Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Understanding Reflection of Light: Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 - Light GCKL 2011
Understanding Reflection of Light: Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 - Light GCKL 2011
Uploaded by
xai_hafeezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Understanding Reflection of Light: Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 - Light GCKL 2011
Understanding Reflection of Light: Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 5 - Light GCKL 2011
Uploaded by
xai_hafeezCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Module Form 4
5.1
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
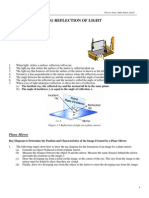
UNDERSTANDING REFLECTION OF LIGHT
What light is?
Is a form Light travel in a .................. and high speed about 300,000 km s-1.
How the light
ray reflected
by the surface
of mirror?
1. The light ray that strikes the surface of
the mirror is called .ray.
2. The light ray that bounces off from the
surface of the mirror is called
..
3. The is a line perpendicular
to the mirror surface where the reflection
occurs.
4. The angle between the incident ray and
the normal is called the
5. The angle between the reflected ray and
the normal is called
.
What is the
Law of
Reflection ?
Draw the ray
diagram of the
plane mirror
AO = incident ray
OB = reflected ray
i = angle of incident
r = angle of reflected
The Laws Of Reflection
1. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal ..The
angle of incident, i, is ..to the angle of reflection, r.
1. Consider an object O placed in front of a
plane mirror.
2. Measure the distance between the object
o and the mirror.
3. Measure the same distance behind the
mirror and mark the position as the image.
4. Draw the diverging ray from a point on
the image to the corner of the eye. The rays
from the image to the mirror must be
dotted to show that are virtual.
5. Finally, draw two diverging rays from
the object to the mirror to meet the
diverging rays from the image.
5-1
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
State the
characteristics
of the image
formed by
plane mirror
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
What is meant
by virtual
image?
Image that ..be seen on a screen.
What is meant
by real image?
GCKL 2011
Image that be seen on a screen.
CURVED MIRRORS:
Concave mirror
Convex mirror
r
1.Light (diverged, converged)
2. (virtual,real) principal focus
3. PF=
= Distance between the real principal focus
and the pole of the mirror.
State the
differences
between
concave mirror
and convex
mirror
1.Light (diverged, converged)
2.(virtual,real) principal focus
3.PF =
= Distance between the virtual
principal focus and the pole of the
mirror.
Common
terminology of
reflection of
light on a
curved mirror
Refer to the diagrams above and give the names for the following:
1.Centre of curvature ,C = .
...........................................................................................................
2.Pole of mirror, P = .
3.Radius of curvature ,r = CP =
4.Focal length, f = .
................................................................................................................
5.Object distance, = ..
6.Object distance , v = ..........................................................................................................
Construction
Rules for
Concave
Mirror
Ray 1
Ray 2
5-2
Ray 3
Physics Module Form 4
A ray parallel to the
principle axis is reflected to
pass through F.
Image formed
by concave
mirror:
Chapter 5 - Light
A ray through F is reflected
parallel to the principle
axis.
GCKL 2011
A ray through C is reflected
back along its own path.
Using the principles of construction of ray diagram, complete the ray diagrams for each of the
cases shown below:
u = object distance; v = image distance ; f = focal length ; r = radius of curvature
Note: Point of intersection in the position of the image
A
u < f ( Object between F and P )
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2.
3.
Application:
1.
2.
3.
u = f ( Object, O is at F )
Characteristics of
image:
1.
Application:
A reflector to
produce parallel
beam of light
such as a reflector in
1.
2.
f < u < 2f or f < u < r ( Object O is
between F and C
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2.
3.
u = 2f or u = r ( Object ,O is at C)
5-3
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2.
3.
Application:
1.
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
Eu > 2f or u > r ( Object, O is beyond C )
GCKL 2011
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2
3.
F u = ( Object ,O very far from the lens)
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2.
3.
Application:
Construction
Rules for
Concave
Mirror
Ray 1
A ray parallel to the
principal axis is reflected as
if it came from F.
Image formed
by concave
mirror:
Ray 2
A ray towards F is reflected
parallel to the principal
axis.
Ray 3
A ray towards C is reflected
back along its own path.
Using the principles of construction of ray diagram, complete the ray diagrams for each of the
cases shown below:
u = object distance; v = image distance ; f = focal length ; r = radius of curvature
A u < f ( Object between F and P )
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2.
3.
5-4
Application:
1.
2.
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
Check Yourself:
Objective Question:
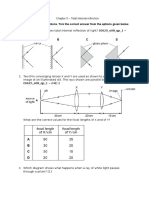
1. Which of the following is true of the laws of
reflection f light?
A The angle of incident is equal to the angle of
refraction
B The incident ray and the reflected ray are
always perpendicular to each other.
C The incident ray , the reflected ray and the
normal line through the point of incidence, all
lie on the same plane.
4.
A boy stands in front of a plane mirror a distance
5 m . When the boy moves toward the mirror by 2
m , what is the distance between the boy and his
new image?
A
C
E
2. The diagram shows a single ray of light being
directed at a plane mirror.
5.
What are the angles of incidence and reflection?
Angle of incidence
Angle of reflection
o
A
40
40o
o
B
40
50o
C
50o
40o
D
50o
50o
virtual
smaller
bigger
three times as far away
A light ray incident onto a plane mirror at an
angle of 50o
The characteristics of an image , formed by a
convex mirror for all positions of the object are
A
diminished, real and inverted
B
magnified , real, and upright
C
diminished ,virtual and upright
D
magnified , virtual and inverted
7.
A concave mirror has a focal length 20 cm.
What happen to the size of image when an object
is placed at a distance of 40 cm in front of the
mirror?
A
B
C
5-5
4m
8m
6.
3. The diagram shows a ray of light from a small bulb
strikes a plane mirror.
Where is the image of the bulb formed and its
characteristic?
A
At P and virtual
B
At Q and real
C
At R and virtual
B
D
An object is placed in front of a plane mirror.
