Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LukePark'SKoreanGrammarGuide (6!23!2011)
Uploaded by
SaiAungOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LukePark'SKoreanGrammarGuide (6!23!2011)
Uploaded by
SaiAungCopyright:
Available Formats
Korean Grammar Guide
Welcome
Korean Alphabets
Sentence Order
Particles - ,
Particles - , ,
Pronouns- This, It, That
Nouns - Present, Past
Nouns - Nominalizing Verbs
Nouns - Numbers and ounting
Ad!ecti"es - Present, Past
Ad!ecti"es - Polite #Present, Past$
Ad!ecti"es - %escripti"e
Ad!ecti"es - onnecti"e
Verbs - Present, Past
Verbs - Polite #Present, Past$
Verbs - &uture #Will$
Verbs - ontinuous
Verbs - onnecti"e
Verbs - an
Verbs - 'a"e
Verbs - Want
Verbs - %escripti"e I
Verbs - %escripti"e II
Verbs - Speech
Ad"erbs -
Particles - ((
Particles - (
Particles - ,
Particles - #onl)$
Possessi"e -
on!unctions - And
on!unctions - *ut
on!unctions - *ut #($
on!unctions - *ecause, So
on!unctions - *ecause #$
on!unctions - I+
on!unctions - When
on!unctions - While
,W-'
Advanced Grammar
omparati"es . Superlati"es
Imperati"es - ,
'a"e to -
Allo/ed to -
I li0e doing - ,
I thin0 - 1 2Opinion3
I thin0 - 24eneral3
Special Expressions
Are )ou doing5 - 1 5 #In+ormal$
Are )ou doing5 - 1 5 #Polite$
Are /e doing5 - ( 5
To do something - 1
Tr) doing -
O+ course, I6"e done it be+ore -
4i"e the +a"our o+ doing -
Would )ou li0e to go5 - 5
Shall /e do something5 - 5
It6s cold, isn6t it5 - 5
7et6s do it -
8as) to do ( %i++icult to do - 1 ( 1
I 0no/ ho/ -
I6m in the habit o+ - 1 1
Miscellaneous
Addressing people
Welcome: The Beginning
Welcome You All to the Korean Grammar Guide!
This blog was first created in 2006 as an experiment to help people who would lie to learn Korean b!
pro"iding some basic grammar lessons on Korean#
$"er the !ears% & was able to put up more and more lessons% and as of now% in 'anuar! 20((% there are more
than 60 lessons on Korean grammar in this blog#
The principles in writing these lessons ha"e been that & remain intentional about maing them as eas! to
understand and readil! applicable in dail! life as & can% and comprehensi"e enough to co"er ma)or points of
Korean grammar which include both the Written and *poen forms#
+ow% what do & mean b! written and spoen forms,
&n Korean% the "erb endings change depending on whether the language is used in writing or speech#
Note: &n Korean grammar% the "erbs come at the end of a sentence# -or more on the sentence order% please
read *entence $rder#
-or example% . . which means .& went to school. is a written form% and .
. is a spoen form#
/ & went to school 0written form as in writing% boos% diar! and newspaper1
/ & went to school 0spoken form as in con"ersations% mo"ies and dramas1
As !ou can see% the ending of a "erb changes from to % both of which mean .went.#
Therefore !ou2d write in one wa! but spea in a slightl! different wa!# 3ut don2t be too alarmed at the
difference% as there are simple patterns to it% and !ou2ll get to learn them along the wa!#
&t is also important to learn the differences in degrees of formalities in the Korean language#
There are three ma)or t!pes in the degrees of formalit!4
&nformal
5olite
6onorific
&n expressing the politeness in the speech% Korean differs from 7nglish in that the "erb endings change
depending on the age and ran of the person being addressed to and the social setting one finds oneself in# -or
example% when &2m ased% .Where are !ou going,. & might answer% .&2m going to school. in the following
wa!s4
8 9&nformal% to people of the same age as me or !ounger than me% especiall! among close
friends:
8 95olite% to people older than me% and in formal social situations:
8 96onorific% this is rarel! used in normal con"ersations# & would sa! this t!pe of
speaing is onl! found in "er! formal settings such as on the news or in the arm!#:
You would use the polite form e"en when the person !ou2re speaing to is of the same age as !ou or !ounger
than !ou if !ou2re not "er! close to the person and;or !ou2re in a formal social setting# &2d sa! it2s best to stic
to the polite form first and then use the informal form later as !ou gain more understanding of the Korean
language#
The ma)or mar of the di"ision is probabl! the age# The polite language is used to people abo"e one2s age and
informal language to people e<ual to and below one2s age#
6owe"er% generall!% the polite language is generall! used in man! social situations and the informal language
is usuall! used among close friends#
& am tr!ing to la! out some basics to the language of Korean# 6owe"er it2d be good at this point to di"e into
the lessons and learn them for !ourself#
You can start reading the grammar guide from the top to bottom in the order as it2s designed to guide !ou from
the basics to intermediate and ad"anced grammar#
3efore !ou go% here is a bit of histor! of 0Hangeul% the Korean alphabet14
Korean is the official language of Korea% both +orth and *outh# There are around => million people who
spea Korean around the world#
9(:
0the Korean alphabet1 was in"ented b! *e)ong the Great in the (?th centur!# 3efore that time% people
used 6an)a 0the e<ui"alent of the @hinese characters1 which was not onl! difficult to learn but was also
considerabl! different to the Korean grammar and sentence order#
92:
is a phonetic writing s!stem which means that the words correspond to pronunciation#
The 7nglish alphabet is phonetic whereas the @hinese characters are not#
&f !ou learn the 7nglish alphabet% !ou can read an 7nglish writing fairl! well although !ou ma! not
understand the meaning#
Korean is e"en more phonetic than that of 7nglish and man! other languages% in that each consonant and
"owel in Korean mostl! ha"e onl! one sound#
-or example%
/ n
/ a 0as in car and mama% short sound1
A/ 9na: 0which means .&. as in .&. am Bue1
-ollowing the guide down the column on the right8hand of the page% we2re now mo"ing onto learning the
sounds of the consonants and "owels of #
You2ll learn to write and pronounce each of these consonants and "owels% and how to form a character in this
next lesson#
Keep on reading!
& hope !ou en)o! this )ourne! of learning a new language!
& thin it2s alwa!s exciting to learn a new language! CD
Bue
References
9(: Wiipedia4 Korean language% http4;;en#wiipedia#org;wii;KoreanElanguageF6istor!% accessed 'an 20((#
92: Wiipedia4 *e)ong the Great% http4;;en#wiipedia#org;wii;*e)ongEtheEGreatF6angul% accessed 'an 20((#
The Korean Alphabet
Hangeul or 0the Korean alphabet1 literall! means .the Korean writing#.
&n % the Korean alphabet% consists of (G consonants and (0 "owels#
@osonants4
Howels4
&n addition% there are ? double consonants and (( double "owels#
Double consonants4
Double "owels4
Additionall!% there are (( final double consonants#
-inal double consonants4
You will get to learn these basic consonants and "owels% learning how to read% write and pronounce#
-or the purpose of learning the alphabet% & highl! recommend the following resources to help !ou with
familiariIing !ourself with the consonants and "owels in #
Bearn 6angeul4 Korean Wii 5ro)ect
Bearn to read and write 6angeul b! TTJ&K
Click on the alphabet to listen to their corresponding pronunciations.
[Consonants
/ g
/ n
/ d
/ l% r 0 is a sound somewhere between l and r1
/ m
/ b
/ s
/ .no sound. when used as a first consonant% .ng. when used as a final consonant#
/ )
/ ch
/
/ t
/ p
/ h
[!owels
/ a
/ !a
/ eo
/ !eo
/ o
/ !o
/ u
/ !u
/ eu
/ i
["ouble consonants
/ gg @lic on the lin to hear the difference between the sounds of % and #
/ dd +ote the difference in soundsC % and #
/ bb +ote the difference in soundsC% and #
/ ss +ote the difference in soundsC and
/ )) +ote the difference in soundsC % and
Jore lins4 % % % %
["ouble !owels
/ ae
/ !ae 0rarel! used1
/ e
/ !e
/ wa
/ wae
/ oe
/ wo
/ we 0rarel! used1
/ wi
/ ui
# How to form a character
There are two wa!s of maing a character% using the consonants and "owels as building blocs#
&nitial consonant A Howel (#
&nitial consonant A Howel A -inal consonant 2#
(# 7xamples
/ A / ga
/ A / neo
/ A / do
/ A / lu;ru
/ A / meu
/ A / bi
2# 7xamples
/ A A / gag
/ A A / neon
/ A A / dod
/ A A / leul;reul
/ A A / )aeng
@haracters with final consonants of % and % all sound the same# Thus % and will sound exactl!
the same#
$or e%ample&
% % Their final consonants all sound the same# @lic on the lins to hear#
+ow% below is a list of the final consonants and their respecti"e sounds#
;; /
;; /
;;;;;; /
/
/
/
/
$or e%ample&
9: / fishing
9: / itchen
9: / front
9: / seed
9: / da!
-or a more detailed explanation and audio files% clic here#
When the initial consonant of second and;or third characters is % for example% and % the sound
of the final consonant of each letter is pronounced with the next "owel# 3ecause has no sound% is
pronounced as and as # These are )ust made8up words to show !ou how these wor#
9:
9:
-or more examples on this pronunciation% clic on the lin#
[$inal 'ouble consonants
There are also (( additional final double consonants# Their sounds are as follows# As !ou can see% the first
consonant of the double consonants is pronounced# 0except / % / and / 1 & do not
recommend that !ou learn these exhausti"el! right awa! because that is a hard wor and & rarel! emplo!ed
them in m! grammar lessons an!wa!# *o it would be better to come bac to these when !ou come across
them from time to time#
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
(g)
9: / amount
9: / sit
9: / man!
9: / read
9: / boil
9: / spacious
9: / a single wa!
9: / lic
9: / recite 0a poem1
9: / lose 0a thing1
9: / price
7xcellent pronunciation lessons b! *ogang Kn"ersit!
*ource4 http4;;orean#sogang#ac#r;
-or writing practices%
@onsonants
Howels
@onsonants A Howels
*ource4 *low but *T7ADY4 http4;;c!)n#com;(6?
*entence +r'er
&n regards to the order of a sentence% there are four basic t!pes in Korean# These are4
* A +
* A H
* A A
* A $ A H
L * / sub)ect% + / noun% A / ad)ecti"e% $ / ob)ect and H / "erb#
The tense of a sentence is determined b! the last part of a sentence% namel!% b! a noun% "erb or ad)ecti"e#
&n Korean% ad)ecti"es function lie "erbs in that the! can be con"erted to different forms to determine the
tense of a sentence#
-or example%
&n 7nglish% the past tense of .go. is .went#.
&n Korean% the past tense of .. 0gada% go1 is .. 0gatta% went1#
The "erbs function in the same wa! in 7nglish and Korean#
6owe"er% in the case of ad)ecti"es% the past tense of .good. in 7nglish is not .gooded. but it is written% .was
good#.
@ontrar! to this% in Korean% .. 0jota% good1 has a past tense form of .. 0joatta% was good1#
@ompare4
&n 7nglish% .good. 0present1 M .was good. 0past1
&n Korean% .. 0present1 M .. 0past1
Therefore% the ad)ecti"es in Korean function lie "erbs in that the! can be con"erted to a past tense or future
tense% or an! other tense forms#
This con"ersion of a "erb0or ad)ecti"e1 to its past% future% present continuous or past continuous tense forms is
called a "erb 0or ad)ecti"e1 .con)ugation#.
3efore proceeding to the explanation section below% & recommend that !ou read the .particles. alongside this
post#
To understand Korean grammar% it is crucial that !ou become familiar with the concept of a distinct part of
speech called% ,particles),
5articles are function words that indicate what the sub)ect or ob)ect is in a sentence#
-or example%
; is a topic particle
; is a identifier particle
; is an ob)ect particle
-or more information and explanation on particles% please refer to 05articles 8 % % % % 1#
+ow% let2s ha"e a loo at the four main t!pes of Korean sentences#
+ote4 * / *ub)ect% + / +oun% H / Herb% A / Ad)ecti"e% $ / $b)ect
-) * . N
/ & am a student
/ Bisa is a teacher
/ Andrew was a doctor
/ & am a middle school student [polite spoken form
-or more explanations on the * A + pattern% please read +ouns 8 5resent% 5ast)
/ &
/ student
/ Bisa
/ teacher
/ Andrew
/ doctor
/ & 0polite1
/ a middle school student
/) * . !
/ 'u8!oung runs [written form
/ 'u8!oung runs [polite spoken form
/ 'u8!oung "igorousl! runs
LAn ad"erb comes before a "erb#
/ 'u8Young 0a Korean male name1
/ run
/ run [spoken form
/ run [polite spoken form
/ "igorousl!
-or more information and explanations on "erbs% please read Herbs 8 5resent% 5ast and Herbs 8 5olite 95resent%
5ast:#
0) * . A
/ 6e is big
/ *he is small
/ Anne is prett! [written form
/ Anne is reall! prett! [polite spoken form
/ The mountain is beautiful
/ The weather is "er! good
/ he
/ big
/ she
/ small
/ Anne
/ reall!% "er!
/ prett!
/ mountain
/ beautiful
/ weather
/ good
-or more information and explanations on ad)ecti"es% please read% Ad)ecti"es 8 5resent% 5ast% Ad)ecti"es 8
5olite 95resent% 5ast: and Ad)ecti"es 8 @onnecti"e#
1) * . + . !
/ & ate an apple#
/ 'i8sung drins water#
/ The birds are singing songs#
/ Anna attends college 0uni"ersit!1 [written form
/ Anna attends college 0uni"ersit!1 [spoken form
/ Young8hee planted a flower in the garden !esterda!#
L+otice that the time01 and place01 are inserted between * and $#
/ &
/ apple
/ ate
/ water
/ drin
/ a bird
/ birds
/ song
/ sing
/ attend [written form
/ attend [polite spoken form
/ !esterda!
/ garden
/ flower
/ plant 0"erb1
&n addition% unlie 7nglish% it is <uite common to lea"e out the sub)ect in a sentence in Korean# When the
sub)ect is nown b! the readers or speaers% it is often left out# Therefore% depending on a situation or
context% it is $K to write or spea without beginning the sentence with a sub)ect#
A sub)ect ma! not be used in a sentence if it is nown who or what the sub)ect is# *o% the sentences below are
also correct and it is common in spoen Korean 0con"ersations1#
/ 0am;is1 a student
/ 0am;is1 a teacher
/ was a doctor
/ 0am;is1 a middle school student
/ runs
/ "igorousl! ran
/ 0am;is;are1 big
/ 0am;is;are1 small
/ 0am;is;are1 reall! good [spoken form
/ ate an apple
/ dran water [spoken form
/ sang songs [spoken form
/ planted a flower !esterda! [polite spoken form
-or more help with the particles% please refer to the following posts4
5articles 8 ;;
5articles 8 ;
5articles 8 %
5articles 8 9onl!:
5ossessi"e 8
2articles 3 &
This particles section is di"ided into two parts# The first part is on Topic and &dentifier particles 9% :% and
the second part% here% is on the remaining particles% 9% % :#
&n these two posts% we2re going to learn about ? common particles used in a sentence in Korean# These are4
; 8 Topic particle N *ub)ect particles
; 8 &dentifier particle O
8 Additi"e particle
; 8 $b)ect particle
8 Time;place particle
+ote4 & ha"e grouped ; and ; into one categor!% the 2*ub)ect particles#2 The explanations are gi"en
below in the 2*ub)ect 5articles2 section#
5articles are functional words that do not ha"e an! meaning in themsel"es# The! are lie helpers in that the!
are attached to the end of nouns to indicate what that noun is and how it functions in a sentence#
-or example%
/ & am a student
% the topic particle% is attached to the end of % which means the pronoun .&.% to show that the topic is
about .&. or the sub)ect is .&.#
6ere is another example%
/ & am a student% too#
&n this sentence% % the additi"e particle% is attached to to show that in addition to a person or people who
are students% .&.% too% am a student#
+ow% let us go through each of these particles#
4 [Topic 2article
The first particle% we2ll learn% is ;% the topic particle# ; is used for a sub)ect or topic of a sentence#
is used for nouns without a final consonant% and for nouns with a final consonant#
Bet me explain%
/ & am
/ A person is
consists of A
/ n 0an initial consonant1
/ a 0a "owel1
As !ou can see% is a word without a final consonant% therefore is attached to it#
$n the other hand% which means 2a person2 has as a final character% and
consists of AA
/ r%l 0an initial consonant1
/ a 0a "owel1
/ m 0a final consonant1
is a word with a final consonant# Therefore% is attached to it#
The reason for these two different t!pes of the topic particle% ;% is that for words with a final consonant% it
is easier to pronounce them with rather #
@ompare these two pronunciations%
/ sa8ram8nun
/ sa8ram8un M sa8ra8mun 9:
As !ou can see% is more rigid and awward to pronounce% whereas is more fluid and eas! to
pronounce# is actuall! pronounced # The final consonant of % which is % is transferred to
to mae it sound #
0 sounds a bit lie .*arah Joon. whereas ma! sound lie .*aram +oon.#1
Bisten to the pronunciations for !oursel"es in the Google Translate#
The following are example sentences using ;% the topic particle#
/ & am a student
/ 6e is ind
/ This is a pencil
/ The s! is high
/ *he studies
/ 'ohn went
/ Young8su ate
/ & 0pronoun1
/ a student
/ he
/ ind
/ this
/ pencil
/ s!
/ high
/ she
/ stud!
/ 'ohn
/ go
/ Young8su 0a male name1
/ eat
Kse Google Translate to listen the pronunciations of these words#
+ote4 There are no articles in the parts of speech in Korean# .A% an and the. which are used to identif! and
specif! a noun in 7nglish and other languages are absent in Korean grammar#
4 [5'entifier 2article
; is used similarl! as ; in that the! indicate a sub)ect but ; is used when it is necessar! to
identif! the person or thing that is taled about in a sentence#
-or example%
/ & bought
/ & bought
+ote4 is changed to when it is used before #
3oth of these two sentences mean .& bought. but puts more emphasis on the sub)ect of the
sentence% .&.#
&n the sentence% % it is more concerned about 6who6 bought rather than 2what2 & did#
$n the other hand% % is more concerned about 6what6 & did#
/ & bought 9&t wasn2t an!one else but I who bought:
/ & bought 9& bought rather than doing something else:
&t is similar to the wa! in 7nglish where a person stresses a certain word to gi"e it more emphasis or
importance#
-or example%
Who bought a new t8shirt,
/ 5 bought it#
Note: &t is incorrect to sa!% % because the person is asing about who bought a new t8shirt rather
than asing about what the! did#
What did !ou do in the par,
/ & slept 0& too a nap1
Note: The person ma! be asing to se"eral people about what the! did in the par# $ne person might sa! the!
too a stroll while another person ma! ha"e had lunch there# 3ut as for me% what & did was 6sleeping6#
Therefore%
/ & slept
&t is wrong to sa! in this case because the person is not asing about who slept but what the! did
in the par# &f the person ased me% 2Who slept in the par,2% & would answer% or
0Jar slept1#
The identifier particle% ;% identifies the sub)ect of a sentence# ; is concerned about who did the things
ased#
Bie the ; example abo"e% is used for words without a final consonant and for words with a final
consonant#
6ere are example sentences4
/ & dran 0&t wasn2t an!one else but me1
/ Younger brother;sister ate 0&t wasn2t someone else but them1
/ Jin8)i came 0&t wasn2t some other person but Jin8)i1
/ Anthon! went 0&t wasn2t some other person but Anthon!1
/ That is the 6an Pi"er
/ The building is high
/ The par is large;spacious
/ drin
/ !ounger brother;sister
/ eat
/ Jin8)i 0a female name1
/ come
/ Anthon!
/ go
/ that
/ the 6an Pi"er 0in *eoul1
/ a building
/ high
/ a par
/ spacious% large
Kse Google Translate to listen the pronunciations of these words#
*ub7ect 2articles [ 4 an' 4
; and ; both are used for the sub)ect of a sentence but ; introduces a topic or a sub)ect whereas
; identifies a sub)ect#
&n addition to their differences alread! explored abo"e% here is another big difference between the two
particles#
The topic particle% ;% is used in cases when we mae a general or factual statement whereas ; is not#
-or example%
/ A cheetah is fast
/ A cheetah is slow 0This would be a wrong statement1
6owe"er% if !ou "isited a Ioo and saw a cheetah who seems to mo"e "er! slowl!% !ou might sa!%
/ 0That1 cheetah is slow
*o the identifier particle% ;% indicates a certain person or thing that the speaer and listener now or are
aware of# &n this case% it would be that cheetah in the Ioo#
6ere is another example%
/ The sea is blue
/ The sea is blac 0&n general% this is a wrong statement#1
3ut sa!% !ou saw the sea at night and !ou ma! exclaim%
! / The sea is blac!
