Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exercise#1 Solutions
Uploaded by
Michele Medeiros0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageThis document contains solutions to an exercise involving calculations of work done (W) during various thermodynamic processes. It provides the equations to calculate work done for constant pressure, constant temperature, and constant PV^1.5 processes. It also calculates the work done for a reversible cycle represented by a circle on a PV diagram, finding it to be 4712 kJ/kg.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains solutions to an exercise involving calculations of work done (W) during various thermodynamic processes. It provides the equations to calculate work done for constant pressure, constant temperature, and constant PV^1.5 processes. It also calculates the work done for a reversible cycle represented by a circle on a PV diagram, finding it to be 4712 kJ/kg.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageExercise#1 Solutions
Uploaded by
Michele MedeirosThis document contains solutions to an exercise involving calculations of work done (W) during various thermodynamic processes. It provides the equations to calculate work done for constant pressure, constant temperature, and constant PV^1.5 processes. It also calculates the work done for a reversible cycle represented by a circle on a PV diagram, finding it to be 4712 kJ/kg.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
(Handout 03)
Exercise #1 Solutions 9/2/2014
Q = t Ap D
4
/(128 L)
Q = C t Ap D*
4
/(128 L*)
D = 0.025 D* [m] = [0.025 m / in] - [in]
L = 0.025 L* [m] = [0.025 m / in] - [in]
Q = t Ap D
4
/(128 L) = t Ap (0.025 D*)
4
/(128 0.025 L*)
= (0.025)
3
t Ap D
4
/(128 L) = 1.5625 x 10
-5
t Ap D
4
/(128 L)
C = 1.5625 x 10
-5
1.
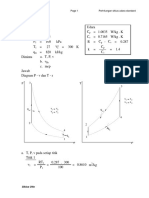
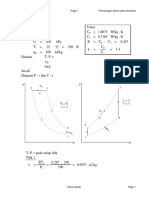
a). A constant pressure process
W = - } P dV = - P AV = - 100 kPa x (0.08 - 0.04) m
3
= - 4 kJ
b). A constant temperature process
W = - } P dV = - } RT/V dV = - RT ln V = -PV ln V
W = = 100 kPa x 0.04 m
3
ln (0.08/0.04) = - 2.77 kJ
c). A process followed the expression PV
1.5
= constant
W = - } P dV = - } constant/V
1.5
dV = - constant V
-0.5
/(-0.5)
W = = (P
2
V
2
- P
1
V
1
) /0.5
P
2
= P
1
(V
1
/V
2
)
1.5
W = -2.34 kJ
d). A constant volume process with final pressure at 50 kPa
W = 0
3. A reversible cycle of a work-producing machine is represented by a circle of 5 cm diameter on a
P-V diagram. The pressure and specific volume scales are
P-scale: 1 cm = 200 kPa and V-scale: 1 cm = 1.2 m
3
/kg
Compute the work done on 1 kg of fluid.
t D
2
/4 = t (5 cm)
2
/4 = t (5 cm)
2
/4 x 200 kPa /cm x 1.2 m
3
/kg /cm = 4712 kJ/kg
You might also like
- Exercise #1 9/2/2014 Incompressible Flow in PipesDocument1 pageExercise #1 9/2/2014 Incompressible Flow in PipesMichele MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Pump. Slurry Selection Typical WarmanDocument44 pagesPump. Slurry Selection Typical WarmanJuan Pablo Apaza100% (1)
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGFrom EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document6 pagesChapter 7Marco LuigiNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Air Receivers Volume CalculationDocument19 pagesAir Receivers Volume CalculationKenny Ruiz100% (4)
- Engineering Mechanics: Second PartDocument9 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Second Partاحمد سلمان عزيز , مسائيCNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics and Control, Ch. 9 Solution ManualDocument17 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control, Ch. 9 Solution ManualBen Spearman100% (3)
- Name: Nguyễn Hải Đăng Advanced program class k6 ID:1521010052 Subject: ECH 152BDocument6 pagesName: Nguyễn Hải Đăng Advanced program class k6 ID:1521010052 Subject: ECH 152BLe Anh QuânNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Chapter 3 Solution Sta Maria PDFDocument7 pagesThermodynamics Chapter 3 Solution Sta Maria PDFZandie Garcia75% (4)
- Nota PemampatDocument49 pagesNota PemampatweafareezNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Chapter 3 Solution Sta MariaDocument7 pagesThermodynamics Chapter 3 Solution Sta MariaJean PD81% (21)
