Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Media Studies - Camera Shots
Media Studies - Camera Shots
Uploaded by
jessrichards98Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Media Studies - Camera Shots
Media Studies - Camera Shots
Uploaded by
jessrichards98Copyright:
Available Formats
Media Studies- Camera
Shots
By Jess Richards
Extreme Close Up (ECU)
Pretty much an extreme version
of the close up shot. This shot
generally magnifies things to
what we could not normally see
in reality. There is no
background detail and it is a very
artificial shot.
Big Close Up (BCU)
A Big close up shot is can still
include minimal background
detail. However, the focus of the
character/object is more defined
and important. E.g if the shot
was on a character, the eyes and
mouth would be shown, but not
the whole head.
Close Up (CU)
There is very minimal
background detail in close up
shots, and it mainly focuses on
either a face or an object. The
shot magnifies things and shows
the importance of things. The
close up takes us into the mind
of the character, as the close up
is a very intimate shot.
Medium Close Up (MCU)
A medium close up shot is in
between a close up shot and
medium shot. It still gives a small
impression of the whole picture.
However, it zooms in on detail.
For example a character.
Medium Shot (MS)
The medium shot contains a
character from the hips/waist up
and normally is used in dialogue
scenes. The background detail is
minimal as the location normally
would have been set earlier in
the scene. However, it still gives
an impression of the whole
picture.
Medium Long Shot (MLS)
The medium long shot (also
known as the three quarter
shot) shows a character from the
knee up. It shows the object in
regards to its surroundings.
Long Shot (LS)
The long shot is used to portray
something or someone as life
size to the audience. For
example, on TV, a man appears 6
foot tall because of the long shot
making it realistic. Even though
the main focus is on the
characters, the background
detail is not drained out.
Establishing Shot (ES)
An establishing shot is normally
the first shot of a scene. It is
used to set the scene for the
audience, giving them
knowledge of the surroundings
and location. This shot is
normally a wide-shot or an
extreme wide-shot.
High Angle Shot (HA)
This shot helps the audience get
a general overview of the action.
This makes the object focused
on seem less significant and
smaller. The object or character
seems part of a wider picture as
they get swallowed by the
setting from a higher up angle.
Low Angle Shot (LA)
The low angle shot increases
height to the object or character.
It gives the audience a sense of
powerlessness or confusion. The
surroundings are normally bare,
adding to the sense of
disorientation.
Birds Eye View (BEV)
Birds eye view is a shot from
directly above. It is a very
unnatural shot, and sometimes
seems unrecognisable. This shot
makes the audience feel more
important looking down on the
action.
Dutch Angle (DA)
The Dutch angle is when the
camera is deliberately tilted to
one side. It can create a sense of
unease, disorientation,
intoxication, madness and so on.
Eye Level Shot (EL)
Eye level shot is a more neutral,
realistic shot. It seems as if the
picture is what a human is
seeing instead of a camera view.
Reverse Angle Shot (RA)
The reverse angle shot is
normally a shot from the
different side of the subject.
Normally used in dialogue, the
camera is facing the other
participate.
