Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is CASE? Background
Uploaded by
Anas ImaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is CASE? Background
Uploaded by
Anas ImaCopyright:
Available Formats
3/16/2014
1
What is CASE?
Computer aided software
engineering (CASE) is the use of
software tools to assist in the
development and maintenance of
software
Background
To speed up the software system
building process, a new concept of
designing software is introduced in the
'70s, called Computer Aided Software
Engineering (CASE). This term is used
for a new generation of tools that
applies rigorous engineering principles
to the development and analysis of
software.
Why is CASE important?
CASE allows for rapid development of
software because of the increasing
speed of changing market-demands
new products replace old ones much
earlier than before, so the development
of new products has to go faster.
4
CASE Tools
Prerequisites to tool use
Need a collection of useful tools that help
in every step of building a product
Need an organized layout that enables
tools to be found quickly and used
efficiently
Need a Skilled craftsperson who
understands how to use the tools
effectively
3/16/2014
2
5
CASE Tools
Upper CASE
requirements
specification
planning
design
Lower CASE
implementation
integration
maintenance
6
CASE Building Blocks - 1
CASE tools
Integration framework
specialized programs allowing CASE tools
to communicate with one another
Portability services
allow CASE tools and their integration
framework to migrate across different
operating systems and hardware platforms
without significant adaptive maintenance
7
CASE Building Blocks - 2
Operating system
database and object management services
Hardware platform
Environmental architecture
hardware and system support
8
A Taxonomy of CASE Tools
business systems planning
project management
support
analysis and design
integration &testing
reengineering
prototyping/simulation tools
CASE
Database
programming
framework
3/16/2014
3
9
CASE Tool Taxonomy - 1
Business process engineering tools
represent business data objects, their
relationships, and flow of the data objects between
company business areas
Process modeling and management tools
represent key elements of processes and provide
links to other tools that provide support to defined
process activities
Project planning tools
used for cost and effort estimation, and project
scheduling
10
CASE Tool Taxonomy - 2
Risk analysis tools
help project managers build risk tables by
providing detailed guidance in the
identification and analysis of risks
Requirements tracing tools
provide systematic database-like approach
to tracking requirement status beginning
with specification
11
CASE Tool Taxonomy - 3
Metrics and management tools
management oriented tools capture project
specific metrics that provide an overall indication
of productivity or quality, technically oriented
metrics determine metrics that provide greater
insight into the quality of design or code
Documentation tools
provide opportunities for improved productivity by
reducing the amount of time needed to produce
work products
12
CASE Tool Taxonomy - 4
System software tools
network system software, object management
services, distributed component support, and
communications software
Quality assurance tools
metrics tools that audit source code to determine
compliance with language standards or tools that
extract metrics to project the quality of software
being built
3/16/2014
4
13
CASE Tool Taxonomy - 5
Database management tools
RDMS and OODMS serve as the foundation for
the establishment of the CASE repository
Software configuration management tools
uses the CASE repository to assist with all SCM
tasks (identification, version control, change
control, auditing, status accounting)
Analysis and design tools
enable the software engineer to create analysis
and design models of the system to be built,
perform consistency checking between models
14
CASE Tool Taxonomy - 6
PRO/SIM tools
prototyping and simulation tools provide software
engineers with ability to predict the behavior of
real-time systems before they are built and the
creation of interface mockups for customer review
Interface design and development tools
toolkits of interface components, often part
environment with a GUI to allow rapid prototyping
of user interface designs
15
CASE Tool Taxonomy - 7
Prototyping tools
enable rapid definition of screen layouts, data
design, and report generation
Programming tools
compilers, editors, debuggers, OO programming
environments, fourth generation languages,
graphical programming environments, applications
generators, and database query generators
Web development tools
assist with the generation of web page text,
graphics, forms, scripts, applets, etc.