Compare to the object, the image formed in the
mirror is always
A
B
C
D
40
2m
6m
10 m
diminished
magnified
same size of object
Physics Module Form 4
8.
Chapter 5 - Light
The figure shows a candle placed in front of a
concave mirror of focal length, f.
GCKL 2011
Section A (Paper 2)
Structure Question:
1. Diagram 3.1 shows a mirror at the corner of a shop.
The image formed is
A
B
C
D
9.
real, upright and magnified
real, inverted and diminished
virtual, inverted and magnified
virtual, upright and diminished
DIAGRAM 3.1 / RAJAH 3.1
(a) Name the type of mirror shown in Diagram 3.1
When an object is placed at a point 20 cm in
front of a concave mirror, a real image of the
same as the object is formed on a screen placed
next to the object. What is the focal length of the
mirror?
A
B
C
D
..
[1 mark]
(b) Name one characteristic of the image formed
by the mirror.
5 cm
10 cm
15 cm
20 cm
..
[1 mark]
(c) Sketch a ray diagram to show how the image
is formed.
10. Which of the following states the right reason for
replacing a plane mirror are used as rear- view
mirrors in motor vehicles with a convex mirror ?
A
B
C
D
To shine the object
To widen the field of view
To produce a brighter image
To produce a sharper image
Answer:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[3 marks]
(d) What is the advantage of using this type of
mirror in the shop?
[1 mark]
5-6
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
2. Diagram 4.1 shows the image of a patients teeth
seen in a mirror used by a dentist.
GCKL 2011
Section B(Paper 2)
Essay Question(20 marks)
Diagram 7.1 shows two cars, P and Q , travelling in
the opposite directions, passing through a sharp band.
A mirror is placed at X .
DIAGRAM 4.1
(a) Name the type of the mirror used by the
dentist.
.
[ 1 mark ]
DIAGAM 7.1
(b) State the light phenomenon that causes the
image of the teeth.
(a) Diagram 7.2 shows an incomplete ray
diagram when a plane mirror is placed at X.
...
[ 1 mark ]
(c) State two characteristics of the image
formed.
[ 2 marks ]
(d) In the diagram below, the arrow represents
the teeth as the object of the mirror.
Complete the ray diagram by drawing the
required rays to locate
the position of
the image.
DIAGRAM 7.2
(i)
Complete the ray diagram in Diagram 7.2
[2 marks]
[ 3 marks]
5-7
Physics Module Form 4
(ii)
Chapter 5 - Light
State the light phenomenon involved in (a)(i).
GCKL 2011
(ii)
Complete the ray diagram in Diagram 7.3
[2 marks]
[1 mark]
(iii) Based on your answer in (a)(i), state the problem
experienced by the driver in car P.
..
..............................................................................
[1 mark]
(b) Diagram 7.3 shows an incomplete ray diagram
when a curve mirror is placed at X to replace the
plane mirror in Diagram 7.2. The curve mirror is used
to overcome the problem that occur in (a)(iii).
(iii) Based on your answer in b(ii), how the curve
mirror solved the problem in (a) (iii)?
[1 mark]
( C) The characteristics of the image formed by the
curved mirror in Figure 7.3 is diminished,
virtual and upright.
(i) What happen to the characteristics of the
image when the focal length of the curved mirror
is increased?
DIAGRAM 7.3
(i)
Give the name of the curve mirror.
..
[1 mark]
..
[1 mark]
(ii) Give the reason for your answer in (c)(i).
..
[1 mark]
5-8
Physics Module Form 4
5.2
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2010
UNDERSTANDING REFRACTION OF LIGHT
The diagram shows the spoon bent when put inside the water.
State the
phenomenon
occurs.
How the
phenomenon
occurs?
Light travel from ..medium which is air to .(water), light will
be deviated .to the normal. Thus the spoon seems like bending after putting
inside the water.
Why light is
refracted?
It due to change in the of light as it passes from one medium into another.
Light travel more in water (or glass) than in air.
When a light beam passes from air into glass, one side of the beam is slowed before the other.
This makes the beam .
Three different
cases of refraction
Case 1:
Case 2:
Case 3:
i = 0 ,r = 0
i>r
i<r
5-9
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
When a ray of light crosses
the boundry between two
different mediums at a right
angle or the incident ray
..to normal,
State the Laws of
Refraction
GCKL 2010
Ray is light passes from
air(less dense) to
glass(denser).
the ray is
but
the speed of light is
.
The angles of
incidence and
refraction
are.
ray is bent
...
the normal
the speed of light
after
entering the glass
Ray of light passes from
glass(dense) to air(less
dense)
ray bent
..from
the normal
the speed of light
.
after emerging from
the glass.
The Laws Of Refraction
When the light travel from one medium to another medium which has a different optical density:
1
2. .
Refractive Index
1. When light travels between two mediums with different optical densities, it changes speed
and bends.
2. The speed of light will decrease when it enters an optically denser medium and increases when
it enters an optically less dense medium.
3. The angle of bending of light depends on the refractive index of the mediums and the angle of
incidence ,i.
How to define
refractive index
1. Refractive index, n is defined as,
n = sin i
sin r
where
Example:
The diagram shows a ray of light passing from
air to the block X.
n = Refractive index
i = the angle in medium less
dense
r = the angle in denser medium
A material with a higher
refractive index has a higher
density.
The value of refractive index , n
1
The refractive index has no units.
Calculate the refractive index of the block X.
Solution:
n = sin 50
sin 40
= 1.2
5-10
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
2.
GCKL 2010
Example:
n = speed of light in vacuum (air)
speed of light in medium
The speed of light in vacuum is 3 x 108 ms-1
and the speed of light in glass is 2 x 108 ms-1 .
Determine the refractive index of glass.
Solution:
0r
n = 3 x 108 ms-1
2 x 108 ms-1
= 1.5
n = va
vm
The refraction of light gives us a false
impression of depth.
