Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Read and Translate The Text Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Uploaded by
Irina Zakharkiv0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views2 pagesThe CPU and memory handle data processing in a computer. They are located on the motherboard, which connects the CPU to other hardware. The CPU, consisting of microprocessors, manipulates data and has two parts: the control unit and arithmetic logic unit (ALU). The control unit manages resources and directs data flow, while the ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations on data in registers according to the CPU's instruction set. Each time the CPU executes an instruction it goes through a machine cycle consisting of instruction and execution cycles.
Original Description:
English for computer engineering.
Original Title
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe CPU and memory handle data processing in a computer. They are located on the motherboard, which connects the CPU to other hardware. The CPU, consisting of microprocessors, manipulates data and has two parts: the control unit and arithmetic logic unit (ALU). The control unit manages resources and directs data flow, while the ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations on data in registers according to the CPU's instruction set. Each time the CPU executes an instruction it goes through a machine cycle consisting of instruction and execution cycles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views2 pagesRead and Translate The Text Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Uploaded by
Irina ZakharkivThe CPU and memory handle data processing in a computer. They are located on the motherboard, which connects the CPU to other hardware. The CPU, consisting of microprocessors, manipulates data and has two parts: the control unit and arithmetic logic unit (ALU). The control unit manages resources and directs data flow, while the ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations on data in registers according to the CPU's instruction set. Each time the CPU executes an instruction it goes through a machine cycle consisting of instruction and execution cycles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1.
Read and translate the text
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
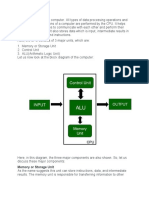
Two components handle processing in a computer: the central processing unit,
or CPU, and the memory. They are located on the computer's motherboard, the circuit
board that connects the CPU to the other hardware devices.
The CPU, or processor, is the place where data is manipulated. In a personal
computer, the processor usually consists of one or more microprocessors (sometimes
called "chips") which are slivers of silicon or other material with many tiny electronic
circuits. The CPU has two basic parts: the control unit and the arithmetic logic unit.
The Control Unit
All the computer's resources are managed from the control unit. The control unit
directs the flow of data through the CPU, and to and from other devices. The CPU's
instructions for carrying out commands arebuilt into the control unit. The instructions,
or instruction set, list all the operations that the CPU can perform. Each instruction in
the instruction set is expressed in microcode – a series of basic directions that tells the
CPU how to execute more complex operations. When the control unit
encounters an instruction that involves arithmetic or logic, it passes that instruction to
the second component of the CPU, the arithmetic logic unit, or ALU.
The Arithmetic Logic Unit
Because all computer data is stored as numbers, the processing involves
comparing numbers or carrying out mathematical operations. The computer performs
two types of operations: arithmetic operations and logical operations. Arithmetic
operations include addition, subtraction,multiplication, and division. Logical
operations include the following ones: “equal to”, “not equal to”, “greater than”, or
“less than”. The ALU includes a group of registers – high-speed memory locations in
the CPU that are used to hold the data currently being processed. For example, the
control unit may load two numbers from memory into the registers in the ALU.Then it
may tell the ALU to divide the two numbers (an arithmetic operation) or to see whether
the numbers are equal (a logical operation).
Each time the CPU executes an instruction, it takes a series of steps that is called
a machine cycle. A machine cycle can be broken down into two smaller cycles: the
instruction cycle and the execution cycle.During the instruction cycle the CPU takes
two steps: fetching (the control unit retrieves, or “fetches”,a command or data from the
computer's memory)and decoding (the control unit breaks down, or decodes, the
command into instructions that correspond to those in the CPU's instruction set).
At this point, the CPU is ready to begin the execution cycle. When the command
is executed, the CPU carries out the instructions in order by converting them into
microcode. The CPU may be required to store the results of an instruction in memory
(but this condition is not always required).
2. Answer the questions.
1. What components of a computer system handle data processing?
2. Where are the memory and the central processing unit located?
3. What is the computer’s motherboard?
4. What is a microprocessor?
5. What are the basic parts of a microprocessor?
6. What is the function of the control unit?
7. What does the instruction set include?
8. What is a microcode?
9. What two types of operations does the computer perform?
10.What do arithmetic operations include?
