Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tsu and TH
Tsu and TH
Uploaded by
Bhai BaiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tsu and TH
Tsu and TH
Uploaded by
Bhai BaiCopyright:
Available Formats
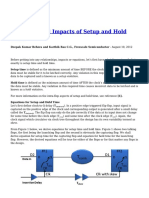
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
Considering D-type edge-triggered, Flip Flops (FFs)
Just before and just after the clock edge, there is a critical time
region where the D input must not change.
The region just before the clock edge is called setup time (t
s u
)
The region just after the clock edge is called hold time (t
h
)
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
Every FF has minimum required values for t
s u
and t
h
.
Usually found in the data sheet or .lib le.
From saed90nm typ ht.lib:
cell(AODFFARX2) {
pin(D) {
timing() {
timing_type : setup_rising;
related_pin : "CLK";
fall_constraint(vio_0_7_7) {
values( " 0.129318, 0.130474, 0.134615, 0.143814, 0.164042, 0.205415, 0.275800",\
" 0.126790, 0.128403, 0.132544, 0.141743, 0.161972, 0.203344, 0.273730",\
rise_constraint(vio_0_7_7) {
values( " 0.181503, 0.183574, 0.188631, 0.198288, 0.216227, 0.246614, 0.286787",\
" 0.178975, 0.181046, 0.186103, 0.195759, 0.213699, 0.243627, 0.284258",\
.............
timing() {
timing_type : hold_rising;
related_pin : "CLK";
fall_constraint(vio_0_7_7) {
values( " -0.073929, -0.075542, -0.079683, -0.088882, -0.108653, -0.146363, -0.206220",\
" -0.071858, -0.073471, -0.077155, -0.086354, -0.106582, -0.144293, -0.204150",\
.............
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
FFs in ASIC libraries have t
s u
s about 3-10x the t
pd
of a 1x inverter.
They have t
h
s ranging from about negative 1 x the t
pd
of an
inverter to positive 1-2x the t
pd
of the same inverter.
t
s u
and t
h
vary strongly with temperature, voltage and process.
t
s u
and t
h
are functions of the G
bw
of the FF transistors.
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
If the D input changes within the t
s u
and t
h
window, Q may:
Follow D correctly
Follow D incorrectly
Assume a metastable state for an indeterminate time followed by a
transition to logic 1 or logic 0.
For correct operation, D inputs must be stable for a t
s u
prior to
clock and stay stable for a t
h
afterwards.
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
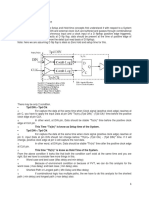
Synchronous circuit minimum cycle time is eected by setup time.
Between clock edges, the path between two FFs is composed of:
clock to Q delay of FF0 (t
c kq
)
propagation delay through combo logic (t
pd
)
the required setup time (t
s u
) of FF1
t
c kq
and t
pd
are both delays. t
s u
is a constraint of FF operation.
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
The circuit provides setup time as a function of the clock period,
t
c kq
and combo logic delay t
pd
.
The FF requires a specied t
s u
to operate correctly.
The dierence between the two is called setup time slack.
setup time slack = (provided setup time) - (required setup time)
We always want positive slack.
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
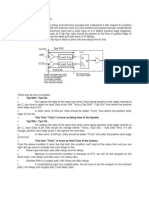
An example: nd the setup slack
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
What is the minimum cycle time for the circuit?
minimum cycle time
= t
c kq
+ t
pd
+ t
s u
= 200 + 300 + 100
= 600pS
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
What is the minimum cycle time for the circuit?
minimum cycle time
= t
c kq
+ t
pd
+ t
s u
= 200 + 300 + 100
= 600pS
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
Hold time is the amount of time that FF0s old data must persist at
the D input of FF1 after the clock edge.
FFs have a specied minimum hold time.
The circuit provides hold time to the FF of (t
c kq
+ t
pd
).
Hold time slack = (hold time provided - hold time required)
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
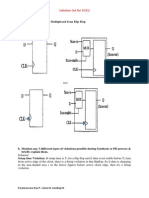
Worst case hold time scenario: FFs directly connected D-to-Q.
In this case, the provided hold time is the t
c kq
of the previous FF.
This places a restriction on FF timing such that t
c kq
>t
h
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
So far, we have looked at FF timing assuming an ideal clock.
Each FF saw the clock edge at exactly the same time.
