Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hvac Formulas
Hvac Formulas
Uploaded by
zoded0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views25 pagesHvac Formulas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHvac Formulas
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views25 pagesHvac Formulas
Hvac Formulas
Uploaded by
zodedHvac Formulas
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 25
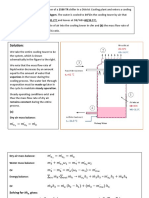
HVAC FORMULAS
CFM = ______BTU/Hr / ( 1.08 x Temperature Difference)
TON OF REFRIGERATION -
The amount of heat required to melt a ton (2000 lbs.) of ice at 32F
288,000 BTU/24 hr.
12,000 BTU/hr.
APPROXIMATELY 2 inches in Hg. (mercury) = 1 psi
WORK =
Force (energy exerted) X Distance
Example: A 150 lb. man climbs a flight of stairs 100 ft. high
Work = 150 lb. X 100 ft.
Work = 15,000 ft.-lb.
ONE HORSEPOWER =
33,000 ft.-lb. of work in 1 minute
ONE HORSEPOWER =
746 Watts
CONVERTING KW to BTU:
1 KW = 3413 BTUs
Example: A 20 KW heater (20 KW X 3413 BTU/KW = 68,260 BTUs)
CONVERTING BTU to KW
3413 BTUs = 1 KW
Example: A 100,000 BTU/hr. oil or gas furnace
(100,000 / 3413 = 29.3 KW)
COULOMB =
6.24 X 1018 (1 Coulomb = 1 Amp)
OHM'S LAW =
E = I x R
I = E / R
R = E / I
Where:
E = voltage (emf)
I = Amperage (current)
R = Resistance (load)
WATTS (POWER) =
volts x amps or P = E x I
P(in KW) = (E x I) / 1000
U FACTOR =
Reciprocal of R factor
1 / R = U
Example:
If R = 19:
U = 1 / 19 = .05 (BTUs transferred / 1 Sq.Ft. / 1F / 1 Hour)
VA
(how the secondary of a transformer is rated) = volts X amps
Example: 24V x .41A = 10 VA
ONE FARAD CAPACITY =
1 amp. stored under 1 volt of pressure
MFD (microfarad) =
1 MFD = 1 Farad / 1,000,000
LRA (Locked rotor amps) =
LRA = FLA x 5 (NOTE: This is a commonly used rule-of-thumb, not a direct conversion)
TEV (shown in equilibrium)
46.7# (Bulb Pressure) = 9.7# (Spring Pressure) + 37# (Evaporator Pressure)
Where:
Bulb Pressure = opening force
Spring and Evaporator Pressures = closing forces
RPM of motor = (60Hz x 120) / (No. of Poles)
1800 RPM Motor slippage makes it about 1750
3600 RPM Motor slippage makes it about 3450
DRY AIR =
78.0% Nitrogen
21.0% Oxygen
1.0% Other Gases
WET AIR =
Same as dry air plus water vapor
SPECIFIC DENSITY = 1 / Specific Volume
SPECIFIC DENSITY OF AIR = 1 / 13.33 = .075 lbs./cu.ft.
STANDARD AIR =
24 Specific Heat (BTUs needed to raise 1 lb. 1 degree)
SENSIBLE HEAT FORMULA (Furnaces):
BTU/hr. Specific Heat X Specific Density X 60 min./hr. =
X CFM X DT
.24 X .075 X 60 X CFM X DT = 1.08 X CFM X DT
ENTHALPHY = h =
Sensible heat + Latent heat
TOTAL HEAT FORMULA
(for cooling, humidifying or dehumidifying)
BTU/hr. = Specific Density X 60 min./hr. X CFM X Dh
= 0.75 x 60 x CFM x Dh
= 4.5 x CFM x Dh
Where Dh = Change in Enthalpy
RELATIVE HUMIDITY =
Moisture present / Moisture air can hold
SPECIFIC HUMIDITY =
Grains of moisture per dry air
7000 GRAINS in 1 lb. of water
DEW POINT =
When wet bulb equals dry bulb
TOTAL PRESSURE (Ductwork) =
Static Pressure + Velocity Pressure
CFM =
Area (sq. ft.) X Velocity (ft. min.)
