Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Charge and Current: Chapter 1 Basic Concepts
Uploaded by
Brandon Worster0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views7 pagesbasic concepts
Original Title
Chapter 1 Basic Concepts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbasic concepts
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views7 pagesCharge and Current: Chapter 1 Basic Concepts
Uploaded by
Brandon Worsterbasic concepts
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Chapter 1 Basic Concepts
Charge and Current
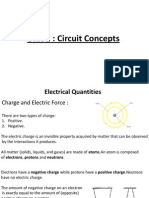
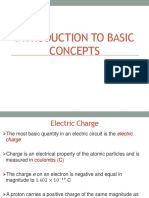
Charge is an electrical property of the atomic particles of which matter
consists, measured in coulombs (C)
The coulomb (named after Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, unit symbol: C) is a fundamental unit of
electrical charge, and is also the SI derived unit of electric charge (symbol: Q or q). It is equal to the
charge of approximately 6.24110
18
electrons.
Electric current is the time rate of change of charge, measured in
amperes (A).
A direct current (dc) is a current that remains constant with time.
An alternating current (ac) is a current that varies sinusoidally with time.
Voltage
Voltage (or potential difference) is the energy required to move a unit
charge through an element, measured in volts (V).
Power and Energy
Power is the time rate of expending or absorbing energy, measured in
watts (W).
Passive sign convention is satisfied when the current enters through
the positive terminal of an element and p vi. If the current enters
through the negative terminal, p vi.
_Power absorbed _ _Power supplied
Energy
Energy is the capacity to do work, measured in joules (J).
Circuit Elements
An ideal independent source is an active element that provides a
specified voltage or current that is completely independent of other
circuit elements.
An ideal dependent (or controlled) source is an active element in
which the source quantity is controlled by another voltage or current.
1. A voltage-controlled voltage source (VCVS).
2. A current-controlled voltage source (CCVS).
3. A voltage-controlled current source (VCCS).
4. A current-controlled current source (CCCS).
SUMMARY
EXAMPLES
You might also like
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Electrical Engineering Interview QuestionDocument9 pagesElectrical Engineering Interview QuestionRohan BoseNo ratings yet
- 01 Fundamental of Electrical Engineering 20170621Document26 pages01 Fundamental of Electrical Engineering 20170621Sabita Talukdar100% (1)
- Basic Electricity Chapter OneDocument76 pagesBasic Electricity Chapter OneGetahun shankoNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory 1 MidtermDocument101 pagesCircuit Theory 1 MidtermMcHaley HalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument12 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionHazem DoufeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument80 pagesChapter OnemagnifcoNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 1 (Final Term)Document20 pagesINTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 1 (Final Term)Abdul Halil AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Rangkaian Listrik: By: Hendra Kusuma Hendraks@ee - Its.ac - IdDocument24 pagesRangkaian Listrik: By: Hendra Kusuma Hendraks@ee - Its.ac - IdEko AdiNo ratings yet
- Rabia Pls Mujhe Chor deDocument23 pagesRabia Pls Mujhe Chor de;(No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basic Concept NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Basic Concept NotesGangga RobleNo ratings yet
- 1-Ohms Law, KCL and KVL and Other Basics-05-Dec-2019Material I 05-Dec-2019 EEE1002-Module 1-DC CircuitsDocument23 pages1-Ohms Law, KCL and KVL and Other Basics-05-Dec-2019Material I 05-Dec-2019 EEE1002-Module 1-DC CircuitsAnantha ReddyNo ratings yet
- EE320 - DC/AC Circuits (Part 1) : Electric ChargeDocument11 pagesEE320 - DC/AC Circuits (Part 1) : Electric ChargeIamellahollic KathportsNo ratings yet
- BE Circuit ConceptsDocument15 pagesBE Circuit ConceptsVivekPatelNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Electrical Quantities and SI Units: Chapter One: Basic ConceptsDocument9 pages1.1 Electrical Quantities and SI Units: Chapter One: Basic ConceptsTesfa EyesusNo ratings yet
- 1.system of Units Circuit ElementsDocument41 pages1.system of Units Circuit ElementsKim OpenaNo ratings yet
- NAME: Rahnuma Amin Rumi Id No: 20201086010 Corse Code:1321 Course Tittle: EEEDocument10 pagesNAME: Rahnuma Amin Rumi Id No: 20201086010 Corse Code:1321 Course Tittle: EEEমোছা. রাহনুমা আমিন রুমিNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Fundamental Quantities) PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 1 (Fundamental Quantities) PDFmohamedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Circuit Theory: Prepared By: Aaron U. Aquino, EceDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Circuit Theory: Prepared By: Aaron U. Aquino, EceGanmarie DuqueNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Terms and DefinitionsDocument7 pagesBasic Electronics Terms and Definitionspondu888No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1von_science08No ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument38 pagesBasic ConceptsAzzam SalehNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Basic ConceptsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Basic ConceptsDanialNo ratings yet