In reality, this does not happen.
Interconnect metal length to FF clock pins diers slightly.
Some FFs have diering capacitance at their clock pins.
The t
pd
of the clock tree buers will be eected by diering
temperature and voltage across the die. These eects are dynamic
and cannot be determined apriori.
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
Imperfections in clock arrival time are called clock skew.
If clock skew causes clock to arrive later at FF1 than FF0, data
leapfrogs past FF1.
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
If clock skew casues clock to arrive earlier at FF1 than FF0, data
has less time to reach FF1.
This requires the clock period must be lengthened over what it
could have been without skew.
i.e., the system is slower.
Review of Flip Flop Setup and Hold Time
The presence of skew simply takes away directly from any slack
(setup or hold) that may exist.
A more complete picture of setup and hold slack would be:
setup slack = (cycle time - t
c kq
- t
pd
-t
s u
) - clock skew
hold slack = (t
c kq
+ t
pd
-t
h
) - clock skew
We can get more setup slack by slowing down a system.
There is nothing you can do to x hold time slack after fabrication!
You might also like
- 1494 The Roles of Construction Management in Super High Rise Building ProjectsDocument7 pages1494 The Roles of Construction Management in Super High Rise Building Projectsvin ssNo ratings yet
- 05 May 1997Document92 pages05 May 1997sys_64759No ratings yet
- ESARM Unit-III and IV Slides MergedDocument301 pagesESARM Unit-III and IV Slides MergedShashipreetham LakkakulaNo ratings yet
- Phy Interface Pci Express Sata Usb3 1 Architectures 4 2Document90 pagesPhy Interface Pci Express Sata Usb3 1 Architectures 4 2madhukirNo ratings yet
- California Enterprise Architecture FrameworkDocument95 pagesCalifornia Enterprise Architecture Frameworkoscarette100% (1)
- Equations and Impacts of Setup and Hold TimeDocument5 pagesEquations and Impacts of Setup and Hold TimeShravan Kumar AshannagariNo ratings yet
- SAP PP Sample QuestionsDocument15 pagesSAP PP Sample QuestionsPaulo BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Training JtagDocument44 pagesTraining JtagDonald Charles FernoughtyNo ratings yet
- Otro Proyecto Ejemplo de SettingDocument17 pagesOtro Proyecto Ejemplo de SettingDanilo Josue Urdaneta ChirinosNo ratings yet
- System Ver I Log Functional CoverageDocument12 pagesSystem Ver I Log Functional CoverageLakshmisree SajitNo ratings yet
- DFF Setup Hold ReviewDocument50 pagesDFF Setup Hold ReviewAkanksha221291No ratings yet
- Pipelining & Retiming of Digital CircuitsDocument47 pagesPipelining & Retiming of Digital CircuitsGautham PopuriNo ratings yet
- What Is Setup and Hold Time?Document12 pagesWhat Is Setup and Hold Time?Minu MathewNo ratings yet
- A Synthesizable Design of Amba-Axi Protocol For Soc IntegrationDocument8 pagesA Synthesizable Design of Amba-Axi Protocol For Soc IntegrationvjemmanNo ratings yet
- John Crane Metastream Coupling.Document53 pagesJohn Crane Metastream Coupling.SOHAIB100% (1)
- Setup and Hold TimeDocument6 pagesSetup and Hold TimeShobhit GargNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction: Arto Perttula TIE-50206 Logic Synthesis Tampere University of Technology 2017-2018Document57 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction: Arto Perttula TIE-50206 Logic Synthesis Tampere University of Technology 2017-2018antoniocljNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design - VerilogDocument30 pagesVLSI Design - Veriloganand_duraiswamyNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco Boomer L2D Operators InstructionsDocument120 pagesAtlas Copco Boomer L2D Operators InstructionsHai Van100% (14)
- Arm7 ArchitectureDocument20 pagesArm7 ArchitectureCharitha CherryNo ratings yet