HOW TO CALCULATE AREA
Rectangular Duct
A = L x W
Round Duct
A = (Pi)r ...or...(Pi)D/4
RETURN AIR GRILLES
Net free area = about 75%
3 PHASE VOLTAGE UNBALANCE =
(100 x maximum deg. from average volts) / Average Volts
NET OIL PRESSURE =
Gross Oil Pressure Suction Pressure
NOTE: The suction pressure must be measured at the crankcase, not the service valve
COMPRESSION RATIO =
Discharge Pressure Absolute / Suction Pressure Absolute
HEAT PUMP AUXILIARY HEAT
Sized at 100% of load
ARI HEAT PUMP RATING POINTS =
47F and 17F
NON-BLEND REFRIGERANTS:
Constant Pressure = Constant Temperature during
Saturated Condition in an evaporator or condenser
BLENDS
Changing Temperature during Saturated Condition in an evaporator or condenser (See Glide)
28 INCHES OF WC =
1 psi
NATURAL GAS COMBUSTION:
Excess Air = 50%
15 ft.3 of air to burn 1 ft.3 of methane produces:
16 ft.3 of flue gases:
1 ft.3 of oxygen
12 ft.3 of nitrogen
1 ft.3 of carbon dioxide
2 ft.3 of water vapor
Another 15 ft.3 of air is added at the draft hood
GAS PIPING (Sizing CF/hr.) =
Input BTUs
Heating Value
Example:
80,000 Input BTUs
1000 (Heating Value per CF of Natural Gas)
= 80 CF/hr.
Example:
80,000 Input BTUs
2550 (Heating Value per CF of Propane)
= 31 CF/hr.
FLAMMABILITY LIMITS
Propane Butane Natural Gas
2.4-9.5 1.9-8.5 4-14
COMBUSTION AIR NEEDED
(PC=Perfect Combustion)
(RC=Real Combustion)
Propane
23.5 ft.3 (PC)
36 ft.3 (RC)
Natural Gas
10 ft.3 (PC)
15 ft.3 (RC)
ULTIMATE CO2 13.7% 11.8%
CALCULATING OIL NOZZLE SIZE (GPH):
BTU Input = Nozzle Size (GPH)
140,000 BTUs
OR
BTU Output
140,000 X Efficiency of Furnace
FURNACE EFFICIENCY:
% Efficiency = energy output / energy input
OIL BURNER STACK TEMPERATURE (Net) =
Highest Stack
Temperature minus
Room Temperature
Example: 520 Stack Temp. 70 Room Temp. = Net Stack
Temperature of 450
KELVIN TO CELSIUS:
C = K 273
CELSIUS TO KELVIN:
K = C + 273
ABSOLUTE TEMPERATURE MEASURED IN KELVINS
SINE = side opposite
COSINE = side adjacent
Sin = hypotenuse
Cos = hypotenuse
TANGENT =
side opposite / side adjacent
PERIMETER OF SQUARE:
P = 4s
Where: P = Perimeter and s = side
PERIMETER OF RECTANGLE:
P = 2l + 2w P Perimeter
l = length
w = width
PERIMETER OF SQUARE
P = a + b + c + d (P = Perimeter)
a = 1st side
b = 2nd side
c = 3rd side
d= 4
th
side
PERIMETER OF CIRCLE:
C = (Pi)D = 2(Pi)r
Where:
C = Circumference
(Pi) = 3.1416
D = Diameter
r = radius
AREA OF SQUARE:
a = s = s x s
A = Area
s = side
AREA OF RECTANGLE:
A = l x w
Where:
A = Area
l = length
w = width
AREA OF TRIANGLE:
A = 1/2bh
Where:
A = Area
b = base
h = height
AREA OF CIRCLE:
A = (Pi)r = (Pi) D/4
Where:
A = Area
(Pi) = 3.1416
r = radius
D = Diameter
VOLUME OF RECTANGULAR SOLID:
V = l x w x h
Where:
V = Volume
l = length
w = width
h = height
VOLUME OF CYLINDRICAL SOLID:
V = (Pi)rh = (Pi) D/4 x h
Where:
V = Volume
p = 3.1416
r = Radius
D = Diameter
h = height
CAPACITANCE IN SERIES:
C = 1 / (C1 + C2)
CAPACITANCE IN PARALLEL:
C = C1 + C2 + . . . . .
