Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Hussain JiffryOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Hussain JiffryCopyright:
Available Formats
EDT Mathematics Formula Sheet
FORMULAE SHEET Trigonometric Identities cos 2 + sin 2 = 1 sin 2 = 2 sin cos cos 2 = cos 2 sin 2 = 2 cos 2 1 = 1 2 sin 2 sin (A B) = sin A cos B cos A sin B cos (A B) = cos A cos B sin A sin B
Version 4 November 2011
1 1 ( e j e j ), cos = ( e j + e j ); 2j 2 and the hyperbolic equivalent 1 1 sinh = ( e e ), cosh = ( e + e ). 2 2 sin =
where j = 1
NewtonRaphson method for estimating the solution for f(x) = 0 .
x n +1 = x n
f ( xn ) f' ( xn )
) + 2{f ( x1 ) + f ( x 2 ) + f ( x n 1 )} + f ( x n )] 1 xn n
Trapezoidal Rule with n intervals of length h .
f ( x )dx = 2 [f ( x
h
Mean
Standard Deviation Binomial Expansion
1 x n2 2 n
( a + b ) n = a n b 0 + na n 1 b1 +
CALCULUS
n( n 1 ) n 2 2 n( n 1 )( n 2 ) n 3 3 a b + a b + 2! 3!
The following formulae may be used without proof. Differentiation f(x) xn f(x) nxn 1 Integration f(x) xn
f ( x )dx
x n +1 + C (n 1) n +1
ln x ex sin x cos x
1 x
ex cos x sin x
1 x
ex sin x cos x
ln x + C
ex + C cos x + C sin x + C
EDT Mathematics Formula Sheet
Product Rule
Version 4 November 2011
Quotient Rule
y = uv
du dv dy =u +v dx dx dx
u dy y= = v dx
dv du u dx dx 2 v
Chain Rule
Integration by Parts
dy dy du y = f ( u ), u = g ( x ) = dx du dx
u dx dx = uv v dx dx
1 ( f ( x )) n +1 + c , n 1 and n +1
dv
du
Two Integration Formulas
( f ( x ))
b
f ' ( x )dx =
f ( x ) dx = ln( f ( x )) + c , f ( x ) > 0
2 The Volume of Revolution = y dx , where y = f ( x ) for rotation of 2 about the x-axis. a
f' ( x )
The centroid of a region bounded by the curve y = f(x) and the lines x = a and x = b is given by
x=
xf ( x )dx
a b
and y =
(f ( x ))2 dx
2
f ( x )dx
a
f ( x )dx
a
Fourier Series of f(t)
f(t ) =
T
1 2 n 2 n a0 + an cos t + bn sin t ( n = 1,2 , ) where 2 T T n =1
2 2 a0 = f (t )dt T T
2
2 an = T
2 n f ( t ) cos t dt T
2 bn = T
2 n f ( t ) sin t dt T
FOURIER TRANSFORMS:
f ( ) = f ( t )e
jt
dt
1 f (t ) = 2 f (t ) = f (t ) =
f ( )e jt d
f s ( ) = f (t )sin(t )dt
0
0 0
2
f s ( )sin(t )d f c ( )cos(t )d
f c ( ) = f (t )cos(t )dt
0
Fourier Integral Representation of f(t)
f ( t ) = [a( ) cos( t ) + b( ) sin( t )]d where
0
a( ) =
f ( t ) cos (t )dt
b( ) =
f ( t ) sin (t )dt
EDT Mathematics Formula Sheet
Useful Integrals
Version 4 November 2011
sin( at )dt = a cos( at ) + c t sin( at )dt = a t cos( at ) + a e
bt
cos( at )dt = a sin( at ) + c t cos( at )dt = a t sin( at ) + a e
bt
1
2
sin( at ) + c
1
2
cos( at ) + c
sin( at )dt = e bt
b sin( at ) a cos( at ) +c a2 + b2
cos( at )dt = e bt
b cos( at ) + a sin( at ) +c a2 + b2
LAPLACE TRANSFORMS Given that for the function y = f ( t ) then L{f ( t )} = e st f ( t )dt = F ( s )
0
f(t )
1
F( s )
f(t )
F( s )
1
t
tn u( t ) , unit step e at
sin at cos at sinh at cosh at
1 s 1 s2 n! s n +1 1 s 1 s a a 2 s + a2 s 2 s + a2 a 2 s a2 s 2 s a2
(t ) (t a)
H( t a ) f ( t a )H ( t a ) t n e at e bt sin at e bt cos at e bt sinh at e bt cosh at
e as
e as s e as L{ f ( t )}
n! ( s a ) n +1 a ( s b )2 + a 2 sb ( s b )2 + a 2 a ( s b )2 a 2 sb ( s b )2 a 2
F( s a )
f ( t ) + g ( t )
f' ( t ) = df dt
F ( s ) + G( s )
sL{ f ( t )} f ( 0 )
e at f (t )
t nf ( t )
f(t ) t
n
d nF ( 1 ) , n = 1,2 , ds n
u =s
d 2f f' ' ( t ) = 2 dt
s 2 L{ f ( t )} sf ( 0 ) f ' ( 0 )
F ( u )du
You might also like
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- X X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos CosDocument4 pagesX X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos Cossharanmit2039No ratings yet
- The Fourier Series EditedDocument46 pagesThe Fourier Series EditedSarah HillmanNo ratings yet