- Setup & Hold ViolationDocument20 pagesSetup & Hold ViolationdeepaNo ratings yet
- DVD2 JNTU Set1 SolutionsDocument12 pagesDVD2 JNTU Set1 Solutionsకిరణ్ కుమార్ పగడాలNo ratings yet
- Advanced Asic Chip SynthesisDocument126 pagesAdvanced Asic Chip SynthesispravinNo ratings yet
- Occupancy Permit Source: Iloilo City Engineer's OfficeDocument2 pagesOccupancy Permit Source: Iloilo City Engineer's OfficeKatherine B. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Amba 4axi StreamDocument2 pagesAmba 4axi StreamNGUYỄN HOÀNG LINHNo ratings yet
- Register and Its OperationsDocument56 pagesRegister and Its OperationsSARTHAK VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- Interview Question UsefullinkDocument3 pagesInterview Question UsefullinkMOHAMMED JUNED RAHINo ratings yet
- ARM7 9 FamilyDocument46 pagesARM7 9 FamilySaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- CPFDocument47 pagesCPFcknishuNo ratings yet
- Timing in Digital Circuits - NotesDocument9 pagesTiming in Digital Circuits - NotesKowshick GuruNo ratings yet
- Negative and Positive Clock SkewDocument27 pagesNegative and Positive Clock SkewSupriya AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Setup and Hold - PDF Version 1Document15 pagesSetup and Hold - PDF Version 1naniNo ratings yet
- ARM7 Processor FamilyDocument8 pagesARM7 Processor FamilySaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- ARM - An Understanding and MoreDocument87 pagesARM - An Understanding and MoreSivasini Netra S ANo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture 1Document39 pagesComputer Architecture 1ARAFAT GaamanNo ratings yet
- SystemVerilog and Direct Programming InterfaceDocument25 pagesSystemVerilog and Direct Programming InterfaceLiudeNo ratings yet
- Setup1 1210Document32 pagesSetup1 1210Akhila PurushothamanNo ratings yet
- Assembly LanguageDocument15 pagesAssembly LanguageStephanie Bush100% (1)
- UVM QuestionsDocument2 pagesUVM QuestionsVigna VinodNo ratings yet
- VHDL Coding Tips and TricksDocument209 pagesVHDL Coding Tips and TricksvinutaNo ratings yet
- Sva FV Tutorial HVC2013Document118 pagesSva FV Tutorial HVC2013passep08No ratings yet
- Digital Electronics QuestionsDocument8 pagesDigital Electronics QuestionsShivamahendar SunkaNo ratings yet
- IHI0024C Amba Apb Protocol SpecDocument28 pagesIHI0024C Amba Apb Protocol SpecAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- APBDocument29 pagesAPBsuneeldvNo ratings yet
- Vlsi World - Verilog Code For RAM & ROM12456Document6 pagesVlsi World - Verilog Code For RAM & ROM12456gssharma888No ratings yet
- 1 Clock Domain CrossingDocument15 pages1 Clock Domain Crossingkrishna chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- EE520 ASIC Design PDFDocument44 pagesEE520 ASIC Design PDFthiendoan_bkNo ratings yet
- Timing Analysis: Elec 326 Sequential Circuit TimingDocument43 pagesTiming Analysis: Elec 326 Sequential Circuit TimingArpit KapoorNo ratings yet
- Ec1461 Vlsi DesignDocument17 pagesEc1461 Vlsi DesignArunkumarNo ratings yet
- Timing Design in Digital Systems: Dr. Paul D. FranzonDocument24 pagesTiming Design in Digital Systems: Dr. Paul D. FranzonMaheshNo ratings yet
- Negative Setup and Hold TimeDocument3 pagesNegative Setup and Hold TimeMasterbrain BrainNo ratings yet
- Implementing A Source Synchronous Interface v2.0Document47 pagesImplementing A Source Synchronous Interface v2.0Gautham PopuriNo ratings yet
- 19 MooreMealyDocument23 pages19 MooreMealynvsrox100% (1)
- Zynq 7020Document4 pagesZynq 7020NGUYỄN HOÀNG LINHNo ratings yet
- Ahb-Lite To Apb Protocol: BY Shraddha Devaiya EC - 018 Anand Therattil EC - 092Document29 pagesAhb-Lite To Apb Protocol: BY Shraddha Devaiya EC - 018 Anand Therattil EC - 092AnandNo ratings yet
- UART Protocol 00 For BC3MM Module Rev1.0Document12 pagesUART Protocol 00 For BC3MM Module Rev1.0kaaashuNo ratings yet