16
CASE Tool Taxonomy - 8
Integration and testing tools
Data acquisition
get data for testing
static measurement
analyze source code without using test cases
dynamic measurement
analyze source code during execution
Simulation
simulate function of hardware and other externals)
test management
cross-functional tools
3/16/2014
5
17
CASE Tool Taxonomy - 9
Static analysis tools
code-based testing tools, specialized testing
languages, requirements-based testing tools
Dynamic analysis tools
intrusive tools modify source code by inserting
probes to check path coverage, assertions, or
execution flow, non-intrusive tools use a separate
hardware processor running in parallel with
processor containing the program being tested
18
CASE Tool Taxonomy - 10
Test management tools
coordinate regression testing, compare
actual and expected output, conduct batch
testing, and serve as generic test drivers
Client/server testing tools
exercise the GUI and network
communications requirements for the client
and server
19
CASE Tool Taxonomy - 11
Reengineering tools
reverse engineering to specification tools
generate analysis and design models from
source code, where used lists, and other
design information
code restructuring and analysis tools
analyze program syntax, generate control flow
graph, and automatically generates a
structured program
on-line system reengineering tools
used to modify on-line DBMS
20
CASE tool support
Requirements storage
Requirements should be managed in a secure,
managed data store
Change management
The process of change management is a workflow
process whose stages can be defined and
information flow between these stages partially
automated
Traceability management
Automated retrieval of the links between
requirements
3/16/2014
6
21
CASE Workbenches
A coherent set of tools that is designed to
support related software process activities
such as analysis, design or testing
Analysis and design workbenches support
system modelling during both requirements
engineering and system design
These workbenches may support a specific
design method or may provide support for a
creating several different types of system
models
22
Integrated CASE Environments -1
Provide mechanism for sharing information among all
tools contained in the environment
Enable changes to items to be tracked to other
information items
Provide version control and overall configuration
management
Allow direct access to any tool contained in the
environment
Establish automated support for the chosen software
process model, integrating CASE tools and SCI's into
a standard work break down structure
23
Integrated CASE Environments -2
Establish automated support for the chosen software
process model, integrating CASE tools and SCI's into
a standard work break down structure
Enable users of each tool to experience a consistent
look and feel at the human-computer interface
Support communication among software engineers
Collect both management and technical metrics to
improve the process and the product
24
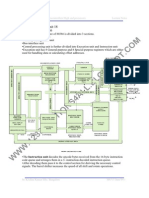
The Challenge: Putting it Together
Operating
System
Portability
Services
Integration
Framework
IPSE
CASE
Tools
3/16/2014
7
25
An Integration Framework
user i nterface l ayer
obj ect management l ayer
shared reposi tory l ayer
tool s l ayer
interface tool kit
presentation protocol
tools management services
CASE
tool
integration services
configuration management services
CASE database
access control functions
26
Integration Architecture - 1
User Interface Layer
interface toolkit
contains software for UI management and library of
display objects
common presentation protocol
guidelines that give all CASE tools the same look and
feel (icons, mouse behavior, menu names, object names)
Tools Layer
tools management services
control behavior of tools inside environment
CASE tools themselves
27
Integration Architecture - 2
Object management layer (OML)
performs the configuration management
function, working with the CASE repository
OML provides integration services
Shared repository layer
CASE database and access control
functions enabling the OML to interact with
the database
28
CASE Repository Functions - 1
Data integrity
includes functions to validate entries to the
repository and ensure consistency among related
objects
Information sharing
provides mechanism for sharing information
among multiple developers and multiple tools,
controls modification of information
Data-tool integration
establishes shared data model and performs
configuration management functions
3/16/2014
8
29
CASE Repository Functions - 2
Data-data integration
database management system allowing access to
related objects so functions can be achieved
Methodology enforcement
E-R model used to define steps needed to be
conducted to build the repository contents
Document standardization
definition of objects in the database leads directly
to a standard approach for creation of engineering
documents
30
Data Integration:
The CASE Repository
CASE Database
Objects
Object Management Layer
integration services
SCM services
Shared Repository Layer
database
access control functions
31
CASE Repository Content Summary
Problem to be solved.
Problem domain.
Emerging solution.
Rules pertaining to software process
methodology.
Project plan.
Organizational content.
32
DBMS Features Needed for
CASE Repositories
Non-redundant data storage
High-level access
Data independence
Transaction control
Ad hoc data queries and reports
Openness
Multi-user support
3/16/2014
9
33
CASE Repository Features - 1
Storage of sophisticated data structures
diagrams
documents
files
simple variables
information model describing relationships
and semantics of data stored in repository
34
CASE Repository Features - 2
Integrity enforcement
business rules
policies, constraints
requirements on the information being
entered into repository, triggers may be
used to check the validity of the design
models in real time
35
CASE Repository Features - 3
Semantic-rich tool interface
repository meta-model contains semantics that
enable a variety of tools to interpret meaning of
data stored in the repository
Process/project management
contains information about the software
application
characteristics of each project
organization's general process for software
development - phases, tasks, deliverables
36
Configuration Management
Features Need by CASE Tools
Versioning
Dependency tracking and change
management
Requirements tracing
Configuration management
Audit trails
3/16/2014
10
37
CASE tools for
Configuration Management
Configuration management processes are
standardized and involve applying pre-
defined procedures
Large amounts of data must be managed
CASE tool support for configuration
management is essential
Mature CASE tools to support configuration
management are available ranging from
stand-alone tools to integrated workbenches
38
Change Management Tools
Change management is a procedural process
so it can be modelled and integrated with a
version management system
Change management tools
Form editor to support processing the change
request forms
Workflow system to define who does what and to
automate information transfer
Change database that manages change proposals
and is linked to a VM system
39
Version Management Tools
Version and release identification
Systems assign identifiers automatically when a
new version is submitted to the system
Storage management.
