Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solar Energy
Uploaded by
Palls the kingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solar Energy
Uploaded by
Palls the kingCopyright:
Available Formats
Photovoltaic cells convert sunlight into electricity
A photovoltaic (PV) cell, commonly called a solar cell, is a nonmechanical device
that converts sunlight directly into electricity. Some PV cells can convert artificial light
into electricity.
The flow of electricity in a solar cell
The movement of electrons, each carrying a negative charge, toward the front
surface of the solar photovoltaic cell creates an imbalance of electrical charge
between the cell's front and back surfaces. This imbalance, in turn, creates a voltage
potential like the negative and positive terminals of a battery. Electrical conductors
on the cell absorb the electrons. When the conductors are connected in an electrical
circuit to an external load, such as a battery, electricity flows through the circuit.
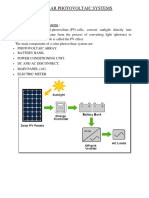
Photovoltaic cells, panels, and arrays
The PV cell is the basic building block of a PV system. Individual cells can vary from
0.5 inches to about 4.0 inches across. However, one cell only produces 1 or 2 Watts,
which is only enough electricity for small uses, such as powering calculators or
wristwatches.
Photovoltaic cells generate direct current (DC) electricity. DC electricity can be used
to charge batteries that power devices that use direct current electricity. Nearly all
electricity is supplied as alternating current (AC) in electricity transmission and
distribution systems. Devices called inverters are used on PV panels or in arrays to
convert the DC electricity to AC electricity.
PV cells and panels will produce the most electricity when they are directly facing the
sun. PV panels and arrays can use tracking systems that keep the panels facing the
sun, but these systems are expensive. Most PV systems have panels in a fixed
position that are usually facing directly south in the northern hemisphere—directly
north in the southern hemisphere—and at an angle that optimizes the physical and
economic performance of the system.
Applications of photovoltaic systems
The smallest photovoltaic systems power calculators and wristwatches. Larger
systems can provide electricity to pump water, power communications equipment,
supply electricity for a single home or business, or supply electricity to thousands of
electricity consumers.
You might also like
- Role of Solar Farm in Power Factor Improvement of Grid Connected SystemsDocument20 pagesRole of Solar Farm in Power Factor Improvement of Grid Connected SystemsDevyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Solar Power For Beginners - The Ultimate Guide On Mastering The Basics Designs and InstallationsDocument78 pagesSolar Power For Beginners - The Ultimate Guide On Mastering The Basics Designs and InstallationsC. A.100% (1)
- InverterDocument23 pagesInverterBittu Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- SolarDocument57 pagesSolarRaghavendra Raghav100% (1)
- Solar Electricity Generation System with a DIY Sun-Tracking PropositionFrom EverandSolar Electricity Generation System with a DIY Sun-Tracking PropositionNo ratings yet
- Solar Street Light Project ReportDocument27 pagesSolar Street Light Project ReportVinod JadavNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument2 pagesSolar EnergyPalls the kingNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument7 pagesSolar SystemPalls the kingNo ratings yet
- Artice For Magazine Solar Energy by Naman Pandey B.Tech 2nd YearDocument9 pagesArtice For Magazine Solar Energy by Naman Pandey B.Tech 2nd YearNaman PandeyNo ratings yet
- History of Solar PowerDocument3 pagesHistory of Solar PowersmshivaNo ratings yet
- 22661-RET Notes-UNIT 02Document25 pages22661-RET Notes-UNIT 02jayeshdeore398No ratings yet
- SOLARDocument5 pagesSOLARKim CanilloNo ratings yet
- Report and ExplanationDocument2 pagesReport and ExplanationJasyne Jen DasmariñasNo ratings yet
- How A PV System Works - pdf-20200211100803465Document9 pagesHow A PV System Works - pdf-20200211100803465ahmed abusnoubarNo ratings yet
- Solar Power Plant: Government Engineering College BharatpurDocument29 pagesSolar Power Plant: Government Engineering College BharatpurHinduja KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Photo Voltaic CellsDocument2 pagesPhoto Voltaic CellsRomina NitaNo ratings yet
- Bypass Diodes in Solar PanelsDocument4 pagesBypass Diodes in Solar PanelsKeshav JhaNo ratings yet
- CO4 Material 1Document5 pagesCO4 Material 1SAI MNo ratings yet
- Peres Unit 3Document86 pagesPeres Unit 3ulaganathanNo ratings yet
- PHOTOVOLTAICSDocument27 pagesPHOTOVOLTAICSbrian otienoNo ratings yet
- Cell, Module, Panel, ArrayDocument2 pagesCell, Module, Panel, ArrayPNo ratings yet
- Main Components: Solar PanelsDocument2 pagesMain Components: Solar PanelsElmer Bayani BardonNo ratings yet
- SOLAR 101: HOW SOLAR ENERGY WORKS (STEP BY STEPDocument36 pagesSOLAR 101: HOW SOLAR ENERGY WORKS (STEP BY STEPAbhay UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Safari - Oct 8, 2020 at 10:40 AMDocument1 pageSafari - Oct 8, 2020 at 10:40 AMMustafa SalahNo ratings yet
- Solar Power PlantDocument65 pagesSolar Power PlantHil GloriosoNo ratings yet