- Since Volume Is Constant, Use Charles' Law On Constant VolumeDocument7 pagesSince Volume Is Constant, Use Charles' Law On Constant VolumetrishaNo ratings yet
- Logical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeFrom EverandLogical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeNo ratings yet
- Tech Drilling SurgeSwabPressDocument40 pagesTech Drilling SurgeSwabPressdaongocha108No ratings yet
- MMMDocument9 pagesMMMBoddupalli Lohith KumarNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Soal 5.1: Perhitungan Siklus Udara StandardDocument3 pagesSoal 5.1: Perhitungan Siklus Udara StandardAdiNo ratings yet
- SOAL 5.2: Perhitungan Siklus Udara StandardDocument3 pagesSOAL 5.2: Perhitungan Siklus Udara StandardAdiNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid Dynamics: Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandComputational Fluid Dynamics: Principles and ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Non Flow Processes Gases Closed SystemDocument9 pagesNon Flow Processes Gases Closed SystemNjabulo NgobeseNo ratings yet
- Drilling HydraulicDocument52 pagesDrilling HydraulicHeris Sitompul100% (1)
- CH 13Document32 pagesCH 13hirenpatel_universalNo ratings yet
- 432 ProjectDocument19 pages432 ProjectSahil PalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6Marco Luigi100% (1)
- Barachina Ecm3Document9 pagesBarachina Ecm3ALDRIAN BARACHINANo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document34 pagesChapter 7ShahrizatSmailKassimNo ratings yet
- Duct Pressure Loss CalculationDocument24 pagesDuct Pressure Loss CalculationbernardsilvanoNo ratings yet
- Lohith PDFDocument8 pagesLohith PDFBoddupalli Lohith KumarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 2 - Lesson 1 - Example ProblemsDocument9 pagesHydraulics 2 - Lesson 1 - Example ProblemsAngelo RosNo ratings yet
- Exercícios Resolvidos - Cap. 02 (B) - AtkinsDocument26 pagesExercícios Resolvidos - Cap. 02 (B) - AtkinsRosiane VieiraNo ratings yet
- AlphaDocument7 pagesAlphaJojenNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli and Torricelli Theorem Basics.Document49 pagesBernoulli and Torricelli Theorem Basics.shubhamcholeNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Solution Manual English Unit ProblemsDocument27 pagesThermodynamics: Solution Manual English Unit Problems06fmTCNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Answers: Well Performance Case StudiesDocument7 pagesModule 7 Answers: Well Performance Case StudiesDwinta PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Full Revised Chapter 7Document55 pagesFull Revised Chapter 7Diovinyl Kartil67% (3)
- Sludge ThickenerDocument15 pagesSludge ThickenerDavid LambertNo ratings yet
- Cycles PDFDocument10 pagesCycles PDFratchagarajaNo ratings yet
- Termodinamica de Hidrocarburos: Maria A. BarrufetDocument61 pagesTermodinamica de Hidrocarburos: Maria A. Barrufet13670319No ratings yet
- Bab Iv Pembahasan: 4.1 Perhitungan Data PercobaanDocument9 pagesBab Iv Pembahasan: 4.1 Perhitungan Data PercobaanBahtiar NurhakimNo ratings yet
- Reviewlecture-I 20081001 48e3c2399f4d65 74115154Document37 pagesReviewlecture-I 20081001 48e3c2399f4d65 74115154Austin BarrilleauxNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1 by Sta. Maria Chapter 3 Solution ManualDocument7 pagesThermodynamics 1 by Sta. Maria Chapter 3 Solution ManualAllen MalabarbasNo ratings yet
- Design of Valve TrayDocument4 pagesDesign of Valve TrayVirendra BhagatNo ratings yet
- Solve ItDocument12 pagesSolve ItMarvin100% (1)
- QuickieDocument34 pagesQuickieLhester Navasca0% (1)
- H H. W W W 358.9628.D - .H 6.31533.W D.: AGA Flow Orifice Calculation RoutinesDocument24 pagesH H. W W W 358.9628.D - .H 6.31533.W D.: AGA Flow Orifice Calculation RoutinescincaohijauNo ratings yet
- Blower Air LineDocument52 pagesBlower Air LineJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Unit Twelve - Refrigeration and Air Standard Cycles OutlineDocument5 pagesUnit Twelve - Refrigeration and Air Standard Cycles OutlinebarelihbNo ratings yet
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1396)