Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nescy
Uploaded by
api-264509612Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nescy
Uploaded by
api-264509612Copyright:
Available Formats
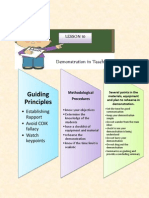
ESTABLISHING
RAPPORT
Greet your audience. Make them feel at
ease by your warmth and sincerity.
Simulate their interest by making your
demonstration and yourself interesting.
AVOID THE COLK
FALLACY
It is the assumption that what is clear to the
expert demonstrator is also clearly known to
the person for whom the message is extended.
WATCH FOR KEY
FORMATS
They are the ones at which an error is likely to be
made the places at which many people stumble and
where the knacks and tricks of the trade are
especially important.
Lesson 10
MAKING THE MOST OF
COMMUNITY
RESOURCES AND
FIELD TRIPS
Make preliminary
contacts, a tour
arrangement with the
place to be visited
Make final
arrangements with the
school principal about
the details of the trip,
schedule,
transportation,
arrangements,
finances, and
permission slips from
parents
Make a tentative route
plan, subject to later
alteration based on class
planning and objectives
Try to work out
mutually satisfactory
arrangements with
other teachers if the
trip will conflict with
their classes.
Prepare
preliminary lists of
questions or other
materials which will
be helpful in
planning with the
students.
Discuss the objectives
and write them down.
Lesson 11
Lesson 12
THE POWER OF FILM, VIDEO AND TV IN
THE CLASSROOM
Transmit a wide range of
audio.
Bring models of
excellence to the viewer.
Bring the world of
reality to the home and
to the classroom through
a live broadcast or as
medicated through film
or videotape.
Make us see and hear
ourselves world events as
they happen
Be the most believable
news source.
Make some programs
understandable and
appealing to a wide
variety of age and
educational levels.
Become a great equalizer of
educational opportunity
because programs can be
presented over national and
regional networks.
provide us with sounds and
sights not easily available
even to the viewer of a real
event through long shots,
close ups, zoom shots,
magnification and split screen
made possible by the TV
camera.
Can give opportunity to
teachers to view themselves
while they teach for purposes
of self-improvement
Can be both instructive and
enjoyable.
Lesson 13
TEACHING WITH VISUAL SYMBOL
DRAWINGS
may not be real thing but better to have a concrete
visual aid than nothing
avoid confusion, it is good our drawing correctly
represents the real thing
CARTOONS
another useful visual symbol that can bring novelty to our
teaching
it tells the story metaphorically
STRIP DRAWINGS
commonly called as comics or comic strip
make use of strip that are educational and entertaining at
the same time.
DIAGRAM
any drawing that shows arrangement and relations as part
of the whole
such as relative, value, origins and development,
chronological fluctuations, distribution and etc.
CHARTS
is a diagrammatic represenatations of
relationship among individual whether as
organization
examples of this are time chart, comparison
and contrast chart, organizational, pareto
and trend chart
GRAPHS
examples of this are pine, bar , line and
pictorial graph
MAPS
representation of the surface of the earth
or some part of it
representation of the surface of the earth
or some part of it
CHALKBOARD
Write clearly and legibly on the
board
It helps if you have a hard copy of
your chalkboard diagram or outline
Dont crowd your notes on the board
Make use of colored chalk to highlight
key points
Dont turn your back to your class
while you write the chalkboard
Provide the lines for your board if
needed with the grade level you teach
Make sure your board works are
readable in all sides of the room
Replace chalkboard with a detail concaved
from left to right to avoid glare
Write Please Save if there are board works for
tomorrow and cover with curtains
Make full use of the chalkboards
OVERHEAD PROJECTOR (OHP
Show pictures and diagrams
using a pointer on the
transparency
You can use a marker or
wax based pencil to add
details
You can control the rate or
presenting information by using
progressive disclosure technique
Lesson 14
students do not
learn by using
multimedia
produce by
others but can
learn by
creating it
themselves
MULTI
MEDIA
working
together jointly
to accomplish a
common
intellectual
purpose
COLLABORATION
determining what
substantive content
would be included
is their projects as
well as the process
for producing
them
STUDENT
DECISION
MAKING
extend over a
significant time
EXTENDED TIME
FRAME
seek to connect
students work in
school with the
wider world in
which students
live
REAL
WORLD
CONNECTION
address the
basic
knowledge
and skills of
all students
are expected
to acquire
CORE
CURRICULUM
Lesson 15
Dimensions of Project Based Multimedia Learning
Lesson 17
Assessment
in a
contructivist,
technology
supported
learning
Complex learning cannot be assessed or
evaluated using any single measure. We must
examine both the processes and products of
students learning
Contructivist
classroom
Ideas were gripped on how we value it in our daily life
Construction of ideas out from collected facts occurs
Discourages memorization of facts
5 Es of constructivism
ENGAGE
EXPLORE
EXPLAIN
ELABORATE
EVALUATE
Lesson 18
Rules and functions of an Educational Media Center
-It functions as a vital instrument.