3.Real Depth and Apparent Depth
Example:
A) The fish in the pond appears to be closer to
the surface than it actually is.
n = Real depth , H
Apparent depth, h
The following terms are defined:
Or
Real depth,H = The distance of the real
n = H O from the surface of the water.
h h= The distance of the
Apparent depth,
..I from the surface of the water.
5-11
(B) The apparent depth a swimming pool
looks shallower than it really is.
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2010
( C) A straight object place in water
looks bent at the surface.
Explanation:
1.Rays of light from the object travel from
2.Water is a ..medium
compared to air.
3. Therefore, rays of light
.from the normal as they
leave the water. The rays of light then enter the
eyes of the observer.
4. So the object appears to be
the surface of the water.
Experiment to investigate the relationship between the
angle of incidence and the angle of refraction.
Experiment to investigate the relationship between
real depth and apparent depth.
Hypothesis:
Hypothesis:
The angle of refraction . as the angle of
incidence
The apparent depth ..as the real depth
..
.
Aim of the experiment :
Aim of the experiment :
To investigate the relationship between
. and ..
Variables in the experiment:
To investigate the relationship between
.and the ..
Variables in the experiment:
Manipulated variable: ..
Responding variable:
Fixed variable: ..
List of apparatus and materials:
Manipulated variable: .
Responding variable: ..
Fixed variable:
List of apparatus and materials:
Glass block, ray box, white paper protactor, power
supply .
Pin, ruler, water, retort stand ,tall beaker
5-12
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
Arrangement of the apparatus:
Arrangement of the apparatus:
The procedure of the experiment which include the
method of controlling the manipulated variable and
the method of measuring the responding variable.
The procedure of the experiment which include the
method of controlling the manipulated variable and
the method of measuring the responding variable.
The glass block is placed on a white paper.
The outline of the sides of the glass block are traced on
the white paper and labelled as ABCD.
The glass block is removed.
The normal ON is drawn.
By using a protractor , the angle of incidence, i , is
measured = 20.
The glass block is replaced again on its outline on the
paper.
A ray of light from the ray box is directed along
incidence line.
The ray emerging from the side CD is drawn as line PQ.
The glass block is removed again.
The point O and P is joined and is drawn as line OP.
The angle of refraction, r is measured.
The experiment is repeated 5 times for the other angles of
incidence, i= 30 , 40,50, 60 and 70.
A pin is placed at the base of the beaker as object O.
The another pin is clamped horizontally onto the retort
stand as image position indicator, I
The beaker is filled with water.
By using a ruler ,the real depth of the pin is measured, H=
8.0 cm
The pin O is seen vertically above the surface of the
water.
The position of pin I is adjusted until parallax error
between the pin O and the pin I is non- existent.
By using the ruler again ,the position of pin I is measured
as the apparent depth = h
The experiment is repeated 5 times for the other value of
the real depth of water, ,i.e. D=10 cm,12 cm,14 cm and
16 cm.
Tabulate the data:
H/cm
Tabulate the data:
Sin i
Sin r
Analysis the data:
Plot the graph Sin r against Sin i
GCKL 2010
h/cm
Analysis the data:
Plot the graph h against H
5-13
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2010
Check Yourself:
Objective Question:
1
When light travels from one medium to another,
refraction take place. Refraction is caused by the
change in the
A
B
C
D
Figure shows a light ray travelling from medium
R to medium S.
amplitude of light rays
intensity of light rays
strength of light rays
velocity of light rays
Which of the following is true?
An observer cannot see the coin in an empty glass
as shown in Figure(a). However , he can see the
coin when the glass is filled with water as shown
in Figure(b).
A
B
C
The speed of light in medium R is larger than
the speed of light in medium S
The optical density of medium R is larger
than the optical density of medium S
The refractive index of medium R is larger
than the refractive index of medium S
The diagram shows a light ray directed into a
glass block.
Which is the angle of refraction?
Figure (a)
Figure (b)
The observer can see the coin in Figure (b) due to
A
B
C
D
the total internal reflection of light
the refraction of llight
the reflection of light
the diffraction of light
Which of the following is not caused by the
refraction of light ?
A light ray travels from medium P to medium Q.
Which of the following diagrams correctly shows
the path of the light ?
A fish in pond appears nearer to the surface
of the water
B The sunlight reaches to the earth in a curve
path
C A ruler appears to bend at the water surface.
D The sea water appear in blue colour
[ Medium P denser medium and Medium Q less
dense ]
5-14
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
9
GCKL 2010
Which of the following formulae can be used to
determine the refractive index of a medium?
A
B
C
7
Angle of incidence
Angle of refraction
Apparent depth
Real depth
Speed of light in vacuum
Speed of light in the medium
The diagram shows a light ray travels from liquid
L to liquid M.
10 The diagram shows a light ray travels from the air
into medium X.
Which of the following diagrams correctly shows
the path of the light ?
[ Refractive index of liquid M > Refractive index
of liquid L ]
What is the refractive index of medium X?
A
0.85
B
1.24
C
1.31
D
1.41
E
1.58
11 The diagram shows a light ray travels from the oil
into the air.
The diagram shows a light ray which travels from
the air to the glass.
What is the value of k?
[ Refractive index of oil = 1.4 ]
What is the refrective index of the glass?
A
Sin S
Sin Q
Sin Q
Sin R
Sin P
Sin R
Sin R
Sin S
5-15
A
B
C
D
44.4o
45.6o
54.5o
55.4o
58.9o
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
12 The diagram shows a light of ray travels from the
air into a glass block.
GCKL 2010
15 The diagram shows a coin is put at the base of
the beaker. The image of the coin appears to be 5
cm from the base of the beaker.
What is the refractive index of the glass block?
A
B
C
D
E
1.38
1.45
1.51
1.62
1.74
A
C
E
13 The speed of light in the air is 3 x 108 ms-1 .
What is The speed of light in a plastic block?
[ Refractive index of plastic = 1.2 ]
A
B
C
D
E
1.0 x 108 ms-1
1.5 x 108 ms-1
2.0 x 108 ms-1
Answer:
2.5 x 108 ms-1
3.0 x 108 ms-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
14 The diagram shows a boy appearing shorter when
he is in a swimming pool. The depth of the water
in the pool is 1.2 m.
