Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Air Conditioning Formulas
Basic Air Conditioning Formulas
Uploaded by
Anji Reddy D0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageHVAC
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHVAC
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageBasic Air Conditioning Formulas
Basic Air Conditioning Formulas
Uploaded by
Anji Reddy DHVAC
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
AC/IN-13
For complete equipment / combination selections,
installation instructions and warranty information,
please refer to Product Data/Ratings and/or Installers
Guides and Limited Warranty Handbooks.
Effective 4/4/11
14-1011-26
Basic Air Conditioning Formulas
Application
Guide
Basic Air Conditioning Formulas
COOLING TO DETERMINE
Total Airflow
Infiltration or Ventilation
Number of Air Changes
Per Hour Total
Number of Air Changes
Per Hour Outdoor Air
Total Heat (H
T
)
Sensible Heat (H
S
)
Latent Heat (H
L
)
Leaving Air D.B.
Temperature (T
2
)
Enthalpy Leaving Air (h
2
)
Leaving Air W.B. Temperature
Heat Required to Evaporate
Water Vapor Added to
Ventilation Air
Humidification Requirements
CFM
T
CFM
o
N
T
N
o
V
H
T
H
S
H
L
h
1
h
2
T
1
T
2
T
adp
t
1
t
2
W
1
W
2
W
3
W
o
*
*
Btu/lb.
Btu/lb.
F.D.B.
F.D.B.
F.D.B.
Grains/lb.
Grains/lb.
Grains/lb.
Grains/lb.
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
Total airflow cubic feet/min.
Outdoor air cubic feet/min.
Total air changes per hour
Outdoor air, air changes per hour
Volume of space cubic feet
Total heat Btuh
Sensible heat Btuh
Latent heat Btuh
Enthalpy or total heat of entering air
Enthalpy or total heat of leaving air
Temperature of entering air
Temperature of leaving air
Apparatus dewpoint
Indoor design temperature
Outdoor design temperature
Grains of water/lb. of dry air at entering condition
Grains of water/lb. of dry air at leaving condition
Grains of water/lb. of dry air at indoor design conditions
Grains of water/lb. of dry air at outdoor design conditions
The air constants below apply specifically to standard air which is
defined as dry air at 70F and 14.7 P.S.I.A. (29.92 in. mercury column).
They can, however, be used in most cooling calculations unless extremely
precise results are desired.
4.5 (To convert CFM to lbs./hr.)
Where 13.33 is the specific volume of standard air (cu.ft./lb.) and
.075 is the density (lbs./cu.ft.)
4.5 =
60 min./hr.
13.33
or 60 X .075
Required Airflow
Entering Air Temperature (T
1
)
(Mixed Air)
CFM
T
=
N
T
V
60 min./hr.
H
T
= CFM
T
x 4.5 x (h
1
h
2
) = Btuh
H
S
= CFM
T
x 1.08 x (T
1
T
2
) = Btuh
H
L
= CFM
T
x .68 x (W
1
W
2
) = Btuh
T
2
= T
1
= F.D.B.
Refer to Enthalpy Table and read W.B. temperature
corresponding to enthalpy of leaving air (h
2
) (see #17).
Refer to Enthalpy Table and read W.B. temperature
corresponding to enthalpy of leaving air (h
2
) (see #18).
H
L
= CFM
o
x .68 (W
3
W
o
) = Btuh
= = lbs./hr.
(Industrial Process Work)
H
L
= CFM
o
x .68 (W
3
W
o
) = Btuh
Make up
Moisture ( )
T
1
= t
1
+
1 If duct heat gain is a factor, add to T
1
:
x (t
2
t
1
) = F.D.B. 1
H
T
= CFM
T
x 4.5 x (h
2
h
1
) = Btuh
H
S
= CFM
T
x 1.08 x (T
2
T
1
) = Btuh
H
L
= CFM
T
x .68 x (W
2
W
1
) = Btuh
CFM
T
CFM
o
N
T
N
o
Btuh
Btuh
Btuh
F. D.B.
Btu/lb.
dry air
F.W.B.
Btuh
Lbs.
water/hr.
CFM
T
F. D.B.
1.
2.
3.
4.
6.
8.
10.
14.
18.
20.
22.
24.
16.
12.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
7.
9.
13.
17.
19.
21.
23.
15.
11.
LEGEND DERIVATION OF AIR CONSTANTS
HEATING and/or HUMIDIFYING
EXPRESSED
AS
CFM
T
=
N
T
V
60 min./hr.
CFM
o
=
N
O
V
60 min./hr.
N
T
=
CFM
T
(60 min./hr.)
V
N
T
=
CFM
T
(60 min./hr.)
V
N
o
=
CFM
o
(60 min./hr.)