- Calculus BookletDocument6 pagesCalculus Bookletangie81No ratings yet
- (A) If F (X) and G (X) Have Period P, Show That H (X) Af (X) + BG (X) (A, B, Constant)Document15 pages(A) If F (X) and G (X) Have Period P, Show That H (X) Af (X) + BG (X) (A, B, Constant)Heather JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Math ReferenceDocument24 pagesMath ReferenceSujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- Exam - 2011 10 28Document5 pagesExam - 2011 10 28lieth-4No ratings yet
- Table of Common Fourier Transform PairsDocument8 pagesTable of Common Fourier Transform Pairsmain2510No ratings yet
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 pagesMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument2 pagesBasicsmadcow_scribdNo ratings yet
- Revision FourierDocument19 pagesRevision FourierHazim NaharNo ratings yet
- Uraian FourierDocument91 pagesUraian FourierAgus Dian PratamaNo ratings yet
- Basic (1) MathDocument2 pagesBasic (1) MathIan KrebsNo ratings yet
- Table of Fourier Transform PairsDocument8 pagesTable of Fourier Transform PairsmayankfirstNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- 2.odd Even Function1Document12 pages2.odd Even Function1Atikah JNo ratings yet
- Multivariable calculus exam with 7 problemsDocument5 pagesMultivariable calculus exam with 7 problemslieth-4No ratings yet
- Sysc Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesSysc Cheat Sheetmonstertruck_135No ratings yet
- Basic Formulas and Rules for Derivatives and IntegralsDocument4 pagesBasic Formulas and Rules for Derivatives and IntegralsAkshay Singh RajputNo ratings yet
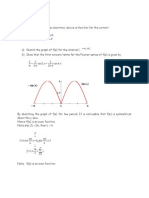
- A) Sketch The Graph of The Periodic Function Over Interval (-3, 3 )Document5 pagesA) Sketch The Graph of The Periodic Function Over Interval (-3, 3 )Cer No RusNo ratings yet
- Elementary Laplace Transforms TableDocument3 pagesElementary Laplace Transforms Tablecaravansary_vNo ratings yet
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 pagesAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Fourier Finite TransformsDocument8 pagesFourier Finite Transformserev_20No ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument2 pagesFormulaeMahatama Sharan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Laplace transformacije i konvolucijeDocument2 pagesLaplace transformacije i konvolucijeKerberZNo ratings yet
- , dac˘a t ≥ 0, θ (t), ,Document4 pages, dac˘a t ≥ 0, θ (t), ,ocsssishorrNo ratings yet
- Maths FormulaDocument4 pagesMaths Formulamickey_disney93No ratings yet
- List of exercises on series and sequencesDocument8 pagesList of exercises on series and sequencesp1tru1mariusNo ratings yet
- Math F211 - Compre-QbDocument2 pagesMath F211 - Compre-Qbf20221235No ratings yet
- RespuestasDocument18 pagesRespuestasAndres HerediaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document20 pagesChapter 5Iman NoorNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Set ADocument17 pagesFinal Exam Set AAtikah J100% (1)
- "The Are Instructed by by The, by And, by ." - Cicero "A Man's Judgement Is No Better Than His Information." - From Bits & PiecesDocument23 pages"The Are Instructed by by The, by And, by ." - Cicero "A Man's Judgement Is No Better Than His Information." - From Bits & PiecesnitalsandoNo ratings yet
- Trig formulas & PDE solutionsDocument2 pagesTrig formulas & PDE solutionsVasil GorgievNo ratings yet
- Answers 2009-10Document19 pagesAnswers 2009-10Yoga RasiahNo ratings yet
- Integrals FormulasDocument10 pagesIntegrals Formulas007phantomNo ratings yet
- Formulas Math Midterm Test I DEDocument2 pagesFormulas Math Midterm Test I DEUmesh Rao H NNo ratings yet
- Ee602 Fourier SeriesDocument110 pagesEe602 Fourier SeriesArryshah DahmiaNo ratings yet