GAS LAWS:
Boyles Law: P1 V1 = P2 V2
Where:
P = Pressure (absolute)
V = Volume
Charles Law:
P1 / T1 = P2 / T2
Where:
P = Pressure (absolute)
T = Temperature (absolute)
General Gas Law:
(P1 x V1) / T1 = (P2 x V2) / T2
Where:
P = Pressure (absolute)
V = Volume
T = Temperature (absolute)
PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM:
c2 = a2 + b2
Where:
c = hypotenuse
a & b = sides
Capacity of Schedule 80 steel pipe in foot per length in US gallons:
1 = .0374
1-1/4 = .0666
1-1/2 = .0918
2 = .1535
2-1/2 = .22
3 = .344
4 = .5970
5 = .947
Example 2-1/2" pipe = .22 x 10 feet = 2.2 gallons capacity
Infrared Thermometer Adjustment Values:
Material/Emissivity
Aluminum
Bright/0.09
Anodized/0.55
Oxidized/0.2 to 0.3
Brass
Bright/0.03
Oxidized/0.61
Chromium
Polished/0.08
Copper
Bright/0.05
Oxidized/0.78
Iron and Steel
Polished/0.55
Oxidized/0.85
Nickel
Polished/0.05
Oxidized/0.95
Zinc
Bright/0.23
Oxidized/0.23
Brick
Building/0.45
Paints
White/0.9
Black/0.86
Oil Paints (all)/0.92
Roofing Paper /0.91
Rubber /0.94
Silica /0.42 to 0.62
Water /0.92
Weights and Specific Heats of Substances
Material/Weight (Ib./ft)/Specific Heat (Btu/lb)
Gases
Air (normal temp)/0.075/0.24
Metals
Aluminum/166.5/0.214
Copper/552/0.094
Iron/480/0.118
Lead/710/0.030
Mercury/847/0.033
Steel/492/0.117
Zinc/446/0.096
Liquids
Alcohol/49.6/0.60
Glycerin/83.6/0.576
Oil/57.5/0.400
Water/62.4/1.000
Others
Concrete/147/0.19
Cork/15/0.48
Glass/164/0.199
Ice/57.5/0.504
Masonry/112/0.200
Paper/58/0.324
Rubber/59/0.48
Sand/100/0.195
Stone/138-200/0.20
Tar/75/0.35
Wood, Oak/48/0.57
Wood, Pine/38/0.47
Linear Measurement Equivalents (U.S. Conventional - SI Metric)
1 inch =
2.54 cm
25.4 mm
25400 m
1 foot =
12"
0.304 m
30.48 cm
1 yard =
3'
0.914 m
91.44 cm
1 micron =
0.0000394"
1 millimeter =
1000 m
0.0394"
1 centimeter =
10 mm
0.3937"
1 meter =
100 cm
39.37"
1 kilometer =
1000m
0.62137 miles
Area Equivalents ( U.S. to Metric )
1 in=
0.0065m
1 ft=
144 in
0.093 m
1 yd=
1296 in=
9 ft=
0.836 m
Volume Equivalents ( U.S. and Metric )
1 in=
0.016 L=
16.39 cm
1 ft=
1728 in=
7.481 gal=
28.317 L=
0.0283 m=
28317 cm
1 yd=
27 ft=
46656 in
1 gal=
0.1337 ft=
3.79 L=
231 in=
3785 cm
1 cm=
0.0610237 in
1 L=
61.03 in
1000 cm
0.2642 gal
Velocity Equivalents
1 mi/hr=
1.47 ft/sec
0.87 knot
1.61 km/hr
0.45m/sec
1 ft/sec=
0.68 mi/hr
60 ft/min
0.59 knot
o 1.1 km/hr
0.305 m/sec
1 m/sec=
3.28 ft/sec
2.24 mi/hr
1.94 knot
3.6 km/hr
1 km/hr=
0.91 ft/sec
0.62 mi/hr
0.54 knot
0.28 m/sec
Heat Equivalents
1 Btu=
252 calories
1054.4 J (Joules)
1 kcal (kilocalorie)=
1000 cal
4.1840 kJ
1 Btu/lb=
0.5556 kcal/kg
2.3244 kJ/kg
1kcal/kg=
1.8 Btu/lb
Btu/hr=
0.2931W
You might also like
- Basic HVAC Formulas - Tech TipDocument2 pagesBasic HVAC Formulas - Tech Tipgauravgujar24100% (1)
- Pan Humidifier Load Calculation: Air Conditioning SystemDocument1 pagePan Humidifier Load Calculation: Air Conditioning SystemRamachandran Venkatesh100% (1)
- Sizing Industrial DehumidifiersDocument7 pagesSizing Industrial DehumidifiersTanveer AzizNo ratings yet
- CTDocument3 pagesCTSundar DAACNo ratings yet
- D2.07 Non Segregated Phase Bus DuctsDocument3 pagesD2.07 Non Segregated Phase Bus DuctsSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Scada IO ListDocument3 pagesScada IO ListSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Equations: Hvac Equations, Data, and Rules of ThumbDocument21 pagesEquations: Hvac Equations, Data, and Rules of ThumbzodedNo ratings yet