-It reflects and supports the philosophy of the
School.
-It shares and implements the school aims and
objectives
-It is involved in the teaching and learning
process.
-It is a source center.
-It is a learning laboratory.
-It is a teaching agency.
-It is a service agency.
-It is a coordinating agency.
-A center for recreational reading, viewing, and
listening.
You might also like
- Piano Technicians: Official Publication of The Piano Technicians Guild January 2014 Vol. 57 No.1Document44 pagesPiano Technicians: Official Publication of The Piano Technicians Guild January 2014 Vol. 57 No.1TuongNo ratings yet
- Dales Cone of ExperienceDocument12 pagesDales Cone of ExperienceRexson Dela Cruz TagubaNo ratings yet
- Theories in Nursing InformaticsDocument31 pagesTheories in Nursing InformaticsShahad HakimuddinNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Ability Sample QuestionsDocument2 pagesCognitive Ability Sample QuestionsPrithi Usha Rao100% (1)
- Tpack Lesson TemplateDocument7 pagesTpack Lesson Templateapi-31235889350% (2)
- 50 LettersDocument29 pages50 LettersMursidul Alam56% (34)
- Characteristics of Good Teaching AidsDocument7 pagesCharacteristics of Good Teaching AidsFahdly Palis86% (14)
- MYP Unit Planner: INQUIRY: Establishing The Purpose of The InquiryDocument7 pagesMYP Unit Planner: INQUIRY: Establishing The Purpose of The Inquirysolany perez100% (1)
- Organizational AnalysisDocument187 pagesOrganizational Analysiskodiakk100% (7)
- JM S (Teaching Prof)Document12 pagesJM S (Teaching Prof)Myrel Joy Fabiaña LucdayNo ratings yet
- Do's and Don'Ts of Demo-TeachingDocument5 pagesDo's and Don'Ts of Demo-TeachingRegin PaildenNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Foundations of Nursing 8th Edition by Cooper RN MSN PDF ScribdDocument45 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Foundations of Nursing 8th Edition by Cooper RN MSN PDF Scribddanny.bradt610100% (43)
- Lesson 10: Demonstration in TeachingDocument11 pagesLesson 10: Demonstration in Teachingapi-264468141No ratings yet
- Lesson 10Document9 pagesLesson 10api-264511068No ratings yet
- Conceptmap 2Document18 pagesConceptmap 2api-264187866No ratings yet
- Lesson10 EdtechDocument9 pagesLesson10 Edtechapi-266582672No ratings yet
- Conceptmap Momi ElibDocument9 pagesConceptmap Momi Elibapi-264382729No ratings yet
- Concept Map FinalDocument19 pagesConcept Map Finalapi-266353521No ratings yet
- Teaching Interactively With Electronic Whiteboards in Primary Phase - Becta Ict AdviceDocument36 pagesTeaching Interactively With Electronic Whiteboards in Primary Phase - Becta Ict Adviceluiz carvalhoNo ratings yet
- Virtual Studio INFO For StudentsDocument14 pagesVirtual Studio INFO For StudentsRick LeBrasseurNo ratings yet
- Getting Ready For Virtual StudioDocument26 pagesGetting Ready For Virtual StudioRick LeBrasseurNo ratings yet
- Complex Learning Cannot Be Assessed or Evaluated Using Any Single MeasureDocument4 pagesComplex Learning Cannot Be Assessed or Evaluated Using Any Single MeasureJessa Mae David TuazonNo ratings yet
- Information SheetDocument29 pagesInformation SheetJohn Rey SR SoveranoNo ratings yet
- Av AidsDocument12 pagesAv Aidsmonisha100% (1)
- Elyn-Concept Map 2Document10 pagesElyn-Concept Map 2api-266639833100% (1)
- Teaching Tools: B.Ed Course Code 8601 Unit: 9Document31 pagesTeaching Tools: B.Ed Course Code 8601 Unit: 9muhammad zeshanNo ratings yet
- M3, L1Document10 pagesM3, L1Denosta Mercurio JonelNo ratings yet