System stores the differences between versions
rather than all the version code
Change history recording
Record reasons for version creation
Independent development
Only one version at a time may be checked out for
change. Parallel working on different versions
You might also like
- Software Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandSoftware Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- CASE Tools OverviewDocument28 pagesCASE Tools OverviewAbha DwivediNo ratings yet
- CASE ToolsDocument49 pagesCASE ToolsBhuvnesh SinghNo ratings yet
- CASE Tools Assist Software EngineersDocument6 pagesCASE Tools Assist Software EngineersRoshan KCNo ratings yet
- CASE Tools: CIS 376 Bruce R. Maxim UM-DearbornDocument53 pagesCASE Tools: CIS 376 Bruce R. Maxim UM-DearbornGabriel KamauNo ratings yet
- CASE ToolsDocument5 pagesCASE ToolsMAHANT COLLEGE RAIPURNo ratings yet
- Texonomy of Case Tools: Business Process Engineering ToolsDocument4 pagesTexonomy of Case Tools: Business Process Engineering ToolsMAHANT COLLEGE RAIPURNo ratings yet
- Chapter 31 Computer-Aided Software EngineeringDocument5 pagesChapter 31 Computer-Aided Software Engineeringbhuvi2312No ratings yet
- CASE Tool TaxonomyDocument4 pagesCASE Tool Taxonomycoolneha33No ratings yet
- CASE ToolsDocument20 pagesCASE ToolsJanhvi KagranaNo ratings yet
- CASE ToolsDocument21 pagesCASE ToolsgaurmishNo ratings yet
- Case Tools 1Document47 pagesCase Tools 1Karthika. NNo ratings yet
- Case ToolsDocument21 pagesCase ToolsNavneet Kaur GillNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Implementation Strategies PDFDocument32 pagesChapter 4 Implementation Strategies PDFVince AmeliaNo ratings yet
- CS8494 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING SYLLABUSDocument23 pagesCS8494 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING SYLLABUSTamizharasi ANo ratings yet
- Information Systems Building Blocks & Development MethodsDocument6 pagesInformation Systems Building Blocks & Development Methodsproshanto salmaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I: Software Engineering & Process Models: Dual Role of SoftwareDocument4 pagesUNIT-I: Software Engineering & Process Models: Dual Role of SoftwareAnsh GoelNo ratings yet
- CASE Tools 1Document53 pagesCASE Tools 1Liiswag MpNo ratings yet
- Ses05 GSLC Chap05 Implementation StrategiesDocument26 pagesSes05 GSLC Chap05 Implementation StrategiesRonan WisnuNo ratings yet
- CASE Building BlocksDocument20 pagesCASE Building BlocksArun VinodhNo ratings yet
- Rup & Case ToolDocument17 pagesRup & Case ToolsafizaNo ratings yet
- Practical 7Document4 pagesPractical 721ce63No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 OoadDocument22 pagesChapter 3 Ooadsujitha14No ratings yet
- u1.Software Proc - Models.pptDocument72 pagesu1.Software Proc - Models.pptakhil2113139No ratings yet
- Database Design ApproachesDocument35 pagesDatabase Design ApproachesMyra Lea MedranoNo ratings yet
- N109 - SE - Exp 10Document8 pagesN109 - SE - Exp 10Shadow MistryNo ratings yet
- CASE ToolsDocument5 pagesCASE ToolscoolhemakumarNo ratings yet
- Tools and ArchitecturesDocument7 pagesTools and ArchitecturesAniela OlteanuNo ratings yet
- Systems Analysis and Design9th Edition: Toolkit B: CASE ToolsDocument19 pagesSystems Analysis and Design9th Edition: Toolkit B: CASE ToolsCobaNo ratings yet
- Case ToolsDocument13 pagesCase Toolssaipriya pulipatiNo ratings yet
- Arman KanooniDocument5 pagesArman Kanooniprabu2125No ratings yet
- Case 1Document13 pagesCase 1Tista BhaduriNo ratings yet
- CBSE-10Document29 pagesCBSE-10Rajput RahateNo ratings yet
- SE411 - Matt Heinzelman Software Quality Assurance PresentationDocument39 pagesSE411 - Matt Heinzelman Software Quality Assurance Presentationannaji03No ratings yet
