Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stresses in Vessel On Two Sad... Ports Using ZICK Analysis
Uploaded by
PEJU0007Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stresses in Vessel On Two Sad... Ports Using ZICK Analysis
Uploaded by
PEJU0007Copyright:
Available Formats
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF HEAT EXCHANGER Page : 121 of 136
According to ASME Code, Sec. VIII, Div. 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 / TEMA "R" 7th Edition 88. Sheet : 1 of 8
Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (Assistant) Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Fabrication of Heat Exchanger for APRC Refinery Date : 11.4.2004
Project : Design & Fabrication of Heat Exchanger for APRC Refinery Location : Alex.
Dwg. No. : 7443-33-1A, Rev. 1 Client : APRC
Exchanger : Residue Cooler, Type : AES, TEMA class : R Items : E-323A/B & E-514C/D
X. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method.
Shell material ASME SA106 Grade B
Heads material ASME SA234 Grade WPB
Saddles material ASME SA106 Grade B
Heads type Ellipsoidal 2:1
Design temperature 302
o
F 150
o
C
Vessel internal pressure, P 284.776 PSIG 20.04826 Kg/CM
2
G
Allowable stress in shell, Sts 17100 PSIG 1203.84 Kg/CM
2
G
Allowable stress in heads, Sth 17100 PSIG 1203.84 Kg/CM
2
G
Allowable stress in web, Sw 15700 PSIG 1105.28 Kg/CM
2
G
Shell compression yield point, Y 45000 PSIG 3168 Kg/CM
2
G
Saddle & anchor bolt compression yield point, Re 30000 PSIG 2112 Kg/CM
2
G
Outer shell diameter, Do 20 INCH 508 MM
Wall nominal thickness of shell, ts 0.5 INCH 12.7 MM
Wall nominal thickness of heads, th 0.5 INCH 12.7 MM
Corrosion allowance for shell & heads, CA 0.197 INCH 5 MM
Shell joint efficiency, Es 0.85
Head joint efficiency, Eh 0.85
Head internal depth, h 5.785 INCH 146.935 MM
Head depth -to- tangent line (external depth), Ho 6.285 INCH 159.635 MM
Insulation thickness, tis 0 INCH 0 MM
Wear (reinf./top flange) plate width, B 7.087 INCH 180 MM
Wear (reinf./top flange) plate thickness, tf 0.5 INCH 12.7 MM
Wall corroded thickness of shell 0.366 INCH 9.28625 MM
Wall corroded thickness of heads 0.366 INCH 9.28625 MM
Wall corroded thickness of shell + reinf. plate 0.866 INCH 21.98625 MM
Outer shell radius, Ro = Do / 2 10 INCH 254 MM
Shell length from Tangent - to - tangent (T/T) , L 254.843 INCH 6473 MM
Saddle - to - saddle distance (S/S) , L" 165.354 INCH 4200 MM
Transverse distance between anchor bolts, Y 21.6535 INCH 550 MM
Distance from tangent line -to- center of saddle support , A 47.244 INCH 1200 MM
Saddle contact angle, B 120 Degree
Longitudinal width of saddle at shell, b 7.087 INCH 180 MM
Transverse width of saddle at shell (baseplate length), m 20.551 INCH 522 MM
Height of saddle to vessel center line, Z 17.913 INCH 455 MM
Web width of saddle, hs = m - 2 cl 19.37 INCH 492 MM
Web thickness of saddle, tw 0.591 INCH 15 MM
Equivalent diameter of vessel, Deq = 1.5 (Do + 2 * tis) 30 INCH 762 MM
Equivalent length of vessel, Leq = L + 2Ho + 2 tis 267.412 INCH 6792.27 MM
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF HEAT EXCHANGER Page : 122 of 136
According to ASME Code, Sec. VIII, Div. 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 / TEMA "R" 7th Edition 88. Sheet : 2 of 8
Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (Assistant) Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Fabrication of Heat Exchanger for APRC Refinery Date : 11.4.2004
Job No. : 7443-33 Location : Alex.
Dwg. No. : 7443-33-1A, Rev. 1 Client : APRC
Exchanger : Residue Cooler, Type : AES, TEMA class : R Items : E-323A/B & E-514C/D
X. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.)