The sea in this sentence is identified as a particular sea at night% and both the speaer and listener now which
sea is being taled about# This is not a general statement# Therefore the identifier particle% ;% is used in
this case#
$f course% is also perfectl! acceptable# 6owe"er% the difference is that the sea in this
sentence is also a particular sea that is nown b! both the speaer and the listener#
/ The sea is blue 0A general statement1
/ The sea is blue 0The sea is identified and nown b! the speaer and listener1
&t2s similar to the wa! articles are used in 7nglish#
-or example%
An apple is red / 0A general or factual statement about an apple1
The apple is red / 0A particular apple that the speaer identifies and indicates to the
listener1
2articles 3 & &
This is the second part of the particles section on 9% % % % :# This post is on the remaining 9% %
: particles# 5lease read the first part on 9% :% the *ub)ect particles% if !ou missed it#
[A''iti8e 2article
The additi"e particle% % is similar to sub)ect particles ; and ; in that it is used for a sub)ect 0or
topic1# 6owe"er% adds the meaning of 2too2 or 2also2 to a sub)ect#
6ere are example sentences4
/ & am a student% too
/ 6e is ind% too
/ This is a pencil% too
/ The s! is high% too
/ *he studies% too
/ 'ohn went% too
/ Young8su ate% too
As a further explanation% please ha"e a loo at the following example4
/ Da"id was a ing
/ *olomon was a ing% too
alwa!s refers to the sub)ect# -or example% describes *olomon in terms of the fact that
he was a ing% too# +ot onl! was Da"id a ing but *olomon was also a ing#
/ Da"id
/ a ing
/ *olomon
6ere is another example%
/ 'enn! went outside
/ Yuri went outside% too
/ 'enn!
/ go outside% lea"e
/ Yuri
As !ou can see% is used when one wants tal about the same <ualit! or description about a different
sub)ect#
When we want to tal about additi"e <ualities and;or descriptions about the same sub)ect% is used#
-or example%
/ Da"id was a shepherd#
/ Da"id was also a ing#
The two sentences abo"e both describe a certain thing about the same sub)ect% % and refers to the
rest of the sentence rather than the sub)ect# describes a fact that Da"id .was also a ing#.
Therefore Da"id was both a shepherd and ing#
is used to gi"e an additi"e <ualit! or description about the same sub)ect#
6ere is one more example%
/ 'enn! is a college 0uni"ersit!1 student
/ 'enn! is also a music teacher
'enn! is both a college student and music teacher#
+ote4 &n spoen Korean% is usuall! used instead of #
/ 'enn! is a college 0uni"ersit!1 student
/ 'enn! is also a music teacher
4 [+b7ect 2article
The ob)ect particle% ;% is attached to an ob)ect which the "erb describes#
6ere are example sentences4
/ & ate noodles 9Literally, noodles ate:
/ read a boo
/ dran coe
TH / watched TH
/ wore clothes
/ built a house
/ made a cae
/ &
/ noodles
/ eat
/ a boo
/ read
/ coe
/ drin
/ see% watch
/ clothes
/ wear
/ house
/ build
/ a cae
/ mae
The usage difference between and is that is used for nouns without a final consonant% and for
nouns with a final consonant for the pronunciation2s sae#
/ too a photo
/ planted a tree
/ bought some bread
/ sold a car
/ crossed a ri"er
/ passed a bridge
/ did homewor
/ a photo
/ tae 0a photo1
/ a tree
/ plant 0"erb1
/ bread
/ bu!
/ a car
/ sell
/ a ri"er
/ cross 0"erb% motion1
/ bridge
/ pass 0"erb% motion1
/ homewor
/ do
[Time42lace 2article
The Time;5lace 5article% % is used for an! words related to time and place# The particle phrase is usuall!
placed at the beginning of a sentence after a sub)ect#
/ *am went to Korea 9*am% to Korea% went:
? / 'un8su came in Ja! 9'un8su% in Ja!% came:
/ *am
/ Korea
/ go
/ 'un8su
? / Ja!
/ come
+ote4 ( is 'anuar!% 2 is -ebruar! and so on#
You can also mae long sentences lie the following examples4
(0 / *am went to Korea last !ear in $ctober during the autumn
season 9*am% last !ear% in $ctober% in Autumn% to Korea% went:
2000 / 'un8su came to Australia in summer 2000# 9'un8su% in 2000%
in summer% to Australia% came:
/ last !ear
(0 / $ctober
/ autumn
2000 / in the !ear 2000
/ summer
/ Australia
+ote4 is used for words both with or without a final consonant#
/ to school
/ to hospital
5lease note also that when is used as a 5lace 5article% it is usuall! used with 2go2 and 2come2 to indicate a
place to which !ou2re going or coming% and functions lie 2to2 in 7nglish# -or example% / to a par%
/ to 3ritain and / to the airport#
When !ou want to sa! !ou did something at a particular place 6for a certain perio' of time&6 is used for
that location or place# &n this case% the function of is similar to .in% at or on. in 7nglish# -or example%
/ pla!ed 0had fun1 at the par 9At the par% 0we1 pla!ed 0had fun1:
/ sta!ed in 3ritain 9&n 3ritain% 0&1 sta!ed:
/ waited at the airport 9At the airport% 0we1 waited:
/ a par
/ pla!% ha"e fun
/ 3ritain
/ sta!
/ airport
/ wait
6owe"er% in the case of 2was2% !ou can use instead of for some strange reason & do not now# The
following two sentences mean exactl! the same#
/ & was in 3ritain
/ & was in 3ritain
3ut in the case of other "erbs% is not allowed#
6ere are a few more examples4
/ went to a countr!side
/ A friend of mine came 0to "isit me1 to hospital
/ was home
/ listen to a lecture at the uni"ersit!
/ A lot of people came to the theme par
/ & ate cereal in the morning 9&n the morning% & ate cereal:
2 / &t started raining at 2 o2cloc in the afternoon 9Lit# The rain fell:
/ countr!side
/ go
/ a friend
/ a hospital
/ a "isit
/ come
/ came to "isit
/ home% house
/ be
/ college% uni"ersit!
/ a lecture
/ listen% hear
/ a lot% man!
/ a person
/ people 0 is attached to a noun to mae it plural1
/ a theme par
/ morning
/ cereal
/ eat
/ afternoon% pm
2 / 2 o2cloc 0( is ( o2cloc% = is = o2cloc and so on1
/ rain
/ fall down
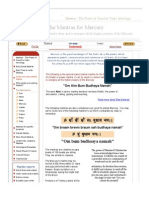
This& 5t an' That
&n this lesson% we learn about some of the most common and useful words% 2This% &t and That#2
This /
&t /
That /
(%ample sentences
[5nformal written form
# / This is a pencil#
# / &t is a window#
# / That is a flower#
[2olite written form
# / This is a pencil#
# / &t is a window#
# / That is a flower#
+ote4 -or more information on the formalit! and the written and spoen forms% please read +ouns 8 5resent%
5ast#
% and are mainl! used in the written form# The e<ui"alent spoen forms are % and
#
5lease note that % and are actuall! contracted forms of % and #
M
M
M
6ere are the sentences in the spoken form)
[5nformal spoken form
#
#
#
[2olite spoken form
#
#
#
.6ere% there and o"er there. are used in similar wa!s to .This% it and that.#
6ere /
There 0it1 /
$"er there /
Alternati"el!% 0A bit more formal1
6ere / 0Lit. This place1
There 0it1 / 0Lit. That place 0it1 1
$"er there / 0Lit. That place o"er there1
(%ample sentences
, / Where is this place, 0Where are we,1
# / This place is *eoul 0We2re in *eoul#1
, / What is that place o"er there,
# / That place 0&t1 is a *eoul @it! @ouncil#
, / Where is that o"er there,
# / That is +amdaemun 0shopping center1#
# / And this place is *e)ong @ultural @enter#
is also usuall! contracted to for the pronunciation2s sae#
M
M
M
*imilarl!% % and are used with to mae the following words to denote a certain direction#
/ This direction
/ That direction 0it1
/ That direction
(%ample sentences
# / This wa! is 0to1 the li"ing room#
# / That wa! 0&t1 is 0to1 to the "erandah#
# / That wa! is 0to1 the exit#
9*am:4 , 9Where is the toilet here,:
9Jin)i:4 # 0The toilet is that wa!#1
9*am:4 , 9What about a boostore, 0Lit. Where is a boostore,1:
9Jin)i:4 # 9The boostore is this wa!#:
% and are used with nouns to mean 2this% it and that2 respecti"el!#
/ This tree
/ That house 0&t1
/ That mountain
/ This apple is delicious
/ That apple is delicious% too#
/ This restaurant is famous for 3ibimbap# 0Lit. This restaurant%
3imbimbap is famous#1
6Q / That building is the 6Q building# 0The landmar building in *eoul1
Note:
3ibimbap 8 is a popular Korean dish# The word literall! means .mixed meal#. 3ibimbap is ser"ed as a bowl of
warm white rice topped with % namul 0sautRed and seasoned "egetables1 and % gochu)ang 0chili
pepper paste1# A raw or fried egg and sliced meat 0usuall! beef1 are common additions# The ingredients are
stirred together thoroughl! )ust before eating# &t can be ser"ed either cold or hot#9(:
Peference4 9(: Wiipedia4 3ibimbap% http4;;en#wiipedia#org;wii;3ibimbap
Nouns 3 2resent& 2ast
Nouns [
&n this lesson% we2re going to learn how to sa! a word in present and past tenses plus how to use the same
expression in polite forms#
2resent an' 2ast Tenses
7ach table below show how to sa! 2an apple2 and 2a pencil2 in four different wa!s# The table is di"ided into
present and past tenses% and positi"e and negati"e forms# Also% the first table shows the written form of
Korean and the second table shows the spoen form#
The written form is used in literature such as boos% newspapers and an! form of writing that is not
2con"ersational#2 The written form% in essence% is literar!% factual and declarati"e# &t is rarel! used in
normal e"er!da! con"ersations# 6owe"er% the news on TH uses this written form of Korean# &t is also
used in public speeches# The reason is probabl! due to the fact that the news and public announcements
or speeches are usuall! all declarati"e and;or factual#
The spoken form is the usual wa! in which people spea and ha"e a con"ersation# &t is used in all t!pes
of spoen Korean such as normal con"ersations% dramas% and mo"ies% with the possible exceptions of
news% documentaries and other factual% formal t!pes of programs on TH and radio#
5nformal Written
$orm
2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
5nformal *poken
$orm
2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e () () () ()
() () () ()
() () () ()
() () () ()
/ an apple
/ a pencil
/ is an apple
/ is not an apple
/ was an apple
/ was not an apple
/ is a pencil
01 / is not a pencil
/ was a pencil
01 / was not a pencil
Note: The "erb ending% % is used for nouns without a final consonant% and for nouns with a final
consonant# Biewise% in the spoen form% is used for nouns without final consonant and for nouns
with a final consonant# Therefore4
Note: &n spoen Korean% the particles are usuall! omitted# &n the abo"e example% ; are in bracets to
show that the! are usuall! left out#
-or more information on the ; particle% please read 5articles 8 % #
2olite $orm
7ach table below shows the polite form of the respecti"e written and spoen forms we2"e looed at abo"e
which were in the informal form#
2olite Written $orm 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
Note: To change the informal form to the polite form% the following rules appl!4
&n the case of the present tense%
M / 0or in the case of nouns with a final consonant% e#g# 1 is taen
off and replaced b!
M / is changed to
&n the case of the past tense% is changed to #
M
M
2olite *poken $orm 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e () () () ()
() () () ()
() () () ()
() () () ()
Note: To change the informal form to the polite form% the following rules appl!4
&n the case of the present tense4
M / changes to 0or in the case of nouns with a final consonant% e#g#
1
M / changes to
&n the case of the past tense% is attached at the end#
M
M
6ere are some example sentences in the written form#
/ is a shop
/ is a bag
/ was beef
/ was a teacher
/ is not a flower
/ was not a port
/ was not an animal
Tr! translating the following sentences in the spoen form# What do the! mean,
01
01
01
Answers:
is a cloc;watch
is a house
was a pigeon
was a person
is not a cloud
was not a building
was not chicen 0meat1
+ow tr! rewrite the 7nglish sentences abo"e in the polite spoen form of Korean% and pronounce them one
b! one#
At this point% &2d recommend that !ou get hold of someone who is Korean to teach !ou the correct
pronunciation of each sentence% but & thin man! of !ou would not ha"e that ind of luxur!# *o alternati"el!%
as imperfect as it ma! be% &2d recommend the Google Translate2s 2Bisten2 feature# &t allows !ou to listen to the
pronunciation of the words !ou put in#
Google Translate
-or those of !ou who would lie to now how to t!pe in Korean% please tr! the google results for 26ow to
t!pe in Korean#2
Nouns 3 Nominali9ing !erbs
&n this lesson% we2re going to learn how to nominaliIe a "erb% which means con"erting a "erb to a noun#
-irst% tae off the plain form of a "erb% and then attach to it# 0-or a list of "erbs in the plain from% please
refer to Herbs 8 5resent;5ast1
The following is a list of some of the "erbs which ha"e been con"erted to nouns#
M / reading
M / writing
M / listening
M / speaing
M / doing
M / going
M / coming
M / watching
M / eating
M / drining
M / sleeping
M / waling
M / running
M / bu!ing
M / selling
M / standing
M / sitting
M / li"ing
M / d!ing
(%ample *entences
/ Waling is an exercise that 0we1 can do easil!
/ & lie shopping 0Lit. & lie doing shopping1
/ 6annah lies eating an icecream
/ &t2s not eas! going to school in a rain! da!
@D / 'ane wanted 2selling2 an old @D pla!er
/ shopping
/ lie
/ 6annah 0Also a Korean female name1
/ icecream
/ rain 0noun1
/ come
/ a da!
/ a rain! da! 0Lit. a rain8coming da!1 0-or more information% refer to Herbs 8 Descripti"e &1
/ a school
/ eas!
/ eas! 0Ad)ecti"es 8 Descripti"e1
/ exercise
/ 'ane
/ old
@D / a @D pla!er
/ want 05lease refer to Herbs 8 Want to learn how to form 2want to do21
6ere are some more example sentences using nominaliIed "erbs#
# / 3u!ing and selling are the business2s basis#
/ business
/ basis% foundation
# / 'i8!oung lied waling in the par and
listening to birds singing#
/ 'i8!oung 0A female name1
/ a par
/ wal
/ a bird
/ a song
/ listen% hear
% % % # / When we learn a foreign
language% reading% writing% listening and speaing are all "er! important#
/ a foreign language
/ learn
/ When we learn 0To learn how to use 'when'% please read @on)unctions 8 When1
/ all
/ "er!
/ important
Nouns 3 Numbers an' Counting
There are two wa!s of pronouncing numbers in Korean# These are4
*ino8Korean numerals 8 % % % ###
+ati"e Korean numerals 8 % % % ###
The *ino8Korean numerals are used for dates% minutes and prices#
The nati"e Korean numerals are used for counting% age and hours#
*ino3Korean Numerals ["ates& :inutes an' 2rices
The e! to memoriIing the pronunciations of the *ino8Korean numerals is to learn from (01 to (001% and
use these ten numbers as building blocs to learn the rest of the numbers# 6ere is a list of the first ten
numbers4
( /
2 /
Q /
G /
? /
6 /
= /
> /
S /
(0 /
-rom (( to (S% what !ou need to do is sa! (001 first and sa! the ones2 number#
-or example%
(( / (0 A ( ; A /
(2 / (0 A 2 ; A /
(Q / (0 A Q ; A /
(= / (0 A = ; A /
(S / (0 A S ; A /
-rom 20 and onward% it wors in the same wa!# 3ut in addition% 20% Q0% ###% S0 are pronounced in the following
wa!4
20 / A / 0Lit. two8ten1
Q0 / A / 0Lit. three8ten1
?0 / A /
>0 / A /
S0 / A /
Additionall!%
2( / A / 0Lit# two8ten one1
22 / A /
Q2 / A /
G? / A /
?= / A /
>S / A /
(00 is % and 200 is which literall! means 2two8hundred#2 Then how do !ou sa! Q00 as a *ino8Korean
numeral, Yes% it2s 0Lit. three8hundred1
(00 /
(0( /
(0? /
(2= /
200 /
2(S /
Q2G /
?0> /
=Q( /
SG? /
(000 is % then 2000 is, Yes% it2s # Then how do !ou sa! Q2>Q in a *ino8Korean wa!, &t2s
# 9Lit# three8thousand two8hundred eight8ten three:
(000 /
(00( /
(0Q? /
2G2= /
>GS2 /
What is (0000, &t2s # &t is not 0or ten8thousand1# 20000 is % Q0000 is and so on#
(0000 /
(0002 /
(00QG /
206=Q /
>G>Q2 /
+ow (00000 is and 200000 is # At this point% it2d help !ou understand the naming s!stem of these
numbers if !ou thin them in terms of their number of Ieros# 6ere is what & mean4
(0000 is
(0%0000 is
(00%0000 is
(000%0000 is
(%0000%0000 is 0+$T 1
(0%0000%0000 is
(00%0000%0000 is
(000%0000%0000 is
(%0000%0000%0000 is
You can see that numbers obtain a new name e"er! time the! get additional G Ieros# This is different to
7nglish where the name of numbers change after e"er! additional Q Ieros# -or example% 2thousand2% 2million2
and 2billion2#
6owe"er% when we write numbers% we follow the international standard in that the comma is placed after
e"er! threes# The examples abo"e where the comma is placed after e"er! G Ieros are for the purpose of easier
understanding onl!# Therefore4
/ (0%000
/ (00%000 0+$T (0%00001
/ (%000%000 0+$T (00%00001
Bet2s re"ise what we2"e learned abo"e4
(( /
(2 /
(Q /
20 /
2? /
Q0 /
G0 /
?0 /
?6 /
=0 /
>0 /
(00 /
(0( /
(0= /
(20 /
(?0 /
200 /
202 /
?Q= / 9?00 AQ0 A = ; A A / :
(000 /
2000 /
2?00 /
(0000 /
(0?00 / 9(0000 A ?00 ; A / :
?Q>G= / 9?0000 A Q000 A >00 A G0 A = ; A A A A /
:
The following are the examples of how the *ino8Korean numerals are used for dates% minutes and prices#
["ates
The order in which the date is written is re"ersed in Korean# A da! of the wee comes first% then a month and
then a !ear# 9a !ear / % a month / % a da! of the wee / :
+otice how the *ino8Korean numerals are used in pronouncing dates#
2> 'an 20(0 M 20(0 ( 2> /
(=;(0;20(( M 20((;(0;(= / 20(( (0 (= /
+ote4 (0 is not % but rather # This exception is due to the awwardness of pronouncing %
which is <uite cumbersome to pronounce# Therefore (0 is for the pronunciation2s sae#
[:inutes
The *ino8Korean numerals are also used for 2minutes2 but not for 2hours2# The nati"e Korean numerals which
are used for pronouncing the number of 2hours2 are explained below in the second section of this post#
9an hour% o2cloc / % a minute0s1 / % am / % pm / :
S4Q> am M S Q> /
64(S pm M 6 (S /
[2rices
The Korean currenc! is called 2won#2 &ts s!mbol is 22% and it2s pronounced #
(2%>00 M (2%>00 /
QS%(Q0 M QS%(Q0 /
Nati8e Korean numerals [Counting& Age an' Hours
The basic numbering s!stem of the nati"e Korean numerals is the same as that of the *ino8Korean numerals#
6owe"er% in addition to one to ten% there is a need to learn the special pronunciations of tens% i#e# 20% Q0% G0%
?0% 60% =0% >0 and S0#
-rom (00% the pronunciation is the same as the *ino8Korean numerals we2"e looed at abo"e# 9hundred 0(001
/ % thousand 0(0001 / % ten thousand 0(00001 / :
( /
2 /
Q /
G /
? /
6 /
= /
> /
S /
(0 /
(( /
(2 /
(Q /
(= /
/< =
2( /
22 /
2Q /
0< =
1< =
>< =
?? /
?< =
@< =
=? / 9=0 A ? ; A / :
A< =
B< =
(00 /
(>S / 9(00 A >0 A S ; A A / :
3elow are the examples of how the nati"e Korean numerals are used in counting% age and hours#
[Counting
The nati"e Korean numerals are used for counting% e#g# the number of people in a class% the number of cars in
a car par% the numbers of apples on an apple tree% the numbers of pencils or pens on a des% etc#
(% 2% Q% G% ? ### / % % % % % ###
When counting% we use distincti"e identifier words called counters# 7ach ind of ob)ect 0or person for that
matter1 has their own counter to distinguish them from other inds# This counter s!stem is a bit lie the
s!stem found in 7nglish% i#e# Q cups of )uice% ? glasses of water# 6owe"er% the Korean counting s!stem extends
to e"er! ob)ect#
-or example%
three cups of )uice /
fi"e glasses of water /
six people / C D
fi"e cars /
three apples /
two pencils /
four boos /
ten roses /
Bisted below are some of the most common counters used in counting#
/ people
/ animals
/ cars
/ ob)ects 0this is "er! widel! used for an! inanimate ob)ects1
/ long% lean ob)ects
/ trees
/ flowers
/ shoes
/ paper
/ boos
/ age
/ floor 9The *ino3Korean numerals are used for counting the number of floors% i#e# the first floor /
% the second floor / % and the eighth floor / :
5lease also note that becomes % and the final consonant of each of % % and is omitted
when the! are attached to counters# -or example%
01 / a glass of water 0+$T 1
01 / two pieces of paper 0+$T 1
01 / three pairs of shoes 0+$T 1
01 / four people 0+$T 1
01 / twent! 0!ears of age1 0+$T 1
The counters wor in a similar wa! to some of the counter words in 7nglish% e#g# is similar to 2pieces2 and
is similar to 2pairs2#
[Age
As we2"e looed at abo"e% the counter% % is attached to !ears of age# -or example4
( /
2 /
Q /
G /
? /
= /
(0 /
(( /
(2 /
(Q /
(= /
20 /
2G /
Q2 /
?> /
[Hours
The nati"e Korean numerals are also used for 2hours2 but not for 2minutes2 which use the *ino8Korean
numerals#
(042? am M (0 2? /
=4Q0 pm M = Q0 / or 0 means 2a half21
[:onths
/ ( month
/ 2 months
/ Q months
/ G months
/ ? months
/ 6 months
/ = months
/ > months
/ S months
/ (0 months
(%ample sentence
2 2 / & went to school for 2 months and had a
brea0holida!s1 for 2 wees#
A'7ecti8es 3 2resent& 2ast
[A'7ecti8es
We2re going to loo at ad)ecti"es in this post# -irst of all% please ha"e a loo at the two tables below% which are
similar to the wa! the 2nouns2 were presented in the pre"ious post% +ouns 8 5resent% 5ast#
As &2"e mentioned before in +ouns 8 5resent% 5ast% there are two primar! forms in which Korean is used% the
written and spoen forms#
The written form is used in literature such as boos% newspapers and an! form of writing that is not
2con"ersational#2 The written form% in essence% is literar!% factual and declarati"e# &t is rarel! used in
normal e"er!da! con"ersations# 6owe"er% the news on TH uses this written form of Korean# &t is also
used in public speeches# The reason is probabl! due to the fact that the news and public announcements
or speeches are usuall! all declarati"e and;or factual#
The spoken form is the usual wa! in which people spea and ha"e a con"ersation# &t is used in all t!pes
of spoen Korean such as normal con"ersations% dramas% and mo"ies% with the possible exceptions of
news% documentaries and other factual% formal t!pes of programs on TH and radio#
5lease also note that there are two wa!s of expressing negati"es% for example% means 2good2 and
means 2man!2% and the! can be expressed in the negati"e form in the following two wa!s4
-) Take off the present tense of an a'7ecti8e& an' attach Cor for the spoken formD)
The Written $orm
/ not good
/ not man!