- AE - 01 - Basic ElectricityDocument24 pagesAE - 01 - Basic ElectricitydhakaeurekaNo ratings yet
- LS - Electricity - NotesDocument5 pagesLS - Electricity - NotesAyushNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory 1 MidtermDocument101 pagesCircuit Theory 1 MidtermEL DamascoNo ratings yet
- BEE Electricity Basic PrinciplesDocument20 pagesBEE Electricity Basic PrinciplesMondaya, Jake Armond D.No ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Theory PDFDocument22 pagesBasic Circuit Theory PDFElya OraNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument38 pagesBasic ConceptsLaith AmroNo ratings yet
- DEL1202 CIRCUIT THEORY-Unit 1 & 2Document30 pagesDEL1202 CIRCUIT THEORY-Unit 1 & 2Ogwal EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts in Electrical TechnologyDocument31 pagesChapter 1 - Basic Concepts in Electrical TechnologyDouglas OngomNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Basic ConceptsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Basic ConceptsM Hussnain JavedNo ratings yet
- Electronic Curcuit Chapter 1Document42 pagesElectronic Curcuit Chapter 1AbcdNo ratings yet
- C1 Basic ConceptsDocument54 pagesC1 Basic ConceptsPEi PAiNo ratings yet
- Review of Basic Circuit ConceptsDocument52 pagesReview of Basic Circuit ConceptsIsmail kabirNo ratings yet
- EEE120 Cicuit TheoryDocument21 pagesEEE120 Cicuit TheoryZohair macapodiNo ratings yet
- EC100 Elements of ECE: Module - I: RLC CircuitsDocument17 pagesEC100 Elements of ECE: Module - I: RLC CircuitsJustin S BudarpurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basic Concepts: Sung-Liang Chen VE215 Fall 2022Document39 pagesChapter 1 Basic Concepts: Sung-Liang Chen VE215 Fall 2022yi yang GuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - MechDocument40 pagesLecture 1 - MechHassan El SayedNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledJoyce LonzagaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineers Interview GuideDocument3 pagesElectrical Engineers Interview GuideबिपुलकुँजNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of E EDocument128 pagesFundamental of E EAlimah AzeliNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering: Fall 2015 Instructor: Dr. Hassan DawoodDocument34 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering: Fall 2015 Instructor: Dr. Hassan Dawoodbakhtawar saeedNo ratings yet
- EST 130 BEE Module 1Document94 pagesEST 130 BEE Module 1Gayathri VijayachandranNo ratings yet
- 1 - IntroductionDocument74 pages1 - IntroductionNikhil PatelNo ratings yet
- EEEB113 Circuit Analysis I: Basic ConceptsDocument41 pagesEEEB113 Circuit Analysis I: Basic ConceptsGabriel Carl AlpuertoNo ratings yet
- EE331 Lecture1 NotesDocument21 pagesEE331 Lecture1 NotespaulamarieestrellalengascoNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts: Prof. Dr. Mustafa Kemal UygurogluDocument31 pagesBasic Concepts: Prof. Dr. Mustafa Kemal UygurogluJonatan SilveraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document78 pagesUnit 1Atharva RaksheNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 DC Circuits Electrical Engineering Is The Field of Engineering That Generally Deals With The StudyDocument60 pagesUnit 1 DC Circuits Electrical Engineering Is The Field of Engineering That Generally Deals With The StudyAayush SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Linear Circuit AnalysisDocument10 pagesLesson 1 - Linear Circuit AnalysisYungho Edickson boboNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity Concepts: Week 1Document50 pagesBasic Electricity Concepts: Week 1HEAD OF THE DEPARTMENT BMENo ratings yet
- 1.1 Electrical Quantities and Units: Circuit, and Each Component of The Circuit Is Known As An ElementDocument19 pages1.1 Electrical Quantities and Units: Circuit, and Each Component of The Circuit Is Known As An ElementAbrha FtsumNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electrical Engineering: Dr. Mohammed SaeedDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Electrical Engineering: Dr. Mohammed SaeedAhmed AshrafNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory 1 MidtermDocument101 pagesCircuit Theory 1 MidtermBryan PongaoNo ratings yet
- DEL1202-ELE1202 CIRCUIT THEORY I-Unit 1-Basic ConceptsDocument13 pagesDEL1202-ELE1202 CIRCUIT THEORY I-Unit 1-Basic ConceptsOgwal EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document77 pagesLecture 1عقيل الفهداويNo ratings yet
- Volt Curr ResisDocument12 pagesVolt Curr ResisVíctor Manuel Villegas EscobarNo ratings yet
- UNIT I Electrical Circuits:: BE8253 Basic Electrical, Electronics and InstrumentationDocument16 pagesUNIT I Electrical Circuits:: BE8253 Basic Electrical, Electronics and InstrumentationBalu ChanderNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 DC Circuits Electrical Engineering Is The Field of Engineering That Generally Deals With The StudyDocument60 pagesUnit 1 DC Circuits Electrical Engineering Is The Field of Engineering That Generally Deals With The StudyAtharv BhedaNo ratings yet