1. Seismic & wind forces on vessel
a. Seismic force UBC-1997
Total design force or shear at the base, F = z . I . C . Wt / Rw 1490.53 lb 676.0875 Kg
Seismic Zone 2A :
For zone 2A : z = Seismic zone factor [Table No. 23-I] 0.15
I = Importance factor [Table No. 23-L] 1
C = Numerical coefficient [Table No. 23-P] 2.75 Max.
Rw = Numerical coefficient [TableS NoS. 23-O & 23-Q] 3
= 3 ( horizontal vessel on pier)
Total vessel dead weight, Wt 10840.2 lb 4917 Kg
b. Wind force ANSI A58.1
F = Cf . Gh . qz . Af
qz = 0.00256 . kz . (I V)
2
27.0848 PSF 13.49792 N/M
2
For exposure C :
h = Height 0-15 ft
kz = Velocity pressure exposure coefficient 0.8
Wind Velocity, V = Basic wind speed 115 MPH 51.399 M/Sec.
Gh = Gust response factor 1.32
Cf = Force coefficient 0.8
c. Forces in longitudinal direction
Figure (11)
Seismic longitudinal force, Fls = z . I . C . Wt / Rw 1490.53 lb 676.0875 Kg
Wind longitudinal exposed area, Afl = (pi/8*Deq + Z) * Deq 6.18624 ft
2
0.574721 M
2
Wind longitudinal force, Flw = Cf . Gh . qz . Afl 176.936 lb 80.25607 Kg
Fl = Greater value of Fls & Flw 1490.53 lb 676.0875 Kg
A
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF HEAT EXCHANGER Page : 123 of 136
According to ASME Code, Sec. VIII, Div. 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 / TEMA "R" 7th Edition 88. Sheet : 3 of 8
Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (Assistant) Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Fabrication of Heat Exchanger for APRC Refinery Date : 11.4.2004
Job No. : 7443-33 Location : Alex.
Dwg. No. : 7443-33-1A, Rev. 1 Client : APRC
Exchanger : Residue Cooler, Type : AES, TEMA class : R Items : E-323A/B & E-514C/D
X. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.)
d. Forces in transverse direction
Figure (12)
Seismic transverse force, Fts = 0.5 Fls = 0.5 x z x I x C x Wt / Rw 745.267 lb 338.0438 Kg
Wind transvere exposed area, Aft = Deq * Leq 55.7108 Ft
2
5.175706 M
2
Wind transverse force, Ftw = 0.5 x Cf x Gh x x qz x Aft 796.708 lb 361.377 Kg
Ft = Greater value of Fts & Ftw 796.708 lb 361.377 Kg
2. Reaction force per saddle support
a. Reaction due to full vessel weight, Qo = Wt/2 5420.12 lb 2458.5 Kg
b. Reaction in longitudinal direction due to earthquake & wind :
By taking moments about saddle support : Fl . Z = Ql . L"
Ql = Fl . Z / L" 161.471 lb 73.24138 Kg
c. Reaction in transverse direction due to earthquake & wind :
By taking moments about saddle support : Ft . Z = Qt . (m/2)
Qt = 3 ( 2 . Ft . Z / m) 4166.64 lb 1889.936 Kg
d. Max. reaction due to earthquake & wind, Qmax. = Max. (Ql , Qt) 4166.64 lb 1889.936 Kg
e. Total reaction due to full vessel weight, earthquake and wind, Q
Total longitudinal reaction, Qlt = Qo + Ql 5581.59 lb 2531.741 Kg
Total transverse reaction, Qtt = Qo + Qt 9586.76 lb 4348.436 Kg
Q = Greater value of Qlt & Qtt 9586.76 lb 4348.436 Kg
3. Modified stresses at saddles :
Ratio (Qo + Qmax.) / Qo 1.76874
a. Modified circumferential stresses, SIG 5' = Ratio . < OK
SIG 5' = Ratio . < OK
SIG 4' = Ratio . < OK
SIG 4' = Ratio . < OK
b. Modified tangential stresses, SIG 2' = Ratio . < OK
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF HEAT EXCHANGER Page : 124 of 136
According to ASME Code, Sec. VIII, Div. 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 / TEMA "R" 7th Edition 88. Sheet : 4 of 8
Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (Assistant) Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Fabrication of Heat Exchanger for APRC Refinery Date : 11.4.2004
Job No. : 7443-33 Location : Alex.
