Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8051 Microcontroller Features and Its Applications
8051 Microcontroller Features and Its Applications
Uploaded by
Sharath Sogi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views42 pagesOriginal Title
8051microcontrollerfeatures-120903114834-phpapp02
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views42 pages8051 Microcontroller Features and Its Applications
8051 Microcontroller Features and Its Applications
Uploaded by
Sharath SogiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 42
1
8051 Microcontroller Features and
its Applications
Contents
2
Microcontrollers
Applications of microcontrollers
Microprocessor vs microcontrollers
History of 8051 microcontroller
Features of microcontroller
Block diagram and pin description of 8051
Registers
Memory mapping in 8051
Timers and counters
Serial communication
Interrupts
Applications of 8051 microcontroller
Microcontrollers
3
Microcontrollers are small computing systems on a single chip.
A microcontroller will also be referred to as an MCU.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Program memory
Random Access Memory (RAM)
EEPROM - Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory
USARTs, Timer/Counters, ADC, DAC, I/O Ports, CANs, SPIs, etc.
Examples : Motorolas 6811,Intels 8051,Zilogs Z8 and PIC 16X.
Serial
Port
CPU RAM ROM
I/O
Port
Timer
A single chip
Applications of microcontrollers
4
Cell phone
Pager
Watch
Calculator
video games
Alarm clock
Air conditioner
TV remote
Microwave oven
Washing machines
An electronic smart weight display system
Robotic system
An anti-lock braking system monitor
5
6
Applications contd
Microprocessor vs Microcontroller
7
Microprocessor
CPU is stand-alone,
RAM,
ROM, I/O, timer are
separate
designer can decide on
the
amount of ROM, RAM
and
I/O ports.
Expansive
versatility
general-purpose
Microcontroller
CPU, RAM, ROM, I/O
and
timer are all on a single
chip
fix amount of on-chip
ROM, RAM, I/O ports
Highly bit addressable
for applications in which
cost, power and space
are critical
single-purpose
History of 8051 microcontroller
8
In the year 1980 Intel corporation introduced an 8 bit
microcontroller called 8051.
It has 4K bytes of ROM,128 Bytes of RAM , a serial
port, two
16-bit Timers and 32 I/O pins.
CPU can work with 8 bit of data at a time.
Data larger than 8 bit can be broken into 8 bit pieces to
be
processed by the CPU
Important Features of 8051
9
4K bytes ROM
128 bytes RAM
Four 8-bit I/O ports
Two 8/16 bit timers
Serial port
64K external code memory space
64K data memory space
Multiple internal and external interrupt sources
Architecture of 8051 Microcontroller
10
Oscillator
and timing
4096 Bytes
Program Memory
(ROM)
128 Bytes
Data Memory
(RAM)
Two 16 Bit
Timer/Event
Counters
8051
CPU
64 K Byte Bus
Expansion
Control
Programmable
I/O
Programmable
Serial Port Full
Duplex UART
Synchronous Shifter
Internal data bus
External interrupts
subsystem interrupts
Control
Parallel ports
Address Data Bus
I/O pins
Serial Input
Serial Output
Pin Description of 8051
11
The 8051 is a 40 pin
device, but out of
these 40 pins, 32
are
used for I/O.
24 of these are dual
purpose, i.e. they
can operate as I/O
or a control line or
as part of address or
data bus.
8051 CPU Registers
12
A (8-bit Accumulator)
B (8-bit register for Mul
&Div)
PSW (8-bit Program Status
Word)
SP (8-bit Stack Pointer)
PC (16-bit Program
Counter)
DPTR (16-bit Data Pointer)
List of registers
13
List of registers contd..
