Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Light Electricity Photovoltaic Effect
Uploaded by
Sindhu SundaraiyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Light Electricity Photovoltaic Effect
Uploaded by
Sindhu SundaraiyaCopyright:
Available Formats
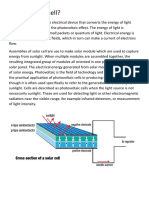
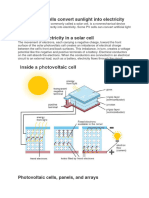
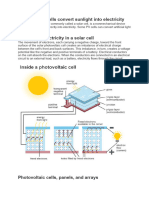
A solar cell (also called a photovoltaic cell) is an electrical device that converts the energy of
light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect. It is a form of photoelectric cell, defined
as a device whose electrical characteristicse.g. current, voltage, or resistancevary when
exposed to light.
Cells can be described as photovoltaic even when the light source is not necessarily sunlight
(lamplight, artificial light, etc.) Photovoltaic cells are used as a photodetector (for example
infrared detectors), detecting light or other electromagnetic radiation near the visible range, or
measuring light intensity.
The operation of a photovoltaic (PV) cell requires 3 basic attributes:
The absorption of light, generating either electron-hole pairs or excitons.
The separation of charge carriers of opposite types.
The separate extraction of those carriers to an external circuit.
In contrast, a solar thermal collector supplies heat by absorbing sunlight, for the purpose of either
direct heating or indirect electrical power generation from heat. A "photoelectrolytic cell"
(photoelectrochemical cell), on the other hand, refers either to a type of photovoltaic cell (like
that developed by Edmond Becquerel and modern dye-sensitized solar cells), or to a device that
splits water directly into hydrogen and oxygen using only solar illumination.
You might also like
- PV Questions Arjun - MergedDocument148 pagesPV Questions Arjun - MergedArjun Sankar0% (1)
- EXP-01 Current-Voltage Charcteristic, Power Curve & Efficiency of A Solar ModuleDocument6 pagesEXP-01 Current-Voltage Charcteristic, Power Curve & Efficiency of A Solar ModulevincentNo ratings yet
- Photo Voltaic CellDocument1 pagePhoto Voltaic CellSarath YarramalliNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell 1Document1 pageSolar Cell 1Samira Kumar beheraNo ratings yet
- TEN100: Quiz 02 - Solar Power Study GuideDocument2 pagesTEN100: Quiz 02 - Solar Power Study GuidenhstechnologyNo ratings yet
- Solar CellDocument1 pageSolar CellDinesh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Current-Voltage Charcteristic, Power Curve & Efficiency of A Solar ModuleDocument6 pagesCurrent-Voltage Charcteristic, Power Curve & Efficiency of A Solar ModuleKzandra KatigbakNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell A Solar Cell, or Photovoltaic Cell, Is An Electrical Device That Converts The Energy of Light Directly IntoDocument2 pagesSolar Cell A Solar Cell, or Photovoltaic Cell, Is An Electrical Device That Converts The Energy of Light Directly IntoET163018 Khaled ArjuNo ratings yet
- CO4 Material 1Document5 pagesCO4 Material 1SAI MNo ratings yet
- What Is Solar Cell Working Mechanism Why We Use Solar Cell P-V System Describe Different Types of Solar Cell Efficiency Uses of Solar CellDocument9 pagesWhat Is Solar Cell Working Mechanism Why We Use Solar Cell P-V System Describe Different Types of Solar Cell Efficiency Uses of Solar CellrishabhNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell Working PrincipleDocument9 pagesSolar Cell Working PrincipleWinry Rockbell0% (1)
- A Solar CellDocument22 pagesA Solar CellSejal andraskarNo ratings yet
- Examen Final de Práctica 2 - How Does Photovoltaics WorkDocument2 pagesExamen Final de Práctica 2 - How Does Photovoltaics Workdaniela BroccardoNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic EffectDocument2 pagesPhotovoltaic EffectSarwan KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity: Electronics Engineering DepartmentDocument50 pagesBasic Electricity: Electronics Engineering DepartmentMartin John RamirezNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic ModuleDocument3 pagesPhotovoltaic ModuleAung MyatNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic CellDocument12 pagesPhotovoltaic CellChristopher WalkerNo ratings yet
- Solar LunaaDocument36 pagesSolar Lunaasuraj choudhuryNo ratings yet
- Uasenglishc431 20 0099muhamadnasfaalfiDocument1 pageUasenglishc431 20 0099muhamadnasfaalfinasfaalfiNo ratings yet
- Electronics in Daily LifeDocument40 pagesElectronics in Daily LifeBlind LuvNo ratings yet