- SEpdfDocument17 pagesSEpdfNilesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Alex Persentation OrgDocument22 pagesAlex Persentation OrgBizuneh getuNo ratings yet
- Review of Known MethodologiesDocument114 pagesReview of Known MethodologiesMuhammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument10 pagesSoftware EngineeringHET JOSHINo ratings yet
- CARLL Is SAD Again Chapter 2Document5 pagesCARLL Is SAD Again Chapter 2CarllNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 SummaryDocument3 pagesLecture 5 SummaryPaul PaulNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Computer Aided Software Engineering ToolsDocument18 pagesCharacteristics of Computer Aided Software Engineering ToolsNilesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Case Tools and StudyDocument19 pagesCase Tools and StudyRAJ PATELNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Course Code: 210253Document76 pagesSoftware Engineering Course Code: 210253Shubhangi PingleNo ratings yet
- Chapter2-Software ProcessDocument63 pagesChapter2-Software Processapi-237335979No ratings yet
- SDLC Stages for Systems DevelopmentDocument59 pagesSDLC Stages for Systems DevelopmentOscar FrizziNo ratings yet
- The Systems Development EnvironmentDocument47 pagesThe Systems Development EnvironmentAditya BhusalNo ratings yet
- CaseDocument5 pagesCaseSalman JavedNo ratings yet
- Introduction to CASE Tools for Software EngineeringDocument18 pagesIntroduction to CASE Tools for Software EngineeringAmina Muhammad AminNo ratings yet
- DFD and CASE ToolsDocument32 pagesDFD and CASE ToolsSwati MallickNo ratings yet
- Dasar Rekayasa Perangkat Lunak untuk Pengembangan SistemDocument41 pagesDasar Rekayasa Perangkat Lunak untuk Pengembangan Sistemvalorant abangNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Assurance PresentationDocument39 pagesSoftware Quality Assurance PresentationDebjit PaulNo ratings yet
- Software Lab 6th SemDocument21 pagesSoftware Lab 6th Semsalonia.it.21No ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument203 pagesSoftware Engineeringamitauti100% (4)
- Zbook Computer Aided Software Engine C55aedDocument23 pagesZbook Computer Aided Software Engine C55aedpouriaNo ratings yet
- SPM Unit-2 Part-1Document19 pagesSPM Unit-2 Part-1agrawaldeepti917No ratings yet
- SE-Nature-SoftwareDocument30 pagesSE-Nature-SoftwareJess sicaNo ratings yet
- Software Design Concepts OverviewDocument7 pagesSoftware Design Concepts OverviewYugendra BabuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To System AnalysisDocument29 pagesIntroduction To System Analysisjheneryjane mariñoNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Fundamentals - 2021Document24 pagesSoftware Engineering Fundamentals - 2021Incog NitoNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Development Life Cycle and MethodologiesDocument24 pagesInformation Systems Development Life Cycle and MethodologiesZyra MediosNo ratings yet
- M3 Unit 3Document11 pagesM3 Unit 3Anas ImaNo ratings yet
- ANAS CV June 2015 UpdatedDocument6 pagesANAS CV June 2015 UpdatedAnas ImaNo ratings yet
- SEO Project Management QuestionsDocument39 pagesSEO Project Management QuestionsAnas ImaNo ratings yet
- M3 Unit 1Document15 pagesM3 Unit 1Anas ImaNo ratings yet
- M3 Unit 2Document14 pagesM3 Unit 2Anas ImaNo ratings yet
- What Is CASE? BackgroundDocument10 pagesWhat Is CASE? BackgroundAnas ImaNo ratings yet
- Schemekerala University B Tech Computer Science SyllabusDocument103 pagesSchemekerala University B Tech Computer Science SyllabusAbhijith MarathakamNo ratings yet
- 8 1Document28 pages8 1Anas ImaNo ratings yet
- User Interface Design Principles for Consistency and UsabilityDocument5 pagesUser Interface Design Principles for Consistency and UsabilityAnas ImaNo ratings yet
