Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Studysmart Chapter 5
Studysmart Chapter 5
Uploaded by
Siti UmairahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Studysmart Chapter 5
Studysmart Chapter 5
Uploaded by
Siti UmairahCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Study Smart
www.studysmart.page.tl
STUDYSMART
CHEMISTRY FORM 4
CHAPTER 5 : CHEMICAL BONDS
5.1 Understanding formation of compounds
5.2 Synthesising ideas on formation of ionic bond
5.3 Synthesising ideas on formation of covalent bond
5.4 Analysing properties of ionic and covalent compounds
5.1 UNDERSTANDING FORMATION OF COMPOUNDS
Condition for the formation of chemical bonds include
the followings
a) Electron in completely filled shell do not take part in
bond formation
b) Only valance electron are involved in bond formation
c) The combining atoms will change their electron arrangement to achieve stable octet electron
arrangements
d) The octet rules :- 2.8 ; 2.8.8 ; 2.8.8.8
5.2 SYNTHESISING IDEAS ON FORMATION OF IONIC BOND
Formed between atoms of metal and non-metal through the transfer of electron. Metal atom
donate/release electron whereas non-metal atoms accepts/receive electrons to achieve the
stable octet electron arrangement
Atoms of elements that donate the electron from positive ions (cations) and atoms that receive
the electrons from negative ions (anions) to achieve a stable electron arrangement.
Examples: Na Na
+
+ e O + 2e O
2-
2.8.1 2.8 2.6 2.8
The positive ions and negative ions are attracted to one another with strong electrostatic force.
The attractive force between the ions is called the ionic bond.
Ionic bond (electrovalent bond) is usually formed by atoms from group 1,2, and 13(metal) with
group 15,16, and 17(non-metal).
The maximum number of electrons transferred in the formation of ionic bond is usually three.
For example, atoms of elements in group 1,2 and 13 donates 1,2, and 3 electrons respectively to
form charged ions with +1, +2, and +3. Atoms of elements in group 15, 16 and 17 receive 3,2,
and 1 electrons respectively to form -3,-2 and -1 charged ions.
Example:
Predict the formula for Sodium Chloride
Na Na
+
+ e Na
+
Cl
-
= NaCl
Cl + e Cl
-
1 1
a) The electron arrangement of sodium is 2.8.1
ELEMENT PROTON
NUMBER
ELECTRON
ARRANGEMENT
Na 11 2.8.1
Cl 17 2.8.7
2
Study Smart
www.studysmart.page.tl
b) Sodium atom has one valence electron. By releasing this electron, sodium atom forms sodium
ion, Na
+
to achieve a stable octet electron arrangement that is 2.8
c) Electron arrangement of chlorine atom is 2.8.7
d) Chlorine atom has seven valence electrons. By receiving 1 electron, chlorine atom forms
chloride ion, Cl
-
with an octet electron arrangement that is 2.8.8
e) Na
+
ions attract Cl
-
ions with strong electrostatic forces. The bond formed is called ionic bond.
f) Draw the diagram
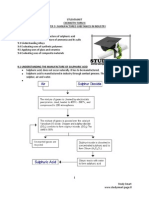
5.3 SYNTHESISING IDEAS ON FORMATION OF COVALENT BOND
This bond is formed when two or more similar or different non-metal atoms share valence
electrons between them, so that each atom gets the duplet or octet electron arrangement that
is a stable electron arrangement for noble gas.
This bond is formed when non-metal atoms bond together [atom-atom from group 12,15,16
and 17]
The number of electron shared can be 1 pair, 2 pairs or 3 pairs. The products of the electron
sharing cause weak Van der Waals forces. These forces become stronger when the molecules
size increases.