Dwg. No. : 7443-33-1A, Rev. 1 Client : APRC
Exchanger : Residue Cooler, Type : AES, TEMA class : R Items : E-323A/B & E-514C/D
X. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.)
a. Stresses in longitudinal direction
Longitudinal force, Fl 1490.53 lb 676.0953 Kg
Max. moment, Mmax. = Fl . Z 26699.9 lb-in. 307.6167 Kg-M
Figure (13)
Cross-sectional Area, A = Lw * tw + 2 Sw * ts+ 2(n-2) Rw * ts 15.3915 INCH
2
9930 MM
2
Moment of inertia, Ix-x = Lw*tw
3
/12 + 2ts*Sw
3
/12+ (n-2) ts(Sw
3
-tw
3
)/12 12.3045 INCH
4
5121500 MM
4
Section modulus, Wx-x = Lw*tw
2
/6+2ts*Sw
2
/6+2ts(Sw
3
-tw
3
)/(6 Sw) 7.14931 INCH
3
117156.3 MM
3
Dimension, X1 = Ix-x / Wx-x 1.72107 INCH 43.71512 MM
Bending stress, Sb = Mmax. / Wx-x 3734.61 PSI 262.9168 Kg/CM
2
G
Allowable bending stress, S' = 1.2 . S 18840 PSI 1326.336 Kg/CM
2
G
OK
Shear stress, T = Fl / A 96.8411 PSIG 6.817615 Kg/CM
2
G
Allowable shear stress, S' = 0.5 . S 7850 PSIG 552.64 Kg/CM
2
G
OK
b. Stresses in transverse direction
Transverse force, Ft 796.708 lb 361.3811 Kg
Max. moment, Mmax. = Ft . Z 14271.4 lb-in. 164.4249 Kg-M
Figure (14)
Cross-sectional Area, A 15.3915 INCH
2
9930 MM
2
Moment of inertia, Iy-y = tw*Lw
3
/12+Sw[(Lw+2ts)
3
-Lw
3
]/12+2Rw((Ss(n-1-2)+ts727.502 INCH
4
3.03E+08 MM
4
Section modulus, Wy-y =tw*Lw
2
/6+Sw*[(Lw+2ts)
3
-Lw
3
]/6(Lw+2ts)+2Rw[(Ss+ts87.4027 INCH
3
1432273 MM
3
Dimension Y1 = Iy-y / Wy-y 8.32357 INCH 211.4187 MM
Bending stress, Sb = Mmax. / Wy-y 163.284 PSIG 11.49517 Kg/CM
2
G
Allowable bending stress, S' = 1.2 . S 18840 PSIG 1326.336 Kg/CM
2
G
OK
Shear stress, T = Ft / A 51.7628 PSIG 3.644098 Kg/CM
2
G
Allowable shear stress, S' = 0.5 . S 7850 PSIG 552.64 Kg/CM
2
G
OK
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF HEAT EXCHANGER Page : 125 of 136
According to ASME Code, Sec. VIII, Div. 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 / TEMA "R" 7th Edition 88. Sheet : 5 of 8
Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (Assistant) Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Fabrication of Heat Exchanger for APRC Refinery Date : 11.4.2004
Job No. : 7443-33 Location : Alex.
Dwg. No. : 7443-33-1A, Rev. 1 Client : APRC
Exchanger : Residue Cooler, Type : AES, TEMA class : R Items : E-323A/B & E-514C/D
X. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.)
1. Bending moment & bending stress at saddles
Bending moment at saddle in tension & compression, M
1
452744 lb-in 5216.177 Kg-M
Longitudinal bending stress in tension, S
1
= M
1
/ K
1
R
2
ts 2883.72 PSIG 203.0137
Kg/CM
2
G
Longitudinal bending stress in compression, S
1
= - M
1
/ K8 R
2
ts -15016.4 PSIG -1057.153
Kg/CM
2
G
2. Bending moment & bending stress at midspan
Bending moment at midspan, M
2
558078 lb-in 6429.767 Kg-M
Longitudinal bending stress at midspan, S
1
' = - M
1
'
/ 3.14 R
2
ts -3552.84 PSIG -250.1198
Kg/CM
2
G
3. Stress in the shell due to internal pressure,
S = P R / (2 Es ts) 3350.31 PSIG 235.8619 Kg/CM
2
G
4. Sum of tensile stress
Value of S
1
+ S 6234.03 PSIG 438.8756
Kg/CM
2
G
Value of S
1
'
+ S -202.527 PSIG -14.2579
Kg/CM
2
G
Greater value of (S
1
+ S) & (S
1
'
+ S) 6234.03 PSIG 438.8756
Kg/CM
2
G
Shell allowable tensile stress 17100 PSIG 1203.84 Kg/CM
2
G
Stress ratio = Greater stress/Allowable stress 0.36456 < 1 Passed
5.Tangential shear stress, S
2
5.a. Tangential shear stress on shell, S
2
In case of A > R/2 and ring not used or rings are adjacent to the saddle.