[ Refractive index of water = 1.33 ]
What is the apparent depth of the pool?
A
C
E
0.1 m
0.9 m
1.6 m
What is the refractive index of the liquid?
8
B
5
13
8
11
D
13
5
8
19
14
B
D
0.3 m
1.1 m
5-16
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2010
Section A
(Paper 2)
Structure Question:
(C ) (i) Draw a Diagram of the light ray shown on
diagram 3.1, meeting the water surface RS, and show
its path after meeting the surface.
[1 mark]
1. The Diagram shows a side view of a water-filled
aquarium RSTU. An electric lamp, surrounded by a
shield with a narrow transparent slit, is immersed in
one corner of the aquarium at U. The light ray from
the slit shines on the water surface RS at an angle of
40o as shown in diagram below.
Water
40o
R
Water
40
Aquarium
Light
ray
Light ray
U
U
DIAGRAM 3.1
(a)
ii. Calculate the angle that this new path makes with
RS and label the angle.
[2 ma
[1 mark]
What is meant by refractive index of a
substance?
(d)
The lamp is then placed outside underneath
the aquarium with the light striking to the bottom of
the aquarium as shown in Diagram 3.2. Draw the light
ray on Diagram 3.2, after striking the aquarium.
[1 mark]
(b) If the refractive index of water is 1.33,
calculate the critical angle for a ray travelling
from water to air.
[1 mark]
[ 2 marks]
water
Light ray
Lamp
5-17
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2010
3. Figure(a) shows an object in a small pond. The
depth of the water in the pond is H. The image of
the objet appears to be h from water surface.
2. An observer is looking at a piece of coin at the
bottom of a glass filled with water as shown in
Diagram 3. He found that the image of the coin is
nearer to the surface of the water.
[
2
m
a
r
Figure(a)
k
s
]
(a) State the relationship between H and h
....................................................................
(a)(i)
State a characteristic of image in
Diagram 3.
(1 mark)
(b) When H = 4.5 m and the refractive index of
water is 1.33,[ determine the value of h .
[1 mark]
1
1
(2 marks)
]
(ii)
(b)
Name the science phenomenon
involve in the observation above.
[1 mark]
Explain why the image of the coin
appears nearer to the surface of the
water.
[2 marks]
(c) What happen to value of h when the pond is
poured with water of refractive index 1.40 ?
(c)
On Diagram 3, complete the ray
diagram from the coin to the observer's
eye.
[2 marks]
(1 mark)
[
1
]
5-18
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2010
Section B (Paper 2)
Essay Question
ii. Observe Figure 4(a) and Figure 4(b) carefully.
Compare the common characteristics of the pencil
and the print before and after they are removed
from the water and the glass block respectively.
Use a physics concept to explain the appearance
of the pencil and the print in water and under the
glass block respectively.
[5 marks]
1. Figure 4(a) shows a pencil placed in a glass of
water. Figure 4(b) shows the appearance of print
viewed from the top of a thick block of glass placed
over it.
pencil
Glass block
water
Figure 4(a)
Figure 4(b)
(a) i. Why does the pencil appear bent to our eyes?
Why does the print appear raised?
[1 mark]
Answer:
5-19
Physics Module Form 4
5.3
What is meant by
total internal
reflection?
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
UNDERSTANDING TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION
Total internal reflection is the complete reflection of light ray travelling from a
to a .................................medium.
Total: because 100% of light is reflected
Internal: because it happens inside the glass or denser medium.
What is meant by
critical angle ,c?
The critical angle, c, is defined as the angle of incidence (in the denser medium) when the angle
of refraction (in the denser medium), r is 90.
What are the
relationship
between the
critical angle and
total internal
reflection ?
5-20
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
When the angle of
incidence, i keeps on
increasing, r too
increases
And the refracted ray
moves further away
from the normal
And thus approaches
the glass- air
boundary.
State the two
conditions for
total internal
reflection to occur
GCKL 2011
The refracted ray
travels along the
glass-air boundary.
Angle of refraction, r
= 90.
This is the limit of
the light ray that can
be refracted in air as
the refracted in air
cannot be any larger
than 90.
The angle of
incidence in the
denser medium at the
limit is called the
critical angle, c.
If the angle of
incidence is
increased is
increased further so
that it is greater than
the critical angle,
(i > c):
- no refraction
- all the light is
totally in the
glass
This phenomenon is
called total internal
reflection.
1.
2.
What are the
relationship
between the
refractive index, n
and critical angle,
c?
What are the
phenomena
involving total
internal reflection?
1. Mirage
5-21
In hot days, a person traveling in a
car will see an imaginary pool of
water appearing on the surface of
the road.
The layes higher up are cooler and
denser.
Light ray from the sky travels from
denser to less dense medium and
will refracted away from the normal.
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
The angle of incidence increases
until it reach an angle greater than
the critical angle.
Total internal reflection occurs and
the light is reflected towards the aye
of the observer.
If the observers eye is in the correct
position, he will see a pool of
water(image of the sky) appearing
on the road surface.
This is known as a mirage.
When sunlight shines on millions of
water droplets in the air after rain, a
multi coloured arc can be seen.
When white light from the sun
enters the raindrops, it is refracted
and dispersed into its various colour
components inside the raindrops.
When the dispersed light hit the
back of the raindrop, it undergoes
total internal reflection.
It is then refracted again as it leaves
the drop.
The colours of a rainbow run from
violet along the lower part of the
spectrum to red along the upper part.
2. Rainbow
5-22
Physics Module Form 4
Give some
examples of
application of total
internal reflection.
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
1. The sparkling of a diamond
2. Periscope
A diamond has a high refractive
index.
The higher the refractive index, the
smaller the critical angle.
A small critical angle means total
internal reflection readily occurs.
Light is easily reflected inside the
diamond.
In this way, more light will be
confined within the diamond before
refracting out into the air.