Examples:
i) Nitrogen Molecules
a) Nitrogen atom with a 2.5 electron arrangement needs 3 electrons to achieve stable octet
electron arrangement
b) Two nitrogen atoms share 2 pairs of electrons to achieve an octet electron arrangement,
form a nitrogen molecules. Each nitrogen atom can achieve stable electron arrangement.
c) Diagram :
3
Study Smart
www.studysmart.page.tl
ii) Draw the diagram of formation of Water molecule (ESSAY QUESTIONS)
STEP 1 : PREDICT FORMULA
STEP 2 : WRITE THE EXPLANATION (about the number of valence electron, number electron
needed and the way of sharing electron)
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
STEP3 : DRAW THE DIAGRAM
ELEMENT PROTON
NUMBER
ELECTRON
ARRANGEMENT
H
O
4
Study Smart
www.studysmart.page.tl
5.4 ANALYSING PROPERTIES OF IONIC AND COVALENT COMPOUNDS
Comparison between The Formation of Ionic and Covalent.
CHARACTERISTICS IONIC BOND CONVALENT BOND
Element Between metals ( Group 1,2 and 13)
and non-metal (Group 15,16 and 17)
Between non-metal and non-metal
(Group 14,15,16 and 17)
Bond Formation Electron is release by metal atoms
and received by non-metal atoms
(Electron transfer)
Pairs of electrons are shared by the
same or different non-metal atoms.
Types of particles
formed
Metal positive ion (cation)
Non metal negative ion (anions)
Neutral molecules
How to predict
the formula
Determine the charge of ions and
criss-cross
Determine the number of electrons
needed to achieve duplet/octet and
criss-cross
Diagram
Comparison between the physical properties of ionic and covalent compound.
PROPERTIES IONIC COMPOUND COVALENT COMPOUND
Melting
Poing/
Boiling
Point
High because positive ions and
negative ions are attracted by strong
electrostatic forces.
A lot of energy is needed to
overcome the strong forces
Low because of the weak
intermolecular force
Less hear energy is required to
overcome these forces.
Electrical
conductivity
Cannot conduct electricity when in
solid state but able to conduct
electricity when in molten state or
aqueous solution.
In molten state/aqueous solution,
the ions are free to move but in solid
state the ions are not free to move
Cannot conduct electricity in any state
As covalent compound is made up of
neutral molecules, it does not conduct
electricity
Water
solubility
Most are soluble in water but
insoluble in organic solvent
Most are insoluble in water but are
soluble in organic solvent.
Volatility Non-volatile because ions are
attracted by strong electrostatic
forces
Highly volatile because of the weak
intermolecular forces.
You might also like
- Chemistry Malaysian Matriculation Full Notes & Slides For Semester 1 and 2Document1,743 pagesChemistry Malaysian Matriculation Full Notes & Slides For Semester 1 and 2Jay Bee90% (58)
- Physics Malaysian Matriculation Semester 1 Notes CompleteDocument474 pagesPhysics Malaysian Matriculation Semester 1 Notes CompleteJay Bee96% (68)
- Latihan Mip Kimia 2021 Form 4 & 5Document81 pagesLatihan Mip Kimia 2021 Form 4 & 5unknown :)100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Document13 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Helene_mbbt100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 4Document25 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 4Helene_mbbt94% (17)
- BIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 3 - Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument25 pagesBIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 3 - Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membranealpha centauri100% (6)
- Nota Padat Fizik F4 Forces and Pressure NotesDocument24 pagesNota Padat Fizik F4 Forces and Pressure Notesslokkro98% (61)
- DC CircuitDocument2 pagesDC CircuitChocomalteeChocomaltee100% (1)
- Machines Physics CXCDocument5 pagesMachines Physics CXCdemetri lanezNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMDocument11 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMJay Bee83% (29)
- CHEM SPM Chapter 4 Periodic Tble TeacherDocument24 pagesCHEM SPM Chapter 4 Periodic Tble Teacherangie0812No ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Document6 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Mur_nie91% (22)