14
Memory mapping in 8051
ROM memory map in 8051
family
0000H
0FFFH
0000H
1FFFH
0000H
7FFFH
8051
8752
4k
DS5000-32
8k 32k
from Atmel
Corporation
from Dallas
Semiconductor
15
RAM memory space allocation in the 8051
7FH
30H
2FH
20H
1FH
17H
10H
0FH
07H
08H
18H
00H
Register Bank 0
(Stack) Register Bank 1
Register Bank 2
Register Bank 3
Bit-Addressable RAM
Scratch pad RAM
16
Timers /Counters
17
The 8051 has 2 timers/counters:
Timer/Counter 0
Timer/Counter 1
Timer :
Used as a time delay generator.
Many microcontroller application requires the
counting of external events such as frequency,
time delay.
Registers Used in Timer/Counter
18
8051 has two 16-bit Timer registers ,Timer 0 & Timer 1.
As 8051 has 8-bit architecture , each Timer register is
treated as two 8-bit registers namely TH0, TL0, TH1,
TL1.
One 8-bit mode register -TMOD.
One 8-bit control register-TCON.
Timer
19
Set the initial value of registers
Start the timer and then the 8051 counts up.
Input from internal system clock (machine cycle)
When the registers equal to 0 and the 8051 sets a bit to
denote time out
to
LCD
P1
8051
TL0
TH0
P2
Set
Timer 0
Counter
20
Count the number of events
Show the number of events on registers
External input from T0 input pin (P3.4) for Counter 0
External input from T1 input pin (P3.5) for Counter 1
External input from Tx input pin.
We use Tx to denote T0 or T1.
T0
to
LCD
P3.4
P1
8051
a switch
TL0
TH0
TMOD Register
21
Both Timer 0 &Timer 1 use the same Mode register
TMOD.
It is an-8-bit register .
The lower 4-bits are meant for Timer 0 &the upper 4-
bits are meant for Timer 1
It is used similar to any other register of 8051 .
GATE C/T M1 M0 GATE C/T M1 M0
Timer 1 Timer 0
(MSB) (LSB)
TMod contd.
22
C/T : Timer or counter selected cleared for timer
operation (input from internal system clock).
Set for counter operation (input from Tx input pin).
M1,M0 : Used for mode selection. Because the Timers of
8051 can be set in 4-different modes.
M1 M0 Mode Operation
0 0 0 13-bit timer mode 8-bit THx + 5-bit
TLx
0 1 1 16-bit timer mode 8-bit THx + 8-bit TLx
1 0 2 8-bit auto reload THx holds a value which
is to be
reloaded
into TLx each time it overflows.
1 1 3 Split timer mode
Gate
23
Every timer has a mean of starting and stopping.
GATE=0
Internal control
The start and stop of the timer are controlled by way of
software.
GATE=1
External control
The hardware way of starting and stopping the timer by
software and an external source.
Timer/counter is enabled only while the INT pin is high and the
TR control pin is set (TR).
24
TCON Register
Timer control register TMOD is a 8-bit register which is
bit addressable and in which Upper nibble is for
timer/counter,
lower nibble is for interrupts
Tcon contd
25
TR (Timer run control bit)
TR0 for Timer/counter 0; TR1 for Timer/counter 1.
TR is set by programmer to turn timer/counter on/off.
TR=0 : off (stop)
TR=1 : on (start)
TF (timer flag, control flag)
TF0 for timer/counter 0; TF1 for timer/counter 1.
TF is like a carry. Originally, TF=0. When TH-TL roll over to 0000
from FFFFH, the TF is set to 1.
TF=0 : not reach
TF=1: reach
If we enable interrupt, TF=1 will trigger ISR.
26
8051- SERIAL COMMUNICATION
RxD and TxD pins in the 8051
27
The 8051 has two pins for transferring and receiving data
by
serial communication. These two pins are part of the
Port3(P3.0 &P3.1)
These pins are TTL compatible and hence they require a
line
driver to make them RS232 compatible
Max232 chip is one such line driver in use.
Serial communication is controlled by an 8-bit register
called
SCON register, it is a bit addressable register.