The *poken $orm
/ not good
/ not man!
/) Attach to the present tense of an a'7ecti8e)
The Written $orm
/ not good
/ not man!
The *poken $orm
/ not good
/ not man!
3elow are the two tables showing the informal written and spoen forms of the ad)ecti"e% # 05lease
read Ad)ecti"es 8 5olite for polite forms1
5lease note that the words in bold indicate which of the two negati"es are more common in each form% i#e#
is more commonl! used than in the written form whereas is more commonl!
used than in the spoen form#
5nformal Written
$orm
2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
5nformal *poken
$orm
2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
6ere are the meanings of the different forms of an ad)ecti"e% #
/ fast
; / not fast
/ was;were fast
; / was;were not fast
/ fast
; / not fast
/ was;were fast
; / was;were not fast
The List of Common Adjectives
2resent 2ast
2ositi8e Written *poken Written *poken
High
Eow
Big
*mall Csi9eD
*pacious
Crampe'
:anF
*mall CGuantitFD
Kin'
$ast
*low
(asF
"ifficult
5nteresting
New
Hot CtangibleD
Col' CtangibleD
Warm
Cool
Won'erful
Beautiful
Honest
Eo8elF
Humble
The following are the rules for the con)ugation of ad)ecti"es4
5D 2resent CWrittenD M 2ast CWrittenD
-) $or a'7ecti8es whose last character contain a final consonant& a'' or )
for the "owels% and
for the "owels% % % and
()g)
M / was thin
M / was high
M / was small 0<uantit!1
M / was thic
M / was thin
M / was interesting;fun
Note: The rules / to ? o8erri'e the rule -)
/) $or a'7ecti8es whose last character is & it changes to )
()g)
M / was ind
M / was warm
M / was cool
M / was amaIing
M / was wonderful
0) $or a'7ecti8es whose last character contain as a final consonant& take it off an' a'' ) C(%cept
for which changes to D
()g)
M / was beautiful
M / was hot 0tangible1
M / was cold 0tangible1
M / was cold 0feeling1
1) $or a'7ecti8es whose last character contain no final consonant an' the 8owel& & take it off an' a''
& )
()g)
M / was big
M / was prett!
Howe8er& when the 8owel before the last character is & then & can be use' instea')
M ; / was sic 0illness1
M ; / was bad
Also& in the case of as the last character& & is use')
M / was fast
>) $or a'7ecti8es whose last character contain the 8owel& & take it off an' a'' & )
()g)
M / was slow
M / was handsome;good8looing
M / was ugl!
?) $or a'7ecti8es whose last character contains as a 8owel an' as a final consonant& theF change
to an' & i)e) changes to )
()g)
M / was red
M / was !ellow
M / was blue
55D 2resent CWrittenD M 2resent C*pokenD
$irst of all& take off a'7ecti8es an' then:
-) $or a'7ecti8es whose last character contain a final consonant& a'' or )
for the "owels% and
for the "owels% % % and
()g)
M / small 0siIe1
M / high
M / small 0<uantit!1
M / thic
M / thin
M / interesting;fun
/) $or a'7ecti8es whose last character is & it changes to )
()g)
M / boring
M / cool
M / humble
M / amaIing
0) $or a'7ecti8es whose last character contain as a final consonant& take it off an' a'' ) C(%cept
for which changes to D
()g)
M / cold 0feeling1
M / difficult
M / hot 0tangible1
M / lo"el!
1) $or a'7ecti8es whose last character contain as a 8owel an' no final consonant& change to )
C(%cept for which changes to D
()g)
M / big;large
M / prett!
Howe8er& when the 8owel before the last character is & then can be change' to instea')
M ; / sic 0illness1
M ; / bad
>) $or a'7ecti8es whose last character contain as a 8owel an' no final consonant& change to )
()g)
M / slow
M / handsome;good8looing
M / ugl!
?) $or a'7ecti8es whose last character contains as a 8owel an' as a final consonant& is change'
to & an' is taken off) Ci)e) is change' to D
()g)
M / red
M / !ellow
M / blue
555D 2ast CWrittenD M 2ast C*pokenD
*implF change to )
M / was big;large
M / was high
M / was slow
M / was red
M / was warm 0both tangibilit! and feeling1
M / was hot 0tangible1
A'7ecti8es 3 2olite [2resent& 2ast
2olite $orm
&n the pre"ious post% Ad)ecti"es 8 5resent% 5ast% we learned to distinguish between the written and spoken
forms of Korean# &n addition to it% we2re going to further distinguish between the polite and informal forms in
Korean#
What are the difference between the informal and polite forms,
5nformal 8 Generall! speaing% the informal form is used among people of the same age or to people
who are !ounger b! older people# &t is also used b! people who are closel! related such as such famil!
members and relati"es# 5eople who are close friends would use this form depending on the familiarit!
and acceptabilit!#
2olite 8 The polite form is used when speaing to people who are older than !ou or of a higher ran
than !ou such as in the compan!% arm! and other institutions# 6owe"er% people generall! use the polite
form in man! social settings regardless of one2s age# &nitiall!% it would be best to stic to the polite form
when learning Korean% as this would be the predominant form of speaing to people in man! social
en"ironments# 6owe"er% if !ou attend school or other similar institutions where !ou2d mae friends and
the en"ironment is more casual% it might be more appropriate to use the informal form#
3elow are the two tables showing the polite form of the written and spoen forms of Korean# 5lease note that
the words in bold indicate which of the two negati"es are more common in each form% i#e#
is more commonl! used than in the written form whereas is more commonl! used
than in the spoen form#
2olite Written $orm 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
2olite *poken $orm 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
Con7ugations rules
5D 5nformal written form ; 2olite written form C2resent tenseD
$irst of all& take off a'7ecti8es& an' then:
-) $or a'7ecti8es whose final character has no final consonant& a'' )
()g)
M / big;large
M / strong
M / fast
M / slow
M / ind
M / warm 0touch% feeling1
M / cool 0touch% feeling1
/) $or a'7ecti8es whose final character has a final consonant& attach )
()g)
M / small 0siIe1
M / man!
M / small 0<uantit!1
M / eas!
M / difficult
M / hot 0touch1
M / new
55D 5nformal written M 2olite written C2ast tenseD
Take off the past tense of a'7ecti8es& an' then attach )
()g)
M / was big;large
M / was small 0siIe1
M / was good
M / was fast
M / was slow
M / was eas!
M / was difficult
M / was hot 0touch1
M / was cold 0touch1
M / was new
555D 5nformal M 2olite C*pokenD
Attach at the en' of the a'7ecti8es of all forms)
()g)
M / high
M / not high
M / was high
M / was not high
M / man!
M / not man!
M / were man!
M / were not man!
M / big;large
M / not big;large
M / was big;large
M / was not big;large
-or help with the pronunciations of these ad)ecti"es in "arious forms% please use the 6listen6 feature on
Google Translate#
A'7ecti8es 3 "escripti8e $orm
&n the pre"ious posts% Ad)ecti"es 8 5resent% 5ast and Ad)ecti"es 8 5olite 95resent% 5ast:% we learned that
ad)ecti"es in Korean function lie "erbs in that the! can be con)ugated into present and past tenses% and
"arious other forms#
6owe"er% when describing nouns using ad)ecti"es placed in front of them% for example% 2a beautiful bird2% the
ad)ecti"es must be con)ugated to the descripti"e form#
()g)
M 9A plain form M A descripti"e form:
/ a beautiful bird
The Table of Common Adjectives and Their Descriptive Forms
Written $orm 2lain 2ositi8e "escripti8e
High
Eow
Big
*mall Csi9eD
*pacious
Crampe'
:anF
*mall CGuantitFD
Kin'
$ast
*low
Han'some
HglF
(asF
"ifficult
5nteresting
Boring
Hot
Col'
Warm
Cool
Won'erful
Beautiful
2rettF
Humble
Eo8ing
Re'
Iellow
Con7ugations rules
$irst of all& take off a'7ecti8es an' then:
-) Attach to anF a'7ecti8es of one character with a final consonant)
CNote: The ne%t rules o8erri'e this rule)D
()g)
M / man!
M man! people
M / small
M a small dwarf
M / thin
M a thin arm
M / high
M a high s!
/) Attach to anF a'7ecti8es whose final character is an' )
()g)
M / delicious
M delicious food
M / handsome;good8looing
M a good8looing car
M / interesting;fun
M a fun mo"ie
M / not interesting 0boring1
/ a boring drama 0soap opera1
Note4 The meaning of is 2to exist2% and its opposite is which means 2to not exist2# Therefore% the
ad)ecti"es which ha"e a stem of can also be used with #
()g)
M 9tast!;delicious M not tast!;delicious:
M 9handsome;good8looing M not handsome;good8looing 0ugl!1:
M 9interesting;fun M not interesting;fun 0boring1:
0) $or a'7ecti8es whose final character has a final consonant of either or & replace them with )
()g)
M / long
M a long pencil
M / sweet 0taste1
M sweet chocolate
M / red
M a red apple
M / !ellow
/ a !ellow umbrella
1) $or a'7ecti8es who final character has a final consonant& & take it off an' attach to them)
()g)
M / eas!
M an eas! problem;<uestion
M / beautiful
M a beautiful flower
M / cold 0tangible1
/ a cold floor
M / hot 0tangible1
/ hot coffee
J(%ception:
M / narrow% small% cramped 0space1 0+$T 1
/ a small;cramped pla!ground
>) $or a'7ecti8es whose last character 'oes not ha8e a final consonant& 7ust attach to it)
()g)
M / nice;cool
M a nice;cool hat
M / prett!
M prett! shoes
M / fast
M a fast car
M / slow
M a slow speed
5rregular
M / good
M a good man
5lease note% howe"er% that the descripti"e form is usuall! used in writings% as in written Korean#
&n spoen Korean% it is more natural to sa! 2beautiful flowers2 as 2 2 rather than 2
#2 0-or more on the 6spoken form&6 please read Ad)ecti"es 8 5resent% 5ast1
()g)
/ The flowers are beautiful#
/ The car is good8looing#
/ The <uestion is eas!#
Also% in spoen Korean% the particles are often omitted except for the ; particle#
/ The flowers are beautiful#
/ The car is good8looing#
/ The <uestion is eas!#
Again% in casual con"ersations% these sentences would more naturall! flow b! using 2#2
The difference between 2 2 and 2 2 is that 22 is less blunt than 22 which
sounds more factual and generalised#
/ 0& see that1 The problem;<uestion is eas!#
/ The problem;<uestion is eas!#
/ 0& see that1 The room is spacious;large#
/ The room is spacious;large# 0&t can sound <uite blunt and )ust factual#1
A'7ecti8es 3 Connecti8e $orm
This lesson is about the connecti8e form of ad)ecti"es# This form is used to list se"eral ad)ecti"es in a
se<uence% and to connect one sentence to another#
The con)ugation rule for the connecti"e form is eas!#
Tae off ad)ecti"es and then attach to them#
Written $orm 2resent Connecti8e
High
Eow
Big
*mall Csi9eD
*pacious
Crampe'
:anF
*mall CGuantitFD
Kin'
$ast
*low
+utgoing
Kuiet
(asF
"ifficult
5nteresting
Boring
Hot CtangibleD
Col' CtangibleD
Warm
Cool
Won'erful
Beautiful
2atient
Humorous
Calm
Humble
Eo8elF
The connecti8e form of a'7ecti8es is use' in two situations:
To list adjectives in a sequence
To connect one sentence to another
-) To list a'7ecti8es in a seGuence
&f & was to sa! 2ind% beautiful and humble2 in Korean% the ad)ecti"es must be changed to their connecti"e
forms except the last ad)ecti"e of a sentence which determines its tense#
()g)
M / ind
M / beautiful
/ humble
M ind% beautiful and humble
M was ind% beautiful and humble
Alternati8elF&
M was beautiful% humble and ind
M was humble% ind and beautiful
As !ou can see% the last ad)ecti"e determines the tense of a sentence#
/) To connect one sentence to another)
The connecti"e form of ad)ecti"es is also used to connect sentences#
/ Yuri is ind
/ Jina is beautiful
/ 'insu is humble
% % #
= Yuri is ind% Jina is beautiful and 'insu is humble#
/ And! is humorous;funn!
/ -ranlin is <uiet
/ 'essica is outgoing
% %
/ And! is humorous;funn!% -ranlin is <uiet% and 'essica is outgoing#
/ A soft drin is cool
/ Tea is hot
/ Grapes are sweet
% % #
/ A soft drin is cool% tea is hot% and grapes are sweet#
!erbs 3 2resent& 2ast
[!erbs
+ow% we come to learn% possibl!% the most important sub)ect of all Korean grammar% the 68erbs)6
& ha"e drawn up tables below to displa! "arious con)ugations of "erbs# 3ut first of all% we need to pa!
attention to a distinct feature in Korean "erbs% namel!% the plain form#
The plain form is the most basic form of "erbs% from which all the other con)ugations of "erbs are deri"ed and
produced#
6owe"er% the plain form is almost ne"er used in both written and spoen Korean# The onl! instance where
the plain form is used is when "erbs are listed in the dictionar!# Therefore% it is necessar! to now the plain
form if !ou2d lie to now the meaning of certain "erbs and find them in the dictionar!#
(%amples of the plain form of 8erbs
/ do
/ eat
/ go
/ run
5nformal
Written $orm
lain 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
5nformal
*poken $orm
lain 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
Note: The words in bold indicate which of the two negati"es are more commonl! used in each case% i#e#
is more commonl! used than in the written form% and is more commonl! used
than in the spoen form#
A Table of Commonl! "sed #erbs
Written *poken
lain 2resent 2ast 2resent 2ast
Lo
Come
Run
(at
*tan'
*it
BuF
*ell
Lrow
Throw
Borrow
Een'
2laF
Write
Rea'
Eisten
Ei8e
"ie
Con7ugations Rules
5D 2lain M 2resent CWrittenD
-) $or 8erbs whose last character has a final consonant& replace with )
()g)
M / eat
/ eat an apple
M / wal
/ A human wals
M / belie"e
/ & belie"e 'esus
/) $or 8erbs whose last character has no final consonant& replace with )
()g)
M / sleep
/ +ow birds sleep 0/ At the moment% the birds are sleeping1
M / go
/ Jina goes to school
M / watch;loo;see
/ 6!un8)u often loos outside
0) $or 8erbs whose last character has as a final consonant& replace it with )
()g)
M / sell
/ This shop sells fruit
M / li"e
/ 'i8u li"es here
M / push
/ push a car
55D 2lain M 2ast CWrittenD
$irst of all& take off a 8erb& an' then:
-) $or 8erbs whose last character has no final consonant& attach as a final consonant)
()g)
4 A / / went
4 A / / bought
4 A / / stood
4 A / / slept
4 A / / grew
(%ception:
M / did 0+$T 1
Note: The following rules o8erri'e the rule -)
/) $or 8erbs whose last character has a final consonant& a'' or )
$or 8owels& an' & a'' )
$or 8owels& & & an' & a'' )
()g)
4 A / / flew
4 A / / li"ed
4 A / / pla!ed 0had fun1
4 A / / ate
4 A / / died
4 A / / lifted up
4 A / / pushed
0) $or 8erbs whose last character has as a 8owel& an' no final consonant& change to an' attach
as the final consonant)
()g)
4 M M / ran
4 M M / borrowed
4 M M / won
4 M M / threw
4 M M / attended
1) $or 8erbs whose last character has as a 8owel an' no consonant& change to an' attach as
the final consonant)
()g)
M / came
M / saw;looed;watched
>) $or 8erbs whose last character has as a 8owel& replace it with an' then attach as the final
consonant)
()g)
4 M M / grew
4 M M / wrote
4 M M / sprouted
5rregular form
()g)
M
M
555D 2lain ; 2resent C*pokenD
-) $or 8erbs whose last character has a 8owel& or an' no final consonant& 7ust 'rop off)
()g)
M / go
M / stand
M / bu!
M / grow
(%ception: changes to )
()g)
M / do
M / want
M / sa"e 0a life1
/) $or 8erbs whose last character has a 8owel& or an' no final consonant:
changes to
changes to
()g)
M / come
M / see;watch;loo
M / place 0something1 on% lea"e 0something as it is1
M / gi"e
M / lend
0) $or 8erbs whose last character is & 'rop it off an' then attach a final consonant& & to the
character prece'ing & an' then attach or to them)
for 8erbs whose character prece'ing has a 8owel& or )
for 8erbs whose character prece'ing has a 8owel& & or )
()g)
M / di"ide
M / cut
M / climb
M / filter% sift
M / hurr!