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 3 CHEMICAL FORMULAE AND EQUATIONSDocument8 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 3 CHEMICAL FORMULAE AND EQUATIONSJay Bee94% (18)
- SPM Form 4 Chemistry Chap 4 ExercisesDocument14 pagesSPM Form 4 Chemistry Chap 4 ExercisesTee Xin Rui67% (3)
- Chemical Bond (SPM Q)Document11 pagesChemical Bond (SPM Q)Luna LatisyaNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 NotesDocument16 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 NotesHongYu Hui100% (4)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Document5 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Azsyerrah Jahini67% (3)
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2013 Question and SchemeDocument283 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2013 Question and SchemeCikgu Faizal87% (15)
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 6 NutritionDocument5 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 6 NutritionzaedmohdNo ratings yet
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2013Document151 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2013Cikgu Faizal100% (15)
- Definition Chemistry Form 4 KSSMDocument4 pagesDefinition Chemistry Form 4 KSSMprebasubah100% (1)
- F4 Chapter 2&3 Essay QDocument4 pagesF4 Chapter 2&3 Essay QNoor Azlin JusohNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 6 ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument14 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 6 ELECTROCHEMISTRYJay Bee91% (11)
- Chemistry SPM State Trial Papers-Form5chap2Document16 pagesChemistry SPM State Trial Papers-Form5chap2Law Jin YaoNo ratings yet
- PBD Assessment Physics Form 4 Chapter 3Document4 pagesPBD Assessment Physics Form 4 Chapter 3Nor ShuhadaNo ratings yet
- Modul Formula Dan Persamaan KimiaDocument25 pagesModul Formula Dan Persamaan Kimiaanon_991690121100% (1)
- Definition Chem SPMDocument6 pagesDefinition Chem SPMSarah Wong100% (1)
- BELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F4Document8 pagesBELONGS TO: .. : Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F4Amalina Kasmunee100% (1)
- Chemistry Quiz Chapter 4 Form 4 @Document3 pagesChemistry Quiz Chapter 4 Form 4 @Mohd Norihwan100% (1)
- SPM Biology 2007 k2Document22 pagesSPM Biology 2007 k2pss smk selandar67% (3)
- Bio-Score Form 4 Chapter Answers SheetDocument23 pagesBio-Score Form 4 Chapter Answers SheetUmair Hisham100% (10)
- Quiz Chapter 2 Form 4 @Document4 pagesQuiz Chapter 2 Form 4 @Mohd Norihwan100% (4)
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2013 SKEMADocument91 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2013 SKEMACikgu Faizal100% (3)
- CompleteDocument17 pagesCompleteTelNo ratings yet
- Solution 1:: Class X Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding ChemistryDocument18 pagesSolution 1:: Class X Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding ChemistryArihant KumarNo ratings yet
- Solution 1:: Class X Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding ChemistryDocument18 pagesSolution 1:: Class X Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding ChemistryvikasNo ratings yet
- 05 Chem Bond - Modul - ChemistryDocument11 pages05 Chem Bond - Modul - Chemistryrudi_z100% (1)
- Chemical BondingDocument13 pagesChemical BondingJonathan MathewNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 ChemicalbondingDocument23 pagesChapter2 ChemicalbondingAbbyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChapter 5 - Chemical BondingSudhan NairNo ratings yet
- Pages From Glencoe - Chemistry - Matter and Change (Mcgraw 2008) ch7Document32 pagesPages From Glencoe - Chemistry - Matter and Change (Mcgraw 2008) ch7api-261034721No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument13 pagesChemical Bondingyashikakhattar043No ratings yet
- 4-Copy of Chemical BondDocument59 pages4-Copy of Chemical BondtiwihNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 04: Structure of Molecules (Topic Wise Questions)Document18 pagesChapter # 04: Structure of Molecules (Topic Wise Questions)husain aliNo ratings yet
