Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Critical Path Analysis
Uploaded by
sbmiller87Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Critical Path Analysis
Uploaded by
sbmiller87Copyright:
Available Formats
Critical Path Analysis - 15B
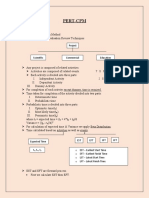
Anatomy:
Please note the edges/lines are the activities.
Doing Work:
Earliest Start Time (EST):
To calculate EST we need to add up all activities that pre-empt the start of the
activity outlined. This value belongs in the triangle, as below.
Float Time:
Float time is the difference in time between a path that can be delayed and one
that cannot.
o A path that cannot be delayed is the longest possible path, critical path.
D to E
o A path that can, will be a path that runs parallel but is shorter in time.
B and G
Float time is kind of like extra time, i.e. It will take 8 minutes to complete D and E
while it will only take 2 minutes to complete B and arrive at the same point.
This means that activity B has a float time of 6 minutes.
LFT LST and logic!
What is the float time for activity G?
Earliest Start Time (EST)
Latest Start Time (LST)
Start/End Node
Latest Start Time (LST):
Latest start time is the bit that allows for the slack, it identifies that activities
with float times dont have to start on time.
For example if the critical path or the longest activity takes 8 minutes and
another activity takes 2 minutes we have 6 minutes of float time. In this case we
dont need to start the task until 6 minutes in, this is the LST.
You will explore this further in 15B.
Why Question 9:
No idea, the answer is to a different question it gives the allowable delay which
is equal to float time, it shouldve given the LST which you will get to know
further in 15B, weird.
You might also like
- Critical Path Analysis: 2008 Spec. Issue 2 Sept. 2009Document5 pagesCritical Path Analysis: 2008 Spec. Issue 2 Sept. 2009tuandinNo ratings yet
- Calculating Critical PathDocument9 pagesCalculating Critical PathPako MogotsiNo ratings yet
- Critical Path MethodDocument8 pagesCritical Path MethodAmy AungNo ratings yet
- Critical Path Method PDFDocument8 pagesCritical Path Method PDFAmy AungNo ratings yet
- Critical PathDocument5 pagesCritical PathErin100% (2)
- Critical Path MethodDocument17 pagesCritical Path MethodWP 2-1-PR Katubedda-CESLNo ratings yet
- Note 6 Feb 2024Document3 pagesNote 6 Feb 2024Risha OsfordNo ratings yet
- PERT Time Estimate: in This Technique, It Is Assumed That The Activity Durations Follow ADocument5 pagesPERT Time Estimate: in This Technique, It Is Assumed That The Activity Durations Follow ASiva Rama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- TQMDocument6 pagesTQMHaidie DiazNo ratings yet
- Pert, CPM (Pom)Document25 pagesPert, CPM (Pom)Aarush Js100% (1)
- CB510P Ch3-1Document10 pagesCB510P Ch3-1Clic PointNo ratings yet
- Project Analysis ToolsDocument50 pagesProject Analysis ToolsChan Siew Chong100% (1)
- Program evaluation review technique (PERT) and critical path method (CPM) planning toolsDocument12 pagesProgram evaluation review technique (PERT) and critical path method (CPM) planning toolssamuel kebedeNo ratings yet
- Critical Path MethodDocument8 pagesCritical Path MethodKnowledge SitholeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: PERT For Project Planning and Scheduling: John W. Chinneck, 2016Document11 pagesChapter 11: PERT For Project Planning and Scheduling: John W. Chinneck, 2016Nouman SabirNo ratings yet
- San Agustin, Michael Angelo - Pert-CpmDocument9 pagesSan Agustin, Michael Angelo - Pert-CpmAnghelikaaaNo ratings yet
- Pert CPM Concept GB SirDocument6 pagesPert CPM Concept GB SirRakesh bhukyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: PERT For Project Planning and Scheduling: John W. Chinneck, 2009Document11 pagesChapter 11: PERT For Project Planning and Scheduling: John W. Chinneck, 2009giok2003No ratings yet
- Critical Path Method (CPM) in Project ManagementDocument27 pagesCritical Path Method (CPM) in Project ManagementendhaNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Critical PathDocument10 pagesHow To Calculate Critical PathSriNo ratings yet
- The Critical Path MethodDocument3 pagesThe Critical Path Methodclewis0077189767% (3)
- ENCE 603 Management Science Applications in Project Management Lectures 5-7Document70 pagesENCE 603 Management Science Applications in Project Management Lectures 5-7Vindraj ChopdekarNo ratings yet
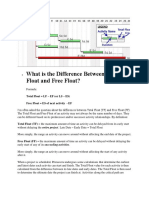
- What Is The Difference Between Total Float and Free FloatDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Total Float and Free FloatPrabu KannanNo ratings yet
- Pert CPMDocument51 pagesPert CPMJun Michael Artates VelascoNo ratings yet
- Program Evaluation and Review TechniqueDocument19 pagesProgram Evaluation and Review Techniquewaqas298100% (1)
- Pert/Cpm: Project Scheduling Project SchedulingDocument51 pagesPert/Cpm: Project Scheduling Project SchedulingSandeep NakireddyNo ratings yet