- Digital QuestionsDocument3 pagesDigital QuestionsCLARITY UDTNo ratings yet
- VHDL Bram BromDocument9 pagesVHDL Bram BromGmit MandyaNo ratings yet
- UVM Interview Questions VLSI Encyclopedia PDFDocument7 pagesUVM Interview Questions VLSI Encyclopedia PDFQuastnNo ratings yet
- 24 LFSRDocument24 pages24 LFSRAbdul RajakNo ratings yet
- Asic DDR PhyDocument1 pageAsic DDR PhylmlululuNo ratings yet
- Design ExercisesDocument13 pagesDesign ExercisesCristal NgoNo ratings yet
- ASIC-System On Chip-VLSI Design - Clock GatingDocument4 pagesASIC-System On Chip-VLSI Design - Clock Gatinguni_saraNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument6 pagesInterview QuestionsarghaNo ratings yet
- Tsu and TH - PdfsdfsdsaDocument15 pagesTsu and TH - PdfsdfsdsaasfagehejhdhdsgdfsdfgNo ratings yet
- Timing (3rd Internal)Document13 pagesTiming (3rd Internal)Utsav ParasharNo ratings yet
- Set Hold BasicsDocument17 pagesSet Hold BasicsMelissa AdamsNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil TransportationDocument7 pagesCrude Oil TransportationTHE TERMINATORNo ratings yet
- Digital - Module For Gen7Document145 pagesDigital - Module For Gen7Ruary CajucomNo ratings yet
- Bolloju Satya Akhil Kumar Mobile: +91-7013868886: Tirumala Junior CollegeDocument2 pagesBolloju Satya Akhil Kumar Mobile: +91-7013868886: Tirumala Junior CollegeAkhil KumarNo ratings yet
- 1c Manual Partes Grand Caravan 1999Document605 pages1c Manual Partes Grand Caravan 1999Sebastian SirventNo ratings yet
- I560 Bubble Jet Printer: Affordability, High Quality and Speed With Direct Photo PrintingDocument4 pagesI560 Bubble Jet Printer: Affordability, High Quality and Speed With Direct Photo PrintingsophieheeNo ratings yet
- Theory Class 1dggfgDocument250 pagesTheory Class 1dggfgKumar GorlaNo ratings yet
- Search Engine Optimization - The Basics - SupportDocument4 pagesSearch Engine Optimization - The Basics - SupportDow JonesNo ratings yet
- Measure Wireless Network Performance Using Testing Tool Iperf PDFDocument7 pagesMeasure Wireless Network Performance Using Testing Tool Iperf PDFmuslim1234No ratings yet
- Research About Business: Processes ofDocument24 pagesResearch About Business: Processes ofPhuong Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- OBS Studio Help Guide 2022-08-31Document272 pagesOBS Studio Help Guide 2022-08-31Zihu66No ratings yet
- Abb - ffwd-2-17 - 20 - Enabling Transformer Intelligence For Smart Operations With Comem EdevicesDocument2 pagesAbb - ffwd-2-17 - 20 - Enabling Transformer Intelligence For Smart Operations With Comem Edeviceslxd.hepNo ratings yet
- FM/AM Compact Disc Player Autoestéreo para Disco Compacto: CDX-S11S CDX-S11Document32 pagesFM/AM Compact Disc Player Autoestéreo para Disco Compacto: CDX-S11S CDX-S11Sabrina HarrisNo ratings yet
- Cd4511be PDFDocument16 pagesCd4511be PDFkaufestiNo ratings yet
- State of E-Governance in Maharashtra 2014Document195 pagesState of E-Governance in Maharashtra 2014Amit Chatterjee100% (1)
- DuraMON GLASS Series User Reference Manual 07052 000 ADocument42 pagesDuraMON GLASS Series User Reference Manual 07052 000 Arohit sonawaneNo ratings yet
- FortiGate Sec 01 IntroductionDocument25 pagesFortiGate Sec 01 Introductionravi pithawalaNo ratings yet
- SATURN v11.3.12 Manual (Main) PDFDocument1,009 pagesSATURN v11.3.12 Manual (Main) PDFLeonardo rojoNo ratings yet
- Power QualityDocument9 pagesPower QualityJuhi PatilNo ratings yet
- Cloud Information Model Overview v2Document19 pagesCloud Information Model Overview v2CharLy HuynhNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document1 pageQuiz 2alitehmNo ratings yet
- Procurement Plan: Al-Janadriyah Exhibition Facility, Ar-RiyadhDocument11 pagesProcurement Plan: Al-Janadriyah Exhibition Facility, Ar-RiyadhJonald DagsaNo ratings yet