You might also like
- Love For Sale - Chet BakerDocument3 pagesLove For Sale - Chet BakerFrancesco Baiguera100% (2)
- How To Take Party PhotosDocument22 pagesHow To Take Party PhotosunknownNo ratings yet
- Rmea Dmea TemplatesDocument9 pagesRmea Dmea TemplatesMervin Hangad100% (1)
- Perceval's Unknown Sin Narrative Theology in Chretien's Story of The Grail (Sylvester George Tan)Document30 pagesPerceval's Unknown Sin Narrative Theology in Chretien's Story of The Grail (Sylvester George Tan)isabel margarita jordánNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12-19 - AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter 12-19 - AnswersPranesvariDeviDasiNo ratings yet
- Hal Foster - Dailiness According To DemandDocument13 pagesHal Foster - Dailiness According To DemandGabino KimNo ratings yet
- Kjimenez Rpms Sy 2021 2022 Teacher Reflection Form TRFDocument7 pagesKjimenez Rpms Sy 2021 2022 Teacher Reflection Form TRFWarren Mark ManguneNo ratings yet
- (Appendix 4B) Teacher Reflection Form For MT I-IV For RPMS SY 2021-2022Document8 pages(Appendix 4B) Teacher Reflection Form For MT I-IV For RPMS SY 2021-2022Ian Santos B. SalinasNo ratings yet
- E-Portfolio: Results-Based Performance Management System (RPMS)Document21 pagesE-Portfolio: Results-Based Performance Management System (RPMS)JUN MICHAEL YABUTNo ratings yet
- Math Department RPMS Cover Sy 2021 2022Document27 pagesMath Department RPMS Cover Sy 2021 2022Roy Allan T. RamoNo ratings yet
- Results Based Performanc e Management System: RPM SDocument14 pagesResults Based Performanc e Management System: RPM SRyan BajoNo ratings yet
- Ipcrf 2021 2022 1Document30 pagesIpcrf 2021 2022 1Jel JelaiNo ratings yet
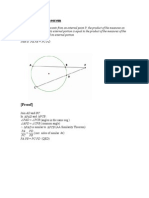
- Secant Secant TheoremDocument1 pageSecant Secant Theoremckhowh_232845246No ratings yet
- Teacher Zhai (Appendix 4A) Teacher Reflection Form For T I-III For RPMS SY 2021-2022. - 10docxDocument3 pagesTeacher Zhai (Appendix 4A) Teacher Reflection Form For T I-III For RPMS SY 2021-2022. - 10docxRhea CastilloNo ratings yet
- Presentation of New RPMS-PPST Standards: Matt Ranillo S. PaguiaDocument29 pagesPresentation of New RPMS-PPST Standards: Matt Ranillo S. PaguiaNIMFA PALMERANo ratings yet
- Kra Objectives Movs Cover PageDocument45 pagesKra Objectives Movs Cover PageEzra Lou TabasondraNo ratings yet
- RPMS 2020 2Document18 pagesRPMS 2020 2Chad Borromeo MagalzoNo ratings yet
- Results-Based Performance Management System: PortfolioDocument48 pagesResults-Based Performance Management System: PortfolioAnthonyYbañezNo ratings yet
- Gifted LPDocument5 pagesGifted LPapi-299976291No ratings yet
- TLE 7 - 8 - Carpentry - Module 2Document26 pagesTLE 7 - 8 - Carpentry - Module 2BELINDA ORIGEN100% (1)
- Lugtu - Israel T. - E-Rpms-Portfolio-2022Document68 pagesLugtu - Israel T. - E-Rpms-Portfolio-2022Yeng Lugtu100% (1)
- Jhayl RpmsDocument8 pagesJhayl RpmsROMAR BRAMANTE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- TRF - Objective 9 - Prompt 1Document2 pagesTRF - Objective 9 - Prompt 1Iza Mari Victoria LechidoNo ratings yet
- Manual CSE Pen Paper Test Revised 2024 01 Lifted Public Health Emergency ADocument34 pagesManual CSE Pen Paper Test Revised 2024 01 Lifted Public Health Emergency A305331No ratings yet
- LDM2 MODULE 1 EugeneDialinoDocument6 pagesLDM2 MODULE 1 EugeneDialinoJOJIE CARINONo ratings yet
- Bais City National High SchoolDocument3 pagesBais City National High SchoolEam OsarNo ratings yet
- Results-Based Performance Management System: PortfolioDocument73 pagesResults-Based Performance Management System: PortfolioJenny EscieteNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Individual Performance Commitment and Review Form (Ipcrf) Part I-IvDocument42 pagesDepartment of Education: Individual Performance Commitment and Review Form (Ipcrf) Part I-IvRhea CastilloNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Tech LESSON 6 1Document35 pagesEmpowerment Tech LESSON 6 1Mr.DoffitiNo ratings yet