The periscope is built using two
right angled 45 made of glass. The
critical angle of the prism is 42.
The angle of incidence is 45 which
is greater than the critical angle.
Total internal reflection occurs.
The characteristics of the image are:
Virtual, upright, same size.
Give the advantages of the prism periscope
compared to mirror periscope.
Answer:
1.
..
2.
5-23
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
3. Prism Binocular
A light ray experiences two total
internal reflections at each prism.
So the final image in binoculars is
virtual, upright and same size.
What are the benefits of using prism in
binoculars?
1.
2.
4. Optical Fibres
The external wall of a fibre optic is
less dense than the internal wall.
When light rays travel from a
denser internal wall to a less dense
external walls at an angle greater
than the critical angle, total internal
reflection occurs.
Give the advantage of using optical fibres
cables over copper cables.
1. .................................................................
2. .................................................................
.................................................................
3. .................................................................
.................................................................
5-24
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
4. .................................................................
.................................................................
Check Yourself:
Objective Question:
1
A ray of red light travelling in glass strikes the
glass-air boundary . Some light is reflected and
some is refracted. Which diagram shows the paths
of the rays?
[ Refractive index of medium X = 1.3
Refractive index of medium Y = 1.5 ]
Which of the following shows total internal
reflection?
The diagram shows light ray XO experiencing
total internal reflection when travelling from the
glass to air.
One of the diagram below shows the path of a
beam of light that is incident on a water-air
surface with angle of incidence greater than the
critical angle.
Which one is it?
Which statements about total internal reflection
are correct?
Which of the following diagram correctly shows
the total internal reflection of ray of light?
5-25
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
P - is more than the critical angle of glass
Q - The speed of light in the glass is higher than
in air
R - The refractive index of glass is greater than
air
A P and Q
B P and R
C Q and R
D P,Q and R
6
In which direction does the light move from O ?
A
B
C
D
The diagram shows a semi-circular plastic block
is placed in a liquid.
9
Which of the following is correct?
A
B
C
D
OQ
OR
OS
OT
A ray of light incident on one side of a
rectangular glass block. If the angle of refraction
in the glass block is 40o ,
which one of the following diagrams best
represents this ray?
[ The critical angle of glass is 42o ]
Density of the plastic block is less than
density of the liquid
Refractive index of the plastic block is
less than refractive index of the liquid
Critical angle of the plastic block is less
than critical of the liquid
Angle of incidence is less than critical
angle of the liquid
The diagram shows a ray of light passing through
medium M to medium N.
10 The diagram shows a light ray, P, directed into a
glass block. The critical angle of the glass is 42o.
In which direction does the light move from point
Q?
Which of the following is correct?
A The angle of reflection is 55o
B The critical angle of medium M less than 35o
C Density of medium M less than the density
of medium N
8
GCKL 2011
The figure shows a ray of light PO traveling in a
liquid strikes the liquid-air boundary.
[ The critical angle of the liquid = 45o ]
5-26
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
C
D
the greatest angle of incidence in optically
more dense medium
the greatest angle of incidence in optically
less dense medium
14 Which of the following shows the correct critical
angle , c of the semi- circular glass block ?
11 The diagram shows a light ray , M, directed into a
glass block. The critical angle of the glass is 42o.
In which diagram does the light move from point
O?
15 The diagram shows a light ray travelling from air
into a plastic block with an angle of incidence ,X.
What is the critical angle of the plastic?
12 The figure shows a ray of light is incident in air
to the surface of Prism A and B.
Which comparison is correct ?
A
B
C
13
16 The diagram shows a light ray travelling from air
into a glass prism.
Density of prism A < density of prism B
Critical angle of prism A < critical angle of
prism B
Refractive index of prism A < refractive
index of prism B
The critical angle is
A
B
the smallest angle of incidence in optically
more dense medium
the smallest angle of incidence in optically
less dense medium
What is the critical angle of the glass?
5-27
Physics Module Form 4
A 40o
C 60o
E 80o
17
18
Chapter 5 - Light
21 The diagram shows a cross- section of a fibre
optic cable.
B 50o
D 70o
The refractive index of water is 1.33.
What is the critical angle of the water.
A
44.5o
B
o
C
48.8
D
o
E
54.3
GCKL 2011
46.9o
49.2o
Which comparison is correct ?
A
B
C
The refractive index of plastic block is 13 .
5
What is the value of the cosine of the critical
angle of the plastic?
5
B
12
12
13
C
13
D
5
12
13
E
13
5
19 The figure shows a ray of light AO traveling in
medium X strikes the medium X-air boundary.
[ The refractive index of medium X = 1.12 ]
Density of P < density of Q
Density of P >density of Q
Density of P = density of Q
Answer:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
In which direction does the light move from O ?
A OE
C OC
B OD
D OB
20 Which of the following not applies the principle
of total internal reflection?
A
B
C
D
Prism binocular
Mirror periscope
Optical fibre
Road mirage
5-28
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
(c)
Section A
(Paper 2)
Structure Question:
Name other optical device that applies the
phenomenon in (a)(i).
[ 1 mark ]
1. Diagram 1 shows a cross-sectional area of an
optical fibre which consist of two layers of glass
with different refractive index. The glass which
forms the inner core, Y is surrounded by another
type of glass which forms the outer layer, X.
2. Figure 4 shows a traveller driving a car on a hot
day. The traveller sees a
puddle of water on the road a short distance ahead
of him.
Puddle of water
Figure 4
DIAGRAM 1
(a) (i) Name the light phenomenon observed in
optical fibre?
a) Which part of the air is denser?
( 1 mark )
[ 1 mark ]
(ii) Compare the refractive index of outer
layer X and inner core Y.
b) Name a phenomena of light that always depends
on the air density when light travels from the sky to
the earth before it reaches point X.
[ 1 mark ]
( 1 mark )
(b) The refractive index of inner core Y is 2.10.
Calculate the critical angle of the inner core
Y.
c) i) What is the phenomenon occurring at point X
..
(1 mark )
[ 2 marks ]
ii)
What is the puddle of water actually?