- Hvac Formulas and ValuesDocument13 pagesHvac Formulas and ValuesRamadan RashadNo ratings yet
- Hvac Formulas PDFDocument25 pagesHvac Formulas PDFManish SinghNo ratings yet
- HVAC FormulasDocument7 pagesHVAC Formulasisaiaspaula80No ratings yet
- Psychrometry Part-2Document11 pagesPsychrometry Part-2Tushar Sharma100% (1)
- HVAC Thermal Load EstimatingDocument28 pagesHVAC Thermal Load EstimatingIntisar Ali SajjadNo ratings yet
- One Btu Equals 1.055 KJ.: Joule (J)Document3 pagesOne Btu Equals 1.055 KJ.: Joule (J)suboo0678No ratings yet
- Example 6 - Cal Supply Air Quantity FCUDocument11 pagesExample 6 - Cal Supply Air Quantity FCUHo Dac ThanhNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Fundamentals PDFDocument27 pagesCooling Tower Fundamentals PDFDarshan Raghunath100% (3)
- Winter Reheat Calculations VimpoDocument7 pagesWinter Reheat Calculations Vimpopsn_kylm100% (2)
- Dehumidification in HVAC System p1 PDFDocument80 pagesDehumidification in HVAC System p1 PDFmanojc68No ratings yet
- HVAC Report FinalDocument50 pagesHVAC Report Finalsohail paracha100% (1)
- CFM and Capacity Calcs 4.5Document9 pagesCFM and Capacity Calcs 4.5hvacrmedicNo ratings yet
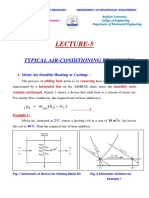
- Lecture-5: Typical Air-Conditioning ProcessesDocument10 pagesLecture-5: Typical Air-Conditioning Processesabrar alhadadNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Efficiency CalculationsDocument3 pagesCooling Tower Efficiency CalculationsPramod SharmaNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE Chiller Course Condenser Water HRDocument36 pagesASHRAE Chiller Course Condenser Water HRabdulzameer100% (1)
- Catalogue Water Cooled Scroll Uwl b5 1Document48 pagesCatalogue Water Cooled Scroll Uwl b5 1rajeshwar sriramNo ratings yet
- VAV PresentationDocument44 pagesVAV PresentationmitasyahuNo ratings yet
- Converting KW Ton To COP or EERDocument2 pagesConverting KW Ton To COP or EERswsw2011No ratings yet
- Bry Air QuestionarysectionDocument7 pagesBry Air Questionarysectionprashant_mahitkar4532No ratings yet
- Understanding Primary Secondary Pumping Part 6 - 5 Ways To Pump An HVAC SystemDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Primary Secondary Pumping Part 6 - 5 Ways To Pump An HVAC SystemDavid O. AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- 6 Tech Specs Hvac 130116 PDFDocument186 pages6 Tech Specs Hvac 130116 PDFBay MưaNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning System LectureDocument9 pagesAir Conditioning System LectureammarNo ratings yet
- Chiller Vs VRF Comparison: October 2020Document7 pagesChiller Vs VRF Comparison: October 2020HR UAENo ratings yet
- P2Document158 pagesP2John MackenzieNo ratings yet
- HVAC SlidesDocument192 pagesHVAC SlidesPato GutigNo ratings yet
- MRI Formulas ConversionsDocument1 pageMRI Formulas ConversionsJoey ManlangitNo ratings yet
- Basic Air Conditioning FormulasDocument1 pageBasic Air Conditioning Formulasravirawat15100% (3)
- Humidification Load Calculation Armstrong PDFDocument3 pagesHumidification Load Calculation Armstrong PDFsyedNo ratings yet