SCON (Serial control) register
28
SM0 , SM1
29
These two bits of SCON register determine the framing
of data
by specifying the number of bits per character and start
bit and stop bits.
There are 4 serial modes.
SM0 SM1
0 0 Serial Mode 0
0 1 Serial Mode 1, 8 bit data,
1 stop bit, 1 start bit
1 0 Serial Mode 2
1 1 Serial Mode 3
REN, TI, RI
30
REN (Receive Enable) also referred as SCON.4.
When it is high, it allows the 8051 to receive data on the
RxD pin. So to receive and transfer data REN must be
set to 1.
When REN=0,the receiver is disabled.
TI,RI Contd
31
TI (Transmit interrupt)
It is the D1 bit of SCON register.
When 8051 finishes the transfer of 8-bit character, it raises the TI
flag to indicate that it is ready to transfer another byte.
The TI bit is raised at the beginning of the stop bit.
RI (Receive interrupt)
It is the D0 bit of the SCON register.
When the 8051 receives data serially ,via RxD, it gets rid of the start
and stop bits and places the byte in the SBUF register.
Then it raises the RI flag bit to indicate that a byte has been
received and should be picked up before it is lost.
RI is raised halfway through the stop bit.
Interrupt Sources
32
8051 has 6 sources of interrupts
Reset
Timer 0 overflow
Timer 1 overflow
External Interrupt 0
External Interrupt 1
Serial Port events (buffer full, buffer empty, etc)
Interrupt Enable Register
33
Upon reset all Interrupts are disabled and do
not
respond to the Microcontroller
These interrupts must be enabled by software in
order for the Microcontroller to respond to them.
This is done by an 8-bit register called Interrupt
Enable Register (IE).
34
EA : Global enable/disable.
--- : Undefined.
ET2 : Enable Timer 2 interrupt.
ES : Enable Serial port interrupt.
ET1 : Enable Timer 1 interrupt.
EX1 : Enable External 1 interrupt.
ET0 : Enable Timer 0 interrupt.
EX0 : Enable External 0 interrupt.
35
If two interrupt sources interrupt at the same time ,the
interrupt with the highest PRIORITY gets serviced first.
All interrupts have a power on default priority order.
1. External interrupt 0 (INT0)
2. Timer interrupt0 (TF0)
3. External interrupt 1 (INT1)
4. Timer interrupt1 (TF1)
5. Serial communication (RI+TI)
Priority can also be set to high or low by IP reg.
Interrupt Priorities
Interrupt Priorities (IP) Register
36
IP.7: reserved
IP.6: reserved
IP.5: Timer 2 interrupt priority bit (8052 only)
IP.4: Serial port interrupt priority bit
IP.3: Timer 1 interrupt priority bit
IP.2: External interrupt 1 priority bit
IP.1: Timer 0 interrupt priority bit
IP.0: External interrupt 0 priority bit
--- PX0 PT0 PX1 PT1 PS PT2 ---
Interrupt inside an interrupt
37
--- PX0 PT0 PX1 PT1 PS PT2 ---
A high-priority interrupt can interrupt a low-priority
interrupt
All interrupt are latched internally
Low-priority interrupt wait until 8051 has finished
servicing
the high-priority interrupt
Applications of 8051 microcontroller
38
Embedded system
Industrial
Computer networking
Power input to the 8051 is very simple and straight
forward.
8051 could be used in low-power applications.
Applications contd
39
The 8051 has been in use in a wide number of
devices, mainly because it is easy to integrate into
a project or build a device around.
Energy Management:
Efficient metering systems help in controlling
energy usage in
homes and industrial applications.
These metering systems are made capable by
incorporating
microcontrollers.
Applications contd
40
Touch screens:
A high number of microcontroller providers incorporate
touch-sensing capabilities in their designs.
Portable electronics such as cell phones, media
players and gaming devices are examples of
microcontroller-based touch screens.