- Solar Photvoltaics: Dr.A.M.Surendra KumarDocument31 pagesSolar Photvoltaics: Dr.A.M.Surendra KumarHarish A.P.No ratings yet
- PV Lesson Plan 2 Solar Electric ArraysDocument4 pagesPV Lesson Plan 2 Solar Electric ArraysaliNo ratings yet
- Bypass Diode For Solar Panel Protection: Bypass Diodes in PV PanelsDocument5 pagesBypass Diode For Solar Panel Protection: Bypass Diodes in PV PanelsvarunNo ratings yet
- Green Engineering Group PresentationDocument11 pagesGreen Engineering Group Presentationkaustubh sarodeNo ratings yet
- Solar Inverter and Tracking SystemDocument20 pagesSolar Inverter and Tracking SystemGANDE SAI KIRANNo ratings yet
- RW 0004PhotovoltaicsRev5Document4 pagesRW 0004PhotovoltaicsRev5Olawale John AdeotiNo ratings yet
- TEN100: Quiz 02 - Solar Power Study GuideDocument2 pagesTEN100: Quiz 02 - Solar Power Study GuidenhstechnologyNo ratings yet
- Group3-SECT W.answersDocument44 pagesGroup3-SECT W.answersJustino BalaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document58 pagesChapter 3digiy40095No ratings yet
- Solar PhotovoltaicDocument9 pagesSolar PhotovoltaicKamalNo ratings yet
- EsquivelVilchisA TermoApl 36 PhotovoltaicSystem Nov152014Document9 pagesEsquivelVilchisA TermoApl 36 PhotovoltaicSystem Nov152014EsquivelAndiieNo ratings yet
- Solar PowerDocument6 pagesSolar PowerkusumchitikaNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaics: What Is Photovoltaic Solar Energy (PV) ?Document4 pagesPhotovoltaics: What Is Photovoltaic Solar Energy (PV) ?Dawit TilahunNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic System: How Do These Systems Work?Document1 pagePhotovoltaic System: How Do These Systems Work?SumiNo ratings yet
- Harnessing the Sun: A Brief History of Solar Energy TechnologyDocument44 pagesHarnessing the Sun: A Brief History of Solar Energy TechnologyBobby SeroNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Vocabulary 2Document3 pagesSolar Energy Vocabulary 2phangiangchau83No ratings yet
- Design and Construction of A Solar Powered Streetlight SystemDocument7 pagesDesign and Construction of A Solar Powered Streetlight Systemsamuel mechNo ratings yet
- Report TextDocument2 pagesReport TextFadlillah IhsanNo ratings yet
- TEE4430 Lecture 8 Notes Solar PVDocument7 pagesTEE4430 Lecture 8 Notes Solar PVJpricarioNo ratings yet
- Effect of Shading On Photovoltaic Cell: Ekpenyong, E.E and Anyasi, F.IDocument6 pagesEffect of Shading On Photovoltaic Cell: Ekpenyong, E.E and Anyasi, F.IM VetriselviNo ratings yet
- Bypass Diodes in Solar PanelsDocument5 pagesBypass Diodes in Solar PanelsEmil Florin TutaNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy L M - U N 4 - Session 15 16Document12 pagesSolar Energy L M - U N 4 - Session 15 16DHANANJAY POPAT MANENo ratings yet
- How Solar Works: Solar Photovoltaic (PV) System ComponentsDocument1 pageHow Solar Works: Solar Photovoltaic (PV) System ComponentsPetros MelakuNo ratings yet
- Paper ViewDocument11 pagesPaper Viewsuresh151971No ratings yet
- Solar Energy - Energy From The SunDocument4 pagesSolar Energy - Energy From The SunAntony RatheeshNo ratings yet
- Solar PV Cells IUT EEE 4531 Energy ConveDocument22 pagesSolar PV Cells IUT EEE 4531 Energy ConveelsyaelizzarNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Solar Power System For Rural Household Purposes: M/s. ENERRSTO Pvt. Ltd. ChennaiDocument20 pagesIntelligent Solar Power System For Rural Household Purposes: M/s. ENERRSTO Pvt. Ltd. ChennaikarthicktamilmaniNo ratings yet
- History and Working Principle of Solar CellsDocument4 pagesHistory and Working Principle of Solar Cellszamzul ariefNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Cells Series and Parallel CombinationsDocument11 pagesPhotovoltaic Cells Series and Parallel CombinationsHasnain AshrafNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic ModuleDocument3 pagesPhotovoltaic ModuleAung MyatNo ratings yet
- Projectreport REDocument15 pagesProjectreport REUnzillahNo ratings yet
- Aquaponics PapersDocument4 pagesAquaponics PapersSheila Marie AmigoNo ratings yet
- Ee 147Document3 pagesEe 147Menchie LabadanNo ratings yet
- Project Topic:Solar Panel: Worked By:lavdimir Ferraj& Briken Shehaj Accepted From Prof - Sonila DaiuDocument16 pagesProject Topic:Solar Panel: Worked By:lavdimir Ferraj& Briken Shehaj Accepted From Prof - Sonila DaiuBriken ShehajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Solar PowerDocument112 pagesChapter 2 Solar PowerBewnet GetachewNo ratings yet
- Vedii 2Document2 pagesVedii 2Palls the kingNo ratings yet
- Sump CapacityDocument1 pageSump CapacityPalls the kingNo ratings yet
- What Are Pumping Systems?: Pumping Systems Account For Nearly 20% of The World's Electrical Energy Demand. FurthermoreDocument1 pageWhat Are Pumping Systems?: Pumping Systems Account For Nearly 20% of The World's Electrical Energy Demand. FurthermorePalls the kingNo ratings yet
- Structure and CompositionDocument11 pagesStructure and CompositionPalls the king100% (1)
- StructrueDocument1 pageStructruePalls the kingNo ratings yet
- The Side Channel Pump - A niche product between displacement pump and centrifugal pumpDocument4 pagesThe Side Channel Pump - A niche product between displacement pump and centrifugal pumpTrần Trung DũngNo ratings yet
- Solar System 2Document1 pageSolar System 2Palls the kingNo ratings yet