Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Computers: Process Data
Uploaded by
Ilyas A HuqqaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Computers: Process Data
Uploaded by
Ilyas A HuqqaniCopyright:
Available Formats
How computers
process data
PRESENTED BY
NAQQASH A HUQQANI
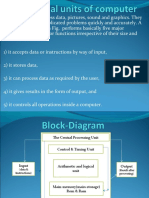
CPU
Arithmetic/
Logic Unit
(ALU)
Control Unit
Central Processing Unit
Synchronizes all computer operations
Faster clock speed means the CPU can
execute more instructions each second
Units: MHz and GHz
System Clock
1. Instruction while being decoded
2. Location from where instruction
was fetched
3. Data while the ALU processes it
4. Results of a calculation
CPU Registers
Temporary storage location used by the CPU
High speed memory in CPU that stores:
4 basic operations:
Fetch obtain a
program instruction or
data item from memory
Decode - translate the
instruction into
commands
Execute - carry out the
command
Store - write the result to
memory
Control Unit
directs and coordinates most
of the computer operations
Arithmetic
(addition, subtraction,
multiplication, and
division)
Comparison
(greater than, equal
to, or less than)
Logical
(AND, OR,
NOT)
Arithmetic and Logic Unit
CPU
Control Unit
Arithmetic/
Logic Unit
(ALU)
Arithmetic and Logic Unit
Performs the execution part of the machine cycle
4 operations of the CPU (control unit)
comprise a machine cycle; also called an
instruction cycle
e-time i-time
Machine Cycle
Instruction time time to fetch and decode
Execution time time to execute and store
A student enters a
math problem into
the memory of the
computer
Example
Example
Step 1: The
control unit
fetches the math
problem from
memory
Example
Step 2: The control
unit decodes the
math problem and
sends it to the ALU
Example
Step 3: The ALU
executes the math
problem
Example
Step 4: The
results of the
math problem are
stored in memory
The result in
memory displays
on the screen of
the monitor
You might also like
- The Central Processing Unit (CPU) and The Machine CycleDocument14 pagesThe Central Processing Unit (CPU) and The Machine Cycletaryll_01No ratings yet
- Decode 3. Execute: I-Time E-TimeDocument2 pagesDecode 3. Execute: I-Time E-Timemonee143No ratings yet
- Computer ScienceDocument31 pagesComputer ScienceOkay NopeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Computer ArchitectureDocument29 pagesChapter 6-Computer ArchitectureEdzai Nyasha TarupiwaNo ratings yet
- Computer Architectur1Document31 pagesComputer Architectur1Abigail ChitongoNo ratings yet
- Computer StrctureDocument11 pagesComputer Strcturenavabnavab786No ratings yet
- A Level Computing ModuleDocument166 pagesA Level Computing ModuleFerguson UtseyaNo ratings yet
- I O D S S D: Nput AND Utput Evices Econda RY Torage EvicesDocument5 pagesI O D S S D: Nput AND Utput Evices Econda RY Torage EvicesBhaskar NaiduNo ratings yet
- Read and Translate The Text Central Processing Unit (CPU)Document2 pagesRead and Translate The Text Central Processing Unit (CPU)Irina ZakharkivNo ratings yet
- The ProcessorDocument13 pagesThe ProcessorchristismithjaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Computer ArchitectureDocument34 pagesChapter 6-Computer ArchitectureVongai MubaiwaNo ratings yet
- The ProcessorDocument19 pagesThe Processortarrant HighNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer ScienceDocument9 pagesBasic Computer Scienceneenu1No ratings yet
- What Is Instruction CycleDocument3 pagesWhat Is Instruction CycleSukhi Dhiman100% (1)
- Computer OrganizationDocument11 pagesComputer OrganizationChristian Jhay OigaNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument10 pagesCentral Processing UnitBushra MemonNo ratings yet
- Computer Arch N Fetch Exc CycleDocument4 pagesComputer Arch N Fetch Exc CycleSarah ShafiNo ratings yet
- Computer OrganizationDocument16 pagesComputer OrganizationInnocent ChukwumaNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Notes (Software & Hardware)Document16 pagesComputer Science Notes (Software & Hardware)Muhammad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems: Huong NguyenDocument19 pagesComputer Systems: Huong NguyenDoski MorebundleNo ratings yet
- 1.4.2 The Fetch-Execute Cycle PDFDocument7 pages1.4.2 The Fetch-Execute Cycle PDFtalentNo ratings yet
- Lect 5, Chap 3, HardwareDocument9 pagesLect 5, Chap 3, HardwareFahad Bin saeedNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of ComputerDocument3 pagesBlock Diagram of Computer1990sukhbirNo ratings yet
- Program Instruction Memory Central Processing Unit BootupDocument4 pagesProgram Instruction Memory Central Processing Unit BootupADSR100% (1)
- CpuDocument14 pagesCpuPranshu021No ratings yet
- CPU Fetch-Execute CycleDocument5 pagesCPU Fetch-Execute CycleDivaNo ratings yet
- L-2 Basic Computer OrganizationDocument14 pagesL-2 Basic Computer OrganizationSakib AhmedNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document21 pagesCH 2Prince Ali JehangirNo ratings yet
- FunctionalunitsofcomputerDocument6 pagesFunctionalunitsofcomputerMEGHA SASINo ratings yet
- Processing DeviceDocument4 pagesProcessing DeviceKundai ChiwesheNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument15 pagesCentral Processing Unithussain korirNo ratings yet
- An Electronic Device Which Is Capable of Receiving InformationDocument2 pagesAn Electronic Device Which Is Capable of Receiving InformationDaljit SinghNo ratings yet