1367.78 PSIG 96.29196 Kg/CM
2
G
Shell allowable tangential stress = 0.8 S 13680 PSIG 963.072 Kg/CM
2
G
Stress ratio = S
2
/ 0.8 S 0.09998 < 1 Passed
L 3
H 4
1
L A 2
H R
L
A
1
1 A Q M
2 2
1
M QL
R H
L
H
L
A
L
1
2 2
2
1 2
1
4
3
4
'
S
K Q
R t
L A
L
H
s
2
2
2
4
3
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF HEAT EXCHANGER Page : 126 of 136
According to ASME Code, Sec. VIII, Div. 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 / TEMA "R" 7th Edition 88. Sheet : 6 of 8
Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (Assistant) Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Fabrication of Heat Exchanger for APRC Refinery Date : 11.4.2004
Job No. : 7443-33 Location : Alex.
Dwg. No. : 7443-33-1A, Rev. 1 Client : APRC
Exchanger : Residue Cooler, Type : AES, TEMA class : R Items : E-323A/B & E-514C/D
X. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.)
5.b. Tangential shear stress on shell, S
2
In case of A > R/2 and ring used in plane of saddle.
372.607 PSIG 26.23154 Kg/CM
2
G
Shell allowable tangential stress = 0.8 S 13680 PSIG 963.072 Kg/CM
2
G
Stress ratio = S
2
/ 0.8 S 0.02724 < 1 Passed
5.c. Tangential shear stress on head, S
2h
In case of A > R/2 and ring not used or rings are adjacent to th saddle.
1367.78 PSIG 96.29196 Kg/CM
2
G
Head allowable tangential stress = 0.8 S 13680 PSIG 963.072 Kg/CM
2
G
Stress ratio = S
2
/ 0.8 S 0.09998 < 1 Passed
5.d. Tangential shear stress on shell
In case of A <= R/2 S
2
= K
4
Q / R ts 1687.27 PSIG 118.7838
Kg/CM
2
G
Shell allowable tangential stress = 0.8 S 13680 PSIG 963.072 Kg/CM
2
G
Stress ratio = S2 / 0.8 S 0.12334 < 1 Passed
5.e. Tangential shear stress on head
In case of A <= R/2 S
2
= K
4
Q / R t
h
1687.27 PSIG 118.7838
Kg/CM
2
G
Shell allowable tangential stress = 0.8 S 13680 PSIG 963.072 Kg/CM
2
G
Stress ratio = S
2
/ 0.8 S 0.12334 < 1 Passed
5.f. Additional tangential shear stress in head
In case of A <= R/2 S
3
= K
5
Q / R t
h
768.858 PSIG 54.12761
Kg/CM
2
G
S
3
+ stress due to int. pres. (PR/(2Es ts) 3350.31 PSIG 235.8619
Kg/CM
2
G
Head allowable tensile stress = 1.25 S 21375 PSIG 1504.8 Kg/CM
2
G
Stress ratio = S
3
/ 1.25 S 0.15674 < 1 Passed
3
H 4
L
A 2 L
t R
Q K
S
h
2
h 2
3
H 4
L
A 2 L
t R
Q K
S
s
3
2
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF HEAT EXCHANGER Page : 127 of 136
According to ASME Code, Sec. VIII, Div. 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 / TEMA "R" 7th Edition 88. Sheet : 7 of 8
Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (Assistant) Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Fabrication of Heat Exchanger for APRC Refinery Date : 11.4.2004
Job No. : 7443-33 Location : Alex.
Dwg. No. : 7443-33-1A, Rev. 1 Client : APRC
Exchanger : Residue Cooler, Type : AES, TEMA class : R Items : E-323A/B & E-514C/D
X. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.)
