Professional Documents
Culture Documents
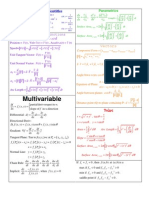
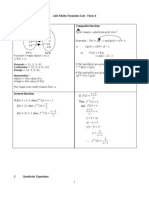
Actual Formula Test #1 Test #2 Formula
Uploaded by
nirakaru123Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Actual Formula Test #1 Test #2 Formula
Uploaded by
nirakaru123Copyright:
Available Formats
Actual Formula Test #1 Test #2 Formula
(a + b)(a
2
ab + b
2
)
a
3
+ b
3
=
(a b)(a
2
+ ab + b
2
)
a
3
b
3
=
x =
b b
2
4ac
2a
Quadratic Formula
f(x) = f( x)
Test for even
functions
f( x) = f(x)
Test for odd
functions
(x h)
2
+ (y k)
2
= r
2
General equation
of a circle
y = r
2
x
2
Equation of a
semi-circle
0
lim
x
1
x
=
1
2
sin
=
1
2
cos
=
1 tan
=
3
2
sin
=
1
2
sin
=
1
2
cos
=
3
2
cos
=
3
tan
=
1
3
tan
=
sin
cos
tan =
cos
sin
cot =
1
sin
2
+ cos
2
=
1 + cot
2
= cosec
2
Other trig identity
tan
2
+ 1 = sec
2
Other trig identity
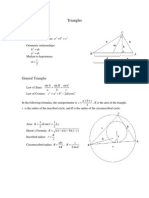
sinA
a
=
sinB
b
Sine rule
a
2
= b
2
+ c
2
2bccosA
Cosine rule for
side
cosA =
b
2
+ c
2
a
2
2bc
Cosine rule for an
angle
A =
1
2
ab sinC
Area of a triangle
using trig
cosx cosy + sinx siny
cos(x y) =
cosx cosy sinx siny
cos(x + y) =
sinx cosy + cosx siny
sin(x + y) =
sinx cosy cosx siny
sin(x y) =
tanx + tany
1 tanx tany
tan(x + y) =
tanx tany
1 + tanx tany
tan(x y) =
2sinx cosx
sin 2x =
cos
2
x sin
2
x
1 2sin
2
x
2cos
2
x 1
cos 2x =
2tanx
1 tan
2
x
tan 2x =
tan
Ratios:
2t
1 t
2
tan =
1 t
2
1 + t
2
cos =
2t
1 + t
2
sin =
rsin( + )
asin + bcos =
rsin( )
asin bcos =
rcos( )
acos + bsin =
rcos( + )
acos bsin =
r = a
2
+ b
2
tan =
b
a
Where r = and =
= n + (-1)
n
General solution
for sine
= 2 n
General solution
for cosine
= n +
General solution
for tan
Graphs
d = (x
2
x
1
)
2
+ (y
2
y
1
)
2
Distance formula
P =
x1 + x2
2
,
y1 + y2
2
Midpoint Formula
m =
y2 y1
x2 x1
Gradient Formula
m = tan
Gradient using trig
y y
1
= m(x x
1
)
Point-gradient
formula
y y1
x x1
=
y2 y1
x2 x1
Two-point formula
m
1
= m
2
Parallel lines proof
m
1
m
2
= -1
Perpendicular lines
proof
d =
|ax1 + by1 + c|
a
2
+ b
2
Perpendicular
distance formula
tan =
m1 m2
1 + m1m2
Angle between two
lines
x =
mx2 + nx1
m+ n
y =
my2 + ny1
m+ n
Dividing interval in
ratio m:n
dy
dx
= lim
h 0
f(x + h) f(x)
h
First principle
differentiation
n x
n 1
d
dx
x
n
f'(x)n [ f(x)]
n 1
d
dx
[ f(x)]
n
=
vu' + uv'
d
dx
uv
vu' uv'
v
2
d
dx
u
v
x =
b
2a
Axis of symmetry
in quadratic
= b
2
4ac
The discriminant
b
a
Sum of roots
c
a
Sum of roots two
at a time
d
a
Sum of roots three
at a time
e
a
Sum of roots four
at a time
x
2
= 4ay
(0, a)
(0, 0)
Equation of basic
parabola.