- 05 LaplaceTableDocument2 pages05 LaplaceTableAmo Amor AmornNo ratings yet
- Laplace TableDocument2 pagesLaplace TableNguyen Tran100% (1)
- Tutorial - Math.lamar - Edu PDF Laplace TableDocument2 pagesTutorial - Math.lamar - Edu PDF Laplace Tablegavrila_1No ratings yet
- Tablica LaplaceDocument1 pageTablica Laplacebhstudent_537083349No ratings yet
- Notas Matematicas para Electronica de PotenciaDocument10 pagesNotas Matematicas para Electronica de PotenciaAndrés David Martínez MarteloNo ratings yet
- Math ReveiwDocument3 pagesMath ReveiwApache_mooNo ratings yet
- Formulas EdDocument4 pagesFormulas EdCarlos Loler NavarroNo ratings yet
- Info Booklet, Revised 2011Document27 pagesInfo Booklet, Revised 2011ordinanceNo ratings yet
- Formula TableDocument1 pageFormula TableAho Chi- ShuenNo ratings yet
- Stochastic Calculus Final Exam With SolutionsDocument11 pagesStochastic Calculus Final Exam With SolutionsTrbvm100% (1)
- Actual Formula Test #1 Test #2 FormulaDocument11 pagesActual Formula Test #1 Test #2 Formulanirakaru123No ratings yet
- Differentiation Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesDifferentiation Cheat SheetjieboNo ratings yet
- MOST Common Transform PairsDocument6 pagesMOST Common Transform PairsRamiNo ratings yet
- Formula2 (1) UpdatedDocument3 pagesFormula2 (1) UpdatedAmm RoehNo ratings yet
- Advanced Calculus Formulas GuideDocument13 pagesAdvanced Calculus Formulas Guidevignes011No ratings yet
- Form FourierDocument1 pageForm FourierLuis FernandoNo ratings yet
- Arfken ExercisesDocument26 pagesArfken Exercisesdoraemon4100% (1)
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)From EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Functional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)From EverandFunctional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)No ratings yet
- 1560 - Lower Floor PlanDocument1 page1560 - Lower Floor PlanHussain JiffryNo ratings yet
- Worked Examples Ec2 Def080723Document120 pagesWorked Examples Ec2 Def080723dan_ospir67% (3)
- Lift CalculationDocument3 pagesLift CalculationHussain JiffryNo ratings yet
- Cantilever Retaining Wall - Metric PDFDocument16 pagesCantilever Retaining Wall - Metric PDFJebin JacobNo ratings yet
- Soil Report - SammanturaiDocument11 pagesSoil Report - SammanturaiHussain JiffryNo ratings yet
- Car ParksDocument32 pagesCar ParksRron BeqiriNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Axially Loaded Square RC Col PDFDocument23 pagesBehavior of Axially Loaded Square RC Col PDFHussain Jiffry0% (1)
- RCCe21 Subframe AnalysisDocument26 pagesRCCe21 Subframe AnalysisHussain JiffryNo ratings yet
- BridgesDocument20 pagesBridgesHussain JiffryNo ratings yet
- Structural Assessment of Low Rise Reinforced Concrete Frames Under Tsunami LoadsDocument6 pagesStructural Assessment of Low Rise Reinforced Concrete Frames Under Tsunami LoadsHussain JiffryNo ratings yet
- Repair of Concrete StructuresDocument14 pagesRepair of Concrete StructuresHussain JiffryNo ratings yet
- CTBUH - Case Study Marina Bay Sands, SingaporeDocument7 pagesCTBUH - Case Study Marina Bay Sands, SingaporeHussain JiffryNo ratings yet
- World of JinnDocument23 pagesWorld of JinnAbu100% (13)
- 3 Soil Phase - RelationshipDocument10 pages3 Soil Phase - Relationshipsoulcivic100% (1)
- Exercise 1-Introduction of ConcreteDocument10 pagesExercise 1-Introduction of ConcreteHussain JiffryNo ratings yet
- 3 Soil Phase - RelationshipDocument10 pages3 Soil Phase - Relationshipsoulcivic100% (1)
- Laplace transform methods for solving differential equationsDocument39 pagesLaplace transform methods for solving differential equationsHussain JiffryNo ratings yet