( 1 mark )
5-29
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
d) Using the diagram above, explain how the traveller
can see the puddle of
water on the road.
( 2 marks )
e) Name one optical instrument that uses the
phenomenon in (d)
( 1 mark )
3. Completing the ray diagram below, to show how a
periscope works: (critical angle of glass = 42o)
object
tctct
Glass
prism
Eye
e
5-30
GCKL 2011
Physics Module Form 4
5.4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
U N D E R S T A N D I N G
L E N S E S
Introduction
Lenses are made of ..material such as glass or clear plastics.
They have two faces, of which at least one is
Types of lenses
State the
differences
between convex
lens and concave
lens
Common
terminology of
reflection of light
on a curved mirror
(a) lens, also known as
converging lens.
It .at the centre of the lens.
(b) lens, also known as
diverging lens.
It is .at the centre of the lens.
Convex lens
Concave lens
When light ray which are parallel and close to
the principle axis .. on a convex lens, they
are and ............... to a point, F on the
principle axis. This point is a .. of the
convex lens.
When light rays are parallel to the principle
axis on a concave lens., they are ..
and appear to . from the
on the principle axis.
1. The focal point, F is a point on the .where all rays are .and
..to the axis that to it after passing through a convex
lens, or appear to ..from it after passing through a concave lens.
2. The focal length, f is the distance between the and the .
3. The optical centre, C is the geometric centre of the lens. It is the point through which light
rays pass through without
4. The principle axis is the line passing through the optical centre, C.
5-31
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
Construction rules
of convex lens
Rule 1:
A ray parallel to the principle axis is
refracted through the focal point, f.
Rule 2:
A ray passing through the focal point is
refracted parallel to the principle axis.
Rule 3:
A ray passing through the optical
centre, C travels straight without
bending.
The point of intersection is
..
The images formed by a convex lens
depend on the object distance, u.
Images form by
convex lens
Using the principles of construction of ray diagram, complete the ray diagrams for each of the
cases shown below:
u = object distance; v = image distance ; f = focal length
Note: Point of intersection in the position of the image
A
u < f ( Object between F and P )
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Application:
1.
2.
u = f ( Object, O is at F )
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Application:
1.
5-32
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
C
f < u < 2f or f < u < r ( Object O is
between F and C
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Application:
1.
2.
3.
4.
u = 2f or u = r ( Object ,O is at C)
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Application:
1.
Eu > 2f or u > r ( Object, O is beyond C )
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2.
3.
Application:
1.
2.
3.
F u = ( Object ,O very far from the lens)
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2.
3.
Application:
1.
2.
3.
5-33
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
Construction rules
of concave lens
GCKL 2011
Ray 1:
A ray parallel to the principle axis is refracted
as if it appears coming from the focal point, F
which is located at the same side of the
incident ray.
Ray 2:
A ray passing through the focal point is
refracted parallel to the principle axis.
Ray 3:
A ray passing through the optical centre, C
travels straight without bending.
The point of intersection is the position of the
image .
The image formed by a concave lens are
always :
Virtual, upright and diminished.
Image formed by
convex mirror:
Using the principles of construction of ray diagram, complete the ray diagrams for each of the
cases shown below:
u = object distance; v = image distance ; f = focal length
A u < f ( Object between F and P )
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2.
3.
Application:
1.
2.
(B ) f<u <2f (Object at between f and 2f)
Characteristics of
image:
1.
2.
3.
Application:
1.
2.
5-34
Physics Module Form 4
Power of lenses
Chapter 5 - Light
Power of a lens =
or
P =
1
f
1
.
Focal length
@
= 100
f( cm)
GCKL 2011
The unit of power of a lens is
Dioptre (D) or m-1
Convex lens : the power is taken to be
positive
Concave lens : the power is taken to be
negative
f = focal length
Linear Magnification (m) :
The linear
magnification , m
define as:
Where
f = focal length
u = object distance
v = image distance
m = linear magnification
ho = object height
hi = image height
Lens Formula
Sign Conventions
Type of lenses
Object distance ,u
Image distance, v
Convex lens
Always +
Object is always placed to the
left of the lens
+ if the image is real ( image
is formed on the right side of
the lens.
- if the image is virtual
( image is formed on the left
side of the lens).
Concave lens
Always +
Object is always placed to the
left of the lens
+ if the image is real ( image
is formed on the right side of
the lens
- if the image is virtual
( image is formed on the left
side of the lens).
Always +
Always +
Always Always -
Focal length, f
Power of length, P
Linear magnification, m
Size of image
ImI =1
Image and object are the same size
ImI >1
Enlarged image
ImI <1
Diminished image
5-35
Physics Module Form 4
Meaning of real
image and virtual
image
Chapter 5 - Light
A real imge is one which can be cast on a
screen.
GCKL 2011
A virtual imge is one which cannot be cast on a
screen.
Check Yourself:
Objective Question:
1
The image produced by a lens is caused by the
A
total internal reflaction of ray
B
diffraction of ray
C
refraction of ray
D
reflection of ray
The diagram shows parallel rays of light is
incident to a combination of plastics with
different refractive index.
Which of the following drawing is not correct
path of the light rays?
Which of the following is true?
Which of the following diagrams is correct?
The diagram shows parallel rays of light passing
through a liquid in glass container.
[ The refractive index of the liquid = 1.35 ]
A The unit of the power of lens is Watt
B The power of a convex lens is negative
C A lens with a shorter focal length has a
lower power
D The rays of light passes through the optical
centre of lens without any refraction
Which of the following diagrams is true?
5-36
Physics Module Form 4
6
Chapter 5 - Light
Diagram shows light rays passing through a
convex lens .
GCKL 2011
10 Figure shows four light rays A,B,C and D passing
through a convex lens. F is the focal point of the
length. Which of the following path of the light
rays is not correct?
What is the distance P ?
A
B
C
D
7
Image distance
Object distance
Focal length
Optical length
11 What is the power of a convex lens which has a
focal length 50 cm ?
