109No ratings yet