- COIL Selection Formulas PDFDocument3 pagesCOIL Selection Formulas PDFWalter100% (1)
- Heat Gain CalculationsDocument17 pagesHeat Gain CalculationsPrabu RajaNo ratings yet
- Sumair Project Report PPT HVACDocument37 pagesSumair Project Report PPT HVACRishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry: © American Standard Inc. 1999Document90 pagesPsychrometry: © American Standard Inc. 1999Lenard de Leon100% (1)
- Energy Efficiency On Chilled Water SystemDocument56 pagesEnergy Efficiency On Chilled Water Systembalraj100% (1)
- Chilled Water Piping Distribution Systems Ashrae 3-12-14Document78 pagesChilled Water Piping Distribution Systems Ashrae 3-12-14haseebamerNo ratings yet
- Rac Solution Set BDocument12 pagesRac Solution Set BxofigoNo ratings yet
- Heat Load CalculationDocument3 pagesHeat Load CalculationEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Tech Student VersionDocument94 pagesRefrigeration Tech Student VersionAbdalhady JoharjiNo ratings yet
- Catalogo - IOM RTAC Plus (RTAC SVX002A EN) PDFDocument138 pagesCatalogo - IOM RTAC Plus (RTAC SVX002A EN) PDFRaduNo ratings yet
- Cooling Load1111 PDFDocument43 pagesCooling Load1111 PDFJason PaquibulanNo ratings yet
- 5.20. Psychrometrics - Example 5. Summer Cycle (Air Flows To Be Calculated)Document10 pages5.20. Psychrometrics - Example 5. Summer Cycle (Air Flows To Be Calculated)tehtehtehNo ratings yet
- Apd CalculationDocument4 pagesApd CalculationRashel Hasan100% (1)
- Water Cooled ChillerDocument7 pagesWater Cooled ChillerKrishna Murari100% (1)
- Cooling Load EstimationDocument37 pagesCooling Load EstimationHazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Efficiency CalculationsDocument4 pagesCooling Tower Efficiency CalculationsMaman HakimNo ratings yet
- Benefits and Design Tipsfor ChillersDocument4 pagesBenefits and Design Tipsfor ChillersSharon LambertNo ratings yet
- Variable Primary FlowDocument58 pagesVariable Primary FlowAlfredo Merizalde Aviles100% (2)
- RAC 32 Important QuestionDocument10 pagesRAC 32 Important QuestionBalvinderNo ratings yet
- Progress in Refrigeration Science and Technology: Proceedings of the XIth International Congress of Refrigeration, Munich, 1963From EverandProgress in Refrigeration Science and Technology: Proceedings of the XIth International Congress of Refrigeration, Munich, 1963No ratings yet
- A Guide in Practical Psychrometrics for Students and EngineersFrom EverandA Guide in Practical Psychrometrics for Students and EngineersNo ratings yet
- 07-11 Basic HVAC Formulas - Tech TipDocument2 pages07-11 Basic HVAC Formulas - Tech TipAslam100% (2)
- Hvac FormulasDocument25 pagesHvac FormulasMuhammadYounusNo ratings yet
- Hvac Formulas - Ii - PDFDocument25 pagesHvac Formulas - Ii - PDFmrcNo ratings yet
- HVAC FormulasDocument7 pagesHVAC FormulasAshok Kumar S100% (4)
- Calculation of Boiler EfficiencyDocument14 pagesCalculation of Boiler EfficiencyBharat Choksi100% (1)
- Bus DuctDocument60 pagesBus Ductkumaratdbg100% (1)
- Bus DuctDocument60 pagesBus Ductkumaratdbg100% (1)