Automobiles:
The 8051 finds wide acceptance in providing
automobile solutions.
They are widely used in hybrid vehicles to manage
engine variants.
Functions such as cruise control and anti-brake
system have been made more efficient with the use of
microcontrollers.
Applications contd
41
Medical Devices:
Portable medical devices such as blood pressure
and glucose
monitors use microcontrollers will to display data,
thus
providing higher reliability in providing medical
results.
42
Thank you
You might also like
- Logic Pro X Plugins Cheat SheetDocument11 pagesLogic Pro X Plugins Cheat SheetHarold André Cross Saints100% (1)
- 1986 IC02b Philips Video and Associated Systems TDA1524A To TEA2000Document878 pages1986 IC02b Philips Video and Associated Systems TDA1524A To TEA2000Przemysław WójcikNo ratings yet
- Pic12c508 and Adf4113Document32 pagesPic12c508 and Adf4113Lê Đình Tiến100% (1)
- Solution of Linear Programming ProblemDocument12 pagesSolution of Linear Programming ProblemTech_MX100% (2)
- How To Draw An ER DiagramDocument96 pagesHow To Draw An ER DiagramTech_MX100% (1)
- Introduction To 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument35 pagesIntroduction To 8051 MicrocontrollerHassan Mustafa JamalNo ratings yet
- SattCon 05-OP Programmers ManualDocument4 pagesSattCon 05-OP Programmers ManualGilbert H. Quiroga G.0% (1)
- ALL 02 ManualDocument47 pagesALL 02 ManualmcabreratNo ratings yet
- LinNWT Doc enDocument60 pagesLinNWT Doc enGuilhermeDuarteHissNo ratings yet
- SBL-1 PDFDocument2 pagesSBL-1 PDFfox7878No ratings yet
- Direct Filter Synthesis Rhea PreviewDocument25 pagesDirect Filter Synthesis Rhea Previewoprakash9291No ratings yet
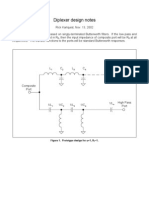
- Diplexer Design Notes: L C L C L Low Pass PortDocument3 pagesDiplexer Design Notes: L C L C L Low Pass Portmathur_mayurNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Motorola Dp3400 enDocument85 pagesService Manual Motorola Dp3400 endottor1No ratings yet
- Simple GAL ProgrammerDocument7 pagesSimple GAL ProgrammerjaimefpolisNo ratings yet
- Motorola R-2001d SMDocument465 pagesMotorola R-2001d SMFernando MartinsNo ratings yet
- PC AT Technical Reference Mar84Document644 pagesPC AT Technical Reference Mar84kgrhoadsNo ratings yet
- TC-508 Service Manual VHF-UHFDocument102 pagesTC-508 Service Manual VHF-UHFsonny_reyes_13100% (1)
- PM2502 MultimeterDocument8 pagesPM2502 MultimeterJaap S.No ratings yet
- 8051 Microcontroller FAQDocument160 pages8051 Microcontroller FAQkranthi633No ratings yet
- Motorola Phase Locked Loop Systems DatabookDocument180 pagesMotorola Phase Locked Loop Systems DatabooktarpinoNo ratings yet
- 9537 Chassis Anubis SDD Manual de ServicioDocument55 pages9537 Chassis Anubis SDD Manual de ServicioTecniksNo ratings yet
- 06119397Document6 pages06119397bpd21No ratings yet
- Circuit TodayDocument30 pagesCircuit TodayBrian GiriNo ratings yet
- Zxevo User Manual Revc EngDocument19 pagesZxevo User Manual Revc EngConrad RussoNo ratings yet
- 8051 PPT For MSCDocument138 pages8051 PPT For MSCvikash sharmaNo ratings yet
- PDF Cmos Analog and Mixed Signal Circuit Design Practices and Innovations Arjuna Marzuki Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Cmos Analog and Mixed Signal Circuit Design Practices and Innovations Arjuna Marzuki Ebook Full Chaptersandra.curtis404100% (3)