Focus
Vertex
(x h
2
) = 4a(y k)
(h, k)
(h, k + a)
General equation
of parabola.
Focus
Vertex
x = 2at
y = at
2
Parametric form of:
x
2
= 4ay
T
n
= a + (n 1)d
Term of an
arithmetic series
S
n
=
n
2
(a + l)
S
n
=
n
2
[ 2a + (n 1)d]
Sum of an
arithmetic series
S = (n 2) 180
Sum of interior
angles of an n-
sided polygon
A = lb
Area of rectangle
A = x
2
Area of a square
A =
1
2
bh
Area of a triangle
A = bh
Area of a
parallelogram
1
2
xy
Area of rhombus
A =
1
2
h(a + b)
Area of trapezium
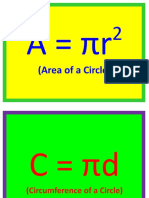
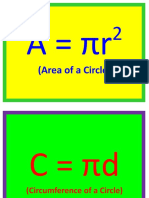
A = r
2
Area of circle
S = 2(lb + bh + lh)
Surface area of a
rectangular prism
V = lbh
Volume of a
rectangular prism
S = 6x
2
Surface area of a
cube
V = x
3
Volume of a cube
S = 2 r
2
+ 2 r h
Surface area of a
cylinder
V = r
2
h
Volume of a
cylinder
S = 4 r
2
Surface area of a
sphere
V =
4
3
r
3
Volume of a
sphere
S = r
2
+ rl
Surface area of a
cone
V =
1
3
r
2
h
Volume of a cone
x
n + 1
n + 1
+ c
x
n
dx
h
2
[ (y
0
+ y
n
) + 2(y
1
+ y
2
+ ... + y
n 1
)]
where h =
b a
n
Trapezoidal rule
h
3
[ (y
0
+ y
n
) + 4(y
1
+ y
3
) + 2(y
2
+ y
4
)]
where h =
b a
n
Simpsons Rule
(ax + b)
n + 1
a(n + 1)
+ c
(ax + b)
n
dx
V =
y
2
dx
Volume about the
x-axis
V =
x
2
dy
Volume about the
y-axis
e
x
d
dx
e
x
f'(x) e
f(x)
d
dx
e
f(x)
e
x
+ c
e
x
dx
1
a
e
ax + b
+ c
e
ax + b
dx
log
a
x + log
a
y
log
a
(xy)
log
a
x log
a
y
log
a
x
y
n log
a
x
log
a
x
n
log
a
x =
log
e
x
log
e
a
Change of base
rule
1
x
d
dx
log
e
x
f'(x)
f(x)
d
dx
log
e
f(x)
log
e
x + c
1
x
dx
log
e
f(x) + c
f'(x)
f(x)
dx
180
radians =
C = 2r
Circumference of a
circle
l = r
Length of an arc
A =
1
2
r
2
Area of a sector
A =
1
2
r
2
( sin)
Area of a minor
segment
sinx x
tanx x
cosx 1
Small Angles
f'(x) cos [ f(x)]
d
dx
sin [ f(x)]
f'(x) sin [ f(x)]
d
dx
cos [ f(x)]
f'(x) sec
2
f(x)
d
dx
tan f(x)
1
a
sin(ax + b) + c
cos(ax + b) dx
1
a
cos(ax + b) + c
sin(ax + b) dx
1
a
tan(ax + b) + c
sec
2
(ax + b) dx
1
2
x +
1
4a
sin 2ax + c
cos
2
ax dx
1
2
x
1
4a
sin 2ax + c
sin
2
ax dx
Exponential
Growth & Decay
kQ
dQ
dt
=
Q = Ae
kt
Quantity
dN
dt
= k(N P)
N = P + Ae
kt
Complex growth
and decay
a =
d
dx
1
2
v
2
Special result for
acceleration
x = a cos(nt + )
Displacement for
SHM
..