6. Circumferential stress
6.a. Circumferential stress at saddle horn
In case of L >= 8 R (unstiffened)
-3074.71 PSIG -216.4598 Kg/CM
2
G
Shell allowable circumferential stress = 1.5 S 25650 PSIG 1805.76 Kg/CM
2
G
Stress ratio = S4 / 1.5 S 0.11987 < 1 Passed
6.b. Circumferential stress at saddle horn
In case of L < 8 R (unstiffened)
-1410.27 PSIG -99.2832 Kg/CM
2
G
Shell allowable circumferential stress = 1.5 S 25650 PSIG 1805.76 Kg/CM
2
G
Stress ratio = S
4
/ 1.5 S 0.05498 < 1 Passed
6.c. Circumferential stress at bottom of shell
(stiffened or unstiffened)
-1377.92 PSIG -97.00559 Kg/CM
2
G
0.5 compression yield point of shell material 22500 PSIG 1584 Kg/CM
2
G
Stress ratio = S
5
/ 0.5 S 0.06124 < 1 Passed
7. Check tension in web saddle
Horizontal force in web, Fw = K
8
Q 5780.82 lb 2622.107 Kg
Effective web area, Aw = h
s
tw 11.4477
INCH
2
7385.579
MM
2
Stress in web, Sw = Fw / Aw 504.977 PSIG 35.55042 Kg/CM
2
G
Allowable stress in web, Saw = 0.6 Y 18000 PSIG 1267.2 Kg/CM
2
G
Stress ratio = Sw / 0.6 Y 0.02805 < 1 Passed
Vertical force in web, Fv = Q 9586.76 lb 4348.436 Kg
Stress in web, Sv = Fv / Aw 837.442 PSIG 379.8534 Kg/CM
2
G
Allowable stress in web (compressiuon), Saw = 0.33 Y 9900 PSIG 696.96 Kg/CM
2
G
Stress ratio = Sv / 0.33 Y 0.08459 < 1 Passed
2
s
6
s s
4
t 2
Q K 3
t R 56 1 b t 4
Q
S
) . (
2
s
6
s s
4
t L
R Q K 12
t R 56 1 b t 4
Q
S
) . (
) . (
s s
7
5
t R 56 1 b t
Q K
S
DESIGN CALCULATIONS OF HEAT EXCHANGER Page : 128 of 136
According to ASME Code, Sec. VIII, Div. 1, Edition 2001, Addenda 2002 / TEMA "R" 7th Edition 88. Sheet : 8 of 8
Designed by : Eng. Abdel Halim Galala, Design General Manager (Assistant) Rev. : 1
Project : Design & Fabrication of Heat Exchanger for APRC Refinery Date : 11.4.2004
Job No. : 7443-33 Location : Alex.
Dwg. No. : 7443-33-1A, Rev. 1 Client : APRC
Exchanger : Residue Cooler, Type : AES, TEMA class : R Items : E-323A/B & E-514C/D
X. Stresses in Vessel on Two Saddle Supports Using ZICK's Method (cont.)
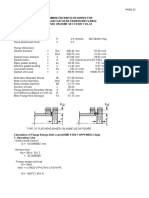
8. Check of the saddle at the lowest section (web plate thickness) :
The saddle at the lowest section must resist the horizontal force (F).
The effective cross section of the saddle to resist this load is R/3.
Figure (15)
F = K11 . Q 1955.7 lb 887.0809 Kg
To resist this force, the effective area of web plate, A = (R/3) . tw 1.9685 INCH
2
1270 MM
2
The calculated stress, Scal. = F / A 993.495 PSIG 69.94205 Kg/CM
2
G
The allowable stress, Sall. = (2/3) Sw 10466.7 PSIG 736.8534 Kg/CM
2
G
Stress ratio = Scal. / Sall. 0.09492 < 1 Passed
So, the thickness of the web plate is satisfactory for horizontal force (F).