M / roll
M / go cross
CAlso& for 8erbs which ha8e a last consonant of & replace it with )D
M / write
M / extinguish 0a fire1
M / float
1) $or 8erbs whose last character has as a 8owel an' no final consonant& change to )
()g)
M / lose
M / win
M / throw
>) $or 8erbs whose last character has a final consonant& attach:
for characters whose 8owel is or
for characters whose 8owel is & & or )
()g)
M / li"e
M / sell
M / sit
M / pla! 0ha"e fun1
M / eat
M / bite
M / age
M / read
5rregular form
M / listen;hear
5!D 2ast CWrittenD M 2ast C*pokenD
*implF change to )
M / went
M / came
M / ran
M / ate
M / dran
!erbs 3 2olite [2resent& 2ast
2olite $orm
This lesson is about the polite form of "erbs% in addition to the informal form which we learned in the
pre"ious lesson# Bet2s go o"er again the differences between the informal and polite forms#
5nformal 8 Generall! speaing% the informal form is used among people of the same age or to people
who are !ounger b! older people# &t is also used b! people who are closel! related such as such famil!
members and relati"es# 5eople who are close friends would use this form depending on the familiarit!
and acceptabilit!#
2olite 8 The polite form is used when speaing to people who are older than !ou or of a higher ran
than !ou such as in the compan!% arm! and other institutions# 6owe"er% people generall! use the polite
form in man! social settings regardless of one2s age# &nitiall!% it would be best to stic to the polite form
when learning Korean% as this would be the predominant form of speaing to people in man! social
en"ironments# 6owe"er% if !ou attend school or other similar institutions where !ou2d mae friends and
the en"ironment is more casual% it might be more appropriate to use the informal form#
Note: The words in bold indicate which of the two negati"es are more commonl! used in each case% i#e#
is more commonl! used than in the written form% and is more commonl!
used than in the spoen form#
2olite Written $orm 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
2olite *poken $orm 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
Con7ugation Rules
5D 5nformal 2lain M 2olite 2resent CWrittenD
$irst of all& take off the plain form of 8erbs& an' then:
-) $or 8erbs whose final character has no final consonant& a'' )
()g)
M / do
M / go
M / come
M / write
M / spea
M / hope
M / grow
/) $or 8erbs whose final character has a final consonant& a'' )
()g)
M / eat
M / wal
M / listen
M / read
M / wear
Note: The rule 0 o8erri'es the rule /)
0) $or 8erbs whose last character has as a final consonant& change it to an' a'' )
()g)
M / li"e
M / pla! 0ha"e fun1
M / now
M / fl!
M / hang 0up1
M / roll 0up1
M / push
55D 5nformal 2ast M 2olite 2ast CWrittenD
Take off the informal past form of 8erbs& an' then a'' )
M / did
M / went
M / came
M / watched
M / ate
M / ran
M / met
555D 5nformal M 2olite C*pokenD
Must a'' to the informal spoken forms)
M / do
M / go
M / come
M / not do
M / not watch
M / not bu!
M / not sleep
M / ate
M / waled
M / met
M / didn2t do
M / didn2t go
M / didn2t eat
M / didn2t borrow
A brief re"ision of the differences between the written and spoken forms
The written form is used in literature such as boos% newspapers and an! form of writing that is not
2con"ersational#2 The written form% in essence% is literar!% factual and declarati"e# &t is rarel! used in
normal e"er!da! con"ersations# 6owe"er% the news on TH uses this written form of Korean# &t is also
used in public speeches# The reason is probabl! due to the fact that the news and public announcements
or speeches are usuall! all declarati"e and;or factual#
The spoken form is the usual wa! in which people spea and ha"e a con"ersation# &t is used in all t!pes
of spoen Korean such as normal con"ersations% dramas% and mo"ies% with the possible exceptions of
news% documentaries and other factual% formal t!pes of programs on TH and radio#
!erbs 3 $uture [Will
We2re going to learn how to form a future tense of "erbs in this lesson#
5lease ha"e a loo at the table below#
5nformal will 'o won6t 'o
Written $orm
*poken $orm
Note: The bold letters indicate which of the two alternati"es in the negati"e form is more commonl! used in
each of the written and spoen forms% i#e#4
is more commonl! used than in written Korean#
is more commonl! used than in spoen Korean#
Con7ugation rules
$irst of all& take off the plain form of 8erbs an' then:
5D Will
-) $or 8erbs whose final character has no final consonant& attach to them)
()g)
M / will do
M / will go
M / will come
M / will meet
M / will grow
/) $or 8erbs whose final character has a final consonant& attach to them)
()g)
M / will eat
M / will sit
M / will read
M / will wear
M / will catch
Note: The rule 0 o8erri'es the rule /)
0) $or 8erbs whose final character has as a final consonant& 7ust attach to them)
()g)
M / will push
M / will fl!
M / will li"e
5rregular form
M / will listen
55D Won6t
*implF attach to 8erbs)
()g)
M / won2t do
M / won2t go
M / won2t come
M / won2t bu!
M / won2t eat
M / won2t wear
M / won2t sit
M / won2t push
(%ample sentences
, / Will !ou go home,
/ *arah will swim
/ Da"id will beat Goliath
/ & will pla! the guitar in m! room
/ 'ohn will enter the museum
/ home
/ 'ohn
/ enter
/ guitar
/ pla! 0the instrument1
/ *arah
/ swim
/ Da"id
/ Goliath
Kuestion $orm
Raise the tone of Four 8oice at the last sFllable to turn it into a Guestion form)
, / Will !ou do0pla!1 soccer,
, / Will !ou go0lea"e1 alread!,
, / Will !ou wash, 0Will !ou tae a shower,;Will !ou tae a bath,1
, / Will !ou watch the $l!mpics,
, / Won2t !ou go to school,
, / Won2t !ou ha"e lunch,
, / Won2t !ou read this boo,
2olite $orm
Bet2s briefl! go o"er the differences between the informal and polite forms again#
While the informal form in the examples abo"e is used b! people who are of the same age and;or close% or
when ol'er people are taling to !ounger people in informal situations% the polite form is commonl! used
b! Founger people addressing older people% and in an! formal situations#
2olite Written
$orm
Will 'o Won6t 'o
2olite *poken
$orm
Will 'o Won6t 'o
Note: The bold letters indicate which of the two alternati"es in the negati"e form is more commonl! used in
each of the written and spoen forms% i#e#4
is more commonl! used than in written Korean#
is more commonl! used than in spoen Korean#
Con7ugations rules
5D 5nformal ; 2olite CWrittenD
*implF change to )
()g)
M / will do
M / will go
M / will eat
M / won2t drin
M / won2t run
55D 5nformal ; 2olite C*pokenD
*implF change to )
()g)
M / will do
M / will come
M / will enter 0go in1
M / won2t see;watch
M / won2t run
(%ample sentences
, / Will !ou go home,
# / *arah will swim#
# / Da"id will beat Goliath#
# / 'ohn will enter the museum#
# / & will pla! the guitar in the li"ing room#
, / Will !ou wash, 0Will !ou tae a shower,;Will !ou tae a bath,1
, / Will !ou go0lea"e1 alread!,
, / Will !ou do0pla!1 soccer,
, / Will !ou watch the World @up,
, / Won2t !ou go to school,
, / Won2t !ou ha"e lunch,
, / Won2t !ou read this boo,
!erbs 3 Contiunous
Continuous $orm [N
&n this lesson% we2ll learn about the 6continuous6 form# &t would be similar to the 63ing6 form in 7nglish#
5nformal Written
$orm
2lain $orm 2resent
Continuous
2ositi8e
Negati8e
/ do
; / not do
/ is doing
; / is not doing
Note: The bold letters indicate which of the two alternati"es in the negati"e form is more commonl! used in
the written form% i#e#4
is more commonl! used than in written Korean#
5nformal Written
$orm
2ast 2ast Continuous
2ositi8e
Negati8e
/ did
; / didn2t do
/ was doing
; / wasn2t doing
Con7ugation Rules
Take off the plain form of 8erbs& an' then a'' C D for their positi8e form an' C D
for their negati8e form)
()g)
M / is writing
/ 5eter is writing a letter#
M / is ser"ing;distributing
/ 3o8!oung is ser"ing school meals to children#
M / was listening
/ 5aul was listening to a Tim Keller2s message#
M / was not sleeping
/ The bab! was not sleeping
M / was standing
/ The 7nglish guardsman was standing
continuousl! in front of the 3ucingham 5alace#
*poken $orm
5nformal *poken
$orm
2resent
Continuous
2ast Continuous
2ositi8e
Negati8e
/ is doing
; / is not doing
/ was doing
; / was not doing
The con7ugation rule is the same as the written form e%cept at the en' of sentences changes to )
/ & am eating lunch
/ 'ulia is not running
/ 6!un8woo is climbing a mountain#
/ Jin8)u is maing a fruit salad and fried salmon#
/ *ince a while ago% the hedgehog was not mo"ing#
2olite $orm
While the informal form in the examples abo"e is used b! people who are of the same age and;or close% or
when ol'er people are taling to !ounger people in informal situations% the polite form is commonl! used
b! Founger people addressing older people% and in an! formal situations#
2olite Written $orm 2resent Continuous 2ast Continuous
2ositi8e
Negati8e
/ is doing
; / is not doing
/ was doing
; / was not doing
2olite *poken $orm 2resent Continuous 2ast Continuous
2ositi8e
Negati8e
/ is doing
; / is not doing
/ was doing
; / was not doing
Con7ugation rules
5D 5nformal M 2olite CWrittenD
*implF at the en' of the informal written 6continuous6 forms changes to
M / is doing
M / is going
M / is coming
M / is waling
M / is maing
55D 5nformal M 2olite C*pokenD
*implF a'' at the en' of the sentences of the informal 6continuous6 spoken form)
/ 'i8h!e is going to school
/ Young8su is swimming
/ @hul8min is watching a mo"ie#
/ 'ung8su was in the li"ing room until a short while ago#
(0 / Kntil about (0 minutes ago% there was
no one standing in front of the 3ucingham 5alace#
!erbs 3 Connecti8e
Connecti8e $orm [
This lesson is about the connecti"e form which is primaril! used in two wa!s4
-) To list 8erbs)
/) To link one sentence to the ne%t)
We2ll ha"e a loo at these functions of the connecti"e form in detail below#
Table of Common !erbs an' Their Connecti8e $orms
Written
$orm
2lain Connecti8e
"o
Lo
Come
(at
"rink
Walk
Run
*tan'
*it
Let up
*leep
BuF
*ell
Lrow
Throw
Borrow
Een'
2laF
Write
Rea'
Eisten
Ei8e
"ie
Con7ugation rule
Take off the plain form of 8erbs& an' then attach to them)
M
M
The connecti8e form of 8erbs is use':
-) To list 8erbs)
/) To link one sentence to the ne%t)
-) To list 8erbs)
-or example% if & wanted to sa! .& get up% eat and go#.% the "erb stems are changed to their connecti"e forms
except the last "erb which determines the tense of a sentence#
M
M
M
/ get up% eat and go
/ got up% ate and went
/ will get up% eat and go
&n each instance% the last "erb determines the tense of a sentence#
/) To link one sentence to the ne%t)
The example below shows how three sentences can be lined together using the connecti"e form of "erbs#
# 0Yuri goes to school1
# 0'insu pla!s outside1
# 0Jina reads a boo1
% % #
= Yuri goes to school% 'insu pla!s outside and Jina reads#
6owe"er% the "erbs in each sentence can be con)ugated into different tenses#
# / Yuri went to school
# / 'insu will pla! outside
# / Jina reads 0or Jina is reading1
% % #
/ Yuri went to school% 'insu will pla! outside and Jina is reading#
(%ample sentences
()g)
& heard and spoe /
& studied% re"ised and taught / % % #
& washed and ate dinner# / #
# / This shop sells and bu!s fruit and "egetables#
% % # / & met m! friend% had fun and ate lunch together#
/ &t2s raining and snowing% the wind is blowing and
the lightning stries#
TH % % # / Daniel is watching
TH% *uIanne is maing breafast and *amson is still in bed#
!erbs 3 Can
Can 'o [
&n this lesson% we2ll learn about how to con)ugate "erbs to form 6can6 and 6cannot6#
5nformal Can 'o Coul' 'o
Written
*poken
5nformal Can6t 'o Coul'n6t 'o
Written
*poken
Note: and is more commnl! used than and in written
Korean# *imilarl!% and is more commonl! used than and in spoen
Korean#
Con7ugation rules
OWritten $ormP
$irst of all& take off the plain form of 8erbs)
-) $or 8erbs whose last character has no final consonant& attach to them& an' for 8erbs
whose last character has as a final consonant& attach to them)
()g)
M / can do
M / can go
M / can see
M / can sleep
M / can drin
M / can run
M / can pla!
M / can li"e
M / can fl!
/) $or 8erbs whose last character has a final consonant& attach to them)
()g)
M / can eat
M / can wear
M / can sit
M / can catch
5rregular forms
M 0can hear1
M 0can wal1
O*poken $ormP
A'' in front of the spoken form of positi8e 8erbs to e%press 6can6t 'o6 an' 6coul'n6t 'o)6
()g)
M / can2t do
M / can2t come
M / can2t see
M / can2t go
M / can2t hear
M / can2t eat
M / couldn2t go
M / couldn2t hear
M / couldn2t eat
(%ample *entences
/ A cheetah can run fast#
/ A lar can fl! in the s!#
/ *olomon can sol"e a difficult riddle#
# / A pet cannot enter the museum#
/ & can pla! the guitar#
/ 'ohn can2t eat seafood#
/ 3ecause *arah was sic% she couldn2t go to school#
/ cheetah
/ fast% <uicl!
/ lar
/ fl!
/ *olomon
/ difficult
/ riddle
/ sol"e
/ a pet
/ museum
/ enter
/ guitar
/ pla! 0the instrument1
/ 'ohn
/ seafood
/ *arah
/ sic
2olite $orm
While the informal form in the examples abo"e is used b! people who are of the same age and;or close% or
when ol'er people are taling to !ounger people in informal situations% the polite form is commonl! used
b! Founger people addressing older people% and in an! formal situations#
$ormal Can 'o Coul' 'o
Written
*poken
$ormal Can6t 'o Coul'n6t 'o
Written
*poken
Note: The ones in bol' characters are more commonlF use' alternati"e of the two in each box#
Con7ugation rules
-) 5nformal M 2olite CWrittenD
Replace with )
M / can do
M / can go
M / can spea
M / could come
M / could stand
/) 5nformal M 2olite C*pokenD
Attach at the en' of sentences)
M / can do
M / can go
M / can gi"e
M / could recei"e
M / could go up
(%ample *entences
/ A cheetah can run fast#
/ A lar can fl! in the s!#
/ *olomon can sol"e a difficult riddle#
# / A pet cannot enter the museum#
/ & can pla! the guitar#
/ 'ohn can2t eat seafood#
/ 3ecause *arah was sic% she couldn2t go to school#
!erbs 3 Ha8e
Ha8e C D 4 "on6t ha8e C D
This lesson co"ers how the "erb% 6ha8e6% is used# &t can be expressed in two wa!s4
/ there is;are 0Lit# is present1
/ ha"e% possess
/ there isn2t;aren2t 0Lit. is not present1
/ do not ha"e;possess
5nformal Written
$orm
Ha8e "on6t ha8e
5nformal *poken
$orm
Ha8e "on6t ha8e
Note: The wor's in bol' letters are the more commonl! used of the two alternati"es in each of the Written
and *poen forms#
Ha8e C D
means 6there is4are6% for example4
/ There is a pupp! in the garden#
/ There2s an ant on the des#
6owe"er% can also mean 6ha8e6# &t is used more fre<uentl! than the alternati"e% 6 6% which
is more cumbersome to pronounce#
Written form M %
*poen form M %
(%ample *entences
Written $orm
# / & ha"e a boo# 0Lit. There is a boo1
# / & ha"e a watch#
# / & ha"e a mobile phone#
# / & ha"e a boo#
# / & ha"e a mobile phone#
*poken $orm
01 #
01 #
01 #
01 #
01 #
Note: (# Kse 4 with , , and 4 with , ,#
2# The particles are usuall! omitte' in spoen Korean#
When !ou sa!% 2& ha"e a brother or sister2% CANN+T be used because it implies ownership#
$nl! can be used in relation to people#
$or e%ample&
Written $orm
# / & ha"e a !ounger brother#
# / & ha"e a !ounger sister#
*poken $orm
01 # / & ha"e an older brother#
01 # / & ha"e an older sister#
01 # / & ha"e a !ounger brother#
01 # / & ha"e a !ounger sister#
"on6t ha8e C D
literall! means 6there isn6t4aren6t6# 6owe"er% it can also mean 6'on6t ha8e6
$or e%ample&
Written $orm
/ don2t ha"e 0Lit. there isn2t;aren2t1
; / don2t ha"e 0Lit. don2t own;possess1
*poken $orm
/ don2t ha"e 0Lit. there isn2t;aren2t1
; / don2t ha"e 0Lit. don2t own;possess1
Note: -or the negati"es% the wor's in bol' letters are the more commonl! used of the two alternati"es in
each of the Written and *poen forms#
(%ample *entences
Written $orm
# / & don2t ha"e a boo#
# / & don2t ha"e a watch#
# / & don2t ha"e a mobile phone#
# / & don2t ha"e;own a boo#
# / & don2t ha"e;own a mobile phone#
*poken $orm
01 #
01 #
01 #
01 #
01 #
Kuestion $orm
&n spoen Korean% in order to change a sentence into a <uestion% !ou simpl! need to raise !our tone at the last
letter#
To see how it2s done% it2d be probabl! best to watch a nati"e Korean do it for !ou# 6owe"er% as & figure most
of !ou would not ha"e that ind of luxur!% ha"ing a nati"e speaer do it for !ou whene"er !ou want% &
encourage !ou to listen to the Korean audios or recordings online or watch Korean dramas or mo"ies and
familiariIe !ourself with the intonation of <uestions# -or excellent free audio and "ideo resources% please tr!
2Tal To Je &n Korean2 0http4;;www#taltomeinorean#com;1#
01 , / Do !ou ha"e an older brother,
01 , / Do !ou ha"e an older sister,
01 , / Do !ou ha"e a !ounger brother,
01 , / Do !ou ha"e a !ounger sister,
01 , / Don2t !ou ha"e a boo,
01 , / Don2t !ou ha"e a watch,
01 , / Don2t !ou ha"e a mobile phone,
2olite $orm
While the informal form in the examples abo"e is used b! people who are of the same age and;or close% or
when ol'er people are taling to !ounger people in informal situations% the polite form is commonl! used
b! Founger people addressing older people% and in an! formal situations#
2olite Written $orm Ha8e "on6t ha8e
2olite *poken $orm Ha8e "on6t ha8e
5D 5nformal M 2olite C*pokenD
Must a'' at the en' of a sentence)
, / Do !ou ha"e an older brother,
, / Do !ou ha"e an older sister,
, / Do !ou ha"e a !ounger brother,
, / Do !ou ha"e a !ounger sister,
, / Don2t !ou ha"e a boo,
, / Don2t !ou ha"e a watch,
, / Don2t !ou ha"e a mobile phone,
55D 5nformal M 2olite CWrittenD
Replace with )
# / & ha"e a boo#
# / & ha"e a watch#
# / & ha"e a mobile phone#
# / & don2t ha"e;own a boo#
# / & don2t ha"e;own a mobile phone#
!erbs 3 Want
!erbs 3 Want [N
5nformal
Written $orm
2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
5nformal *poken
$orm
2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
Note: and both mean .& don2t want to do#. 6owe"er% &n written Korean%
is more commonl! used whereas in spoen Korean% is more commonl! used#
literall! means .& hate to do#.