x = n
2
x
Acceleration for
SHM
a
Amplitude of SHM
2
n
Period of SHM
v
2
= n
2
(a
2
x
2
)
Velocity of SHM
.
x = Vcos
.
y = Vsin
Initial Velocity of
projectile
.
x = 0
.
y = g
Acceleration of a
projectile
x = Vt cos
Horizontal
displacement
y = Vt sin
gt
2
2
Vertical
displacement
y =
gx
2
2V
2
(1 + tan
2
) + xtan
Cartesian equation
of motion
t =
2V sin
g
Time of flight
x =
V
2
sin 2
g
Range
x =
V
2
g
Max Range
h =
V
2
sin
2
2g
Greatest height
f
-1
[ f(x)] = f[ f
-1
(x)] = x
Proof for mutually
inverse functions
sin
-1
x
sin
-1
( x) =
cos
-1
x
cos
-1
( x) =
tan
-1
x
tan
-1
( x) =
2
sin
-1
x + cos
-1
x =
r =
T2
T1
Common ratio in
geometric series
T
n
= ar
n 1
Term of a
geometric series
S
n
=
a(r
n
1)
r 1
for |r| > 1
S
n
=
a(1 r
n
)
1 r
for |r| < 1
Sum of a
geometric series
S
=
a
1 r
Sum to infinity of a
geometric series
A = P
1 +
r
100
n
Compound interest
formula
If f
a + b
2
= 0
Halving the interval
method
a1 = a
f(a)
f' (a)
Newtons method
of approximation
n k + 1
k
b
a
T
K + 1
T
K
=
n!
(n r)!
n
P
r
=
n!
s! t! ...
Arrangements
where some are
alike
(n 1)!
Arrangements in a
circle
You might also like
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 pagesAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- C CN I N (n+1) : Critical ValuesDocument10 pagesC CN I N (n+1) : Critical ValuesFolk NarongritNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2 SummaryDocument2 pagesCalculus 2 Summarydukefvr41No ratings yet
- Essential formulae for Number and AlgebraDocument16 pagesEssential formulae for Number and AlgebraMaruthappan Sundaram100% (1)
- X X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos CosDocument4 pagesX X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos Cossharanmit2039No ratings yet
- Calculus FormulaDocument2 pagesCalculus FormulaleeshiNo ratings yet
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 pagesMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoNo ratings yet
- Math ReveiwDocument3 pagesMath ReveiwApache_mooNo ratings yet
- HSC 3U Maths FormulaeDocument7 pagesHSC 3U Maths FormulaeHotz InatorNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument2 pagesBasicsmadcow_scribdNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Math Resources Trigonometric FormulasDocument10 pagesMath Resources Trigonometric FormulasAnonymous j3w8EmJb8No ratings yet
- Maths Revision Formulas ResultsDocument5 pagesMaths Revision Formulas ResultsDarrenPurtillWrightNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Design Manual (AUS)Document68 pagesHydraulic Design Manual (AUS)rotciv132709100% (1)
- Advanced Calculus Formulas GuideDocument13 pagesAdvanced Calculus Formulas Guidevignes011No ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Practical Vibration Assessment of Girder BridgesDocument140 pagesPractical Vibration Assessment of Girder Bridgesnirakaru123No ratings yet
- Actual Formula Test #1 Test #2 FormulaDocument8 pagesActual Formula Test #1 Test #2 FormulacheyenneNo ratings yet
- Algebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BDocument11 pagesAlgebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BLaissa SerranoNo ratings yet
- Essential FormulasDocument7 pagesEssential FormulasShinigami01001No ratings yet
- Coplex Number FormulasDocument7 pagesCoplex Number FormulasMohan KhedkarNo ratings yet
- Pe Math NotesDocument12 pagesPe Math NotescheshankarNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Formulae ListDocument8 pagesAdd Maths Formulae ListWong Hui SeanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1Document22 pagesMathematics 1RubyJanePartosa100% (1)