- Sabah Pervaiz 826 Assigment No 2Document19 pagesSabah Pervaiz 826 Assigment No 2kashafNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 ICT ResourcesDocument24 pagesUnit 5 ICT ResourcesWAGAYEN , MarvenNo ratings yet
- Educ 85 Reviewer: (GROUP1) Dale'S Cone of ExperienceDocument15 pagesEduc 85 Reviewer: (GROUP1) Dale'S Cone of ExperienceMary Rose ManciaNo ratings yet
- Induction Top Ten Academic StaffDocument2 pagesInduction Top Ten Academic StaffLauraNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1680593759018 7048921125824538377Document46 pagesOrca Share Media1680593759018 7048921125824538377RedMoonLightNo ratings yet
- TananDocument9 pagesTananapi-264308542No ratings yet
- Bpts Basic Productivity Tools Water Cycle Zeya LuoDocument3 pagesBpts Basic Productivity Tools Water Cycle Zeya Luoapi-675381240No ratings yet
- Story Telling Lesson Plan PowerpointDocument2 pagesStory Telling Lesson Plan Powerpointapi-540225952No ratings yet
- Eight Planet Model of The Solar SystemDocument22 pagesEight Planet Model of The Solar SystemVictor Jose Valdehueza SomonodNo ratings yet
- Educ 117 Lesson 10-18 Concept MapDocument9 pagesEduc 117 Lesson 10-18 Concept Mapapi-264443851No ratings yet
- Listening Selection Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesListening Selection Lesson Planfarid kefelNo ratings yet
- How To Create A 5 E Lesson Plan: 1. EngageDocument4 pagesHow To Create A 5 E Lesson Plan: 1. EngageNormina Cagunan100% (1)
- Non-Digital and Digital Skills and Tools in Delivering Technology Enhanced LessonDocument3 pagesNon-Digital and Digital Skills and Tools in Delivering Technology Enhanced LessonMa. Edessa Diona100% (1)
- Midterm ModuleDocument8 pagesMidterm ModuleMarjorie TrazonaNo ratings yet
- Bpts Basic Productivity Tools Lesson Idea TemplateDocument3 pagesBpts Basic Productivity Tools Lesson Idea Templateapi-678572474No ratings yet
- Theories and Principles in The Use and Design of TechnologyDocument14 pagesTheories and Principles in The Use and Design of Technologypenosajoy98No ratings yet
- PortfolioDocument20 pagesPortfolioJosé Puga MedinaNo ratings yet
- Ed 107 ReportDocument4 pagesEd 107 ReportChloe RosalesNo ratings yet
- Innovative Ideas To Promote Creativity in Class RoomDocument7 pagesInnovative Ideas To Promote Creativity in Class Roomkankana borgohainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. What Is Project-Based Multimedia Learning?Document7 pagesChapter 1. What Is Project-Based Multimedia Learning?Romeo Balingao100% (1)
- EED 2101 - Mid Term ExaminationDocument4 pagesEED 2101 - Mid Term ExaminationJOMICA SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Listening Selection Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesListening Selection Lesson Planfarid kefelNo ratings yet
- I.C.T Primer Examen Parcial:: Word Cloud (Or Tag Cloud)Document8 pagesI.C.T Primer Examen Parcial:: Word Cloud (Or Tag Cloud)Aldana CanoNo ratings yet
- k4 TheoriesDocument4 pagesk4 TheoriesBobo YouNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Basic TemplateDocument2 pagesBeyond The Basic Templateapi-523271677No ratings yet
- K To 12: An Answer To 21 Century Learners: Guide QuestionsDocument3 pagesK To 12: An Answer To 21 Century Learners: Guide QuestionsAika Kate KuizonNo ratings yet
- COMPENDIUM in APDocument16 pagesCOMPENDIUM in APMikhaela Jayd AstañoNo ratings yet
- Display PolicyDocument4 pagesDisplay PolicyJoshua JamesNo ratings yet
- Fisher and Frey Assignment - Projects and Performances Cookbook 2 AutosavedDocument32 pagesFisher and Frey Assignment - Projects and Performances Cookbook 2 Autosavedapi-212579279No ratings yet