- OpenGTS Modification and CustomizationDocument2 pagesOpenGTS Modification and CustomizationAnas ImaNo ratings yet
- Advanced MPDocument1 pageAdvanced MPAnas ImaNo ratings yet
- OpenGTS ConfigDocument61 pagesOpenGTS ConfigtestingasdfNo ratings yet
- SE-Unit VDocument37 pagesSE-Unit VAMIT KUMAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Sop PrintDocument2 pagesSop PrintSandeep KocharNo ratings yet
- VW Audit Cheklist - EmptyDocument5 pagesVW Audit Cheklist - EmptySaipul IzaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineer Cover Letter 2018 - GreenDocument2 pagesCivil Engineer Cover Letter 2018 - Greenuche ekeNo ratings yet
- Ampt 1Document1 pageAmpt 1Sanjib GogoiNo ratings yet
- Pengantar BFO - Ihya RamadhanuDocument37 pagesPengantar BFO - Ihya RamadhanuAnggreawan JurinNo ratings yet
- Wood Design Manual 2010Document9 pagesWood Design Manual 2010Simona Ionut0% (1)
- Review of Design Thinking Experiences in Higher EducationDocument8 pagesReview of Design Thinking Experiences in Higher EducationEtti PuspitaNo ratings yet
- XPIP STE03360 Heat Exchanger & Horizontal Vessel Design GuideDocument42 pagesXPIP STE03360 Heat Exchanger & Horizontal Vessel Design Guidemacynthia26100% (1)
- Basalt FRP Reinforcing Bars For Concrete StructuresDocument6 pagesBasalt FRP Reinforcing Bars For Concrete StructuresSuresh ShanmugavelNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis and Optimization of Universal Joint Yoke Using CAE ToolsDocument4 pagesFinite Element Analysis and Optimization of Universal Joint Yoke Using CAE ToolsEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- Santa Clara SupplementDocument1 pageSanta Clara SupplementAppleJuiceNo ratings yet
- JIS (Japan Industrial Standards) : Dwi Marta NurjayaDocument9 pagesJIS (Japan Industrial Standards) : Dwi Marta Nurjayaodongo johnNo ratings yet
- High Performance Concrete M85 Mix DesignDocument33 pagesHigh Performance Concrete M85 Mix DesignraguNo ratings yet
- Construction Quality, Safety & EnvironmentDocument5 pagesConstruction Quality, Safety & EnvironmentSUPRIYANo ratings yet
- CH ENGR 104A Spring 2015 Lab CourseDocument10 pagesCH ENGR 104A Spring 2015 Lab CoursenadimNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Engineering FinalDocument5 pagesWater Resources Engineering FinalShrunkhal DubeNo ratings yet
- TW-70 Plan and Sections of Box Culvert 2Document2 pagesTW-70 Plan and Sections of Box Culvert 2inam khanNo ratings yet
- 33 05 13 Manholes and Structures 10Document4 pages33 05 13 Manholes and Structures 10Mohammed AlkhateebNo ratings yet
- Success, Case #KEL156Document15 pagesSuccess, Case #KEL156kpraneethk100% (2)
- ABET ENVE Program ReviewDocument252 pagesABET ENVE Program ReviewDien NoelNo ratings yet
- Khodabakhshi-Parisa CVDocument5 pagesKhodabakhshi-Parisa CVapi-297430557No ratings yet
- Retrofitting of Concrete Structure With Fiber Reinforced Polymer PDFDocument8 pagesRetrofitting of Concrete Structure With Fiber Reinforced Polymer PDFHemp CretesNo ratings yet
- RCC Is Provision NotesDocument4 pagesRCC Is Provision NotessameerNo ratings yet
- Structure ChartDocument31 pagesStructure ChartTauheed ProltaNo ratings yet
- Slipform construction technique for continuous vertical constructionDocument4 pagesSlipform construction technique for continuous vertical constructionamarnath jagirdarNo ratings yet
- The Virginia Class Submarine ProgramDocument12 pagesThe Virginia Class Submarine Programcjnjr1No ratings yet
- BS Iso 14654-1999Document39 pagesBS Iso 14654-1999hz135874No ratings yet
- 4.3 Mechanical Anchoring-Systems (289-389) PDFDocument104 pages4.3 Mechanical Anchoring-Systems (289-389) PDFpabmataNo ratings yet