- RPMS SY 2021-2022 Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Document2 pagesRPMS SY 2021-2022 Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Michael Lumanog100% (1)
- LDM Module 5Document4 pagesLDM Module 5ALEXANDRA HALASAN75% (4)
- Government Elementary School Profile: Ruby Kris P. AngelesDocument19 pagesGovernment Elementary School Profile: Ruby Kris P. AngelesRuby Kris Perez AngelesNo ratings yet
- Yellow RpmsDocument126 pagesYellow RpmsRac ReoptaNo ratings yet
- RPMS PPST - MOV - Highly Proficient Teachers MT1 MT4Document9 pagesRPMS PPST - MOV - Highly Proficient Teachers MT1 MT4Ameer CalderonNo ratings yet
- Rpms Esat YoursurnamehereDocument8 pagesRpms Esat YoursurnamehereGennie Lane ArtigasNo ratings yet
- RPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Document7 pagesRPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Mark Junix Sarcol100% (1)
- Name of Rater: Department of Education Region Iv-A - Calabarzon Boboy Elementary School Boboy, San Luis, BatangasDocument254 pagesName of Rater: Department of Education Region Iv-A - Calabarzon Boboy Elementary School Boboy, San Luis, BatangasGlenon PesiganNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhotoshopDocument16 pagesIntroduction To PhotoshopAneesha SridharNo ratings yet
- Certificate Guest SpeakerDocument1 pageCertificate Guest SpeakerLance Aldrin AdionNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet (Las)Document23 pagesLearning Activity Sheet (Las)Analiza GavicaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument10 pagesStatistics and Probabilityjn004625No ratings yet
- RPMS PURPLE TEMPLATE For MALE TEACHERS - Results-Based-Performance-Management-SystemDocument46 pagesRPMS PURPLE TEMPLATE For MALE TEACHERS - Results-Based-Performance-Management-SystemFretzelle Hope BadoyNo ratings yet
- Sample Program of Debut PartDocument8 pagesSample Program of Debut PartJonel AlolorNo ratings yet
- Objectives Means of Verification Description of The Movs Presented AnnotationsDocument6 pagesObjectives Means of Verification Description of The Movs Presented AnnotationsJhoy CunananNo ratings yet
- Minutes On Teachers ConferenceDocument3 pagesMinutes On Teachers ConferenceRalph Renzo BabaliNo ratings yet
- National Learning Camp - Overview and General GuidelinesDocument50 pagesNational Learning Camp - Overview and General Guidelinesdenmark.laditNo ratings yet
- NumeracyDocument6 pagesNumeracyAlifiana MaretaNo ratings yet
- Leap-Help (: Earning Nhancement Ctivity Rogram Hrough Ands-On Xposure With The Help of Earning ArtnersDocument21 pagesLeap-Help (: Earning Nhancement Ctivity Rogram Hrough Ands-On Xposure With The Help of Earning ArtnersRex YuzonNo ratings yet
- Schools Division Office of Escalante CityDocument5 pagesSchools Division Office of Escalante CityJoan A. Mondin100% (1)
- RPMS Portfolio - Gilbert - 2022Document49 pagesRPMS Portfolio - Gilbert - 2022Margie RodriguezNo ratings yet
- RPMS - 1-MASTER TEACHER - NewNormal by MAAM LALAYDocument18 pagesRPMS - 1-MASTER TEACHER - NewNormal by MAAM LALAYRosemarie Lozada100% (1)
- TRF Movs For Objective 9Document3 pagesTRF Movs For Objective 9Jake Lester DafangNo ratings yet
- Domain 4 Learning and Development SystemDocument35 pagesDomain 4 Learning and Development SystemBemaf Tomarong Nacalaban100% (1)
- IPBT Checklist Course 1 6Document21 pagesIPBT Checklist Course 1 6Elsa TorionNo ratings yet
- RPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Document7 pagesRPMS SY 2021-2022: Teacher Reflection Form (TRF)Kris Pri FheNo ratings yet