11.What logical operations are performed by the ALU?
12.What is the task of registers?
13.What is a machine cycle?
14.What are the parts of a machine cycle?
15.What operations does the CPU perform during the instruction cycle? execution
cycle?
3. Tell whether the following statements are true or false.
1. The CPU’s instruction set tells the computer what operations any application
program can perform.
2. Data is manipulated in memory.
3. In a personal computer, the processor usually consists of one or more
microprocessors.
4. The computer can perform two types of operations: arithmetic operations and
geometric operations.
5. Arithmetic and logical operations are carried out by the CPU’s arithmetic logic
unit.
6. The control unit directs the flow of data through the CPU, and to and from other
devices.
7. The CPU’s instructions for carrying out commands are built into the arithmetic
logic unit.
8. Processing is a series of basic directions that tells the CPU how to execute more
complex operations.
9. Addition and subtraction are logical operations.
10.Registers are used to hold the data currently being processed.
11.Arithmetic logic unit performs only logical operations.
12.When the CPU executes an instruction, it takes a series of steps, called an
instruction cycle.
4. Fill in the blanks:
1. The CPU has two basic parts: the ____________ and the ____________.
2. When the control unit encounters an instruction that involves
_______________ or _______________, it passes the instruction to the ALU.
3. A machine cycle can be broken down into two smaller steps: the
______________ and the _____________.
4. The central processing unit, or CPU, and the memory are located
on _____________.
5. The control unit directs _________ through the CPU.
6. Each instruction in the instruction set is expressed in ____________.
7. The processing involves __________ numbers or _________ mathematical
operations.
8. Arithmetic operations include ____________, ____________, _____________,
and ______________.
9. A series of steps the CPU takes is called _____________.
10.During the instruction cycle the CPU takes two steps: ____________ and
______________.
You might also like
- Publication 1 389 1610Document4 pagesPublication 1 389 1610Muumini De Souza NezzaNo ratings yet
- Computer ScienceDocument31 pagesComputer ScienceOkay NopeNo ratings yet
- The ProcessorDocument19 pagesThe Processortarrant HighNo ratings yet
- Computer - Archito - Lecture 2Document21 pagesComputer - Archito - Lecture 2Dennis YartelNo ratings yet
- A CpuDocument3 pagesA CpuEllen VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- BBA - HM - III CA Unit 1Document13 pagesBBA - HM - III CA Unit 1Sanika AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Central Processing UnitDocument8 pages2.3 Central Processing UnitHoodrich PabloNo ratings yet
- Class 4 ProcessingDocument13 pagesClass 4 ProcessingSubrat SwainNo ratings yet
- Part'S of ComputerDocument8 pagesPart'S of Computerahmat irwanzuhriNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument18 pagesCentral Processing Unitvinay ramanNo ratings yet
- Computer Processing DevicesDocument21 pagesComputer Processing Devicesaluka porota67% (3)
- Unit 2Document3 pagesUnit 2silkyNo ratings yet
- CpuDocument14 pagesCpuPranshu021No ratings yet
- How Computers Process DataDocument9 pagesHow Computers Process Datascribd102No ratings yet
- Component of A Digital ComputerDocument15 pagesComponent of A Digital Computerreginaamondi133No ratings yet
- 5 Basic Operations Performed by Computer SystemDocument5 pages5 Basic Operations Performed by Computer SystemNuj Wehtam Inairam100% (7)
- CPU Is The Brain of The ComputerDocument3 pagesCPU Is The Brain of The ComputerAshok RathodNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals MODULE 5 LESSON 1Document5 pagesComputer Fundamentals MODULE 5 LESSON 1Delia PenoringanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document11 pagesAssignment 7ajit mhjNo ratings yet