- OptoelectonicsDocument1 pageOptoelectonicswalbrobatNo ratings yet
- Define ElectricityDocument7 pagesDefine ElectricityEdith Stein Ibañez PapaNo ratings yet
- What Is Solar Power and Solar Power PlantDocument4 pagesWhat Is Solar Power and Solar Power PlantKHILY SAXENANo ratings yet
- SOLARDocument5 pagesSOLARKim CanilloNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy - Energy From The SunDocument4 pagesSolar Energy - Energy From The SunAntony RatheeshNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Cell: Solar Energy Can Be Converted To Thermal (Or Heat) Energy and Used ToDocument4 pagesPhotovoltaic Cell: Solar Energy Can Be Converted To Thermal (Or Heat) Energy and Used To123nilNo ratings yet
- Report TextDocument2 pagesReport TextFadlillah IhsanNo ratings yet
- Solar Mobile ChargerDocument19 pagesSolar Mobile ChargerShibu100% (1)
- ReportDocument1 pageReportNishkarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronics TransducerDocument5 pagesOptoelectronics TransducerNoman M HasanNo ratings yet
- Of EnglishDocument6 pagesOf EnglishEduardo Joaquim Guariroba QuintelaNo ratings yet
- 2 Solar PowerPoint PresentationDocument37 pages2 Solar PowerPoint Presentation20cs068No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document58 pagesChapter 3digiy40095No ratings yet
- Some Terms To Remember For Midterm Exam Elec 70Document4 pagesSome Terms To Remember For Midterm Exam Elec 70KentNo ratings yet
- Solar PhotovoltaicDocument9 pagesSolar PhotovoltaicKamalNo ratings yet
- Solarcellreport 180317212808Document61 pagesSolarcellreport 180317212808sumitsharma.280702No ratings yet
- Solar Mobile Charger: Department of Ece - Aits, RajampetDocument1 pageSolar Mobile Charger: Department of Ece - Aits, RajampetMamilla BabuNo ratings yet
- FM-Farm MechanicsDocument13 pagesFM-Farm MechanicsMaidan Ali SultanNo ratings yet
- Unit V Emerging Solar Cell TechnologiesDocument16 pagesUnit V Emerging Solar Cell TechnologiesArchana Diwakar RanjishNo ratings yet
- English PresentationDocument8 pagesEnglish PresentationNabiha PutriNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On SolarmobilechargerDocument25 pagesSeminar Report On SolarmobilechargerSujana Suji100% (1)
- Photovoltaic Cells EssayDocument4 pagesPhotovoltaic Cells EssayIulia NeaguNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Introduction of Photovoltaic CellDocument48 pagesChapter-1 Introduction of Photovoltaic Cellkalyan kingNo ratings yet
- How Solar Cells Convert Sunlight Into ElectricityDocument4 pagesHow Solar Cells Convert Sunlight Into Electricityapi-434997630No ratings yet
- Solar Mobile ChargerDocument21 pagesSolar Mobile ChargerPrabir Kumar Pati33% (3)
- Exp 5Document6 pagesExp 5HR HabibNo ratings yet
- Electrical EnergyDocument1 pageElectrical EnergyBlack ThunderNo ratings yet
- Solar Cells and The PhotoDocument4 pagesSolar Cells and The PhotoLud EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITYDocument6 pagesELECTRICITYsamuel rojasNo ratings yet
- Solar AssignmentDocument52 pagesSolar AssignmentshehzadchoudhryNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument2 pagesSolar EnergyPalls the kingNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument2 pagesSolar EnergyPalls the kingNo ratings yet
- Solar Trainer ManualDocument41 pagesSolar Trainer ManualShah Razin100% (1)
- Solar PowerDocument6 pagesSolar PowerkusumchitikaNo ratings yet
- Example of Electrochemical Cell Producing Energy: Name: D Jay M. MerecueloDocument1 pageExample of Electrochemical Cell Producing Energy: Name: D Jay M. Merecuelod jay mereculoNo ratings yet
- Solar CellDocument127 pagesSolar CellSunil Pandey100% (3)
- JurnalDocument4 pagesJurnalzamzul ariefNo ratings yet
- Mass. It Is Approximately Equal To: Fig.1: Air Mass. Fig.2: Effect of AMDocument6 pagesMass. It Is Approximately Equal To: Fig.1: Air Mass. Fig.2: Effect of AMSajjad HossainNo ratings yet
- GP ProjectDocument19 pagesGP ProjectdhurgeshmalothNo ratings yet
- Documents Required For PassportDocument5 pagesDocuments Required For PassportSindhu SundaraiyaNo ratings yet
- Proof of AddressDocument4 pagesProof of AddressSindhu SundaraiyaNo ratings yet
- w w in radianst Φ Φ in radiansh Y=SinwtDocument7 pagesw w in radianst Φ Φ in radiansh Y=SinwtSindhu SundaraiyaNo ratings yet
- KaveripoompatinamDocument2 pagesKaveripoompatinamSindhu SundaraiyaNo ratings yet
- Intelligent BuildingDocument6 pagesIntelligent BuildingSindhu SundaraiyaNo ratings yet