Values of Constant K
For contact angle B = 120
o
: 120 Degree
K
1
(K
1
= 3.14 if the shell is stiffened by ring or head, A > R/2) 0.335 or 3.14 [A > R/2]
K
2
1.171
K
3
(K
3
is constant for any contact angle) 0.319
K
4
0.88
K
5
0.401
K
6
(K6 depends on the ratio A/R, see chart in vessel handbook)
K
6
for A/R > 1.00 0.053
K
6
for A/R < 0 0.5 0.013
A 47.244 INCH 1199.998 MM
R 10 INCH 254 MM
A/R 4.7244
R/2 5 INCH 127 MM
K
7
0.76
K
8
0.603
K
11
0.204
You might also like
- Design of Saddle Supports & Stresses in Vessel On Two Saddles Using ZICK's Method - by Abdel Halim GalalaDocument16 pagesDesign of Saddle Supports & Stresses in Vessel On Two Saddles Using ZICK's Method - by Abdel Halim GalalaRaymond Metselaar83% (6)
- Flange DesignDocument30 pagesFlange Designravielb9873No ratings yet
- FlangeCalc AS1210 v1.5Document28 pagesFlangeCalc AS1210 v1.5Ben100% (1)
- 1) Design Data: Ref: Procedure No. 3-4 Pg. No. 169, Pressure Vessel Design Manual by Dennis Moss, 4rd EditionDocument6 pages1) Design Data: Ref: Procedure No. 3-4 Pg. No. 169, Pressure Vessel Design Manual by Dennis Moss, 4rd Editionsouren1975No ratings yet
- Powder Coating PDFDocument46 pagesPowder Coating PDFclx75% (4)
- Bolted Flange Thickness CalculationDocument6 pagesBolted Flange Thickness Calculationshazan0% (1)
- ASME VIII CalculationDocument14 pagesASME VIII CalculationWan Wei100% (1)
- External Pressure - Pressure Vessel EngineeringDocument15 pagesExternal Pressure - Pressure Vessel Engineeringarjun100% (1)
- CK Tourqe CalculationDocument7 pagesCK Tourqe Calculationamit amity100% (1)
- Welding ProcedureDocument10 pagesWelding ProcedureWahyu Endra PurwantoNo ratings yet
- Flange CalculationsDocument3 pagesFlange CalculationssanjaysyNo ratings yet
- Appendix 2) : Optional Type Flange (Fig. 2-4 (8) )Document18 pagesAppendix 2) : Optional Type Flange (Fig. 2-4 (8) )hardik5818No ratings yet
- Studding Outlet Calculation - PV Elite 2016Document8 pagesStudding Outlet Calculation - PV Elite 2016Liu YangtzeNo ratings yet
- Bolt TorqueDocument5 pagesBolt TorqueTarunNo ratings yet
- Roundness Check Record of 1St Shell CourseDocument1 pageRoundness Check Record of 1St Shell CourseRhannie GarciaNo ratings yet
- Blind Flange DesignDocument1 pageBlind Flange DesignSachin5586No ratings yet
- PCC1 - Addendum - 31210130 (Feb 2013) - GM1-001-G0000-MS-7880-00003Document2 pagesPCC1 - Addendum - 31210130 (Feb 2013) - GM1-001-G0000-MS-7880-00003Abhay UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Flange DesignDocument26 pagesFlange Designresume Fi-1401No ratings yet
- Flange Analysis - Traditional Method 14sep10Document1 pageFlange Analysis - Traditional Method 14sep10Lava SatNo ratings yet
- Blind Flange Calculation11Document3 pagesBlind Flange Calculation11jaymuscatNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument2 pagesDatasheetnirmalNo ratings yet
- Loads On FlangesDocument16 pagesLoads On Flangesccoollest100% (3)
- Body Flange Design-Appx-2Document4 pagesBody Flange Design-Appx-2Matthieu100% (1)
- FlangeCalculationASMEVIII Version5Document13 pagesFlangeCalculationASMEVIII Version5madodandembe100% (3)
- Shell and Tube HE CalculationDocument16 pagesShell and Tube HE CalculationPradip ShindeNo ratings yet
- Blind Flange Design Calculation As Per Asme Section Vii Division - 1Document4 pagesBlind Flange Design Calculation As Per Asme Section Vii Division - 1mukesh100% (2)
- Flange DesignDocument6 pagesFlange DesignDinesh VaghelaNo ratings yet
- Part-Uhx (U-Tube) .Document5 pagesPart-Uhx (U-Tube) .AKSHAY BHATKARNo ratings yet
- Calc' Diesel Fuel (Rev)Document10 pagesCalc' Diesel Fuel (Rev)joko_tm02No ratings yet
- Weld Neck Body Flange Design Calculation: HE-CGI, HE-CG, Spiral Wound Gaskets For Heat ExchangersDocument25 pagesWeld Neck Body Flange Design Calculation: HE-CGI, HE-CG, Spiral Wound Gaskets For Heat ExchangersLipika GayenNo ratings yet