A
C
E
The diagram shows the action of a magnifying
glass.
Which point is the principal focus of the lens?
-0.2 D
-2.0 D
4.0 D
B
D
0.2 D
2.0 D
12 The power of a lens is - 40 D. What is the type
of the lens and its focal length?
The diagram shows an image ,I is formed by a
convex lens.
Where is the position of the object?
Type of length
A
Concave lens
Focal length
2
-2.5 x 10 m
Concave lens
-2.5 x 10 m
C
D
E
Convex lens
Convex lens
Concave lens
-2.5 x 10 m
-2.5 x 10-2 m
-4.0 x 10-2 m
-2
2
13 A convex lens of focal length ,f. The lens
produces a enlarged , virtual and upright
image.The object distance is
The diagram shows an image ,I is formed by a
concave lens.
Where is the position of the object?
A
B
C
less than f
between f and 2f
same as 2f
more than 2f
14 A light bulb is placed at the principal focus of a
convex lens. After travelling through the lens the
rays of light is
A parallel
B converge
C diverge
5-37
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
15 The focal length of a convex lens is f . Which of
the following object distances , u will produced
an inverted image ?
A
C
u<f
f < u < 2f
B
D
GCKL 2011
19 A convex lens of focal length 20.0 cm is turned
to face a distant object. The position of the screen
is adjusted until a sharp inverted image is formed
on the screen.
What is the distance of the screen from the lens ?
u >f
u > 2f
16 The diagram shows an object which is placed at u
cm from centre of a convex lens. The focal length
of the lens is 20 cm.
A
C
E
15.0 cm
25.0 cm
50.0 cm
B
D
20.0 cm
40.0 cm
20 The characteristics image is produced by a
concave lens is
A
B
C
D
Which of the following characteristics of the
image is not correct when u is 10 cm ,15 cm , 35
cm and 45 cm from the lens?
u / cm Characteristics of the image
A
B
C
D
10
15
35
45
magnified,virtual,upright
diminished,virtual,upright
magnified,real,inverted
diminished,real,inverted
21 An object is placed at 18.0 cm from a convex
lens of focal length 20.0 cm.
What is the the characteristics of image ?
Virtual and bigger
Virtual and bigger
Real and smaller
Real and smaller
A
B
C
D
17 An object is placed 25 cm in front of a convex
lens and its image is formed at infinity. If the
object is placed 20 cm in front of the lens , the
image is
virtual, upright and magnified
real, inverted and magnified
virtual ,upright and diminished
real, inverted and diminished
22 A lens is placed between a light bulb and a
secreen. The distance between the light bulb and
screen is 60.0 cm. The position of the lens is
adjusted until the size of the image is same as the
size of the object.
What is the type and the focal lenghth of the
lens?
A inverted
B smaller than object
C formed on the same side as the object
18 The diagram shows an object ,O is placed in front
of a convex lens produced an image , I.
A
B
C
D
Which of the following is not true?
A The focal length of the lens is 60 cm
B The linear magnification is 1
C The image I is a real image
5-38
Type of lens
Convex lens
Convex lens
Concave lens
Concave lens
Focal length
30 cm
15 cm
30 cm
15 cm
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
23 An object is placed at a distance 10 cm in front of
a convex lens of power 5D.
What is the image distance and the characteristic
of the image?
A
B
C
D
24
Image distance
10.0 cm
10.0 cm
20.0 cm
20.0 cm
27 A convex lens with a focal length of 20.0 cm to
form an image which is 2 times the size of the
object. What is the object distance?
A
C
E
Characteristic of the image
Virtual image
Real image
Virtual image
Real image
A
C
E
C 26.7 cm
D 26.7 cm
A
B
C
B
D
5 cm
15 cm
25 cm
B
D
The upright image is formed
The size of the image is reduced
The brightness of the image is
reduced
1.0
4.0
26 An object is placed at a distance30 cm from a
convex lens with a focal length of 25.0 cm.
What is the linear magnification ?
What is the focal length of the lens?
A
C
E
2
4
6
B
D
10 cm
20 cm
31 The diagram shows a graph of object distance,u
against image distance ,v of the lens.
What is the linear magnification of the image?
0.5
3.0
5.0
15.0 cm
40.0 cm
30 A convex lens is used to produce a real,
magnified and inverted image. What is the effect
on the image produced when the upper portion of
the lens is covered by a coin ?
25 The diagram shows an image I of an object O is
formed by a convex lens.
A
C
E
B
D
29 An object of height 6.0 cm is placed at 8 cm
from a convex lens of power 50 D.
What is the image height?
A
2 cm
B
4 cm
C
5 cm
D
6 cm
E
8 cm
same side of the lens as the
object
the other side of the lens as
the object
same side of the lens as the
object
the other side of the lens as
the object
B 16.0 cm
10.0 cm
30.0 cm
60.0 cm
28 An object of height 5 cm is placed at 15 cm from
a convex lens of focal length 10.0 cm.
What is the image height?
An object is placed at a distance 80 cm in front of
a concave lens of focal length 20 cm.
What is the image distance and the characteristic
of the image?
Image distance Characteristic of the image
A 16.0 cm
GCKL 2011
3
5
A
C
E
5-39
5 cm
20 cm
80 cm
B
D
10 cm
40 cm
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
32 The diagram shows a graph of image distance,v
against linear magnification ,m of the lens.
GCKL 2011
(a) State the light phenomenon that causes the
image FIZIK to be enlarged.
(1 mark)
(b) What is the change size of the image if the
water is replaced with a transparent liquid of
a greater density?
(1 mark)
What is the focal length of the lens?
A
C
E
14.0 cm
16.0 cm
18.0 cm
Answer:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
B
D
15.0 cm
17.0 cm
(c) The glass of water is replaced with a lens M
with focal length of 10 cm. The distance
between the book cover and the centre of the
lens is 8 cm.
It is observed that the image FIZIK is
enlarged.
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
(i)
Name the type of lens M.
(1 mark)
(ii) Calculate the distance of the image from
lens M.