- Pure Mathematics 1: It Doesn't Matter How Many Coordinates Are Given You Have To Just Add and Then Same ProcessDocument12 pagesPure Mathematics 1: It Doesn't Matter How Many Coordinates Are Given You Have To Just Add and Then Same ProcessAttique Rehman100% (1)
- Exam - 2011 10 28Document5 pagesExam - 2011 10 28lieth-4No ratings yet
- Notas Matematicas para Electronica de PotenciaDocument10 pagesNotas Matematicas para Electronica de PotenciaAndrés David Martínez MarteloNo ratings yet
- AIEEE Mock Solved: Sol. (A) Sol. (B)Document7 pagesAIEEE Mock Solved: Sol. (A) Sol. (B)kishangopi123No ratings yet
- Essential Maths and Physics FormulasDocument17 pagesEssential Maths and Physics FormulasdevenderNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)Document4 pagesFormula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)naedkcinNo ratings yet
- Notes MathDocument4 pagesNotes MathNaveed Atta UllahNo ratings yet
- Kcet - Mathematics - 2016: Version Code: C - 3Document13 pagesKcet - Mathematics - 2016: Version Code: C - 3Kamalesh ShenoyNo ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument61 pagesFormulaeFlorence TangkihayNo ratings yet
- Area of A CircleDocument61 pagesArea of A CircleFlorence TangkihayNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Methods Units 1 and 2 Formula Sheet: π θ θ 4 If 0 then 2 − ± − + + = =Document1 pageMathematics Methods Units 1 and 2 Formula Sheet: π θ θ 4 If 0 then 2 − ± − + + = =Scheis ErzaehlenNo ratings yet
- Step Formula Booklet PDFDocument24 pagesStep Formula Booklet PDFA FryNo ratings yet
- Math H Formula Booklet 2016 WebsiteDocument15 pagesMath H Formula Booklet 2016 WebsiteAmeena LundquistNo ratings yet
- Formulas Math Midterm Test I DEDocument2 pagesFormulas Math Midterm Test I DEUmesh Rao H NNo ratings yet
- Basic (1) MathDocument2 pagesBasic (1) MathIan KrebsNo ratings yet
- Calculus BookletDocument6 pagesCalculus Bookletangie81No ratings yet
- Formulae,,key Points,, Algorithm (For Class 12 TH Maths)Document23 pagesFormulae,,key Points,, Algorithm (For Class 12 TH Maths)angusingh60No ratings yet
- ARML TheoremsDocument27 pagesARML Theoremsfreefall014No ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument3 pagesTrigonometric IdentitiesShashwat GamerNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetHussain JiffryNo ratings yet
- I F C F: Pure Math SummaryDocument4 pagesI F C F: Pure Math SummaryRuijia ZengNo ratings yet
- TrigDocument3 pagesTrigxmikelawsonxNo ratings yet
- FORMULAEDocument13 pagesFORMULAEMadhu Pali100% (2)
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Polar and Parametric Equations: Sanaa Charania, Hanna Park, and Danielle ChowDocument18 pagesPolar and Parametric Equations: Sanaa Charania, Hanna Park, and Danielle ChowgulzchrnNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionsmonelmetal100% (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Beam TheoryDocument38 pagesBeam Theorynirakaru123No ratings yet
- REODATA40Document76 pagesREODATA40chanakaNo ratings yet
- Second Order ODE UWSDocument17 pagesSecond Order ODE UWSnirakaru123No ratings yet
- REODATA40Document76 pagesREODATA40chanakaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Charts For The Selection of Highway Culverts: Hec 5 December 1965Document56 pagesHydraulic Charts For The Selection of Highway Culverts: Hec 5 December 1965virgiliovalienteNo ratings yet
- Barrier TypesDocument1 pageBarrier Typesnirakaru123No ratings yet























































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)