The bold letters indicate which one is more commonl! used#
$ule
Take off a plain form of 8erbs an' attach 4 4 4 4 4
etc)
(%amples CWritten $ormD
M / & want to do#
M / & want to eat#
M / & wanted to fl!#
M / & did2t want to pla!#
M / & didn2t want to drin#
/ & didn2t want to eat a banana#
/ & didn2t want to fl! in the s!#
(%amples C*poken $ormD
M / & want to do#
M / & want to eat#
M / & wanted to fl!#
M / & don2t want to pla!#
M / & didn2t want to drin#
/ & don2t want to eat a banana#
/ & didn2t want to fl! in the s!#
Kuestions C*poken $ormD
, / Do !ou want to sleep,
# # / Yes% & want to sleep#
, / What do !ou want to eat,
# / & want to eat noodles#
, / Where do !ou want to go,
# / & want to go to a par#
$ormal $orm
$ormal
Written
$orm
2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
$ormal
*poken $orm
2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
Note: The informal spoen form is used between close frien's or when older people are taling to !ounger
people in informal situations# The formal form is used commonl! between a'ults% b! people in formal
situations or when !ounger people are speaing to older people#
$ules
$or the formal written form& the suffi% & & is replace' bF )
$or the formal spoken form& attach at the en' of a sentence)
(%amples CWritten $ormD
M / & want to do#
M / & want to eat#
M / & wanted to fl!#
M / & did2t want to pla!#
M / & didn2t want to drin#
(%amples C*poken formD
M / & want to do#
M / & want to eat#
M / & wanted to fl!#
M / & did2t want to pla!#
M / & didn2t want to drin#
:ore e%amples
, / Do !ou want to sleep,
# # / Yes% & want to sleep#
, / What do !ou want to eat,
# / & want to eat noodles#
, / Where do !ou want to go,
# / & want to go to a par#
5n a''ition:
When taling about a third person% 2 2 is used instead of % and 2 2 instead of
#
(%amples
M
/ Bue wants to go to the theatre#
/ *unmi wants to drin an apple )uice#
!erbs 3 "escripti8e $orm 5
!erbs 3 "escripti8e $orm 5
The descripti"e form & of "erbs taes the meaning of ,Ning), (ie. Continuous)& or is used as a present tense
clause in"ol"ing .which% that% who etc#.#
Written $orm 2lain "escripti8e 5
2ositi8e
Negati8e
The Table of Common !erbs an' Their "escripti8e $orms 5
Written $orm 2lain "escripti8e 5
Run
(at
Lo
*tan'
Come
*it
BuF
*ell
Lrow
Throw
Borrow
Een'
2laF
Write
Rea'
Eisten to
Ei8e
"ie
These descripti"e forms & are used in front of nouns to describe them% and form a present tense clause
in"ol"ing .who% which% that. of 7nglish# -or example% the descripti"e form & of is and
means a .train which goes.# Biterall!% means .going. therefore / a going train#
# Rules
$irst& take off a 8erb an' then&
-) a''
(g)
M / eating
M a dwarf who eats an apple 0= Lit. an apple8eating dwarf1
M / sleeping
M a princess who sleeps 0= Lit. A sleeping princess1
M / d!ing
M a soldier who is d!ing 0= Lit. a d!ing soldier1
M / not belie"ing;unbelie"ing
M Thomas who does not belie"e 0/ Lit. unbelie"ing Thomas1
/) Take off a 8erb with a final consonant& an' a'' )
(g)
M / selling
M A shop which sells anti<ues 0= Lit. An anti<ue8selling shop1
M
M A place where &2m li"ing 0= Lit. A li"ing place1
:ore e%amples
/ A cactus which grows in the desert 0= Lit. A desert8growing cactus1
# / All the boos that & read are informati"e#
!erbs 3 "escripti8e $orm 55
!erbs 3 "escripti8e $orm 55
The descripti"e form && of "erbs taes the meaning of ,Ne'), (ie. past tense) or is used as a past tense clause
in"ol"ing .who% which% that etc#.#
Written $orm 2lain "escripti8e 55
2ositi8e
Negati8e
The Table of Common !erbs an' Their "escripti8e $orms 55
Written $orm 2lain "escripti8e 55
Run
(at
Lo
*tan'
Come
*it
BuF
*ell
Lrow
Throw
Borrow
Een'
2laF
Write
Rea'
Eisten to
Ei8e
"ie
Herbs can be used in front of nouns to describe them% and form a past tense clause in"ol"ing .who% which%
that. of 7nglish# -or example% the descripti"e form && of is and means a .train which
left.# Biterall!% means .left. therefore / a left train
# Rules
$irst& take off a 8erb an' then&
-) $or 8erbs with a final consonant& a''
(g)
M / ate
M a dwarf who ate an apple
M / died;dead
M a dead soldier 0/ a soldier who died1
M / disbelie"ed
M Thomas who disbelie"ed
M / read (past tense)
M an article that & read
/) $or 8erbs without a final consonant an' 8erbs with as a final consonant& replace it with as a
final consonant)
(g)
M / borrowed
M a boo which & borrowed 0Lit. a borrowed boo1
M / wrote
/ the gospel which *t# Bue wrote
M / stopped
/ a place where the bus stopped
%entences& 'egatives
M / didn2t wait
M a ser"ant who didn2t wait for the Bord
M / didn2t eat
/ a dog who didn2t eat food
M / didn2t gi"e up
/ 'ob who didn2t gi"e up till the end
!erbs 3 *poken $orm
The *poken $orm of !erbs
The following dialogue between two close friends in"ol"e the informal spoen forms of "erbs#
/ well
/ shopping
/ !es
/ am
/ pm
/ &2ll go first
This dialogue should be eas! to comprehend#
/ The con"ersation starts
4 % ,
4 #
4 ,
4 # #
4 ,
4 S#
4 ,
4 #
4 ,
4 # #
4 ,
4 #
4 T ,
4 # ,
4 #
4 ,
4 Q#
4 ,
4 # # # T
4 T
*ang8u4 'i8u% what are !ou doing,
'i8u4 &2m eating#
*ang8u4 Where are !ou going,
'i8u4 &2m going to school#
*ang8u4 When are !ou going,
'i8u4 At S o2cloc#
*ang8u4 Wh!, 9are !ou going to school,:
'i8u4 & stud! at school#
*ang8u4 &s it fun,
'i8u4 Yes% it2s fun#
*ang8u4 6ow do !ou stud!,
'i8u4 J! teacher teaches me#
*ang8u4 Ahh### reall!,
'i8u4 Yeap# 6ow about !ou,
*ang8u4 &2ll go shopping
'i8u4 When,
*ang8u4 At Q o2cloc pm#
'i8u4 Did !ou ha"e a meal,
*ang8u4 Yes# & ha"e# &2ll go first then# 3!eT
'i8u4 3!eT
This is a con"ersation between *ang8u and 'i8u# This is a t!pe of con"ersation that is common between close
friends% !et it is extremel! simple to understand e"en for beginners of Korean# *o pa! attention to how these
,spoken forms, are used#
U A list of written forms and their respecti"e spoen forms#
Written $orm 3 *poken $orm
9-or detailed explanation% refer to 0Herbs 8 5resent% 5ast1:
go / 8
come / 8
do / 8
eat / 8
gi"e / 8
recei"e / 8
pla! / 8
sleep / 8
run / 8
teach / 8
learn / 8
These spoen forms are informal so !ou should onl! use them with "er! close friends#
A'8erbs 3
A'8erbs 3
A'7ecti8e 2resent A'8erb
2ositi8e
Negati8e
Note: is more commonl! used in written Korean while is more common in spoen Korean#
$ules
-) Take off an a'7ecti8e of the present tense an' attach 4 to it)
/) Attach to a positi8e form of a'8erbs to turn it into its negati8e form)
Written 2resent A'8erb
High ,
Eow
Big
*mall Csi9eD
*pacious
"elicious
:anF ,
*mall
CGuantitFD
Kin'
$ast ,
*low
Han'some
Note:
Ad"erbs come )ust before "erbs to describe actions#
% and each ha"e two ad"erbial forms# % and are more commonl! used than
% and #
(%ample sentences
/ & ate m! stea deliciousl!#
/ A tortoise wals slowl!
/ & ate a big meal# 0Lit. & ate a meal a lot#1
! / Bet2s go home <uicl!!
# / @heol8su ran fast to the finish line#
/ *eong8u made a large cae# 0Lit. *eong8u made his cae big#1
/ The higher a bird flies% the farther it sees# 0Lit. A bird which flies high
sees afar#1
2articles 3 4 4
2articles 3 4 4 ["ati8e 2article
The dati"e particle% ;% is mainl! used for someone;something to whom !ou are gi"ing something#
is a honorific form% is a formal form and is an informal form#
(g) -
/ To m! father% & ga"e a present#
/ -ather
/ present
/ gi"e 0honorific form1
/ ga"e 0honorific form1
(g)/
/ To m! dad% & ga"e a present#
/ Dad
/ present
/ gi"e 0honorific form1
/ ga"e 0honorific form1
(g)0
# / To older sister% & ga"e water
/ older sister
/ water
/ gi"e
/ ga"e
01;; is used when !ou are recei"ing something from someone# Again% 01 is
an honorific form% is formal and is informal#
(g)-
/ -rom the president% & recei"ed a priIe#
(g)/
/ -rom mum% & recei"ed a letter
/ mum
/ letter
/ recei"e
/ recei"ed
(g) /
/ -rom older brother% & heard news
/ older brother
/ news
/ hear
/ heard
2articles 3 4
2articles 3 4
Hse for wor's that ha8e a final consonant an' for wor's that 'on6t) C(%ception: Hse for
wor's that ha8e as a final consonant)D
e)g)
= bF truck
= bF4with a computer
= bF4with pencil
5) 4 is use' for tools4metho's4transport with which Fou 'o something)
(g)-
/ With scissors% & cut a paper#
/ With a pencil% & drew a picture#
/ With a bow% & did hunting#
/ scissors
/ paper
/ cut
/ cut 0past1
/ pencil
/ picture
/ draw
/ drew
/ bow
/ hunting
/ do
/ did
/ do hunting
(g) /
/ With his good brain% Da"id beat Goliath#
/ 3! m! imagination% & saw the hea"en#
/ With its large bea% the gull caught a fish#
/ Da"id
/ good
/ head 0brain1
/ Goliath
/ win;beat
/ imagination
/ hea"en
/ see
/ saw
/ a gull
/ big% large
/ bea
/ fish
/ catch
/ caught
(g) 0
/ 3! a plane% & went to an island#
( / 3! car% it taes an hour to school#
KTV Q / 3! KTV% it taes Q hours to go from *eoul to 3usan#
/ plane
/ island
/ go
/ went
/ car
/ school
/ hour
/ tae 0time1
/ tae 0time1
KTV / Korea Train 7xpress
55) 4 is use' for a 'estination4place for which Fou are hea'e')
/ & am headed for the hea"en
/ a door for entering the hea"en
/ +aomi left for Joab
/ 'im went home#
The difference between ; and ; is that ; emphasises where one is headed;has gone whereas
; doesn2t#
/ & went home# 0& didn2t go to an! other place#1
2articles 3 & [$rom& toQ at4in
& [$rom& to
and are used after places;times )ust lie .from. and .to. in 7nglish#
(%ample sentences
/ -rom home to school
( 2 / -rom (pm to 2pm
/ & came from 7ngland
/ & climbed up to the summit of the mountain#
/ @ome bac b! e"ening
/ 7ngland
/ mountain summit
/ e"ening
[At4in
is used after places to mean that something is happening at a particular place#
(%ample sentences
# / At school% we pla!ed American football#
/ At a 'apanese restaurant% & ate sushi#
/ &n a par% we pla!ed badminton#
/ &n m! room% & studied#
/ &n the bathroom% & had a shower#
/ American football
/ 'apanese restaurant
/ sushi
/ par
/ badminton
/ room
/ stud! 0noun1
/ studied
/ bathroom;toilet
/ shower
/ had a shower 0Lit. did a shower1
Note: &n spoen Korean% ; is usuall! omitted#
$or e%ample:
M 0& studied1
M 0 & had a shower1
M 0& had dinner1
2articles 3 [onlF
[+nlF 2article
essentiall! means .onl!. and it is used after a noun# *ometimes% is used before a noun to emphasiIe
the .onl!8ness#.
# / $nl! & left#
TH # / $nl! Dad watched TH#
# / $nl! Puth came to &srael#
# / & dran onl! water#
# / *tephen bought onl! shoes)
# / $nl! & ate#
# / $nl! 5aul studied Korean#
# / $nl! 'ohn left#
can be also used for nominaliIed "erbs#0+ouns 8 +ominaliIing Herbs1 &n this case% is attched after
a nominaliIed "erb#
(g)
# / & did onl! eating#
( # / 5aul% for a wee% did onl! stud!ing Korean#
# / The oala% which & saw at the Ioo% did onl! sleeping#
/ The oala% which & saw at the Ioo
-or a detailed explanation of the descripti"e "erb% see 0Herbs 8 Descripti"e &1
2ossessi8e 3
2ossessi8e 3
Rule
U Add to a noun# (ote! "ainly used in a written #or")
(g)
A M / m!
A M / !our
A M / his
A M / her
6owe"er% in most spoen Korean% the! are simplified for easier pronunciation#
(g)
M
M 0pronounced 1
; M % 0not commonl! used1
0who1 M 0whose1
-or all possessi"es% onl! and 01 are commonl! used in spoen Korean# &n most cases is omitted#
(g#
J! car /
Your shoes / 0pronounced 1
Jichael2s car / 0written form1 or 0spoen form1
+otice that has been omitted% and has been simplified to #
, 0Whose car is it,1
01 0You can either answer b! sa!ing or 1
&n spoen Korean% 2he;she2 or 2his;her2 are rarel! 0almost ne"er1 used# &nstead% his;her name is addressed as a
sub)ect in a first sentence% and then omitted for sentences following# This is the same for possessi"e forms#
&nstead of 2his;her2% 2Jichael2s;Bisa2s2 are used#
(g)
Bisa2s friend(4 # 0Bisa2s handbag is reall! prett!1
Bisa2s friend24 , # 0Peall!, &% too% want to bu! that1
Another thing to note is that is attached to a personal name if a noun being possessed is a
group;organisation# 0*poen -orm1
Bisa2s friend(4 0Bisa2s house is reall! big1
Bisa2s friend24 # 0Bisa2s school% too% is big1
Note: A school% house% compan! and countr! are some of the 2group;organisation2 nouns that re<uire
attached to a personal name which are being possessi"e# An! other personal items such as one2s bag% car and
so on do not need attached to a personal name#
Con7unctions 3 An'
[an'
can onl! be used between sentences#
Yesterda! /
3oo /
3anana /
read /
read9past: /
sleep / slept /
(g)
# # 9Yesterda!% read boo# And slept#:
# # 93anana is delicious# And sweet#:
The two sentences are lined b! but the! are still separate# To lin two or more sentences into one
sentence% please refer to Herbs 8 @onnecti"e#
4 [6an'6 for nouns
; is used for nouns# Kse after nouns without a final consonant% and for nouns with a final
consonant# ; is onl! used to )oin nouns#
(g)
/ *ea and Jountain
/ You and &
/ rice and bread
/ boo% pencil and paper
Con7unctions 3 But
[But
can onl! be used between sentences#
3oo /
3anana /
read /
want to read /
wanted to read / 0Verbs - Want)
sleep / slept /
lie / 0plain1
lie / 0present1 0Verbs - Present/Past)
(g)
# # 9& wanted to read a boo# 3ut & slept#:
# # 93anana is delicious# 3ut & don2t lie it:
The two sentences are lined b! but the! are still separate#
N 4N [But
To lin two or more sentences into one sentence% T or T are used#
# $or 8erbs& a'' to Verbs - Descriptive I
# $or a'7ecti8es& a'' to Adjectives - Descriptive
(g)
M / write but
% / & write words but & cannot read
M / li"e but
% / &t li"es in the water but it cannot li"e on the ground
M / difficult but
/ A foreign language is difficult to learn but it2s interesting#
# $or 8erbs an' a'7ecti8es& a'' to a plain form without )
(g)
M / write but
% / & write words but & cannot read
M / li"e but
% / &t li"es in the water but it cannot li"e on the ground
M / difficult but
/ A foreign language is difficult to learn but it2s interesting#
Con7unctions 3 But [ 4
; is fre<uentl! used in casual spoen Korean# ; means .but.
$or e%ample&
/ & now how to do0spea;write;read1 Gree but &
don2t now how to do0spea;write;read1 &talian#
% # / & eat 0cooed rice1 but & don2t eat side dishes#
% / The room is spacious but the bathroom is cramped0small1#
Rules
-) Take off a plain form of 8erbs an' attach to it)
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
Note: Tae a final consonant% % off a plain form of "erbs and then attach #
M 0now1
M 0sell1
/) A'' to A'7ecti8es 3 "escripti8e form of a'7ecti8es)
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
(%ample sentences Cspoken formD
% # / & go to school toda! but & don2t go to school tomorrow#
% / & went to see a mo"ie but there was no mo"ie that &
wanted to watch#
% # / 0&;6e;*he1 was small 0height1 before but 0&;6e;*he1 am;is
tall now#
% # / This meal loos delicious but it2s not
delicious 0at all1 after &2"e tried it#
Con7unctions 3 Because& *o
Con7unctions 3 Because an' *o [N
T has man! usages and .because and so. is one of them#
$ules
# A'' to a spoken form of the present tense of 8erbs or a'7ecti8es) 0Ad)ecti"es 8 5resent;5ast% Herbs 8
5resent;5ast1
M / 3ecause 0&1 do ; 0&1 do and so
M / 3ecause 0!ou1 go ; 0!ou1 go and so
M / 3ecause 0!ou1 lea"e ; 0!ou1 lea"e and so
M / 3ecause 0&1 lie ; 0&1 lie and so
M / 3ecause 0!ou1 eat ; 0!ou1 eat and so
M / 3ecause 0&1 catch ; 0&1 catch and so
M / 3ecause 0he2s1 fast ; 0he2s1 fast and so
M / 3ecause 0it2s1 high ; 0it2s1 high and so
M / 3ecause 0she2s1 small ; 0she2s1 small and so
M / 3ecause 0it2s1 big ; 0it2s1 big and so
(%ample *entences
/ 3ecause & pla! basetball% &2m tall#
/ & pla! basetball and so &2m tall#
/ 3ecause he2s gone to Korea% now he2s not in America#
/ 6e2s gone to Korea and so he2s not in America#
/ 3ecause a tree is big% & lie it#
/ A tree is big and so & lie it#
/ 3ecause & lie science% & went to college#
/ & lie science and so & went to college#
/ 3ecause the building is high% we ha"e to use an ele"ator#
/ The building is high and so we ha"e to use an ele"ator#
/ basetball
/ Korea
/ America
/ tree
/ science
/ college;uni"ersit!
/ building
/ ele"ator
Con7unctions 3 *o [
A sentence containing T can be di"ided into two separate sentences and is used to lin them#
(%ample sentences
# # / & pla! basetball# *o &2m tall#
# # / 6e2s gone to Korea# *o he2s not in America#
# # / A tree is big# *o & lie it#
# # / & lie science# *o & went to college#
# # / The building is high# *o we ha"e to use an
ele"ator#
Con7unctions 3 Because [
Con7unctions 3 Because [ Q &
is more fre<uentl! used in written Korean and T is fa"oured in spoen Korean because of its
bre"it!#
$ules
Take off a plain form an' past tenses of 8erbs an' a'7ecti8es an' then attach ) CBut N+T a
present tense of 8erbs ie) ; is wrongR ; is rightRD
M / 3ecause & do
M / 3ecause & go
M / 3ecause & bu!
M / 3ecause & see
M / 3ecause & eat
M / 3ecause & lie
M / 3ecause & did
M / 3ecause & went
M / 3ecause & ate
M / 3ecause it2s big
M / 3ecause it2s small
M / 3ecause it2s hot
M / 3ecause it2s cold
M / 3ecause there is a lot
M / 3ecause it2s long
M / 3ecause it2s delicious
M / 3ecause it was high
M / 3ecause it was prett!
M / 3ecause it was fast
M / 3ecause it was strong
(%ample sentences
3 Compare an' contrast an' N )
# / 3ecause & lie @hinese food% & ate @hinese
food# CWritten KoreanD
# / 3ecause & lie @hinese food% & ate @hinese food#
C*poken KoreanD
/ 3ecause & lie @hinese food% & ate @hinese food# C*poken
KoreanD @on)unctions 8 3ecause% *o
# / 3ecause & go to school earl! in the morning% & got
up earl!#
/ 3ecause & go to school earl! in the morning% & got up earl!#
# / 3ecause the winter is cold% people wear
warm clothes#
/ 3ecause the winter is cold% people wear warm
clothes#
# / 3ecause on the internet%
there is a lot of false information% we should be careful about what we read#
# / 3ecause on the internet% there is a lot
of false information% we should be careful about what we read
Note: The ob)ect particle% ;% is omitted and some words are abbre"iated in the spoen form# -or example%
M
M M
Although it is less commonl! used% a sentence containing two clauses can be di"ided into two sentences using
and # is attached to the front of a second clause and replaces
#
# # / & ate @hinese food because & lie
@hinese food#
# 01 # / & ate @hinese food because & lie @hinese
food#
# # / & got up earl! because & go to school
earl! in the morning#
# 01 # / & got up earl! because & go to school earl! in
the morning#
Note:
is abbre"iated to or it is altogether omitted in spoen Korean#
is mainl! used in literature and the news reporters use it often# 6owe"er% people still use
occasionall! in con"ersations instead of T% especiall! when one wants to explain and reason#
Con7unctions 3 5f
Con7unctions 3 5f [N 4
T; is used after a "erb and the clause containing T must alwa!s come first and its meaning is .if & do
such and such#.
$ules
-) Take off a plain 8erb an' a'' to it)
M / &f 0&1 do
M / &f 0!ou1 go
M / &f 0!ou1 throw
/) Take off a 8erb with a final consonant an' a'' to it)
M / &f 0&1 lie
M / &f 0!ou1 eat
M / &f 0&1 catch
(g)
/ &f & go to school% & can stud!#
/ &f !ou go to med school% !ou can become a doctor#
/ &f !ou bring 0me1 a boo% & will read 0it1 to !ou#
/ school
/ can do
/ med school
/ doctor
/ can become
/ boo
/ bring
/ read
Con7unctions 3 When
Con7unctions 3 When [N
# $ules
$irst& take off a plain form of 8erbsCHerbs 8 5resent;5astD then:
-) A'' N to 8erbs with a final consonant
M / when & eat
M / when & sit
M / when & belie"e
M / when & die
/) A'' N to 8erbs without a final consonant)
M / when & go
M / when & come
M / when & sleep
M / when & bu!