- Hs Model Math Ben Ver1Document28 pagesHs Model Math Ben Ver1SaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Salary Slip For The Month of February 2014: Design & Engineering LTDDocument1 pageSalary Slip For The Month of February 2014: Design & Engineering LTDSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Saraswata Palit Senior Design Consultant B.E. (Electrical) : AddressDocument2 pagesSaraswata Palit Senior Design Consultant B.E. (Electrical) : AddressSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Tech. Specs. For Metal Doors, Windows, Ventlators Louvers Etc.Document8 pagesTech. Specs. For Metal Doors, Windows, Ventlators Louvers Etc.SaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Tech. Specs. For Water Supply: Contents: Scope Installation Testing & AcceptanceDocument9 pagesTech. Specs. For Water Supply: Contents: Scope Installation Testing & AcceptanceSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Tech. Specs. For Painting, White Washing & Polishing Etc.,: Contents: Scope Installation Acceptance CriteriaDocument10 pagesTech. Specs. For Painting, White Washing & Polishing Etc.,: Contents: Scope Installation Acceptance CriteriaSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Tech. Specs. For Rolling Steel Shutters and Grills: Contents: Scope Installation Acceptance CriteriaDocument4 pagesTech. Specs. For Rolling Steel Shutters and Grills: Contents: Scope Installation Acceptance CriteriaSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Tech. Specs. For 11 KV DP StructureDocument7 pagesTech. Specs. For 11 KV DP StructureSaraswatapalit100% (1)
- Tech. Specs. For Electrical - General: Contents: General Scope of WorkDocument5 pagesTech. Specs. For Electrical - General: Contents: General Scope of WorkSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Electrical Thumb Rules You MUST Follow (Part 5) : Eight Rules To F OllowDocument3 pagesElectrical Thumb Rules You MUST Follow (Part 5) : Eight Rules To F OllowSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- List of SparesDocument6 pagesList of SparesSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Tender Document For POL Depot, Cochin: Tender # IBP/BL/P-10/COC/01 Due Date 29Document1 pageTender Document For POL Depot, Cochin: Tender # IBP/BL/P-10/COC/01 Due Date 29SaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Scope and Description of Civil & Structural WorkDocument13 pagesScope and Description of Civil & Structural WorkSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Scope and Description of Civil & Structural WorkDocument13 pagesScope and Description of Civil & Structural WorkSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- General Electrical ItemsDocument1 pageGeneral Electrical ItemsSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Practices For Grounding and Bonding of Cable Trays - EEPDocument5 pagesPractices For Grounding and Bonding of Cable Trays - EEPSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Tariff Metering PanelsDocument2 pagesTariff Metering PanelsSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Ziegler Nichols Matlab PDFDocument8 pagesZiegler Nichols Matlab PDFMarco Arcos100% (2)
- Optimal Power Flow Using Genetic AlgorithmDocument6 pagesOptimal Power Flow Using Genetic AlgorithminesNo ratings yet