- Components CFDocument15 pagesComponents CFankudubeyNo ratings yet
- What Is The CPU?Document18 pagesWhat Is The CPU?Christine Mary EspirituNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Machine CycleDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Machine Cyclenrssgy edpmanditNo ratings yet
- Module1 Part BDocument25 pagesModule1 Part BSai SileshNo ratings yet
- Fetch Execute Cycle: Control Unit - Controls All Parts of The Computer System. ItDocument6 pagesFetch Execute Cycle: Control Unit - Controls All Parts of The Computer System. Itsamsung galaxyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document15 pagesLecture 2Priyam ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Computer Organisation: CPU ArchitectureDocument4 pagesComputer Organisation: CPU ArchitectureSamhunguNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Central Processing UnitDocument8 pages2.3 Central Processing UnitHoodrich PabloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer SystemsL1Document34 pagesIntroduction To Computer SystemsL1KuongaNo ratings yet
- CT-Chapter 1Document15 pagesCT-Chapter 1Om MistryNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals MODULE 5 LESSON 1Document5 pagesComputer Fundamentals MODULE 5 LESSON 1Delia PenoringanNo ratings yet
- Von NeumannDocument22 pagesVon NeumannĐường Minh TríNo ratings yet
- ch01 ComputerBasic PDFDocument131 pagesch01 ComputerBasic PDFAbdreyll GerardNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Title: Bachelor of Technology Computer Science and EngineeringDocument10 pagesTerm Paper Title: Bachelor of Technology Computer Science and EngineeringAqUa ForTisNo ratings yet
- 212 CPU & RegistersDocument7 pages212 CPU & RegistersSantosh ChandraNo ratings yet
- BsjddsDocument31 pagesBsjddsJaswanth VemulaNo ratings yet
- CMP 101 Set 6 CPUDocument24 pagesCMP 101 Set 6 CPUNitin GroverNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument12 pagesCentral Processing Unithussain korirNo ratings yet
- Lo5 - 3Document4 pagesLo5 - 3Michael Ramin Vargas AlidoNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 3Document23 pagesUnit-1 3ragulNo ratings yet
- 5 Basic Operations Performed by Computer SystemDocument5 pages5 Basic Operations Performed by Computer SystemNuj Wehtam Inairam100% (7)
- Assignment 7Document11 pagesAssignment 7ajit mhjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Basic Structure of ComputersDocument33 pagesChapter 1 - Basic Structure of Computersanusrini23No ratings yet
- Muhammad Zeeshan CMS ID:17187 Subject:Itc Teacher:Sir Sibghatullah Program:Bs Chemical (2)Document9 pagesMuhammad Zeeshan CMS ID:17187 Subject:Itc Teacher:Sir Sibghatullah Program:Bs Chemical (2)Junaid KhurshidNo ratings yet
- Arsitektur Dan Organisasi Komputer: Basic Structure of ComputersDocument20 pagesArsitektur Dan Organisasi Komputer: Basic Structure of ComputersAndre SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3Norris Nana ChinjongNo ratings yet
- Tutorial3 Question SlidesDocument6 pagesTutorial3 Question SlidesIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- 1 PB PDFDocument15 pages1 PB PDFIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- Application of Fractional Order ABC and GA For Neural Network Training and Clustering ProcessDocument14 pagesApplication of Fractional Order ABC and GA For Neural Network Training and Clustering ProcessIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- Application of Fractional Order ABC and GA For Neural Network Training and Clustering ProcessDocument14 pagesApplication of Fractional Order ABC and GA For Neural Network Training and Clustering ProcessIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- Reproduction or Display. 1Document6 pagesReproduction or Display. 1Ilyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture22 Emag TransformersDocument26 pagesLecture22 Emag TransformersIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- Sample Email CVDocument5 pagesSample Email CVIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- 14 LectureDocument8 pages14 LectureIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- Error Detection and Correction in H.263 Coded Video Over Wireless NetworkDocument11 pagesError Detection and Correction in H.263 Coded Video Over Wireless NetworkIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- Outcome Based EducationDocument187 pagesOutcome Based EducationIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- Ozone Layer & Greenhouse EffectDocument29 pagesOzone Layer & Greenhouse EffectIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- Devaluation of CurrencyDocument23 pagesDevaluation of CurrencyNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Minto Morley ReformsDocument7 pagesMinto Morley ReformsIlyas A Huqqani100% (2)
- How Computers: Process DataDocument13 pagesHow Computers: Process DataIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- How Computers: Process DataDocument13 pagesHow Computers: Process DataIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- How To Weld 4130Document3 pagesHow To Weld 4130MikeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DreamweaverDocument50 pagesIntroduction To DreamweaverIlyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- Plot Time (T) Vs Lift Coefficient (C)Document1 pagePlot Time (T) Vs Lift Coefficient (C)Ilyas A HuqqaniNo ratings yet
- How To CreateDocument23 pagesHow To CreateKirana ShreeNo ratings yet