- Lecturing Effectively: Prepare in AdvanceDocument4 pagesLecturing Effectively: Prepare in AdvanceChat AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Teaching Is Not Only A Job But Is A Way of LifeDocument22 pagesTeaching Is Not Only A Job But Is A Way of LifeSahil NaikNo ratings yet
- PK 3105Document11 pagesPK 3105chaos_92No ratings yet
- Team Legend ReportingDocument37 pagesTeam Legend ReportingleahnmaelNo ratings yet
- BPT Lesson Idea Complete FinalDocument3 pagesBPT Lesson Idea Complete Finalapi-723682795No ratings yet
- CAL ScratchJr Reader Full 710Document4 pagesCAL ScratchJr Reader Full 710kze88844No ratings yet
- Best Practices For Distance Learning in 2020Document4 pagesBest Practices For Distance Learning in 2020Jade MillanteNo ratings yet
- Carlyle Lessonplantemplate-Iste-2022Document6 pagesCarlyle Lessonplantemplate-Iste-2022api-651833621No ratings yet
- 21 Century Learning Space (To Upgrade KPEC Studio Into 21 Century Learning Space)Document26 pages21 Century Learning Space (To Upgrade KPEC Studio Into 21 Century Learning Space)Sulmawati SulaimanNo ratings yet
- My Professional Development PlanDocument3 pagesMy Professional Development Planapi-252938448No ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae DR SumitDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae DR SumitdrsumitpuriNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument47 pagesReviewerRahima AloyodanNo ratings yet
- DLL 5Document3 pagesDLL 5Grace Lumacdag Domawang BayanganNo ratings yet
- Anthony Nnamdi Nwabuisi CV inDocument10 pagesAnthony Nnamdi Nwabuisi CV inNwabuisiNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Dissonance and Investors' Decision Making: A ReviewDocument7 pagesCognitive Dissonance and Investors' Decision Making: A ReviewAiman RashidNo ratings yet
- Kaushal Panjee: Candidate AcknowledgmentDocument1 pageKaushal Panjee: Candidate AcknowledgmentKumar UditNo ratings yet
- Student Induction Timetable 2015 Engineering Version FinalDocument4 pagesStudent Induction Timetable 2015 Engineering Version FinalAmir AbdellaNo ratings yet
- (Currently Under Revision) : Purdue University School of Nursing 2003 - 2008 Strategic PlanDocument28 pages(Currently Under Revision) : Purdue University School of Nursing 2003 - 2008 Strategic Planjhay-r reyesNo ratings yet
- Kgural CommunityresourceauditDocument27 pagesKgural Communityresourceauditapi-158980591No ratings yet
- Presentation - What Is High-Impact TutoringDocument12 pagesPresentation - What Is High-Impact TutoringrotasoNo ratings yet
- The 21st Century TeacherDocument14 pagesThe 21st Century TeacherArJhay ObcianaNo ratings yet
- GDB Solution 2020 Sec SmesterDocument3 pagesGDB Solution 2020 Sec SmesterFarah KhanNo ratings yet
- English-at-Work - Applying Fo A JobDocument6 pagesEnglish-at-Work - Applying Fo A JobYadanis GNo ratings yet
- SSIP Project Proposal FormatDocument9 pagesSSIP Project Proposal FormatPritNo ratings yet
- LRIZALDocument16 pagesLRIZALSHIERA MAE AGUSTINNo ratings yet
- JM Cohen Associates Journal: A Dashboard For Managing ComplexityDocument4 pagesJM Cohen Associates Journal: A Dashboard For Managing Complexityapi-106075618No ratings yet
- Research Q2-Week 2 For StdentsDocument4 pagesResearch Q2-Week 2 For Stdentsjudy bernusNo ratings yet
- Oss-Ched Scholarship FormDocument1 pageOss-Ched Scholarship Formramilsanchez@yahoo.com100% (4)
- RESEARCHDocument62 pagesRESEARCHZyra Angela TinampayNo ratings yet
- Essay StructureDocument12 pagesEssay StructureTodd MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ro3 Obe Me Tool 2022Document3 pagesRo3 Obe Me Tool 2022Jamin Timi RuizNo ratings yet