Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Are Pumping Systems?: Pumping Systems Account For Nearly 20% of The World's Electrical Energy Demand. Furthermore
Uploaded by
Palls the kingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Are Pumping Systems?: Pumping Systems Account For Nearly 20% of The World's Electrical Energy Demand. Furthermore
Uploaded by
Palls the kingCopyright:
Available Formats
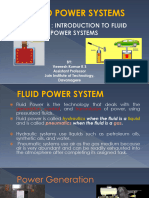
What are Pumping Systems?
Pumping systems account for nearly 20% of the world’s electrical energy demand. Furthermore,
they range between 25-50% of the energy usage in certain industrial plant operations. The use of
pumping systems is widespread. They provide domestic, commercial, and agricultural services.
In addition, they provide municipal water and wastewater services, and industrial services for
food processing, chemical, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and mechanical industries.
The function of a Pump
Pumps have two main purposes:
Transfer of liquid from one place to another place (e.g. water from an underground
aquifer into a water storage tank)
Circulate liquid around a system (e.g. cooling water or lubricants through machines
and equipment)
Components of Pumping System
The main components of a pumping system are:
Pumps (different types of pumps are explained in section 2)
Prime movers: electric motors, diesel engines or air system
The piping used to carry the fluid
Valves used to control the flow in the system
Other fittings, controls, and instrumentation
End-use equipment, which has different requirements (e.g. pressure, flow) and
therefore determines the pumping system components and configuration. Examples
include heat exchangers, tanks and hydraulic machines
Pumping System Characteristics
The pressure is needed to pump the liquid through the system at a certain rate. This pressure has
to be high enough to overcome the resistance of the system, which is also called “head”. The
total head is the sum of the static head and friction head.
You might also like
- B.E Mech - Regulations 2010 Fluid Power Systems Smex1022Document18 pagesB.E Mech - Regulations 2010 Fluid Power Systems Smex1022yuvaraja sNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4actuation System For MechatronicsDocument62 pagesPresentation 4actuation System For MechatronicswabdushukurNo ratings yet
- Module 2 HPDocument18 pagesModule 2 HPU4 CreationZNo ratings yet
- PumpsaDocument1 pagePumpsaJhon HernandezNo ratings yet
- AirSystem - Hydraulic SystemDocument2 pagesAirSystem - Hydraulic SystemYves CaraangNo ratings yet
- Fluid CW HydrDocument7 pagesFluid CW HydrSarah JonesNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic SystemDocument7 pagesHydraulic SystemHamza Munir100% (1)
- Piping System Basics: Delivering The Lifeblood of CivilizationDocument15 pagesPiping System Basics: Delivering The Lifeblood of Civilizationpc_chikyNo ratings yet
- Module 1to 4Document18 pagesModule 1to 4Punith JayramNo ratings yet
- Fluid Power DME 6TH SEMDocument58 pagesFluid Power DME 6TH SEMAman Ahmed MokamiNo ratings yet
- ME 407 M2 Ktuassist - inDocument39 pagesME 407 M2 Ktuassist - inAnirudh Madhav KakkadNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic SystemDocument7 pagesHydraulic SystemJeff UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Intro PDFDocument81 pagesHydraulics Intro PDFavinash babuNo ratings yet
- Amta6 7 Using Hydraulic SystemsDocument26 pagesAmta6 7 Using Hydraulic SystemsMohammed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Design of Oressurized Irrigation SystemsDocument413 pagesDesign of Oressurized Irrigation SystemsCisse Twizeyimana100% (7)
- Design of Oressurized Irrigation SystemsDocument410 pagesDesign of Oressurized Irrigation SystemsCisse TwizeyimanaNo ratings yet
- FPS Module 1 Class 1Document17 pagesFPS Module 1 Class 1Shnzak GiriNo ratings yet
- CH 1 FPSDocument55 pagesCH 1 FPSkidus tsegayeNo ratings yet
- FLUID POWER SYSTEMS Theory and PracticeDocument31 pagesFLUID POWER SYSTEMS Theory and PracticeRAMAR MNo ratings yet
- Mecha 2Document4 pagesMecha 2Clevin DominicNo ratings yet
- R&A - Module 2Document85 pagesR&A - Module 2The UltimateNo ratings yet
- Exercise No.:1 Introduction To Mechatronics SystemDocument5 pagesExercise No.:1 Introduction To Mechatronics SystemPATAN ASIF KHAN STUDENT - MECHNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document86 pagesUnit 1Kalaiselvan PunniyamoorthyNo ratings yet
- 2013 Lect0 Intro MechfluDocument55 pages2013 Lect0 Intro MechflumustikaaryantiNo ratings yet
- 7 BTech Automation Lab ManualDocument48 pages7 BTech Automation Lab ManualA ABHISHEK MARSHALLNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1introduction of Fluid PowerDocument10 pagesChapter 1introduction of Fluid PowerBassant FadelNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic SystemDocument28 pagesHydraulic SystemSamiha Maysoon Nooria0% (1)
- Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument11 pagesApplied Hydraulics and Pneumaticsrajkiran_rajNo ratings yet
- History of Fluid PowerDocument7 pagesHistory of Fluid PowerNEELIMANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pneumatics and Hydraulics: Mr. M.MoadiDocument65 pagesIntroduction To Pneumatics and Hydraulics: Mr. M.MoadiDerrick Maatla MoadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Hydraulic Pump L1 UpdatedDocument75 pagesChapter 2 Hydraulic Pump L1 Updatedkidus tsegayeNo ratings yet
- Notes AM - MODULE 2 Updated - 13062021Document85 pagesNotes AM - MODULE 2 Updated - 13062021MUHAMMED FAISALNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 Introduction To Pneumatics and Hydraulics SystemDocument60 pagesCH - 1 Introduction To Pneumatics and Hydraulics SystemEyasu demsewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document27 pagesChapter 2mohmed4731No ratings yet
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic System, 4th Mechanical Dep. (1) - 1Document107 pagesHydraulic and Pneumatic System, 4th Mechanical Dep. (1) - 1Mina MagdyNo ratings yet
- HYDRAULICS&PNEUMATICScontrol - diagram-AUTOMATION 1Document40 pagesHYDRAULICS&PNEUMATICScontrol - diagram-AUTOMATION 1Marlowe Cris MenceroNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - Hydraulic Transmission - With Numericals - Dec 16Document17 pagesChapter - 2 - Hydraulic Transmission - With Numericals - Dec 16Gaming SukantNo ratings yet
- Report 1: Comparison Between Electric, Hydraulic and Pneumatic Drive SystemsDocument7 pagesReport 1: Comparison Between Electric, Hydraulic and Pneumatic Drive SystemsMohamed HassanNo ratings yet
- Industrial HydraulicsDocument89 pagesIndustrial Hydraulicsnishhhengg100% (2)
- ATA 29-Hydraulic System: SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024Document22 pagesATA 29-Hydraulic System: SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024Ruskee PatawaranNo ratings yet
- Basic Hydraulics: States ofDocument5 pagesBasic Hydraulics: States ofPietr SemiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Power Control - NPTELDocument1,164 pagesFluid Power Control - NPTELSonal Power Unlimitd83% (6)
- Hydraulics LectureDocument20 pagesHydraulics Lecturee_manpreetNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Radial Flow Pump V4Document34 pagesProject Report On Radial Flow Pump V4mecoolguysNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument10 pagesLab ReportANWAR MOHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- LMS Pumps N Pumping SystemsDocument9 pagesLMS Pumps N Pumping SystemsMohd HafizzNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic System:-: Chapter-2 Hydraulic, Pneumatic and Electrical Telemetry SystemsDocument7 pagesHydraulic System:-: Chapter-2 Hydraulic, Pneumatic and Electrical Telemetry SystemsMayur ParmarNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic and Hydraulic SystemsDocument7 pagesPneumatic and Hydraulic SystemsSergioEstevezNo ratings yet
- ActuatorDocument42 pagesActuatorNyandaMadili MalashiNo ratings yet
- AUTOMATION & Drives PDFDocument127 pagesAUTOMATION & Drives PDFMartinez 100No ratings yet
- Automation and Drive Lectures 1 Amd 2Document52 pagesAutomation and Drive Lectures 1 Amd 2Martinez MutaiNo ratings yet
- Free Samples - Amie - Chapters - Mining Pumps and Power Transmission Sec B Mining MachineryDocument26 pagesFree Samples - Amie - Chapters - Mining Pumps and Power Transmission Sec B Mining MachineryNgatcha Ralain BryanNo ratings yet
- Practicas Lorena (Autoguardado)Document24 pagesPracticas Lorena (Autoguardado)Alberto CamposNo ratings yet
- Welcome: TO The Presentation ONDocument30 pagesWelcome: TO The Presentation ONDr. N. S. SriramNo ratings yet
- Neumatic Control For Robotics and Industrial AutomationDocument12 pagesNeumatic Control For Robotics and Industrial AutomationJeet PawarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Sheet Cut Cutting Machine SynopsisDocument4 pagesHydraulic Sheet Cut Cutting Machine SynopsisANAND KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- ME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument79 pagesME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticselabalajiNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideFrom EverandHydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
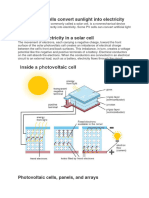
- Solar EnergyDocument2 pagesSolar EnergyPalls the kingNo ratings yet
- Vedii 2Document2 pagesVedii 2Palls the kingNo ratings yet
- Sump CapacityDocument1 pageSump CapacityPalls the kingNo ratings yet
- Structure and CompositionDocument11 pagesStructure and CompositionPalls the king100% (1)