- 86 The Critical Path Method of SchedulingDocument2 pages86 The Critical Path Method of Schedulingspsingh25No ratings yet
- Critical Path Method (CPM) in Project ManagementDocument12 pagesCritical Path Method (CPM) in Project ManagementNihal JannounNo ratings yet
- ITM - 130 Assignment-1Document6 pagesITM - 130 Assignment-1Sashikanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Calculate Critical Path Float ES EF LS LFDocument9 pagesCalculate Critical Path Float ES EF LS LFnazishtila100% (1)
- Ase Study: PERT / CPM - Calculating Floats: Net Work # 1Document6 pagesAse Study: PERT / CPM - Calculating Floats: Net Work # 1CA Gourav JashnaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Project PlanningDocument40 pagesChapter 4-Project Planningselamabrham065No ratings yet
- MM305 Unit 8 SummaryDocument8 pagesMM305 Unit 8 SummaryAimee AimeeNo ratings yet
- Peat ExampleDocument19 pagesPeat Examplelimulsa78No ratings yet
- Project Management PERT/CPM GuideDocument11 pagesProject Management PERT/CPM GuideOji ArashibaNo ratings yet
- Critical Path MethodDocument6 pagesCritical Path MethodjunaediwendiNo ratings yet
- Calculating Slack Time and Identifying The Critical PathDocument3 pagesCalculating Slack Time and Identifying The Critical PathkharismaNo ratings yet
- Illustration - 3Document44 pagesIllustration - 3limulsa78No ratings yet
- Critical Path Method & EvmDocument63 pagesCritical Path Method & EvmBALAYASJ100% (1)
- CPM and PERT Analysis for Project SchedulingDocument36 pagesCPM and PERT Analysis for Project Schedulinglimulsa78No ratings yet
- Certified Associate in Project ManagementDocument4 pagesCertified Associate in Project ManagementlatheefNo ratings yet
- Ch06 Activity PlanningDocument37 pagesCh06 Activity PlanningSrisha Prasad RathNo ratings yet
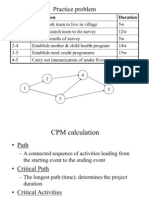
- Practice ProblemDocument37 pagesPractice Problemlimulsa78No ratings yet
- 2 PDFDocument3 pages2 PDFomNo ratings yet
- Gantt: Having Fun WithDocument51 pagesGantt: Having Fun WithDelmar José Ribeiro SábioNo ratings yet
- Modul 9: PERT For Project Planning and SchedulingDocument11 pagesModul 9: PERT For Project Planning and SchedulingMateri BelajarNo ratings yet
- Project SchedulingDocument41 pagesProject Schedulingtalhawasim100% (1)
- Project Scheduling: Prof. DR Amir Azam KhanDocument53 pagesProject Scheduling: Prof. DR Amir Azam KhanKhairul Azhar Abdul LizaNo ratings yet
- Hafizah (Part 11)Document2 pagesHafizah (Part 11)Hafizah ShafeeNo ratings yet
- Difference between Total Float and Free FloatDocument6 pagesDifference between Total Float and Free FloatmacholdingsNo ratings yet
- Activity On NodeDocument14 pagesActivity On NodeAnonymous Ddyoaq3No ratings yet
- Crash Estimates and Resource Loading for Network SchedulingDocument4 pagesCrash Estimates and Resource Loading for Network SchedulingNadeem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Project Planning Techniques: Network Analysis and PERTDocument25 pagesProject Planning Techniques: Network Analysis and PERTDaudi MakelemoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-5 - Project ManagementDocument20 pagesCHAPTER-5 - Project ManagementGvm VamshiNo ratings yet
- A 22 PertDocument32 pagesA 22 Pertlimulsa78No ratings yet
- Critical Path Analysis: The Following Terms Shall Be Used in The Critical Path CalculationDocument34 pagesCritical Path Analysis: The Following Terms Shall Be Used in The Critical Path Calculationlimulsa78No ratings yet
- Network Techniques: PERT and CPM SchedulingDocument31 pagesNetwork Techniques: PERT and CPM SchedulingDejene HailuNo ratings yet
- Elliott Wave Timing Beyond Ordinary Fibonacci MethodsFrom EverandElliott Wave Timing Beyond Ordinary Fibonacci MethodsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- Extended Response/Problem Networks & Directed GraphsDocument6 pagesExtended Response/Problem Networks & Directed Graphssbmiller87No ratings yet
- Extended Response/Problem Business-Related Mathematics Session OneDocument2 pagesExtended Response/Problem Business-Related Mathematics Session Onesbmiller87No ratings yet
- Sac 1Document6 pagesSac 1sbmiller87No ratings yet
- Sac 3Document8 pagesSac 3sbmiller87No ratings yet
- Building The Torch: What Your Doing : You Will Be Creating Your Own SwitchDocument4 pagesBuilding The Torch: What Your Doing : You Will Be Creating Your Own Switchsbmiller87No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Outcome 3 - Collaboratively Solve An Information Problem For A ClientDocument4 pagesUnit 2 - Outcome 3 - Collaboratively Solve An Information Problem For A Clientsbmiller87No ratings yet
- Exam 2 SolutionsDocument12 pagesExam 2 Solutionssbmiller87No ratings yet
- (T) Cover LetterDocument2 pages(T) Cover Lettersbmiller87No ratings yet
- (T) CV of Shaun MillerDocument3 pages(T) CV of Shaun Millersbmiller87No ratings yet
- EXPECTED Level Algebra TaskDocument3 pagesEXPECTED Level Algebra Tasksbmiller87No ratings yet