- Cpu and Its Working MechanismDocument9 pagesCpu and Its Working MechanismBais JumaniNo ratings yet
- Computer Studies: System UnitDocument10 pagesComputer Studies: System Unittayo adeniyiNo ratings yet
- An Electronic Device Which Is Capable of Receiving InformationDocument2 pagesAn Electronic Device Which Is Capable of Receiving InformationDaljit SinghNo ratings yet
- Report On CpuDocument41 pagesReport On Cpubabu75% (4)
- The System Unit: MotherboardDocument13 pagesThe System Unit: MotherboardStevenson CacNo ratings yet
- What Is CPUDocument3 pagesWhat Is CPUVIJAY VADGAONKARNo ratings yet
- What Is The CPU?Document18 pagesWhat Is The CPU?Christine Mary EspirituNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of ComputerDocument3 pagesBlock Diagram of Computer1990sukhbirNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - Computer System HardwareDocument17 pagesUNIT 2 - Computer System HardwareComputer75% (4)
- Computer Architectur1Document31 pagesComputer Architectur1Abigail ChitongoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Computer Architecture Notes EnglishDocument4 pagesChapter - 2 Computer Architecture Notes EnglishAshish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems: Huong NguyenDocument19 pagesComputer Systems: Huong NguyenDoski MorebundleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Central Processing UnitDocument4 pagesLecture 11 - Central Processing UnitPragya SinghNo ratings yet
- Learning Journal Unit 5 CS1104Document3 pagesLearning Journal Unit 5 CS1104pohambadanielNo ratings yet
- Cpu Final NotesDocument6 pagesCpu Final NotesSonu zehen001No ratings yet
- How The Cpu WorksDocument2 pagesHow The Cpu WorksjuliamarkNo ratings yet
- The Central Processing Unit (CPU) .: Transfer of Data Among DevicesDocument4 pagesThe Central Processing Unit (CPU) .: Transfer of Data Among DevicesSarmad Salih Jawad AlkodaryNo ratings yet
- Basic Components of Computer SystemDocument4 pagesBasic Components of Computer SystemAnonymous u64nn35tHCNo ratings yet
- Coa - Lecture 3 - BNCDocument5 pagesCoa - Lecture 3 - BNCShizz denariNo ratings yet
- Components of Computer: Hardware Software HardwareDocument9 pagesComponents of Computer: Hardware Software Hardwarerashidqureshi6944No ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument5 pagesComputer Architectureapi-417400228No ratings yet
- Processing DeviceDocument4 pagesProcessing DeviceKundai ChiwesheNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Computer ArchitectureDocument34 pagesChapter 6-Computer ArchitectureVongai MubaiwaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Computers and Se Chapter 2Document9 pagesIntro To Computers and Se Chapter 2amirNo ratings yet
- It M Question BankDocument52 pagesIt M Question Bankravikiran1955No ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument15 pagesCentral Processing Unithussain korirNo ratings yet
- ProcessorDocument10 pagesProcessorSasha BurkeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Computer ArchitectureDocument29 pagesChapter 6-Computer ArchitectureEdzai Nyasha TarupiwaNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamental, Organization and ArchitectureDocument19 pagesComputer Fundamental, Organization and Architecturepradhumnyadav756No ratings yet
- Cite1004 Activity 1 MidtermDocument3 pagesCite1004 Activity 1 MidtermJoshua LimbagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3Norris Nana ChinjongNo ratings yet
- Computer System Computer ArchitectureDocument7 pagesComputer System Computer ArchitectureSuman Samal MagarNo ratings yet
- Module 1 of Computer OrganizationDocument27 pagesModule 1 of Computer OrganizationNimmymolManuelNo ratings yet
- Cite1004 Activity 1 MidtermDocument3 pagesCite1004 Activity 1 MidtermJoshua LimbagaNo ratings yet
- A Computer Can Process DataDocument3 pagesA Computer Can Process DataMario ToloNo ratings yet