- 1988 Motorola CMOS NMOS Special Functions PDFDocument386 pages1988 Motorola CMOS NMOS Special Functions PDFFLAVIONo ratings yet
- STM32 RS-485Document12 pagesSTM32 RS-485mail87523No ratings yet
- GAL16V8: Features Functional Block DiagramDocument23 pagesGAL16V8: Features Functional Block DiagramWilmar Diaz RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 1990 Fujitsu Linear Products Data Book PDFDocument870 pages1990 Fujitsu Linear Products Data Book PDFvitoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No:: Date: AimDocument5 pagesExperiment No:: Date: AimSRI HARSHA ACHINo ratings yet
- Temperature Sensing/Monitoring Using Lm35 & Atmega8Document6 pagesTemperature Sensing/Monitoring Using Lm35 & Atmega8Suket75% (4)
- 3 Channel IR Remote ControlDocument47 pages3 Channel IR Remote ControlMehmet GüçyetmezNo ratings yet
- 0 - MPMC Lab Manual A.Y. 2020-21 R-18Document53 pages0 - MPMC Lab Manual A.Y. 2020-21 R-18Karthik BoggarapuNo ratings yet
- Important Instructions To Examiners:: (Autonomous)Document29 pagesImportant Instructions To Examiners:: (Autonomous)Rohit Shinde RSNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsDocument2 pagesMicrocontroller and Embedded SystemsIndranilNo ratings yet
- 8051 SerialcommunicationDocument49 pages8051 SerialcommunicationSanthanamari GNo ratings yet
- Channel Coding ExamDocument9 pagesChannel Coding ExamMuhammad Tariq SadiqNo ratings yet
- Dac Interface To 8051 PDFDocument4 pagesDac Interface To 8051 PDFRAVI100% (1)
- DSP Processor FundamentalsDocument58 pagesDSP Processor FundamentalsSayee KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Interfacing Programs For 8085Document37 pagesInterfacing Programs For 8085archankumarturagaNo ratings yet
- A GAL Programmer For LINUX PCsDocument14 pagesA GAL Programmer For LINUX PCsluciednaNo ratings yet
- HCS12 Timer System PDFDocument15 pagesHCS12 Timer System PDFAbhinav KaranNo ratings yet
- Ripple Carry and Carry Lookahead Adders: 1 ObjectivesDocument8 pagesRipple Carry and Carry Lookahead Adders: 1 ObjectivesYasser RaoufNo ratings yet
- EXPT 04 - 4-PSK Modulation & DemodulationDocument6 pagesEXPT 04 - 4-PSK Modulation & Demodulationanika tabassumNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Anna University Important Questions 2 Marks and 16 Marks Questions - Repeated Questions in Anna University Question Papers From All 5 Units ...Document4 pagesMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers Anna University Important Questions 2 Marks and 16 Marks Questions - Repeated Questions in Anna University Question Papers From All 5 Units ...PrettyNo ratings yet
- 17ec563 M01Document28 pages17ec563 M01mohamed036100% (1)
- MPMC Question BankDocument10 pagesMPMC Question BankVasanthNo ratings yet
- 8255Document39 pages8255Mohit VermaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Actel FPGA Architecture PDFDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Actel FPGA Architecture PDFsaipranathiNo ratings yet
- Keyboard I 8051Document3 pagesKeyboard I 8051sachinshymNo ratings yet
- 8085 Complete ArchitectureDocument39 pages8085 Complete ArchitectureSana KhanNo ratings yet
- Microcontrollers and Embedded SystemsDocument35 pagesMicrocontrollers and Embedded SystemsTarek BarhoumNo ratings yet