V
H
S
CFM
T
x 1.08
h
2
= h
1
= Btu/lb. dry air
H
T
CFM
T
x 4.5
Excess Latent Capacity
of System x % Run Time
1060 Btu/lb.
= = lbs./hr.
Make up
Moisture ( )
H
L
loss Btuh (see #22)
1060 Btu/lb.
h
2
= h
1
+ = Btu/lb. dry air
H
T
CFM
T
x 4.5
CFM
T
=
OR
= CFM
H
S
(total)
1.08 x (T
1
T
2
)
CFM
T
= = CFM
H
S
1.08 x (T
2
T
1
)
CFM
T
=
3 Sensible load of outside air not included
= CFM
H
S
(internal)3
1.08 x (t
1
T
2
)
T
2
= T
1
+ = F.D.B.
H
S
CFM
T
x 1.08
Duct Heat Gain (Btuh)
CFM
T
x 1.08
CFM
o
CFM
T
T
1
= t
1
2 If duct heat loss is a factor, subtract from T
1
:
x (t
1
t
2
) = F.D.B. 2
Duct Heat Loss (Btuh)
CFM
T
x 1.08
CFM
o
CFM
T
N
o
=
CFM
o
(60 min./hr.)
V
CFM
o
=
N
o
V
60 min./hr.
1.08 =
.24 X 60
13.33
or .24 X 4.5
.24 BTU = specific heat of standard air (BTU/LB/F)
Where: 1060 = Average Latent Heat of water vapor (BTU/LB.).
7000 = Grains per lb.
.68 =
60
13.33
or 4.5 X X
1060
7000
1060
7000
* See Enthalpy of air (Total Heat Content of Air) Table for exact values.
Figure 5
You might also like
- ATPL Meteorology Complete Jeppesen 2007Document350 pagesATPL Meteorology Complete Jeppesen 2007Pilot100% (5)
- CTDocument3 pagesCTSundar DAACNo ratings yet
- List Mep Contractors Company Dubai6 PDFDocument10 pagesList Mep Contractors Company Dubai6 PDFsojuiype50% (8)
- EGR 360 DesignDocument18 pagesEGR 360 DesignHarris ChackoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Module 1Document26 pagesThermodynamics Module 1Piolo Lim AvenidoNo ratings yet
- Hvac Formulas PDFDocument25 pagesHvac Formulas PDFSaraswatapalit0% (1)
- Equations: Hvac Equations, Data, and Rules of ThumbDocument21 pagesEquations: Hvac Equations, Data, and Rules of ThumbzodedNo ratings yet
- 1-Internal Heat GainDocument15 pages1-Internal Heat GainWunNa100% (1)
- Psychrometry Part-2Document11 pagesPsychrometry Part-2Tushar Sharma100% (1)
- ASHRAE62.1 and FAQsDocument18 pagesASHRAE62.1 and FAQsols3dNo ratings yet
- Converting KW Ton To COP or EERDocument2 pagesConverting KW Ton To COP or EERswsw2011No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning System LectureDocument9 pagesAir Conditioning System LectureammarNo ratings yet
- DesignCompilation (De Jesus)Document13 pagesDesignCompilation (De Jesus)loureniel de jesusNo ratings yet
- Heat Loss and Gain CalculationDocument84 pagesHeat Loss and Gain Calculationafraz_xecNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE Chiller Course Condenser Water HRDocument36 pagesASHRAE Chiller Course Condenser Water HRabdulzameer100% (1)
- Heatload Calculation 2Document44 pagesHeatload Calculation 2Mustansir Pancha50% (2)
- VRV SystemDocument152 pagesVRV SystemKHA120096 StudentNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning (Meng 4711) : PsychrometryDocument58 pagesRefrigeration and Air-Conditioning (Meng 4711) : PsychrometryaddisudagneNo ratings yet
- Calculator For HVAC Measures: Input InstructionsDocument9 pagesCalculator For HVAC Measures: Input InstructionsRagesh KarimbilNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric Chart (Or Humidity Chart)Document38 pagesPsychrometric Chart (Or Humidity Chart)muhammad izzulNo ratings yet
- RAC 32 Important QuestionDocument10 pagesRAC 32 Important QuestionBalvinderNo ratings yet
- Sizing The Dehumidifier - Bry Air PDFDocument16 pagesSizing The Dehumidifier - Bry Air PDFprabhanshu241991100% (1)
- Cooling Unit. Off Coil Temp Room Temp PDFDocument5 pagesCooling Unit. Off Coil Temp Room Temp PDFSundar Ramasamy100% (1)
- Duct Design Rev2Document18 pagesDuct Design Rev2AshokNo ratings yet
- Humidification Load Calculation Armstrong PDFDocument3 pagesHumidification Load Calculation Armstrong PDFsyedNo ratings yet
- HVAC Thumprule HandbookDocument19 pagesHVAC Thumprule HandbookSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Ahu 6 Alternate ArrangementDocument4 pagesAhu 6 Alternate Arrangementnaresh100% (1)
- HPAC Primary Secondary Loop vs. Primary Loop Only SystemsDocument10 pagesHPAC Primary Secondary Loop vs. Primary Loop Only SystemsAntonio LebrunNo ratings yet