0) A'' N to 8erbs with as a final consonant
M / when & sell
M / when & li"e
M / when & pla! 0muc around1
(g)
# / When we were eating dinner% the rain came#
# / When !ou sit on the chair% be careful#
# / When the soldier was d!ing% he left a message#
# / When & go to school% & go b! car#
# / When & come home% & "isit m! friend2s house#
# / When we sleep% we dream#
/ When people bu! food% the! go to a supermaret#
U Take off an' a'' N to the past tense of 8erbs
M / when & ate
M / when & sat
M / when & belie"ed
M / when & died
M / when & sold
M / when & li"ed
M / when & pla!ed 0muced around1
(g)
# / When & li"ed in @hicago% & learned 7nglish#
% / When we pla!ed outside% the weather was good#
Note:
( = When we were eating 'inner& the rain came#
) = When we were eating 'inner& the rain came)
both or can be used and the! mean the same thing# This is because the final "erb% %
determines the tense of a sentence# The former is a more casual form than the latter#
Con7unctions 3 While
Con7unctions 3 While [NC D
$ules
-) Take off a plain form of 8erbs with no final consonant an' a'' to it)
M / while doing
M / while going
M / while gi"ing
M / while bu!ing
M / while watching
M / while speaing
M / while drining
M / while sleeping
/) Take off a plain form of 8erbs with a final consonant an' a'' to it)
M / while eating
M / while recei"ing
M / while looing for
M / while reading
(%ceptions
M / while waling
M / while listening
(%ample sentences
Written Korean
# / While doing exercise% & watched Jatrix#
# / While listening to music% & studied geograph!#
# / While sleeping% 6omer snored#
# / At *tarbucs% while reading a magaIine%
Jin)i dran coffee#
# / While going to wor b! car% 'unho listened to
radio#
*poken Korean
# / While doing exercise% & watched Jatrix
# / While listening to music% & studied geograph!#
01 # / While sleeping% 6omer snored#
01 # / At *tarbucs% while reading a magaIine%
Jin)i dran coffee#
01 # / While going to wor b! car% 'unho listened to radio#
/ Jatrix 0The mo"ie1
/ music% song
/ geograph!
/ 6omer 0a male name as in *impsons1
/ Jin)i 0a female name1
/ *tarbucs
/ magaIine
/ coffee
/ wor% compan!
/ radio
/ 'unho 0a male name1
Note:
The spoen Korean usuall! omits a sub)ect because it is usuall! understood b! the speaers as to who the!
are taling about# -or example% if & were taling about m!self% & wouldn2t need to use to sa! something
about me because it is assumed that & am taling about me#
Biewise% the third person sub)ects lie and can also be omitted when a person being taled
about is alread! nown b! people ha"ing a con"ersation#
The ob)ect particle% ;% is omitted in spoen Korean#
>W-H
>W-H 3 When& Where& Who& What& How an' WhF
Note: 5lease refer to Herbs 8 5resent;5ast for the spoen form of "erbs#
When% where% who% what% how and wh! are "er! useful words to mae a <uestion and the! are con"enient to
use in con"ersations with friends# 6ere are some simple sentences# You ma! hear these this pattern of the
speech a lot from Korean dramas% animations% and people#
To show !ou how the! are used% &2"e made simple sentences using the "erb%.go.#
When4 , / When do !ou go, 0Lit. when go,1
Where4 , / Where do !ou go,
Who4 , / Who is going,
What4 , / What is going,
6ow4 , / 6ow do !ou go,
Wh!4 , / Wh! do !ou go,
Note: The sub)ect is usuall! omitted#
(g)
*am: & will go to school#
MennF: , 96ere% it would mean 2When will !ou go,2:
*am: 5eter told me that we are going to a museum!
MennF: , 9When are we going,:
, / When do !ou come,
, / Wh! do !ou hit me,
, / Wh! do !ou cr!,
, / What do & gi"e to !ou, or What do !ou gi"e to me, 9Depends on the context:
Honorific $orm
While the spoen form abo"e is used between close frien's or when older people are taling to !ounger
people in informal situations# The honorific form is used commonl! between a'ults% b! people in formal
situations or when !ounger people are speaing to older people#
U 'ust add at the end of a sentence#
When4 , / When do !ou go, 0Lit. when go,1
Where4 , / Where do !ou go,
Who4 , / Who is going,
What4 , / What is going,
6ow4 , / 6ow do !ou go,
Wh!4 , / Wh! do !ou go,
, / When do !ou come,
, / Wh! do !ou hit me,
, / Wh! do !ou cr!,
, / What do & gi"e to !ou, or What do !ou gi"e to me, 9Depends on the context:
Comparati8es S *uperlati8es
Comparati8es [N
T is used to compare two persons or things# The person;thing that is referring to is the one that
comes after .Ter than. in 7nglish# The .T. phrase can also come before a sub)ect# *o the sentences
below ha"e the same meaning#
Note: ; particles are more fre<uentl! used than ; particles% and in the spoen Korean% almost
exclusi"el! ; are used#
/ & am taller than 0m!1 !ounger sibling#
/ .&. am taller than 0m!1 !ounger sibling#
/ & am taller than 0m!1 !ounger sibling#
/ & am taller than 0m!1 !ounger sibling# [spoken form
/ & am taller than 0m!1 !ounger sibling# [formal spoken form
/ than !ounger sibling
/ !ounger sibling
/ height
/ big
/ tall
/ short
/ &
/ changes to before ;
/ the honorific form of used in formal expressions
is usuall! added before an ad)ecti"e# / more
:ore e%amples
/ Jan is cle"erer than an animal#
/ The +ile Pi"er is longer than the AmaIon Pi"er#
/ &ron is stronger than copper#
/ 3lood is thicer than water#
/ 'insu is faster than 'inho#
/ J! older brother does it better than me#
/ & lie rice more than bread#
*uperlati8es [
is added before an ad)ecti"e to mae it a superlati"e#
/ 'insu is the fastest
/ The cheetah is the fastest among the land animals#
/ Jt# 7"erest is the highest mountain in the world#
/ 5iIIa is the most delicious food in the world#
/ The most beautiful thing is lo"e# [formal spoken form 0+ouns 8
5resent% 5ast1
/ world
/ delicious
/ delicious 9descripti"e form: Ad)ecti"es 8 Descripti"e
/ beautiful 9descripti"e form:
/ thing
5mperati8es
5mperati8es 3 &
5mperati8e 2ositi8e Negati8e
5nformal
$ormal
Honorific
The informal form is used among "er! close friends or when taling to a !ounger person who is "er! close to
!ou in informal situations#
The formal form and the honorific form are used in formal situations# 6owe"er% if & were to choose which one
to use% & would choose the honorific form because the formal form is a bit casual8ish# &t is safe to use the
honorific form if !ou are unsure which one to use#
Note: The honorific form of "erbs is present in Korean such as4
M / eat
M / sleep
M / die% pass awa!
2s honorific form is # &t is usuall! used when taling to people abo"e !our age or in formal
situations#
$ules
5nformal positi8e C5mperati8eD = 5resent positi"e 0spoen Korean1
! / Do!
! / Go o"er there! 0Bea"e me alone!1
# / 7at some of these snacs#
# / Drin some water#
5nformal negati8e = Tae off a plain form of "erbs and attach to it#
! / Don2t go!
! / Don2t watch this mo"ie!
# / Don2t eat this#
# / Don2t read this boo#
$ormal positi8e an' negati8e = Attach to informal forms
Honorific positi8e =
(# Tae off a plain form of "erbs and then attach to "erbs without a final consonant#
2# Attach to "erbs with a final consonant#
Q# -or "erbs with a final consonant of % drop it off and attach to it#
! / 5lease go!
# / 5lease come here#
! / 5lease lea"e <uicl!!
# / 5lease eat alread!#
# / 5lease catch the fish with !our hands#
! / 5lease wa"e !our hands! 0 / wa"e1
! / 5lease turn round and round! 0 / turn round% spin1
Honorific negati8e = Tae off a plain form of "erbs and attach #
! / 5lease don2t fool around!
# / 5lease don2t go to that place# 0Keep awa! from that place#1
# / 5lease don2t touch things in the museum#
Ha8e to 3
Ha8e to 3
5nformal form
5nformal Ha8e to Ha' to
Written
*poken
5nformal "on6t ha8e to "i'n6t ha8e to
Written
*poken
Note: The words in bold are the more commonl! used alternati"e of the two in each box#
$ules
-) Attach 4 4 4 etc) to the informal spoken form of 8erbs) Herbs 8 5resent% 5ast
M / ha"e to do
M / ha"e to go
M / ha"e to come
M / ha"e to see
M / ha"e to eat
M / ha"e to drin
/) Take off a plain form of 8erbs an' then attach 4 4 etc)
to it)
M / don2t ha"e to do
M / don2t ha"e to go
M / don2t ha"e to come
M / don2t ha"e to see
M / don2t ha"e to eat
M / don2t ha"e to drin
0) Attach an' 4 to the front an' back of the informal spoken form of 8erbs
respecti8elF) Herbs 8 5resent% 5ast
/ don2t ha"e to do
/ don2t ha"e to go
/ don2t ha"e to come
/ don2t ha"e to see
/ don2t ha"e to eat
/ don2t ha"e to drin
(%ample sentences
$ritten %or"
# / *eong8min has to go to *eoul toda!#
# / Jin8)u doesn2t ha"e to go to school tomorrow#
/ 3ecause of her sicness% Ashle! had to tae 0lit#
eat1 medicine e"er!da! last !ear#
&poken %or"
/ & ha"e to finish the science assignment b! this Thursda!#
/ 3ecause Ashle! has been healed now% she doesn2t
ha"e go to the hospital#
/ &f the chillies are too spic!% !ou don2t ha"e to eat them#
$ormal form
$ormal Ha8e to Ha' to
Written
*poken
$ormal "on6t ha8e to "i'n6t ha8e to
Written
.
*poken
Note: The rules for the con)ugation are the same as abo"e#
(%ample sentences
$ritten %or"
# / *eong8min has to go to *eoul toda!#
# / Jin8)u doesn2t ha"e to go to school tomorrow#
/ 3ecause of her sicness% Ashle! had to tae
0lit# eat1 medicine e"er!da! last !ear#
&poken %or"
/ & ha"e to finish the science assignment b! this
Thursda!#
/ 3ecause Ashle! has been healed now% she doesn2t
ha"e go to the hospital#
/ &f the chillies are too spic!% !ou don2t ha"e to eat them#
*ource4 Bearn Korean4 B52s Korean Grammar Guide
Allowe' to 3
Allowe' to 3
5nformal $orm
5nformal are allowe' to were allowe' to
Written
*poken
5nformal aren6t allowe' to weren6t allowe' to
Written
*poken
Note:
means ,allowe' to 'o, and means ,'on6t ha8e to 'o&, N+T ,not allowe' to 'o), This
needs some explanations#
-irst of all% means .o or allowed#. literall! means .doing is o#. literall! means .not
doing. therefore literall! means .not doing is o. which means .don2t ha"e to do#.
means ,not allowe' to 'o), literall! means .if & do. and means .not o. therefore
literall! means .if & do it% it2s not o. which can be expressed as .not allowed to do.
@ompare this with 6a"e to 8
6owe"er% !ou don2t ha"e to now these explanations to use them# Actuall!% &2"e ne"er thought about wh!
these mean what the! mean until toda!# The best wa! to learn them is to use them fre<uentl! until the!
become memorised#
$ules
-) Attach 4 4 4 to the positi8e informal spoken form of 8erbs Herbs 8
5resent% 5ast
M / allowed to do
M / allowed to go
M / allowed to see
M / allowed to hear
M / allowed to eat
M / allowed to drin
M / allowed to run
M / allowed to sit
M / allowed to pla!;muc around
/a) Take off a plain form of 8erbs without a final consonant an' attach 4 4
4 to it) C5nclu'es 8erbs with as a final consonantD
M / aren2t allowed to do
M / aren2t allowed to go
M / aren2t allowed to dance
M / aren2t allowed to pla!;muc around
M / aren2t allowed to push
M / aren2t allowed to spin
/b) Take off a plain form of 8erbs with a final consonant an' attach 4 4
4 to it)
M / aren2t allowed to eat
M / aren2t allowed to sit
M / aren2t allowed to hide
M / aren2t allowed to catch
M / aren2t allowed to pic up
M / aren2t allowed to fold
(%ceptions
M / aren2t allowed to listen
M / aren2t allowed to wal
(%ample sentences
$ritten #or"
/ At a buffet 0restaurant1% people are allowed to eat as
much as the! want#
/ Those who ha"e finished the exam can go home#
# / &t is not allowed to spea loudl! in the librar!#
# / &nfants are not allowed to eat solid food#
/ Kntil last !ear% students were allowed to use
a stall "ending machine#
&poken #or"
TH / You are allowed to watch TH# 0You can watch TH#1
/ You are allowed to eat this cae# 0You can eat this cae%1
/ You are not allowed to bu! alcohol and tobacco#
/ Kntil !esterda!% & was allowed to muc around#
/ Kntil last !ear% people were not allowed to enter
the Hictoria par#
$ormal $orm
$ormal are allowe' to were allowe' to
Written
*poken
$ormal aren6t allowe' to weren6t allowe' to
Written
*poken
Note: The rules are the same as abo"e#
(%ample sentences
$ritten #or"
/ At a buffet 0restaurant1% people are allowed to eat as
much as the! want#
/ Those who ha"e finished the exam can go home#
# / &t is not allowed to spea loudl! in the librar!#
# / &nfants are not allowed to eat solid food#
/ Kntil last !ear% students were allowed to
use a stall "ending machine#
&poken #or"
TH / You are allowed to watch TH# 0You can watch TH#1
/ You are allowed to eat this cae# 0You can eat this cae%1
/ You are not allowed to bu! alcohol and tobacco#
/ Kntil !esterda!% & was allowed to muc around#
/ Kntil last !ear% people were not allowed to
enter the Hictoria par#
5 like 'oing 3 &
5 like 'oing 3
is a contracted form of 0 M 1
means .doing. and if !ou remember% .;. is an identifier particle# &2d also lie to call it a
specificit! particle#
-or example%
/ & lie eating a sandwich at lunch 0among a "ariet! of things to
eat at lunch% a sandwich is m! choice1
/ & lie li"ing in the countr! 0Although & could li"e in the cit! or urban area% &
lie li"ing in the countr!1
means two things
(# & lie
2# &t2s good
Ksuall!% its meaning is .& lie doing. in spoen Korean# &n written Korean% . . is more liel! to
mean .it2s good to do something#. 6owe"er% the meaning depends on the context#
5nformal 2ositi8e Negati8e
Written
*poken
$ormal 2ositi8e Negati8e
Written
*poken
Note: The words in bold are the more commonl! used alternati"es of the two in each box#
$ules
-) Take off a plain form of 8erbs an' then attach
/) 5f a 8erb has a final consonant of & it is omitte')
M / & lie doing% it2s good to do
M / & lie eating% it2s good to eat
M / & lie watching% it2s good to watch
M / & lie listening% it2s good to listen
M / & lie waling% it2s good to wal
M / & lie writing% it2s good to write
M / & lie reading% it2s good to read
M / & lie maing% it2s good to mae
M / & lie li"ing% it2s good to li"e
M / & lie wrapping% it2s good to wrap
(%ample sentences
/ & lie exercising# &t2s good to exercise#
/ & lie going to the beach at weeends# &t2s good to go to the beach
at weeends#
/ $n a -rida! night% & lie eating piIIa# $n a -rida! night% it2s good
to eat piIIa#
/ When &2m bored% & lie watching mo"ies# When !ou2re bored% it2s good
to watch mo"ies#
5 like 'oing 3
is a contracted form of and is an ob)ect particle#
)ust means .& lie doing.
5nformal 2ositi8e Negati8e
Written
*poken
$ormal 2ositi8e Negati8e
Written
*poken
Note: is a contracted form of #
Rules are the same as abo8e)
M / & lie doing
M / & lie eating
M / & lie watching
M / & lie listening
M / & lie waling
M / & lie writing
M / & lie reading
M / & lie maing
M / & lie li"ing
M / & lie wrapping
(%ample sentences
/ & don2t lie exercising#
/ & lie going to the beach at weeends#
/ $n a -rida! night% & lie eating piIIa#
/ When &2m bored% & lie watching mo"ies#
5 think 3 N C+pinionD
5 think 3 N C+pinionD
is usuall! used when !ou are expressing !our opinion on something lie what people should and
shouldn2t do and what people should and should not be allowed to do etc#
Pefer to 6a"e to 8 % Allowed to 8 and & lie doing 8 % to
learn following examples#
$ules
Attach to the present informal written form of 8erbs)
eg)
/ & thin we should do it#
/ & thin it2s $K to go to a par#
/ & thin it2s good to drin mil
Note: / % /
(%ample sentences
#/ & thin people should go to bed earl! at
night and get up earl! in the morning#
# / & thin people should eat a lot of
fruits and "egetables to become health!#
TH / & thin it2s allowable to watch a lot of TH#
/ & thin it2s not acceptable to be late for an appointment
/ & thin it2s good to read a lot of boos#
/ & thin it2s not good to drin a lot of soft
drins#
5 think 3 CLeneralD
5 think 3 CLeneralD
[!erbs
Written $orm 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
*poken $orm 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
Note: &n spoen Korean% is pronounced as for the ease of pronunciation#
$ules
-) Take off a plain form of 8erbs an' attach 4 etc) to it)
/) "rop off a plain form of 8erbs that ha8e as a final consonant)
0) Take off a past tense form of 8erbs an' attach 4 etc) to it)
; / & thin the! do
; / & thin the! eat
; / & thin the! get up
; / & thin the! sleep
; / & thin the! watch
; / & thin the! wash
; / & thin the! run
; / & thin the! muc around
; / & thin the! li"e
; / & thin the! did
; / & thin the! ate
; / & thin the! watched
; / & thin the! li"ed
; / & thin the! muced around
(%ample *entences
/ & thin people are pla!ing soccer o"er there#
/ & thin this dog li"ed in that ennel# / & thin this dog used to
li"e in that ennel#
/ & thin a bab! is sleeping in that room#
/ & thin & don2t eat 0a meal1 fast)
[A'7ecti8es
Written $orm 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
*poken $orm 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
$ules
-) Attach a 'escripti8e form of a'7ecti8es to )
/) Take off a past tense form of a'7ecti8es an' attach )
M / & thin it2s good
M / & thin there2s a lot
M / & thin it2s big
M / & thin it2s small
M / & thin it2s prett!
M / & thin he2s cle"er
M / & thin she2s honest
M / & thin it was good
M / & thin it was delicious
M / & thin it was fun
M / & thin it was eas!