- HACK THE BOX - Omni 10.10.10.204 (Writeup/Walkthrough)Document16 pagesHACK THE BOX - Omni 10.10.10.204 (Writeup/Walkthrough)Jean PierreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document21 pagesChapter 3hailemebrahtuNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic SystemsDocument4 pagesHydraulic SystemsJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- The Calibration and Use of Torque Meters Used in Packaging ApplicationsDocument3 pagesThe Calibration and Use of Torque Meters Used in Packaging ApplicationsfelipeNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Management and Its Impact On Profitability-A Study On British American Tobacco Bangladesh Ltd.Document43 pagesWorking Capital Management and Its Impact On Profitability-A Study On British American Tobacco Bangladesh Ltd.Taz UddinNo ratings yet
- Electricity IjsoDocument3 pagesElectricity IjsoEr Nikunj VelaniNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Ballpoint Ink Ageing Parameters Using GC - MSDocument14 pagesA Comparative Study of Ballpoint Ink Ageing Parameters Using GC - MStweety492No ratings yet
- User Manual: HGM1790N Genset ControllerDocument27 pagesUser Manual: HGM1790N Genset Controllereduardoguerra155_604No ratings yet
- Eng - Manage - Syst - Disc 060125Document12 pagesEng - Manage - Syst - Disc 060125greenNo ratings yet
- Tugas Fisika TerapanDocument8 pagesTugas Fisika TerapanIkha AssipNo ratings yet
- Tds Plexus Ma420 EngDocument2 pagesTds Plexus Ma420 EngCarlos SantosNo ratings yet
- Hardware Manual: Programmable ControllerDocument199 pagesHardware Manual: Programmable ControllerQuang BáchNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Et Al. 2019Document17 pagesAhmed Et Al. 2019Salvador Mansilla BastíasNo ratings yet
- Eagle FormationDocument36 pagesEagle FormationBēn Šāļem HīchēmNo ratings yet
- Attempt Three Questions: ENGG10033Document26 pagesAttempt Three Questions: ENGG10033Kamran AliNo ratings yet
- Domain ModellingDocument33 pagesDomain ModellingZhichaoWangNo ratings yet
- Transient Simulation of Refrigerated and Chilled S PDFDocument9 pagesTransient Simulation of Refrigerated and Chilled S PDFAngel Basurto GilerNo ratings yet
- How To View and Transfer FSMO Roles in The Graphical User InterfaceDocument8 pagesHow To View and Transfer FSMO Roles in The Graphical User Interfaceapi-3774147100% (1)
- Huawei H12 211 PDFDocument106 pagesHuawei H12 211 PDFriyasathsafran100% (1)
- Lab 3Document21 pagesLab 3Zhansaya KozhdanNo ratings yet
- Grid Solutions: Auxilliary RelaysDocument4 pagesGrid Solutions: Auxilliary RelaysAshwini Kumar RaiNo ratings yet
- Technical DataDocument2 pagesTechnical DataSaleh El-hawaryNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic A350Document10 pagesAerodynamic A350HelloWorld100% (1)
- Grade 8 Modal AdverbsDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Modal AdverbsJoshua Lander Soquita Cadayona100% (3)
- New Reference Equation of State For Associating LiquidsDocument13 pagesNew Reference Equation of State For Associating LiquidsDiego Hernández PastorNo ratings yet
- OrCAD PSpice Advanced AnalysisDocument2 pagesOrCAD PSpice Advanced AnalysisdavkavkaNo ratings yet
- Apache Druid: Sudhindra Tirupati NagarajDocument12 pagesApache Druid: Sudhindra Tirupati NagarajAnkit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- FTR TEST REPORT OF MAHINDRA 605 DI I Aug 2020Document57 pagesFTR TEST REPORT OF MAHINDRA 605 DI I Aug 2020Mekh MitraNo ratings yet