- Flange Excel NewDocument26 pagesFlange Excel NewvikasNo ratings yet
- Pd5500 Flange CalculationDocument6 pagesPd5500 Flange CalculationMakrand SakpalNo ratings yet
- Materials Data for Cyclic Loading: Low-Alloy SteelsFrom EverandMaterials Data for Cyclic Loading: Low-Alloy SteelsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- FlangeDocument6 pagesFlangekamardheen majithNo ratings yet
- Blind Flange CalculationDocument12 pagesBlind Flange CalculationrajarajanNo ratings yet
- Blind Flange Thickness CalculationDocument3 pagesBlind Flange Thickness CalculationKannapiran Krishnamoorthy75% (4)
- Reinforcement Pad DesignDocument3 pagesReinforcement Pad DesignAkshat JainNo ratings yet
- Asme Viii CalcsDocument20 pagesAsme Viii CalcsSriram VjNo ratings yet
- F-0201 Special Blind Calculation (N9)Document2 pagesF-0201 Special Blind Calculation (N9)rustamriyadiNo ratings yet
- Saddle v1-5: Fixed Saddle Sliding SaddleDocument9 pagesSaddle v1-5: Fixed Saddle Sliding Saddleduf fuNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Neck CalculationDocument4 pagesNozzle Neck CalculationAkshat JainNo ratings yet
- Flange Input CalcDocument12 pagesFlange Input CalcdharwinNo ratings yet
- SH1 DHI P0100 GE M01 PRO 5304 - Plant Startup & Shutdown Procedure - Rev.3 (Replace)Document45 pagesSH1 DHI P0100 GE M01 PRO 5304 - Plant Startup & Shutdown Procedure - Rev.3 (Replace)nguyễn hữu trườngNo ratings yet
- Blind Thickness CalculatorDocument2 pagesBlind Thickness Calculatorckd71175% (4)
- ASME V111 Div2 APP 3 Flanges Stress Calculation in ExcelDocument16 pagesASME V111 Div2 APP 3 Flanges Stress Calculation in ExcelPanya Purahong100% (1)
- Weld Neck Body Flange Design Calculation: HE-CGI, HE-CG, Spiral Wound Gaskets For Heat ExchangersDocument25 pagesWeld Neck Body Flange Design Calculation: HE-CGI, HE-CG, Spiral Wound Gaskets For Heat ExchangersLipika GayenNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Reinforcing Calculations For A Pressure Vessel Design - by Abdel Halim GalalaDocument5 pagesNozzle Reinforcing Calculations For A Pressure Vessel Design - by Abdel Halim Galalapaary100% (2)
- BlindDocument3 pagesBlindSajal KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- Flat Head Calculation (Based On Ug 34)Document2 pagesFlat Head Calculation (Based On Ug 34)rustamriyadiNo ratings yet
- 15-501-EP-DS-002 (IG Buffer Vessel Datasheet), Rev.2Document4 pages15-501-EP-DS-002 (IG Buffer Vessel Datasheet), Rev.2Umair A. KhanNo ratings yet
- Stresses in Vessel On Two Sad... Ports Using ZICK Analysis PDFDocument8 pagesStresses in Vessel On Two Sad... Ports Using ZICK Analysis PDFanishNo ratings yet
- Sample FLG CalcDocument6 pagesSample FLG CalcameyyammaiNo ratings yet
- Square Blind Flange With Stiffener ULDocument5 pagesSquare Blind Flange With Stiffener ULjoeriji100% (1)
- Design of Flat Head For HydrotestDocument12 pagesDesign of Flat Head For HydrotestSAGARNo ratings yet
- Netting Materials For Fishing Gear - KlustDocument193 pagesNetting Materials For Fishing Gear - KlustTiago Catuxo67% (3)
- Self Etch or Total EtchDocument3 pagesSelf Etch or Total EtchKarlina KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Design Calculations For Pressure ShellDocument33 pagesDesign Calculations For Pressure ShellGeorge GeorgianNo ratings yet
- Input EchoDocument6 pagesInput EchohgagNo ratings yet
- Manual Calc. Welded Storage Tank API-650Document1 pageManual Calc. Welded Storage Tank API-650safar bahariNo ratings yet
- Flange Input Data Values Description: FLGDocument4 pagesFlange Input Data Values Description: FLGAnonymous AyDvqgNo ratings yet
- Job No. Item No: Doc. No. Tag No. Client Fine Filter Skid FD-38063A/B Bharat Heavy Electricals LimitedDocument3 pagesJob No. Item No: Doc. No. Tag No. Client Fine Filter Skid FD-38063A/B Bharat Heavy Electricals LimitedgauravNo ratings yet