- Wan BasicsDocument24 pagesWan BasicsAhmed KhazemNo ratings yet
- The 8051 MicrocontollerDocument212 pagesThe 8051 Microcontollermahmudou100% (1)
- 1977 Fairchild CMOS Data Book PDFDocument418 pages1977 Fairchild CMOS Data Book PDFLu VirNo ratings yet
- Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Nonlinear Systems: An IntroductionFrom EverandActive Disturbance Rejection Control for Nonlinear Systems: An IntroductionNo ratings yet
- MPMC Unit-5Document91 pagesMPMC Unit-5Rasool Nayab100% (1)
- MicroprocessorsDocument38 pagesMicroprocessorssurbhiNo ratings yet
- The 8051 Microcontroller: Lets EXPLORE Inside 8051 !!Document45 pagesThe 8051 Microcontroller: Lets EXPLORE Inside 8051 !!ZuricHuntNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme (I) A) - Which Are The Two Basic Registers of The Timer? Explain TMOD Register Bitwise. (6marks)Document6 pagesAnswer Scheme (I) A) - Which Are The Two Basic Registers of The Timer? Explain TMOD Register Bitwise. (6marks)vishwanath81No ratings yet
- TSR (Terminate and Stay Resident)Document29 pagesTSR (Terminate and Stay Resident)Tech_MX100% (3)
- UNIX Memory ManagementDocument35 pagesUNIX Memory ManagementTech_MX100% (1)
- Primal Dual LPPDocument26 pagesPrimal Dual LPPTech_MXNo ratings yet
- Symbol Table Design (Compiler Construction)Document33 pagesSymbol Table Design (Compiler Construction)Tech_MX100% (1)
- Windows Memory ManagementDocument31 pagesWindows Memory ManagementTech_MXNo ratings yet
- Mobile DBMSDocument34 pagesMobile DBMSTech_MX100% (1)
- Mutable and Immutable Classes in JAVADocument14 pagesMutable and Immutable Classes in JAVATech_MXNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Principles in System Software DesignDocument36 pagesSoftware Engineering Principles in System Software DesignTech_MXNo ratings yet
- Input Output Processing (8086)Document31 pagesInput Output Processing (8086)Tech_MX50% (4)
- Inner Classes & MultiThreading in JAVADocument71 pagesInner Classes & MultiThreading in JAVATech_MXNo ratings yet
- Solaris Memory ManagementDocument35 pagesSolaris Memory ManagementTech_MXNo ratings yet
- Investment Problem (Optimization Technique)Document8 pagesInvestment Problem (Optimization Technique)Tech_MXNo ratings yet
- Combined Paging and SegmentationDocument33 pagesCombined Paging and SegmentationTech_MX100% (1)
- E-Post Office SystemDocument21 pagesE-Post Office SystemTech_MX67% (3)
- Statistical Quality Control 2Document34 pagesStatistical Quality Control 2Tech_MXNo ratings yet
- Client-Server ModelsDocument21 pagesClient-Server ModelsTech_MXNo ratings yet
- Client Computing EvolutionDocument37 pagesClient Computing EvolutionTech_MXNo ratings yet
- Buddy System in Operating SystemsDocument28 pagesBuddy System in Operating SystemsTech_MX43% (7)
- Theory of EstimationDocument30 pagesTheory of EstimationTech_MX100% (1)
- Minimum Cost Spanning Trees & ApplicationsDocument20 pagesMinimum Cost Spanning Trees & ApplicationsTech_MXNo ratings yet
- SpssDocument50 pagesSpssTech_MXNo ratings yet
- P - Communication Systems IIDocument5 pagesP - Communication Systems IIDemal BecirovicNo ratings yet
- P1249 Wind Data Display - Issue 7 25.02.2019Document23 pagesP1249 Wind Data Display - Issue 7 25.02.2019rohit sonawaneNo ratings yet