- 2.2. Electrons, Bonding and StructureDocument14 pages2.2. Electrons, Bonding and StructureAdwaar HassanNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Structure and Properties of Materials, Ionic Bonding, Covalent BondingDocument33 pagesTopic 4 Structure and Properties of Materials, Ionic Bonding, Covalent BondingKaixin HuangNo ratings yet
- All About Chemical Bonding - CovalentDocument7 pagesAll About Chemical Bonding - CovalentKev WattsNo ratings yet
- 2 Chemical Bonding-NotesDocument6 pages2 Chemical Bonding-Notesvaishnavi GNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Class 11Document26 pagesChemical Bonding Class 11Ketan Singh75% (4)
- Chemical Bonding and CatalysisDocument66 pagesChemical Bonding and CatalysisKaran Padvi 03No ratings yet
- Structure and Bonding. JobsjkkDocument77 pagesStructure and Bonding. JobsjkkkokodejoelNo ratings yet
- 4 Chemical Bonding - After Review - 8!10!2019Document24 pages4 Chemical Bonding - After Review - 8!10!2019AFAQ HYDNo ratings yet
- Exam Paper ChemistryDocument7 pagesExam Paper ChemistryalyssatapouhNo ratings yet
- XI CH 4 Chemistry Notes by AkDocument19 pagesXI CH 4 Chemistry Notes by AkappugmenonNo ratings yet
- CB 1Document4 pagesCB 1Mahmudur Rahman27No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Chemical Bonding For 2023 IcseDocument42 pagesGrade 10 Chemical Bonding For 2023 IcsePushpajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Chemical BondsDocument46 pagesChapter 5 Chemical BondsprebasubahNo ratings yet
- Module in Chemical BondingDocument36 pagesModule in Chemical BondingJaycee De LeonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding ModuleDocument35 pagesChemical Bonding ModuleMark Paul Lipata Benitez100% (2)
- Bonding and Structure - WINTK Sheet 2021Document3 pagesBonding and Structure - WINTK Sheet 2021muoyleng27No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Earning UtcomesDocument24 pagesAtomic Structure: Earning UtcomesdiahemaNo ratings yet
- Formation of Ionic BondsDocument8 pagesFormation of Ionic BondsangjellyNo ratings yet
- Lewis Dot StructureDocument25 pagesLewis Dot StructureQuielle TangonanNo ratings yet
- Note-02 (Chemical Bonding) PDFDocument27 pagesNote-02 (Chemical Bonding) PDFAnowar HossainNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 3 CHEMICAL FORMULAE AND EQUATIONSDocument8 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 3 CHEMICAL FORMULAE AND EQUATIONSJay Bee94% (18)
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMDocument11 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMJay Bee83% (29)
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 6 ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument14 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 6 ELECTROCHEMISTRYJay Bee91% (11)
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 7 ACIDS AND BASESDocument4 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 7 ACIDS AND BASESJay Bee100% (7)
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 9 MANUFACTURED SUBSTANCES IN INDUSTRYDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 9 MANUFACTURED SUBSTANCES IN INDUSTRYJay Bee100% (9)
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 8 SALTSDocument10 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 8 SALTSJay Bee75% (4)
- Physics Final Revision - Waves 2013 PDFDocument14 pagesPhysics Final Revision - Waves 2013 PDFCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- SPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 3 Forces and PressureDocument8 pagesSPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 3 Forces and PressureJay BeeNo ratings yet
- SPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 9 ElectronicsDocument9 pagesSPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 9 ElectronicsJay Bee100% (1)
- SPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 8 ElectromagnetismDocument11 pagesSPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 8 ElectromagnetismJay BeeNo ratings yet