M / & thin there was a lot
(%ample sentences
/ & thin Thai food is delicious
/ & thin this house is enormousl! big#
/ & thin the maths test was reall! eas!#
/ According to m! memor!% & thin there were a lot
of flowers on that hill#
[Nouns
Written
$orm
2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
*poken
$orm
2resent 2ast
2ositi8e ( )
Negati8e 01
01
Note: The ob)ect particle% ;% is usuall! omitted in spoen Korean# is also usuall! omitted#
2s original meaning is .loo lie#. Therefore% phrases can ha"e alternati"e translations but
essentiall! the! mean the same thing#
/ & thin the!2re doing# &t loos lie the!2re doing#
/ & thin it2s prett!# &t loos prett!#
/ & thin it2s a chicen# &t loos lie a chicen 0food1#
$ules
Attach 4 4 4 to a noun)
0 1 / & thin it2s a pupp! 0&t loos lie a pupp!1
0 1 / & thin it2s a cat
0 1 / & thin it2s a cucoo
0 1 / & thin it2s a tree
0 1 / & thin it2s a person
0 1 / & thin it2s a school
(%ample sentences
4 , / Do !ou now what that animal is,
4 # / & thin that is a lion# 0That loos lie a lion1
4 # # / & don2t thin that is a lion# & thin it2s a tiger#
4 , , / &s it, Then what is that o"er there afar,
4 # # / & don2t thin it2s a human# & thin it2s an animal#
4 # / &t2s a chimpanIee#
4 # / & thought that was a chimpanIee# 0&t looed lie a chimpanIee1
Note: 2s past tense is and so / & thought it was a cat#
$ormal $orms
$ules
Written Korean = Change to )
*poken Korean = Attach to the en' of a sentence)
eg)
/ & thin Thai food is delicious
/ & thin this house is enormousl! big#
/ & thin the maths test was reall! eas!#
/ According to m! memor!% & thin there were a
lot of flowers on that hill#
TheF4he4she thinkCsD = N
is a shortened form of and it is used to express what the!;he;she thin0s1# is usuall!
used in spoen Korean# Attach to to mae it formal#
/ Grandma thins this dog li"ed in that ennel# /
Grandma thins this dog used to li"e in that ennel#
/ Jum thins a bab! is sleeping in that room#
/ J! friend thins & eat 0a meal1 fast)
/ 5aul thins Thai food is delicious
/ According to m! !ounger 0brother;sister12s
memor!% 6e;she thins there were a lot of flowers on that hill#
0 1 / The!;he;she thin0s1 it2s a pupp! 0&t loos lie a pupp!1
0 1 / The!;he;she thin0s1 it2s a cat
Are Fou 'oingT 3 N T [5nformal
Are Fou 'oingT 3 N T
is commonl! used in situations where !ou see somebod! doing something and !ou want to as them
what the! are doing# Again% can onl! be used when !ou are actuall! watching somebod! doing
something% and !ou want to as them what the! are doing#
# Rule
Take off a plain 8erb an' a'' T
M , / Are !ou doing,
M , / Are !ou going,
M , / Are !ou reading,
M , / Are !ou watching,
M , / Are !ou writing,
M , / Are !ou eating,
M , / Are !ou drining,
M , / Are !ou sleeping,
M , / Are !ou sending,
(g)
, / Are !ou woring,
, / Are !ou doing school homewor,
, / Are !ou ha"ing lunch,
, / Are !ou going home,
, / Are !ou going to church,
, / Are !ou drining water,
, / Are !ou watching a mo"ie,
, / Are !ou writing an essa!,
, / Are !ou sending a txt message,
, / Are !ou sleeping alread!,
You can add % % % % or 9when% where% who% what% how or wh!: in front of T
, to mae these sentences#
, / What are !ou doing,
, / What are !ou reading,
, / What are !ou watching,
, / What are !ou writing,
, / What are !ou eating,
, / What are !ou drining,
, / What are !ou sending,
, / Where are !ou going,
, / Who is sleeping,
, / Who is doing,
, / 6ow are !ou writing,
, / Wh! are !ou doing,
Are Fou 'oingT 3 N T [2olite
Are Fou 'oingT 3 N T [2olite
is commonl! used in situations where !ou want to as somebod! what the!2re doing#
can onl! used when !ou2re actuall! seeing somebod! doing something% and !ou want to as
them what the! are doing#
# Rule
Take off a plain 8erb an' a'' T
M , / Are !ou doing,
M , / Are !ou going,
M , / Are !ou reading,
M , / Are !ou watching,
M , / Are !ou writing,
M , / Are !ou eating,
M , / Are !ou drining,
M , / Are !ou sleeping,
M , / Are !ou sending,
Note: 5rregular 8erbs
M , +$T ,
M , +$T ,
M , +$T ,
(g)
, / Are !ou woring,
, / Are !ou ha"ing lunch,
, / Are !ou going home,
, / Are !ou going to church,
, / Are !ou drining water,
, / Are !ou watching a mo"ie,
, / Are !ou writing an essa!,
, / Are !ou sending a txt message,
, / Are !ou sleeping alread!,
You can add % % % % or 9when% where% who% what% how or wh!: in front of T
, to mae these sentences#
, / What are !ou doing,
, / What are !ou reading,
, / What are !ou watching,
, / What are !ou writing,
, / What are !ou eating,
, / What are !ou drining,
, / What are !ou sending,
, / Where are !ou going,
, / Who is sleeping,
, / Who is doing,
, / 6ow are !ou writing,
, / Wh! are !ou doing,
Are we 'oingT 3 4 T
Are we 'oingT 3 4 T
; , is usuall! used when !ou want to as someone what !ou 0both singular and plural1 are
doing% or will be doing immediatel!#
-or example% when !ou are in a group of people who are doing things as a group% and !ou want to as a leader
of the group what !ou all will be doing#
, / Are we going there, 9&nformal:
, / Are we going there, 95olite:
Note: , / Are !ou;we doing,
H+W(!(R& the polite form of .Are !ou doing,. usuall! uses . ,. whereas the polite form of
.Are we doing,. uses . ,.
*ee Are !ou doing, 8 T , % Are !ou doing, 8 T ,
# Rule
Take off a plain 8erb an' a'' 4 T
M ; , / Are we doing,
M ; , / Are we going,
M ; , / Are we reading,
M ; , / Are we watching,
M ; , / Are we writing,
M ; , / Are we eating,
M ; , / Are we drining,
M ; , / Are we sleeping,
M ; , / Are we sending,
(%ample *entences
, / Are 0we1 exercising,
, / Are 0we1 going there,
, / Are 0we1 going b! this car,
, / Are 0we1 eating this,
, / Are 0we1 eating with this,
, / Are 0we1 sleeping here,
, / Are 0we1 watching that mo"ie toda!,
, / Are 0we1 watching with this,
You can add % % % % or 9when% where% who% what% how or wh!: in front of T
, to mae these sentences#
, / What are we doing toda!,
, / What are 0we1 reading,
, / What are 0we1 watching,
, / What are 0we1 writing,
, / What are 0we1 eating,
, / What are 0we1 drining,
, / What are 0we1 sending,
, / Where are 0we1 going,
, / Where are 0we1 sleeping,
, / Who is doing,
, / 6ow are 0we1 writing,
, / Wh! are 0we1 doing,
:ore (%ample *entences
, / Where are we going,
% # / Ah% we2re going to the cit!#
, / Are 0we1 going b! this car,
% # / Yes% please get in#
, / What will we eat, Herbs 8 -uture 9Will:
# , / We will eat spaghetti# Do !ou lie it,
% # / Yes% & lie it#
To 'o something 3 N
To 'o something 3 N
This is the expression used to show that !ou purpose to do something# -or example%
/ To go to college% Abraham studied hard#
&n the sentence abo"e% the reason wh! Abraham studied hard is because he2s purposed to go to college#
/ To eat lunch% we went into the restaurant#
We went into the restaurant because we2d purposed to eat lunch#
Therefore% the clause containing T is the reason for doing something re"ealed in the rest of the
sentence#
Rules
U Add to a nominaliIed "erb# Also see 0+ouns 8 +ominaliIing Herbs1
/ To read
/ To write
/ To listen
/ To spea
/ To go
/ To come
/ To watch
/ To eat
/ To sleep
/ To run
/ To bu!
/ To sell
/ To stand
/ To sit
/ To li"e
/ To die
(g)
# / To read Korean words% & studied Korean#
# / To see the *tatue of Bibert!% we went to +ew Yor#
# / To go to the 5hilippines% she bought a flight
ticet#
/ Puth% who arri"ed in 'udah% to support her
mother8in8law% she wored# 0An excerpt from 1
/ Korean 0writing1
/ Korean 0language1
/ The *tatue of Bibert!
/ The 5hilippines
/ flight ticet
/ 'udah
/ Puth
/ Jother8in8law
/ support
/ To support
TrF 'oing 3 N
TrF 'oing 3 N
means .see. and T is a special expression which means .tr! doing.# This expression is used "er!
commonl! in ordinar! con"ersations#
U Pule
Add to a spoen form of a "erb# 0Herbs 8 5resent% 5ast1
/ tr! doing
/ tr! going
/ tr! eating
/ tr! drining
/ tr! reading
/ tr! listening
/ tr! bu!ing
/ tr! sitting
/ tr! seeing;looing;watching
/ tr! going up
/ tr! pla!ing 0the instrument1
The tables below is showing the written and spoen forms% and their respecti"e positi"e and negati"e forms#
Pemember that the plain form of "erbs is the most basic from which man! other forms of "erbs deri"e and the
plain form itself is rarel! used in both written and spoen Korean# & ha"e omitted the present negati"es for
both written and spoen forms because people ne"er use it in this wa!# &nstead of sa!ing% .don2t tr! eating.%
people would sa!% .don2t eat. which is # There are two wa!s of expressing past negati"es and one is
more common than the other# .T. form is more commonl! used#
$actual4"eclarati8e
CWrittenD
lain 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
"ialogue4Con8ersation
C*pokenD
lain 2resent 2ast
2ositi8e
Negati8e
(g)
# / Anna tried eating @hinese food#
# / @harles tried reading 'onathan 7dwards2 boo#
/ 3ecause & tried eating it before% & tried bu!ing a coconut
again# 0@on)unctions 8 3ecause% *o1
/ in the past% before
/ again
! / Tr! listening to this music!
! / Tr! drining this tea!
# # / Tr! going up this hill! And tr! looing at the blue
s!!
, / Tried going to German!, 0/ 6a"e !ou been to German!,1
, / Tried sitting on this old sofa,
, / Tried pla!ing the piano,
$ormal $orm
Pefer to Herbs 8 -ormal 95resent% 5ast:
(g)
Written $orm
= tr! eating
/ tried eating
/ ha"en2t tried eating
/ ha"en2t tried eating
*poken $orm
/ tr! eating
/ tried eating
/ ha"en2t tried eating
/ ha"en2t tried eating
+f course& 568e 'one it before 3
C+f courseD& 568e 'one it CbeforeD 3 C D C D
/ $f course
/ before
/ &2"e done it
Ksuall!% when we use % and are implied and omitted# *o if & sa!% . %. it
means% .C+f courseD& 568e plaFe' soccer CbeforeD).
When is used as a <uestion lie , T,% it means% ,Iou ha8e plaFe' soccer before&
ha8en6t FouT,
is a formal form and is an informal form#
is a contracted form of #
(g)
# / 0$f course1% &2"e pla!ed soccer 0before1# [5nformal
, = You ha"e pla!ed soccer 0before1% ha"en2t !ou, [5nformal
Ksuall!% form is used as an answer to a <uestion#
(g)
, / 6a"e !ou pla!ed soccer 0before1,
/ 0$f course1% &2"e pla!ed soccer 0before1#
/ 0$f course1% & ha"en2t pla!ed soccer 0before1#
Alternati8e answers
01% / 0Yea1% &2"e pla!ed soccer 0before1#
01% / 0+o1% & ha"en2t pla!ed soccer 0before1#
'e#erences! Tr! doing 8 % &t2s cold% isn2t it, 8 ,
$ule
&nformal present spoen form of "erbs A
(g)
/ 0$f course1% &2"e done it 0before1
/ 0$f course1% &2"e tried9eaten: it 0before1
/ 0$f course1% &2"e been9gone: there 0before1
/ 0$f course1% &2"e bought it 0before1
/ 0$f course1% &2"e tried it on9worn it: 0before1
/ 0$f course1% &2"e li"ed there 0before1
(%ample *entences
01 , / 6a"e !ou tried imchi 0before1,
01 # / 0$f course1% &2"e tried imchi 0before1#
, / 6a"e !ou been to *eoul 0before1,
# / 0$f course1% &2"e been to *eoul 0before1#
# / 0$f course1% &2"e li"ed in the *tates 0before1#
# / 0$f course1% &2"e made pasta 0before1# 9Therefore% & now how to coo pasta#:
, / You2"e been to 'apan% ha"en2t !ou,
, / You ha"en2t been to @hina% ha"e !ou,
, / You ha"en2t tried curr! before% ha"e !ou,
, / You2"e ne"er li"ed in 7cuador before% ha"e !ou,
+ote4 Kimchi is traditional Korean food# &t is a hot and spic! picled cabbage dish#
Li8e the fa8our of N 3 N
Li8e the fa8our of N 3 N
This is an important lesson because N is "er! fre<uentl! used in ordinar! con"ersations# -irst of all%
means ,gi8e, and when we attach the spoen form of a "erb in front of % it means someone ,gi8es the
fa8our of 'oing something for someone,) -or example% means .gi"e the fa"our of helping to
somebod!. which essentiall! means ,5 help someone,)
/ Jin8hee ga"e the fa"our of helping to Jom# 0Jin8hee helped Jom1
&n the sentence abo"e% Jin8hee helped her Jom and this helping has been done to her and for her# The
concept of gi"ing is profound in the Korean language# &n man! occasions where somebod! does something for
somebod! or to somebod!% the sentences in"ariabl! includes N )
# Rule
Attach the spoken form of 8erbs in front of )
/ gi"e the fa"our of doing
/ gi"e the fa"our of going
/ gi"e the fa"our of coming
/ gi"e the fa"our of eating
/ gi"e the fa"our of drining
/ gi"e the fa"our of reading
/ gi"e the fa"our of writing
/ gi"e the fa"our of seeing
/ gi"e the fa"our of listening
/ gi"e the fa"our of bu!ing
/ gi"e the fa"our of selling
/ gi"e the fa"our of teaching
/ gi"e the fa"our of helping
*entences
/ Young8ho ga"e 0me1 the fa"our of going to town together
0Young8ho went to town with me#1
/ town
/ together
/ 7lliot ga"e 0us1 the fa"our of coming to our home# 07lliot came to
our house#1
/ we
/ house
/ & ga"e m! little brother;sister the fa"our of eating his;her meal# 0& ate
m! little brother2s;sister2s meal for them#1
/ little sibling 0gender neutral1
/ meal% rice
/ 5rofessor 5iper ga"e the fa"our of
teaching 'ohn @al"in2s theolog! to us# 05rofessor 5iper taught us 'ohn @al"in2s theolog!#1
/ professor
/ honorar! suffix 0usuall! attached to the name of professions which in"ol"e teaching1
-or eg# / teacher% / pastor% / professor
/ theolog!
/ 0someone1 ga"e the fa"our of reading a letter to me# 90someone1 read a
letter to me 0for me1:
/ letter
/ 5articles 8 ;;
/ the contracted form of
/ 5eter ga"e the fa"our of listening to m! song# 95eter listened to m! song for
me#:
/ song
/ the contracted form of 0which is the spoen form of 1
/ *ome middle8aged man ga"e the fa"our of helping to me 0*ome
middle8aged man helped me#1
T / some T 0random% passer8b!1
/ middle8aged man 0a general term for e"er! married men or men aged between approx# 2=T??# $n a
side note% some men who are actuall! !oung get offended if some children call him because that
means that !oung man loos older than he actuall! is#1
/ some middle8aged woman
/ a middle8aged woman 0a general term for e"er! married women or women aged between approx#
2=T??# Again% almost all women who are actuall! !oung get offended or e"en hurt if some people call her
because that means that !oung lad! loos old# Bet us ha"e some discernment#1
/ some child
Woul' Fou like to goT 3 T
Woul' Fou like to goT 3 T
T01, is used when !ou express !our desire to do something together with someone% or when !ou
want someone to do something# *o it is similar to .Would !ou lie to do something,;Do !ou want to do
something,. in 7nglish#
# Rule
-) $or 8erbs without a final consonant& a'' )
/ , / Would !ou lie to do,
/ , / Would !ou lie to go,
/ , / Would !ou lie to bu!,
/ , / Would !ou lie to drin,
/) $or 8erbs with a final consonant& a'' )
/ , / Would !ou lie to eat,
/ , / Would !ou lie to sit,
/ , / Would !ou lie to read,
(g)
, / Would !ou lie to drin coffee,
, / Would !ou lie to eat lunch,
, / Would lie to go to the cinema together,
/ cinema% theatre
/ lunch% noon
/ together
Note: &f !ou omit off 01% ie# 01 it becomes an informal form#
, / Would !ou lie to drin coffee,
, / Would !ou lie to eat lunch,
, / Would lie to go to the cinema together,
*hall we 'o somethingT 3 T
*hall we 'o somethingT 3 T
$ules
-) $or 8erbs without a final consonant& attach as a final consonant an' a'' )
eg) ; T = *hall we buFT
/) $or 8erbs with a final consonant& attach )
eg) ; T = shall we wearT
5rregular
eg) ; T
M , / *hall we do,
M , / *hall we go,
M , / *hall we eat,
M , / *hall we drin,
M , / *hall we watch,
M , / *hall we listen to,
M , / *hall we hang out;muc around,
(%ample *entences
, / *hall we go to a theme par,
, / *hall we drin coffee at *tarbucs,
, / *hall we go ha"e lunch together,
, / *hall we go watch the 6arr! 5otter mo"ie,
, / *hall we go to a g!m to exercise,
Note: Attach to ; to mae it formal#
, / *hall we go to a theme par,
, / *hall we drin coffee at *tarbucs,
, / *hall we go ha"e lunch together,
, / *hall we go watch the 6arr! 5otter mo"ie,
, / *hall we go to a g!m to exercise,
5t6s col'& isn6t itT 3 T
5t6s col'& isn6t itT 3 T
is used similarl! to .isn2t it,. of 7nglish# -or example% means .cold.% and means ,5t6s col'&
isn6t itT or 5t6s col'& ehT or 5t6s col'& rightT, This is used when !ou want to chat up somebod! or when !ou
are looing for a confirmation#
# Rule
Tae off an ad)ecti"e and add to it#
M / &t2s cold% isn2t it,
M / &t2s hot% isn2t it,
M / There is a lot% isn2t there,
M / There is little% isn2t there,
M / &t2s high% isn2t it,
M / &t2s low% isn2t it,
M / &t2s large% isn2t it,
M / &t2s small% isn2t it,
M / &t2s good% isn2t it,
M / &t2s bad% isn2t it,
M / &t2s deep% isn2t it,
M / &t2s delicious% isn2t it,
+ote4 is often contracted to in speech# Therefore M #
/ &t2s cold% isn2t it,
/ &t2s hot% isn2t it,
/ There is a lot% isn2t there,
/ There is little% isn2t there,
/ &t2s high% isn2t it,
/ &t2s low% isn2t it,
/ &t2s large% isn2t it,
/ &t2s small% isn2t it,
/ &t2s good% isn2t it,
/ &t2s bad% isn2t it,
/ &t2s "er! deep% isn2t,
/ &t2s delicious% isn2t it,
*entences
, / The weather is cold% isn2t it,
, / The weather in Thailand is "er! hot% isn2t it,
, / Jount 6alla is high% isn2t it,
, / The ri"er water is "er! deep% right,
, / The house is small% eh,
, / Kimchi is delicious% isn2t it,
/ weather
/ Thailand
/ Jount 6alla
/ ri"er water
/ house
/ imchi 0A traditional Korean fermented dish made of cabbages with spic! seasonings1
Eet6s 'o it 3
Eet6s 'o it 3
This should be eas! to learn# 'ust replace of a plain "erb with to mae a phrase% .Bet2s 0"erb1.# Note:
This is an informal form#
M / Bet2s do it
M / Bet2s eat
M / Bet2s drin
M / Bet2s go
M / Bet2s sit
M / Bet2s see
M / Bet2s read
M / Bet2s write
M / Bet2s listen
M / Bet2s run
M / Bet2s wal
M / Bet2s bu!
M / Bet2s sell
(%ample *entences
/ we
/ together
01 01 / Bet2s do basetball# 0Bet2s pla! basetball1
01 01 / Bet2s eat a piIIa 0together1
01 01 / Bet2s drin coffee 0together1
01 01 / Bet2s go to beach 0together1
01 01 / Bet2s sit on the bench 0together1
01 01 / Bet2s watch a mo"ie 0together1
01 01 / Bet2s read a textboo 0together1
01 01 / Bet2s listen to ipod 0together1
01 01 / Bet2s bu! new shoes 0together1
01 01 / Bet2s sell that fridge 0together1
The formal form of )Let*s +verb,) is exactl! the same as that of the formal spoen present form# You ma!
want to refer to Herbs 8 -ormal 95resent% 5ast: .5lease. is implied in the phrase#
M / 05lease#1 Bet2s do it
M / 05lease#1 Bet2s eat
M / 05lease#1 Bet2s drin
M / 05lease#1 Bet2s go
M / 05lease#1 Bet2s sit
M / 05lease#1 Bet2s see
M / 05lease#1 Bet2s read
M / 05lease#1 Bet2s write
M / 05lease#1 Bet2s listen
M / 05lease#1 Bet2s run
M / 05lease#1 Bet2s wal
M / 05lease#1 Bet2s bu!
M / 05lease#1 Bet2s sell
(%ample *entences
/ we
/ together
01 01 / 95lease: Bet2s do basetball 0Bet2s pla! basetball1
01 01 / 95lease: Bet2s eat a piIIa 0together1
01 01 / 95lease: Bet2s drin coffee 0together1
01 01 / 95lease: Bet2s go to beach 0together1
01 01 / 95lease: Bet2s sit on the bench 0together1
01 01 / 95lease: Bet2s watch a mo"ie 0together1
01 01 / 95lease: Bet2s read a textboo 0together1
01 01 / 95lease: Bet2s listen to ipod 0together1
01 01 / 95lease: Bet2s bu! new shoes 0together1
01 01 / 95lease: Bet2s sell that fridge 0together1
(asF to 'o 4 "ifficult to 'o 3 N 4 N
(asF to 'o 4 "ifficult to 'o 3 N 4 N
This one is eas! to learn# All !ou need to do is attach a nominaliIed "erb to or to sa! that
something is eas! or difficult#
Written $orms
/ eas! to do
/ eas! to understand
/ eas! to sol"e
/ eas! to see
/ eas! to listen
/ eas! to sa!
/ eas! to go
*poken $orms
/ eas! to do
/ eas! to understand
/ eas! to sol"e
/ eas! to see
/ eas! to listen
/ eas! to sa!