- AMD 4 S-4135E Sep8.2016 PDFDocument4 pagesAMD 4 S-4135E Sep8.2016 PDFEsmaelyNo ratings yet
- DS1621 Digital Thermometer and Thermostat: Features Pin AssignmentDocument16 pagesDS1621 Digital Thermometer and Thermostat: Features Pin AssignmentlgojfNo ratings yet
- Sec-Erb Materials Standard Specification: Eastern Region Branch Saudi Electricity CompanyDocument15 pagesSec-Erb Materials Standard Specification: Eastern Region Branch Saudi Electricity CompanySuhaib ObeidatNo ratings yet
- SodaPDF Converted AKOL LAB6Document21 pagesSodaPDF Converted AKOL LAB6ballDISCOVERIES PHballDISCOVERIESNo ratings yet
- Model 7Document4 pagesModel 7Saloni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Yamato-ADP21 ManualDocument35 pagesYamato-ADP21 ManualFede BerniNo ratings yet
- Open Access Analog Ic DesignDocument49 pagesOpen Access Analog Ic DesignAnu PillaiNo ratings yet
- Sequence Components Untransposed LinesDocument14 pagesSequence Components Untransposed LinesEduardo777_7770% (1)
- 5 TON SINGLE - WIRE VerlindeDocument7 pages5 TON SINGLE - WIRE VerlindeMahmoud OushaNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi VRF Technical Offer For Al Rabwa Residential VillaDocument11 pagesMitsubishi VRF Technical Offer For Al Rabwa Residential Villaג'אבר אחמדNo ratings yet
- MCCB Type IDMT 25 A, 36, Ka 3PDocument3 pagesMCCB Type IDMT 25 A, 36, Ka 3PBerkah GeriNo ratings yet
- Manual DMM PDFDocument13 pagesManual DMM PDFMujtabaAliNo ratings yet
- HCCM System Technical Specification v1Document12 pagesHCCM System Technical Specification v1Ankita ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Theory AssignmentDocument3 pagesTheory AssignmentDan WkNo ratings yet
- Exercise ElectroHydraulicsbasicDocument157 pagesExercise ElectroHydraulicsbasiczaynab handoum100% (1)
- LG Chem M4860P2SDocument2 pagesLG Chem M4860P2SOpik Kabut100% (1)
- Pam 8002Document15 pagesPam 8002napoleon_velasc3617No ratings yet
- Utp Category 5E Lan Cable (Solid) - Li5704001-Pvc: Cables Superiores Ltda - ColombiaDocument1 pageUtp Category 5E Lan Cable (Solid) - Li5704001-Pvc: Cables Superiores Ltda - ColombiabernardoNo ratings yet
- Emko Genset CatalogueDocument46 pagesEmko Genset Cataloguepaulista76No ratings yet
- v12 Can4 MercedesDocument2 pagesv12 Can4 Mercedesecupro checoNo ratings yet
- JBuds Air ManualDocument4 pagesJBuds Air ManualGustavo RamirezNo ratings yet
- Low Power Vlsi Design QnsDocument18 pagesLow Power Vlsi Design QnsTamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- 2GF 2HF 2SF100 110 Product DescriptionDocument5 pages2GF 2HF 2SF100 110 Product DescriptionsandykiraNo ratings yet
- Electric System - 1: Click The Volvo-Logo in The Lower Right Corner To Return To This Menu Main MenuDocument18 pagesElectric System - 1: Click The Volvo-Logo in The Lower Right Corner To Return To This Menu Main MenuPower MobileNo ratings yet
- Brake Load Test of Squirel Cage Induction Motor 3 PhaseDocument7 pagesBrake Load Test of Squirel Cage Induction Motor 3 Phasejassisc100% (1)
- IEEE For Case StudyDocument6 pagesIEEE For Case StudyRex TejadillaNo ratings yet
- Norme Electrical Standard For Industrial Machinery NFPA-79Document72 pagesNorme Electrical Standard For Industrial Machinery NFPA-79salonmogador mogadorNo ratings yet