- Examples E4.16.1/E4.6.1 and E4.6.2 BPVC VIII-1: ASME PTB-4-2013Document15 pagesExamples E4.16.1/E4.6.1 and E4.6.2 BPVC VIII-1: ASME PTB-4-2013ordenador90No ratings yet
- Special Packings For Rod Seals Nitrile Rubber (NBR) : MaterialDocument2 pagesSpecial Packings For Rod Seals Nitrile Rubber (NBR) : MaterialTeddy NsNo ratings yet
- Blind Flange Design For 8", 600#, 15B Service LineDocument2 pagesBlind Flange Design For 8", 600#, 15B Service LineGohar ZamanNo ratings yet
- Pressure VesselDocument6 pagesPressure VesselKiranNo ratings yet
- Procoat H.08.HT: Technical SpecificationDocument2 pagesProcoat H.08.HT: Technical SpecificationLewoskiNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base TitrationDocument7 pagesAcid-Base TitrationPok Wan SoonNo ratings yet
- Lab Safety SymbolsDocument12 pagesLab Safety SymbolsIrvingNo ratings yet
- 48 Sweet Corrosion Rate in Oil and Gas PipelinesDocument4 pages48 Sweet Corrosion Rate in Oil and Gas PipelinesuktaindraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Methyl Ester SulfonatesDocument8 pagesChemistry of Methyl Ester SulfonatesYusran FachryNo ratings yet
- Kod One PCR Master Mix Kod One PCR Master Mix - Blue-: TM TMDocument15 pagesKod One PCR Master Mix Kod One PCR Master Mix - Blue-: TM TMShima YousefiNo ratings yet
- Rheological Properties: University of Baghdad Collage of Engineering Department of PetroleumDocument4 pagesRheological Properties: University of Baghdad Collage of Engineering Department of Petroleumعلي خالد كاظم عبودNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Immune FunctionDocument4 pagesNutrition and Immune FunctionEngineering and Scientific International JournalNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument62 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinsJay LourenceNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument6 pagesPowder Metallurgyمذکر حمادیNo ratings yet
- 0620 s16 QP 43 PDFDocument16 pages0620 s16 QP 43 PDFkarishmaNo ratings yet
- QB Ch10 EngDocument81 pagesQB Ch10 Eng羅天佑No ratings yet
- Chem Int CC CH 19 - Equilibrium - Answers PDFDocument12 pagesChem Int CC CH 19 - Equilibrium - Answers PDFChristal EcheverriaNo ratings yet
- Ec 301Document59 pagesEc 301Ganis SanhajiNo ratings yet
- List of Books - Pharmacology: Authorname Book Title Publisher EditionDocument2 pagesList of Books - Pharmacology: Authorname Book Title Publisher EditionAsiya ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Basco Type 500Document12 pagesBasco Type 500Robinson MarinNo ratings yet
- 2012 A Transient Vanadium Flow Battery Model Incorporating Vanadium Crossover and Water Transport Through The Membrane (Agar)Document14 pages2012 A Transient Vanadium Flow Battery Model Incorporating Vanadium Crossover and Water Transport Through The Membrane (Agar)Yasmine YouhannaNo ratings yet
- Description of Cells (SOFC and Na+)Document10 pagesDescription of Cells (SOFC and Na+)210TARUSHNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0023643821007775 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0023643821007775 MainErel Bar-IlanNo ratings yet
- Ductile Iron Grade 60-40-18, Low Temperature ServiceDocument2 pagesDuctile Iron Grade 60-40-18, Low Temperature Servicevamsi patnalaNo ratings yet
- Kalyan Chemistry 2Document13 pagesKalyan Chemistry 2Divyanshu PotaliyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document23 pagesChemical Bonding 1Gowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Xmark™ Microplate Absorbance SpectrophotometerDocument2 pagesXmark™ Microplate Absorbance SpectrophotometerdnajenNo ratings yet
- Shirin Naidu-IA - Osmosis - in - PotatoesDocument8 pagesShirin Naidu-IA - Osmosis - in - PotatoesShirin NaiduNo ratings yet
- Identification of Saltwater Intrusion/assessment Scheme in Groundwater Using The Role of Empirical KnowledgeDocument6 pagesIdentification of Saltwater Intrusion/assessment Scheme in Groundwater Using The Role of Empirical KnowledgeErwin AnshariNo ratings yet