/ eas! to go
Written $orms
/ difficult to do
/ difficult to understand
/ difficult to sol"e
/ difficult to see
/ difficult to listen
/ difficult to sa!
/ difficult to go
*poken $orms
/ difficult to do
/ difficult to understand
/ difficult to sol"e
/ difficult to see
/ difficult to listen
/ difficult to sa!
/ difficult to go
(g)
, / 6a"e !ou tried sol"ing this problem, 9Tr! doing 8 :
# # / Yes# This problem is reall! difficult to sol"e#
# / Bet2s go watch a circus#
/ 3ecause of the crowd% it2s difficult to see#
/ &t2s difficult to understand woman#
# / +o# Jan is more difficult to understand#
, / Do !ou thin so,
# # / Yes# & surel! do#
, / @an !ou hear me,
# # / +o# 3ecause of the sound of music% it2s difficult to hear#
/ please teach me how to do fishing 9Gi"e the fa"our of doing 8 :
# # / $# -ishing is eas! to do#
/ problem
/ sol"e
/ tr! sol"ing
/ circus
/ man
/ woman
/ thin
/ thin so
/ reall!% "er!
/ "er!
/ music
/ sound
/ fishing
5 know how 3
5 C'on6tD know how 3 4
Written
$orm
5 know how to 'o 5 'on6t know how to 'o
5nformal
$ormal
#
*poken
$orm
5 know how to 'o 5 'on6t know how to 'o
5nformal
$ormal
Note: & include the written form of this expression for the sae of completeness# 6owe"er% please focus on
the spoen form as the expression is mainl! used in con"ersations#
$ules
-)Take off a plain form4past tense of 8erbs an' attach )
C(%ception: $or those 8erbs which contain as a final consonant& take it off) eg) ;
D
/) Attach to 4 to turn it into a formal form)
/ & now how to do
/ & now how to eat
/ & now how to go
/ & now how to see
/ & now how to listen
/ & now how to use
/ & now how to mae
/ & now how to wear
/ & don2t now how to do
/ & don2t now how to go
(%ample sentences
# / Yong8)un nows how to mae0coo1 imchi stew#
.! ,. / .'ulia! Do !ou now how to boil0coo1 noodle soup,.
, # / Do
!ou now how & caught this big fish, This fish has good strength and so & caught it with a lot of effort#
# / & now how to plant a tree#
, / Do !ou now how to use this remote controller,
, / Do !ou now how to go0get1 to *eoul,
# / & don2t now how to go to 3usan#
# / & don2t now how to tie a nectie#
# / Grandpa doesn2t now how to send a text message#
Note: and are honorific forms of and respecti"el!# and are
onl! used for second8 and third8persons#
-or eg%
& now how to use the subwa!#
#
#
Do !ou now how to use the subwa!,
,
6e;she alread! nows how to use the subwa!#
#
:a'e4compelle' to 3 N N
This phrase has two parts# The first part is T % and the second part is T #
The meaning of .T . is e<ui"alent to .when0e"er1 or if%. and that of .T . is e<ui"alent to .am
made;compelled to. or .habituall!0usuall!1#.
-or example%
% / When0e"er1 & go to a restaurant% & am
made;compelled to order a bibimbap# 0& habituall!;usuall! order a bibimbap#1
/ a restaurant
/ go
/ When0if1 & go
/ a Korean dish 0The dish consists of rice with "arious inds of "egetables% beef0usuall! mince1% fried
egg% Korean red chili paste and sesame oil#1
/ order 0n#1
/ order 0"#1
/ & habituall! order
Note: The plain form of and is 22 which means 2to become#2 Therefore% the literal translation of
the sentence abo"e is4
% / When0e"er1 it becomes that & go to a restaurant% it
becomes that & order bibimbap
Also% in the first part when a noun is used instead of a "erb% ; is used instead#
-or example%
% / When it is morning% & habituall!0usuall!1 read a newspaper
The literal translation of the sentence abo"e is% .When it 2becomes2 morning% & 2become2 reading a newspaper#.
The sentence doesn2t mae sense grammaticall! in 7nglish but & hope the literal translation will help !ou get
the nuance of the phrase#
Con7ugation rule
Take off a plain form of 8erbs an' attach 4 to it)
0do1 M / When0e"er1 & do
0do1 M / & habituall!;usuall! do 0or & am made;compelled to do1
/ & habituall! do
/ & habituall! go
/ & habituall! come
/ & habituall! eat
/ & habituall! sleep
/ & habituall! spea
/ & habituall! listen
/ & habituall! watch
(%ample *entences
% / When0e"er1 it is late at night% & habituall! eat an
icecream
/ When0e"er1 it is noon% because &2m tired0sleep!1% &
habituall! ha"e a nap 0Lit. sleep a nap1#
% / When0e"er1 & turn on the computer% & habituall! listen to
music#
% / When0e"er1 & go to town% & habituall! go to mo"ies 0Lit.
watch mo"ies1#
% / When0e"er1 & exercise% & habituall! drin a lot of water#
HsuallF
As a side note% when !ou would lie express something that !ou ,usuallF, do and not what !ou are
.made;compelled to. do% , , is often used#
-or example%
% .. / When & go to a restaurant% & usuall! order a bibimbap#
0There is no nuance of being .made;compelled to. order a bibimbap#1
.. / After exercise% & usuall! drin a lot of water# 0*ome
people ma! not drin a lot of water and other people ma! not drin water at all but as for me% &
.usuall!.0whether .&2m made;compelled to. or not% we do not now1 drin a lot of water#1
/ When & go to town% & usuall! go to mo"ies# 0Lit# watch mo"ies1
/ & usuall! wal to school#
/ & usuall! go to wor b! car#
A''ressing 2eople
A''ressing frien'6s name
When a person is addressed ; is attached to their name# &f m! name were 9'in8u:% m! friend would
call me% ! 9'in8u8!a:# This is lie .6e! ;'in8u!.
This collo<uialism should onl! be used between close friends# This is an informal expression# At school%
friends call each other this wa!% and teachers to students but not "ice "ersa#
+ote that is used for names without a final consonant and for names with a final consonant#
(g)
M !
This is pronounced 94'i8nu8ga: since has no sound when used as an initial consonant#
M !
&t is pronounced 94'i8nu8!a:
M !
M !
M !
*o when !ou call !our Korean friend2s name% )ust add ; to their name#
You might also like
- Learn Korean ReaderDocument12 pagesLearn Korean ReaderDjRaveWayetBorja40% (5)
- Magic SEA Underground Magic SEA Underground: Who Is Knocking At 3am Annually? (凶煞回魂)Document15 pagesMagic SEA Underground Magic SEA Underground: Who Is Knocking At 3am Annually? (凶煞回魂)tractorbeaming0% (1)
- Buchla Music Easel ManualDocument68 pagesBuchla Music Easel Manualchloe_stamperNo ratings yet
- Korean Grammar TextbookDocument61 pagesKorean Grammar TextbookDiana Madeira75% (4)
- Elementary Korean Second Edition: (Downloadable Audio Included)From EverandElementary Korean Second Edition: (Downloadable Audio Included)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- KoreanDocument66 pagesKoreanJoan Loi100% (2)
- Korean Grammar Guide BookDocument145 pagesKorean Grammar Guide BookJapzter Umali100% (1)
- Korean Language FullDocument882 pagesKorean Language FullCostache Oana50% (2)
- Beginner KoreanDocument141 pagesBeginner KoreanAwi Tiosen100% (1)
- Magic SEA Underground Magic SEA Underground: Taoist 7 Steps Exorcism Method (七步 驱鬼法)Document15 pagesMagic SEA Underground Magic SEA Underground: Taoist 7 Steps Exorcism Method (七步 驱鬼法)tractorbeamingNo ratings yet
- Learn Korean - Quick / Easy / Efficient: 2000 Key VocabulariesFrom EverandLearn Korean - Quick / Easy / Efficient: 2000 Key VocabulariesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Korean Grammar: For BeginnersDocument9 pagesKorean Grammar: For BeginnersĖřřøř Chan100% (2)
- Korean LanguageDocument168 pagesKorean LanguageBdak Agak Skema100% (1)
- RothschildDocument133 pagesRothschildtractorbeamingNo ratings yet
- Magic SEA Underground Magic SEA Underground: The In Between Realm (浅 谈阴阳界)Document18 pagesMagic SEA Underground Magic SEA Underground: The In Between Realm (浅 谈阴阳界)tractorbeamingNo ratings yet
- Grammarpoints KoreanDocument30 pagesGrammarpoints KoreanBrian PerryNo ratings yet
- Durga Shabar MantraDocument5 pagesDurga Shabar Mantradeepaksharma28No ratings yet
- 2000 Most Common Korean Words in Context: Get Fluent & Increase Your Korean Vocabulary with 2000 Korean PhrasesFrom Everand2000 Most Common Korean Words in Context: Get Fluent & Increase Your Korean Vocabulary with 2000 Korean PhrasesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Korean Honorifics: Important Titles, Words, & PhrasesDocument11 pagesKorean Honorifics: Important Titles, Words, & PhrasesCESH50% (2)
- Korean Hangul LessonsDocument29 pagesKorean Hangul LessonsSeeWind67% (6)
- Lesson Plan in ReadingDocument6 pagesLesson Plan in ReadingJesica Varias100% (1)
- Family & Relatives: Conversation Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesFamily & Relatives: Conversation Cheat SheetAdelina OpreaNo ratings yet
- Say It Right in Korean: TheFastest Way to Correct PronunicationFrom EverandSay It Right in Korean: TheFastest Way to Correct PronunicationRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Korean Language Information - Korean Alphabet, Korean Grammar, Korean Pronunciation Rules and MoreDocument3 pagesKorean Language Information - Korean Alphabet, Korean Grammar, Korean Pronunciation Rules and MoreNikkii Sharma100% (1)
- Korean WikibooksDocument109 pagesKorean WikibooksFebiansyahHidayatNo ratings yet
- English to Korean Dictionary: Words Without Borders: Bilingual Dictionary SeriesFrom EverandEnglish to Korean Dictionary: Words Without Borders: Bilingual Dictionary SeriesNo ratings yet
- How To Speak Korean - 14 Steps (With Pictures) - WikiHowDocument6 pagesHow To Speak Korean - 14 Steps (With Pictures) - WikiHowAlfie RidwanNo ratings yet
- Let's Learn Korean For BeginnersDocument60 pagesLet's Learn Korean For Beginnersامينه شهداء عبدللطيف100% (1)
- Registers and RTLDocument46 pagesRegisters and RTLBijay MishraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Basic Korean SentencesDocument7 pagesLesson 1 - Basic Korean SentencesL50% (2)
- Kamadhenu TantraDocument3 pagesKamadhenu Tantratractorbeaming100% (1)
- Korean SourcesDocument6 pagesKorean Sourcesgodoydelarosa2244No ratings yet
- Korean PronunciationDocument43 pagesKorean PronunciationMihaela GrubiiNo ratings yet
- Korean Lesson 1Document12 pagesKorean Lesson 1Ivett97No ratings yet
- Korean Dipthongs: Complex VowelsDocument6 pagesKorean Dipthongs: Complex VowelsOlivia PJMNo ratings yet
- Korean Beginner ClassDocument7 pagesKorean Beginner ClassEliza LimNo ratings yet
- Korean Folktales for Language Learners: Traditional Stories in English and Korean (Free online Audio Recording)From EverandKorean Folktales for Language Learners: Traditional Stories in English and Korean (Free online Audio Recording)No ratings yet
- Mini Korean Dictionary: Korean-English English-KoreanFrom EverandMini Korean Dictionary: Korean-English English-KoreanSeong-Chui ShinRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Tuttle Pocket Korean Dictionary: Korean-English English-KoreanFrom EverandTuttle Pocket Korean Dictionary: Korean-English English-KoreanRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Korean LessonsDocument36 pagesKorean LessonsAsma' Haris100% (2)
- 1 ShukraDocument3 pages1 ShukratractorbeamingNo ratings yet
- Essential Korean: Speak Korean with Confidence! (Korean Phrasebook)From EverandEssential Korean: Speak Korean with Confidence! (Korean Phrasebook)Rating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- Tuttle More Korean for Kids Flash Cards Kit Ebook: [Includes 64 Flash Cards, Audio Recordings, Wall Chart & Learning Guide]From EverandTuttle More Korean for Kids Flash Cards Kit Ebook: [Includes 64 Flash Cards, Audio Recordings, Wall Chart & Learning Guide]No ratings yet
- Practical Korean: Speak Korean Quickly and Effortlessly (Revised with Audio Recordings & Dictionary)From EverandPractical Korean: Speak Korean Quickly and Effortlessly (Revised with Audio Recordings & Dictionary)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- My First Bilingual Book–Colours (English–Korean)From EverandMy First Bilingual Book–Colours (English–Korean)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Elementary Korean: Second Edition (Includes Access To Website & Audio CD With Native Speaker Recordings) - Ph.D. Ross KingDocument5 pagesElementary Korean: Second Edition (Includes Access To Website & Audio CD With Native Speaker Recordings) - Ph.D. Ross Kingwodimogi0% (1)
- Learning Korean: A Language Guide for Beginners: Learn to Speak, Read and Write Korean Quickly! (Free Online Audio & Flash Cards)From EverandLearning Korean: A Language Guide for Beginners: Learn to Speak, Read and Write Korean Quickly! (Free Online Audio & Flash Cards)No ratings yet
- HowtoStudyKorean Unit 0 PDFDocument19 pagesHowtoStudyKorean Unit 0 PDFNguyenVinhPhuc100% (1)
- Korean Pronunciation GuideDocument7 pagesKorean Pronunciation GuidelimbadzNo ratings yet
- I Love to Share (English Korean Bilingual Book): English Korean Bilingual CollectionFrom EverandI Love to Share (English Korean Bilingual Book): English Korean Bilingual CollectionNo ratings yet
- Korean in a Hurry: A Quick Approach to Spoken KoreanFrom EverandKorean in a Hurry: A Quick Approach to Spoken KoreanRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Samayik Sutra With MeaningsDocument43 pagesSamayik Sutra With Meaningsapi-3777146No ratings yet
- Easy Korean lessons to understand K-POP: Let\'s learn Korean Language HangulFrom EverandEasy Korean lessons to understand K-POP: Let\'s learn Korean Language HangulNo ratings yet
- Korean Hangeul for Beginners: Say it Like a Korean: Learn to read, write and pronounce Korean - plus hundreds of useful words and phrases! (Free Downloadable Flash Cards & Audio Files)From EverandKorean Hangeul for Beginners: Say it Like a Korean: Learn to read, write and pronounce Korean - plus hundreds of useful words and phrases! (Free Downloadable Flash Cards & Audio Files)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Korean PhrasesDocument62 pagesKorean PhrasesJose miguel Sanchez gutierrez100% (1)
- Essential Korean Phrasebook & Dictionary: Speak Korean with Confidence!From EverandEssential Korean Phrasebook & Dictionary: Speak Korean with Confidence!Rating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Learn Korean Through K-Dramas 2: A Glance at Issues in Korean SocietyFrom EverandLearn Korean Through K-Dramas 2: A Glance at Issues in Korean SocietyNo ratings yet
- I Love to Brush My Teeth (English Korean Bilingual Book): English Korean Bilingual CollectionFrom EverandI Love to Brush My Teeth (English Korean Bilingual Book): English Korean Bilingual CollectionNo ratings yet
- Devi - DevatasDocument4 pagesDevi - DevatastractorbeamingNo ratings yet
- Lydia Furman (Israel) Wolf Messing. Russian To English TranslationDocument3 pagesLydia Furman (Israel) Wolf Messing. Russian To English Translationtractorbeaming0% (1)
- Ajit Shanti StotramDocument9 pagesAjit Shanti Stotramtractorbeaming0% (1)
- Magic SEA Underground Magic SEA Underground: Curing Spirit Possession DIY (自助 驱 邪法)Document19 pagesMagic SEA Underground Magic SEA Underground: Curing Spirit Possession DIY (自助 驱 邪法)tractorbeamingNo ratings yet
- DevanagariDocument6 pagesDevanagaritractorbeamingNo ratings yet
- Apoemthatenlightens PDFDocument11 pagesApoemthatenlightens PDFtractorbeamingNo ratings yet
- 1 KetuDocument3 pages1 KetutractorbeamingNo ratings yet
- 1 ShaniDocument3 pages1 ShanitractorbeamingNo ratings yet
- Bija (Seed) Mantras: The Single Syllable SoundsDocument3 pagesBija (Seed) Mantras: The Single Syllable SoundstractorbeamingNo ratings yet
- The Mantras For Mercury: To Connect With The Planetary Deity and To Energize All The Higher Powers of The MercuryDocument3 pagesThe Mantras For Mercury: To Connect With The Planetary Deity and To Energize All The Higher Powers of The MercurytractorbeamingNo ratings yet
- The Gayatri Mantra: The Essence of The VedasDocument3 pagesThe Gayatri Mantra: The Essence of The VedastractorbeamingNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Link For Code Composer StudioDocument326 pagesMATLAB Link For Code Composer StudioAthiesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Note On The History of LogicDocument3 pagesNote On The History of Logicnabeel ahmedNo ratings yet
- Honor Discourse and Social Engineering in 1 Thess - David DeSilvaDocument32 pagesHonor Discourse and Social Engineering in 1 Thess - David DeSilva31songofjoyNo ratings yet
- Half Blind Attack MSP430Document6 pagesHalf Blind Attack MSP430foobarNo ratings yet
- Akshay Prakash Patil: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesAkshay Prakash Patil: ObjectiveNaveenJainNo ratings yet
- Using Oracle GoldenGate To Upgrade Database 12c Applications Technology GroupDocument3 pagesUsing Oracle GoldenGate To Upgrade Database 12c Applications Technology GrouptonNo ratings yet
- FullWS Exercise Master IGSS13Document170 pagesFullWS Exercise Master IGSS13Edward NewgateNo ratings yet
- Book of Psalms: Date WrittenDocument2 pagesBook of Psalms: Date WrittenBrince Mathews100% (1)
- UPSD3254Document175 pagesUPSD3254quangtho1413No ratings yet
- Jersey Documentation 1.0.3.1 User GuideDocument34 pagesJersey Documentation 1.0.3.1 User GuideTr TzaraNo ratings yet
- Book-List CompressedDocument21 pagesBook-List Compressedmamta.bdvrrmaNo ratings yet
- My Green Garden! My Green PassportDocument3 pagesMy Green Garden! My Green PassportNexhmije HushiNo ratings yet
- Sexist LanguageDocument2 pagesSexist Languageleah manuelNo ratings yet
- RPP X 2Document55 pagesRPP X 2Fikri R. FauziNo ratings yet
- FOCGB3 Utest VG 2ADocument1 pageFOCGB3 Utest VG 2AVesna ObradovićNo ratings yet
- AntiheroDocument2 pagesAntiheroganniline floresNo ratings yet
- 700credit XML Interface (Ver 6.57 1-27-22)Document69 pages700credit XML Interface (Ver 6.57 1-27-22)Julio Cesar Guerrero GomezNo ratings yet
- Connecting To Attachmate - Bluezone Using Excel VBADocument9 pagesConnecting To Attachmate - Bluezone Using Excel VBAprince jainNo ratings yet
- 7167 0Document3 pages7167 0Ricardo Avila CalvoNo ratings yet
- Wittgenstein in CarrollDocument15 pagesWittgenstein in CarrollenroanNo ratings yet
- SplunkLight-7 1 3-ReleaseNotesDocument8 pagesSplunkLight-7 1 3-ReleaseNotesmx7890No ratings yet
- SPPID 2009 SP3 - Compatibility GuideDocument3 pagesSPPID 2009 SP3 - Compatibility Guidevenkateee57100% (1)
- Msbte News: 22517 Advance Java Programming MCQ PDFDocument9 pagesMsbte News: 22517 Advance Java Programming MCQ PDFAyushi Japsare100% (3)
- AspenONE Engineering Cloud V12 Using Windows Virtual DesktopDocument22 pagesAspenONE Engineering Cloud V12 Using Windows Virtual DesktopKARLA VALERIA MENDOZA JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect Tense Grammar Guides 89570Document12 pagesThe Present Perfect Tense Grammar Guides 89570harold marquezNo ratings yet
- SVG Documentation PDFDocument26 pagesSVG Documentation PDFjcr0ch4No ratings yet
- Fig. 1: Block Diagram Showing Architecture of AVR MicrocontrollerDocument30 pagesFig. 1: Block Diagram Showing Architecture of AVR MicrocontrollerPranav PrNo ratings yet















































![Tuttle More Korean for Kids Flash Cards Kit Ebook: [Includes 64 Flash Cards, Audio Recordings, Wall Chart & Learning Guide]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/342578484/149x198/ca47c580e2/1714131296?v=1)