- Heat Gain CalculationsDocument17 pagesHeat Gain CalculationsPrabu RajaNo ratings yet
- Heat Load Estimation MS1525 DesignDocument10 pagesHeat Load Estimation MS1525 Designhans weemaesNo ratings yet
- HVAC Interview Questions and Answers PDF DownloadDocument4 pagesHVAC Interview Questions and Answers PDF DownloadVenkatesh100% (1)
- Variable Primary FlowDocument58 pagesVariable Primary FlowAlfredo Merizalde Aviles100% (2)
- Experimentno.1:The Psychrometric Processes: Relative Humidity RH %Document31 pagesExperimentno.1:The Psychrometric Processes: Relative Humidity RH %JayZx WayNo ratings yet
- Heat Load CalculationDocument24 pagesHeat Load CalculationpradeepqNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Chiller EfficiencyDocument4 pagesCalculation of Chiller EfficiencyPhyu Mar Thein KyawNo ratings yet
- HVAC Life Cycle CostingDocument18 pagesHVAC Life Cycle CostingmajortayNo ratings yet
- Winter Reheat Calculations VimpoDocument7 pagesWinter Reheat Calculations Vimpopsn_kylm100% (2)
- Project:: Chilled Water Pump Head CalculationDocument1 pageProject:: Chilled Water Pump Head CalculationClarkFedele27No ratings yet
- Ahu & Chiller OkDocument40 pagesAhu & Chiller OkAndy DwiNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Efficiency CalculationsDocument3 pagesCooling Tower Efficiency CalculationsPramod SharmaNo ratings yet
- VS Lab & Office - Hvac Boq 29032016Document16 pagesVS Lab & Office - Hvac Boq 29032016Ganesh RamNo ratings yet
- Household RefrigerationDocument23 pagesHousehold RefrigerationsureshNo ratings yet
- Water Balance ChecklistDocument5 pagesWater Balance ChecklistmohamednavaviNo ratings yet
- ACMV DESIGN: Sample Heat Load Calculation For General Office Meeting RoomDocument5 pagesACMV DESIGN: Sample Heat Load Calculation For General Office Meeting RoomVenkates Adhinarayanan50% (2)
- Benefits and Design Tipsfor ChillersDocument4 pagesBenefits and Design Tipsfor ChillersSharon LambertNo ratings yet
- Dehumidification in HVAC System p1 PDFDocument80 pagesDehumidification in HVAC System p1 PDFmanojc68No ratings yet
- Psychrometric ProcessesDocument14 pagesPsychrometric ProcessesKabin BoraNo ratings yet
- 1Document3 pages1ntt_121987No ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery System For RefrigeratorDocument10 pagesWaste Heat Recovery System For RefrigeratorlalkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Aircon Cooling Load EstimationDocument3 pagesAircon Cooling Load Estimationdokundot80% (5)
- Calculating Cooling LoadsDocument2 pagesCalculating Cooling LoadsHerman SubagioNo ratings yet
- CH2 - Heating System PDFDocument10 pagesCH2 - Heating System PDFAaron AngNo ratings yet
- HvacDocument50 pagesHvacJohn Bennett100% (1)
- Air Compressor Lab PDFDocument4 pagesAir Compressor Lab PDFbernabas100% (2)
- Apd CalculationDocument4 pagesApd CalculationRashel Hasan100% (1)
- CHW Pump - HotelDocument7 pagesCHW Pump - HotelTiffany CombsNo ratings yet
- Cooling Load CalculationDocument21 pagesCooling Load Calculationfaizan abbasiNo ratings yet
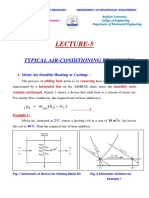
- Lecture-5: Typical Air-Conditioning ProcessesDocument10 pagesLecture-5: Typical Air-Conditioning Processesabrar alhadadNo ratings yet
- AHUDocument5 pagesAHUksahunkNo ratings yet
- DEWALT HVACR Professional Reference Master EditionDocument24 pagesDEWALT HVACR Professional Reference Master EditionLorenc Hysa100% (1)
- Latent HeatDocument2 pagesLatent HeatrohitNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument1 pageFormulasYoesof HilabyNo ratings yet
- Equations, Data and Rules ThumbDocument3 pagesEquations, Data and Rules Thumbsripriya01No ratings yet
- HVAC Supply Airflow Calculation SampleDocument7 pagesHVAC Supply Airflow Calculation Sampletankimsin100% (4)
- Problems On SFD & BMDDocument43 pagesProblems On SFD & BMDmal201182% (11)
- Tech. Spec. For VesselsDocument6 pagesTech. Spec. For Vesselssanjay421No ratings yet