- Physics Final Revision - Electricity 2013 PDFDocument5 pagesPhysics Final Revision - Electricity 2013 PDFCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- SPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 4 Heat and EnergyDocument6 pagesSPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 4 Heat and EnergyJay Bee100% (1)
- SPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 5 Light and VisionDocument8 pagesSPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 5 Light and VisionJay BeeNo ratings yet
- Physics Final Revision - Introduction To Physics 2013 PDFDocument8 pagesPhysics Final Revision - Introduction To Physics 2013 PDFCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- SPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 2 Forces and MotionDocument14 pagesSPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 2 Forces and MotionJay BeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document14 pagesChapter 1John Dave Andales BaguinbinNo ratings yet
- Einstein's Theory of Specific Heats: Classical Concept Review 23Document2 pagesEinstein's Theory of Specific Heats: Classical Concept Review 23Agres KrismantonaNo ratings yet
- Flowguide OP 99-30287Document141 pagesFlowguide OP 99-30287VinodKumarNo ratings yet
- WRC 107 & 297Document10 pagesWRC 107 & 297Anonymous KpVxNXsNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC MODELS AtomicphysicsDocument24 pagesATOMIC MODELS Atomicphysicsahsanbgayo100% (1)
- High WayDocument4 pagesHigh WayAnilkmar P MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - Matrices Study Module Lakshya JEE 2025Document42 pagesChapter 02 - Matrices Study Module Lakshya JEE 2025The JazzNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus Ab FRQ 2017Document7 pagesAP Calculus Ab FRQ 2017ranyNo ratings yet
- Appbrief Porcine TracheaDocument2 pagesAppbrief Porcine TracheamgimohNo ratings yet
- Cap4 (Imperfections in The Atomic Arrangement)Document15 pagesCap4 (Imperfections in The Atomic Arrangement)Azalia TovarNo ratings yet
- Lindeburg ObjectivesDocument21 pagesLindeburg ObjectivesGlendel Alivio EscuyosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Nucleus: 8.1 Properties of Nucleus 8.2 Binding Energy and Mass DefectDocument70 pagesChapter 8: Nucleus: 8.1 Properties of Nucleus 8.2 Binding Energy and Mass DefectJoanne SohNo ratings yet
- Cape Chemistry U2 P1 2010Document10 pagesCape Chemistry U2 P1 2010C.No ratings yet
- Ch.20 ResonanceDocument27 pagesCh.20 ResonanceBeverly PamanNo ratings yet
- 54 - RostamzadehDocument4 pages54 - RostamzadehRidwan FadlikaNo ratings yet
- 10 Deflection-Castigliano TheoremDocument40 pages10 Deflection-Castigliano TheoremGhaffar Laghari100% (1)
- Richard Feynman BiographyDocument5 pagesRichard Feynman Biographyapi-284725456100% (1)
- Chapter7 PDFDocument34 pagesChapter7 PDFWillian DiazNo ratings yet
- Civil Previous Year QuestionsDocument9 pagesCivil Previous Year QuestionsBimal NathNo ratings yet
- Determination of Iron in Cement by Photometric Titration: Titration Application Note T-80Document2 pagesDetermination of Iron in Cement by Photometric Titration: Titration Application Note T-80Xiomara JorgaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Science Fair Projects Using French Fries, Gumdrops, Soap, and Other Organic Stuff PDFDocument129 pagesChemistry Science Fair Projects Using French Fries, Gumdrops, Soap, and Other Organic Stuff PDFale_neiraNo ratings yet
- Experiment Bag FilterDocument14 pagesExperiment Bag FilterMuhammad Adzfar100% (2)
- Near Bit GammaDocument2 pagesNear Bit GammaQiang ZhangNo ratings yet
- 2017 2 Joh MuarDocument3 pages2017 2 Joh MuarLee Shi HockNo ratings yet
- Netflix (Niels Bohr)Document12 pagesNetflix (Niels Bohr)Mico DasilvaNo ratings yet
- Chap 7 Ultra Low Power BioelectronicsDocument3 pagesChap 7 Ultra Low Power BioelectronicsVarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics and Reaction DynamicsDocument3 pagesChemical Kinetics and Reaction DynamicsShri VidhatriNo ratings yet
- Vit MathsDocument2 pagesVit Maths100marksNo ratings yet