- I O D S S D: Nput AND Utput Evices Econda RY Torage EvicesDocument5 pagesI O D S S D: Nput AND Utput Evices Econda RY Torage EvicesBhaskar NaiduNo ratings yet
- Control Processing Unit (CPU) : AssignmentDocument5 pagesControl Processing Unit (CPU) : AssignmentBlackBeardNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- FFDocument2 pagesFFMohamed Al assalNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document106 pagesUnit 3A Good YoutuberNo ratings yet
- Pit Procedures P05Document7 pagesPit Procedures P05Muhd Nazrin Ab RasidNo ratings yet
- A Technical Guide To IPSec Virtual Private NetworksDocument348 pagesA Technical Guide To IPSec Virtual Private NetworksRet SecNo ratings yet
- PHP Project ReportDocument24 pagesPHP Project ReportRohit Duggal73% (15)
- Lumion Tutorials - Reflection AdjustmentsDocument6 pagesLumion Tutorials - Reflection Adjustmentsundrap1No ratings yet
- Azure Repos DocumentationDocument838 pagesAzure Repos DocumentationLagerström EmpreendimentosNo ratings yet
- Dislipidemias: Josías Avila - Interno IV Cesfam Salvador BustosDocument47 pagesDislipidemias: Josías Avila - Interno IV Cesfam Salvador BustosJosías ÁvilaNo ratings yet
- Catalogo de Partes P501-P502Document88 pagesCatalogo de Partes P501-P502escanerdocumentalljsNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: First Quarter - Week 4Document6 pagesMathematics: First Quarter - Week 4MARIE GRACE APARRENo ratings yet
- g11 Css NC II - Week 18 (Updated)Document3 pagesg11 Css NC II - Week 18 (Updated)Lance F. KidNo ratings yet
- Kids Playing Music PowerPoint TemplatesDocument48 pagesKids Playing Music PowerPoint TemplatesKyou KazuneNo ratings yet
- Preset Drag Adjustment Washers: FX Reel 400N 400 500N 500 600NN 600N 600 Internal Parts Blowout (Ipb)Document4 pagesPreset Drag Adjustment Washers: FX Reel 400N 400 500N 500 600NN 600N 600 Internal Parts Blowout (Ipb)PANEUREUS JAYA ABADI PTNo ratings yet
- BMT SPSF Schedule1040Document1 pageBMT SPSF Schedule1040Michael LopesNo ratings yet
- Ecaf White Paper - 6145 PDFDocument15 pagesEcaf White Paper - 6145 PDFeustaquiobrunoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Fig. 1 Flow Chart of Taguchi MethodDocument3 pagesAssignment 1: Fig. 1 Flow Chart of Taguchi MethodNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dimayacyac, Jane Escobido, Ron Ilaw, Lenberd Ortiz, Marielle Anne Kaye DDocument13 pagesDimayacyac, Jane Escobido, Ron Ilaw, Lenberd Ortiz, Marielle Anne Kaye DLenberd IlawNo ratings yet
- SC-S40670S BrochureN PDFDocument2 pagesSC-S40670S BrochureN PDFjohnNo ratings yet
- Lc32le350m PDFDocument70 pagesLc32le350m PDFLouieGonzalesNo ratings yet
- Tool and Die DesignDocument61 pagesTool and Die DesignAshley Kane P. Dumay100% (3)
- Four Wheel Drive SystemsDocument2 pagesFour Wheel Drive Systemsolyga mgolNo ratings yet
- DMANE01000034-Manual System100 Full Hydro LCD STD2 ENGDocument41 pagesDMANE01000034-Manual System100 Full Hydro LCD STD2 ENGDanSaila100% (4)
- Redway Power DeatailsDocument16 pagesRedway Power Deatailscleaningservice423No ratings yet
- Challenges of ''V " C Mmunication Systems For Air Traffic ManagementDocument6 pagesChallenges of ''V " C Mmunication Systems For Air Traffic ManagementLuisNo ratings yet
- NDAC Defense Slides-EjercitoDocument29 pagesNDAC Defense Slides-EjercitoDITEC Direccion de Ciencia y TecnologiaNo ratings yet
- Gregory - Interactive Tic-Tac-Toe Menu Choice Board For VocabularyDocument11 pagesGregory - Interactive Tic-Tac-Toe Menu Choice Board For Vocabularyapi-518413438No ratings yet
- ABIR 2 Mis PDFDocument8 pagesABIR 2 Mis PDFAbir FoysalNo ratings yet
- A5 Brochure - Revise - Centre Pinning - With IndoscopeDocument32 pagesA5 Brochure - Revise - Centre Pinning - With IndoscopeGerman DrumsNo ratings yet
- Phases of A Formal ReviewDocument8 pagesPhases of A Formal Reviewsureshkumar1143No ratings yet
- Ultrawave Cleaning Bath - User ManualDocument14 pagesUltrawave Cleaning Bath - User ManualRAMON CANDIDONo ratings yet