- Piping ComponentsDocument39 pagesPiping Componentsbvenky991100% (1)
- Ibr FormsDocument117 pagesIbr Formsshivabtowin3301No ratings yet
- Jigs and Fixtures: A Basic LookDocument16 pagesJigs and Fixtures: A Basic Lookravirawat15No ratings yet
- Data Bank Consult LoadingDocument151 pagesData Bank Consult Loadingravirawat15No ratings yet
- UsfdaDocument10 pagesUsfdaravirawat15No ratings yet
- IBRDocument37 pagesIBRravirawat15No ratings yet
- Caesar II TrainingDocument61 pagesCaesar II TrainingReaderRRGHT86% (7)
- Piping Material SpecificationDocument36 pagesPiping Material Specificationravirawat15100% (2)
- Team BMM Presents! Greetings SMS!Document6 pagesTeam BMM Presents! Greetings SMS!ravirawat15No ratings yet
- 2.materi Bab II Reciprocating & Sistem CompressorDocument42 pages2.materi Bab II Reciprocating & Sistem CompressorAlfian PrayogaNo ratings yet
- HvacDocument2 pagesHvacMohammed Abdul MoiedNo ratings yet
- ME 512-Chapter 2Document11 pagesME 512-Chapter 2Zernie ReyesNo ratings yet
- Relative Humidity (RH) : Fungi (Mould) and BacteriaDocument3 pagesRelative Humidity (RH) : Fungi (Mould) and BacteriaHARSH VARDHAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Writing PracticeDocument2 pagesWriting PracticeSilmina AdzhaniNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument14 pagesThermodynamicssarathNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric Processes NumericalsDocument16 pagesPsychrometric Processes NumericalsDHADKAN K.C.No ratings yet
- Bogey CurvesDocument9 pagesBogey CurvesGaneshmohite123No ratings yet
- Cooling Tower T P ADocument6 pagesCooling Tower T P AZulhisham ZainiNo ratings yet
- Rac PDFDocument78 pagesRac PDFNarender SinghNo ratings yet
- Articol-Thermal Inertia Effect in Old BuildingsDocument6 pagesArticol-Thermal Inertia Effect in Old BuildingsMicuta LaviniaNo ratings yet
- Etd 2mechDocument2 pagesEtd 2mechgsudhanta1604No ratings yet
- Eq MASTER® AIR HANDLING UNITDocument2 pagesEq MASTER® AIR HANDLING UNITIm ChinithNo ratings yet
- Every Physical Process of Weather Is Accompanied By, or Is The Result Of, ADocument13 pagesEvery Physical Process of Weather Is Accompanied By, or Is The Result Of, ADarielNo ratings yet
- M8 Air Dryer Final Drawing and ManualDocument113 pagesM8 Air Dryer Final Drawing and ManualAnonymous uTO1WINo ratings yet
- Energy Balance (June 17)Document8 pagesEnergy Balance (June 17)Walter HernandezNo ratings yet
- Exp1 Theory Fa2005 p1Document8 pagesExp1 Theory Fa2005 p1Risa HashimotoNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Quarter 4 Week 3 4 CompleteDocument58 pagesScience 7 Quarter 4 Week 3 4 CompleteSheena SusadaNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution and MeteorologyDocument39 pagesAir Pollution and MeteorologyABHISHEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Meteorology (All Grades)Document13 pagesMeteorology (All Grades)George CarinoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical System Modeling Guide: Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) SystemsDocument15 pagesMechanical System Modeling Guide: Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) SystemsAnonymous 73gEYyEtLNo ratings yet
- Volume and Temperature Relationship of A Gas - Charles' Law - Pass My ExamsPass My ExamsDocument4 pagesVolume and Temperature Relationship of A Gas - Charles' Law - Pass My ExamsPass My ExamsDorwinNeroNo ratings yet
- Clay Pot Refrigerator PDFDocument6 pagesClay Pot Refrigerator PDFAvinash RaghooNo ratings yet
- Liquid-in-Glass Thermometer Calibration: Principle of Operation Traceability ChartDocument1 pageLiquid-in-Glass Thermometer Calibration: Principle of Operation Traceability ChartbasdownloadNo ratings yet
- Refrigerator Technical TrainingDocument152 pagesRefrigerator Technical Trainingfunstyles80% (10)
- Cooling ChillerDocument120 pagesCooling ChillerHartanto Hari SusestroNo ratings yet
- Rac Lab Experiment:-1: Aim TheoryDocument36 pagesRac Lab Experiment:-1: Aim TheorySatvinder SinghNo ratings yet