- Sample Template For SMEADocument3 pagesSample Template For SMEAOlgrethil CamongayNo ratings yet
- RICHARD RAQUENO RPMS-ePortfolio - SharedDocument14 pagesRICHARD RAQUENO RPMS-ePortfolio - SharedKring SandagonNo ratings yet
- English Department Minutes of The MeetingDocument4 pagesEnglish Department Minutes of The MeetingMay Grace Salazar100% (1)
- Cot-Rpms: Teacher I-IiiDocument5 pagesCot-Rpms: Teacher I-IiiMyravelle Negro LagrasonNo ratings yet
- TRF 9 10Document8 pagesTRF 9 10Ana ConseNo ratings yet
- Ci Project Proposal Project SevenDocument4 pagesCi Project Proposal Project SevenLovely BalboaNo ratings yet
- RPMS AttachmentsDocument22 pagesRPMS AttachmentsAdee Buniel HuerteNo ratings yet
- Portfolio For IPCRF & MOVS - Margie Rodriguez - MT 2021-2022Document48 pagesPortfolio For IPCRF & MOVS - Margie Rodriguez - MT 2021-2022Margie RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Camera AnglesDocument2 pagesCamera AnglesChristopher ReidNo ratings yet
- Camera Shots and AnglesDocument31 pagesCamera Shots and AnglesRoneth JubayNo ratings yet
- Bible Study GuidanceDocument5 pagesBible Study GuidanceOlivia StrijdNo ratings yet
- Afo Perspective 2 Point LegosDocument2 pagesAfo Perspective 2 Point Legosapi-417919455No ratings yet
- Gnosticism Syllabus01Document6 pagesGnosticism Syllabus01mojarramanNo ratings yet
- God's Wife of Amun 23Document7 pagesGod's Wife of Amun 23Dr-Mahmoud ElhosaryNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Unit 1 - StudentDocument88 pagesGrade 8 Unit 1 - Studentapi-247144952No ratings yet
- Agamemnon, Volume I Prolegomena, Text, and Translation-Clarendon Press (1962) PDFDocument209 pagesAgamemnon, Volume I Prolegomena, Text, and Translation-Clarendon Press (1962) PDFmagliabecchi100% (1)
- JEE 2006 Physics Solved Question PaperDocument11 pagesJEE 2006 Physics Solved Question PaperbubulNo ratings yet
- Ode To My Family - : Doo Doo Doo Doo..Document1 pageOde To My Family - : Doo Doo Doo Doo..salalma6634No ratings yet
- ROM - SEA Complete Book For Additional Attack Ultimate Guide-SheetDocument11 pagesROM - SEA Complete Book For Additional Attack Ultimate Guide-SheetHurtlock HurtlockNo ratings yet
- Turquia ItineraryDocument10 pagesTurquia ItineraryJulián OlayaNo ratings yet
- Jesus Friend of SinnersDocument14 pagesJesus Friend of SinnersFernandoGonzagaNo ratings yet
- Shree Ganesh Puja: What To Do What To SayDocument4 pagesShree Ganesh Puja: What To Do What To Sayhns54100% (1)
- MedGyn AL-106HD ESPECIFICACIONESDocument2 pagesMedGyn AL-106HD ESPECIFICACIONESleopa78100% (1)
- History of The TelescopeDocument15 pagesHistory of The TelescopeVivek Ranjan Maitrey100% (1)
- Primary Six Self Study Home PackagepdfDocument14 pagesPrimary Six Self Study Home Packagepdfbukenya MosesNo ratings yet
- Types of Performing ArtsDocument4 pagesTypes of Performing ArtsKevin Cruz0% (1)
- Marketing Mix - Dove and Amazon PDFDocument2 pagesMarketing Mix - Dove and Amazon PDFkale_ramNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Disc BrakeDocument18 pagesCeramic Disc BrakemaneeshNo ratings yet
- Music 8 Lesson 1 ST GradingDocument11 pagesMusic 8 Lesson 1 ST GradingFarrah MacalinoNo ratings yet
- Deifying Energy and GraceDocument28 pagesDeifying Energy and Gracebshelton295No ratings yet
- Indesign Magazine 59 Design NewsDocument17 pagesIndesign Magazine 59 Design Newsannaguerrero92No ratings yet
- PW Show Daily, Day 2, May 25Document72 pagesPW Show Daily, Day 2, May 25Publishers WeeklyNo ratings yet
- Diego Rivera - Art and LifeDocument22 pagesDiego Rivera - Art and Lifela nina100% (5)
- Faraon I NisutDocument3 pagesFaraon I NisutAjdin RedžićNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument39 pagesLiterature ReviewIbrahim Afganzai0% (1)