Section A
(Paper 2)
Structure Question:
1
The Figure shows an image of letters FIZI when
viewed through a glass of water.
The diagram shows an object is placed in front of
a convex of focal length 15.0 cm.
(a) (i)
5-40
Complete the ray diagram in the
diagram above to show the formation
of the final image
(3 marks)
Physics Module Form 4
(ii)
Chapter 5 - Light
State the characteristics of the image.
GCKL 2011
(b) If the object is now placed in front of the
lens, an image which is 4 times the size of
the object is formed.
............................................................
(2 marks)
(b) Determine the linear magnification
(2 marks)
(c) The object height is 2.5 cm,calculate the
image height.
(2 marks)
(i)
Calculate the object distance.
(2 marks)
(ii)
State the characteristics of the image.
(2 marks)
.................................................
(c) State the light phenomenon that causes the
image is formed by the lens?
( 1 mark)
...................................................................
(d) What is the effect on the image produced
when the lower portion of the lens is covered
by a card?
(1 mark)
(d) What will happen to the characteristis of the
image when
(i) the convex lens is replaced by a
concave lens of focal length 15.0 cm.
................................................................
............................................................
(2 marks)
(ii) the object is placed at the 10 cm
mark.
............................................................
(2 marks)
3
When an object is placed 40 cm from a convex
lens ,the image formed is of the same size as the
object.
(a)
Determine,
(i)
the focal length of the lens
(1 mark)
(ii)
the power of the lens
(1 mark)
5-41
Physics Module Form 4
5.5
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
THE USES OF LENSES IN OPTICAL DEVICES
Introduction
There are many types of optical devices used lenses such as magnifying glass, microscope,
telescope, camera and slide projector etc. For every types of the devices we must learn about the
uses of the instruments, lens characteristics is used, normal adjustment of the instruments , ray
diagrams and the characteristics of the final image which are formed .
1. Compound Microscope
Give the use of a
compound
microscope.
A microscope is used to observe and magnify tiny objects such as bacteria.
Draw a diagram to
describe the
formation of
image formed by
microscope.
1. It consist of two powerful .lenses of short focal length (5.0 cm-10.0 cm)
2. The lens which receives light rays from the objects is called the lens. The
lens which is used for viewing the final image is called the.. lens.
3. The focal length of the objective lens is fo whereas the focal length of the eyepiece lens is fe.
4. The object is placed at a distance between ..so that the imaged formed
is.., and .in front of the eyepiece lens.
5. The position of the eyepiece lens is adjusted until the position of the first image is less than fo
from the eyepiece lens.
Define the
characteristics of
the image formed
by objective lens o
microscope.
The final image formed ,..and
5-42
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
2. Magnifying glass
Give the use of a
compound
microscope.
A microscope is used to observe and magnify tiny objects such as bacteria.
Draw a diagram to
describe the
formation of
image formed by
microscope.
1. It consists of two powerful lenses of ..focal lengths .
2. An object is placed at a position ..the focal length of the lens.
3. The magnifying power if the focal length of the lens is shorter.
4. A shaper and larger image is seen at the near point of the eye. In general, the near point is
taken as 25 cm.
Define the
characteristics of
the image formed
by objective lens o
microscope.
The image formed is , ..and...
3. Astronomical Telescope
Give the use of a
compound
microscope.
A microscope is used to observe and magnify tiny objects such as bacteria.
Draw a diagram to
describe the
formation of
image formed by
microscope.
5-43
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
1. It consist of an ..lens and .lens.
2. The objective lens is used to receive light rays from distant object.
3. The first image formed is at focal point of the objective lens Fo. It is ,
and .
4. The first image now becomes the object for the eyepiece lens.
5. The lens is adjusted so that the first image is situated at the focal point
of the eyepiece lens , Fe.
6. The telescope is said to be in normal adjustment.
7. For normal adjustment of the telescope, the separation between the two lenses is fo + fe.
Define the
characteristics of
the image formed
by objective lens o
microscope.
The first image formed is at focal point of the objective lens Fo.It is , .
and ................................
The final image formed is at
4. Slide Projector
What is the
function of each
component of a
slide projector?
Component
Functions
Slide
Projector Lens
Acts as an object
The lens has to be placed far away from the
screen in order to get a large image.
Acts as a heat filter to protect slide from
getting over heated.
Condenser Lens
Draw a diagram to
describe the
formation of
image formed by
microscope.
1. It uses a lens to form a ., . and image
of the slide or film on a screen.
2. The slide being the is placed between ........ from the projector lens
The lamp is placed at the focal point of the mirror to reflect all light
from the lamp back to the ..
3. The movable projector lens focuses a sharp, and .......... image onto a screen.
4. The slide should be placed upside-down(inverted) in order to form an
image on the screen.
5-44
Physics Module Form 4
Define the
characteristics of
the image formed
by objective lens
of microscope.
Chapter 5 - Light
GCKL 2011
Upright, real , magnified
5. Camera
Draw a diagram to
describe the
formation of
image formed by
microscope.
State the parts in a
camera and their
functions?
1. The lens is used to produce a , and .
image on a light sensitive film at the camera.
2. The is used to adjust the size of the exposure time when taking photographs.
3. The ..speed is used to control the exposure time when taking photographs.
Check Yourself:
Objective Question:
1
Which of the following combinations is the
characteristics of a magnifying lens ?
Object distance/cm
Focal length/ cm
3
A
B
C
D
5
8
10
20
10
5
5
8
Which of the following is true about the eyepiece
of a microscope?
A
B
A convex lens is used as a magnifying glass.
What are the characteristics of the image?
A
B
C
D
magnified,upright,virtual
magnified,upright,real
magnified,inverted,virtual
magnified,inverted,real
5-45
Consist of a concave lens which has lower
power than the objective lens.
Consist of a convex lens which has lower
power than the objective lens.
Consist of a concave lens which has higher
power than the objective lens.
Consist of a convex lens which has higher
power than the objective lens.
Physics Module Form 4
4
Which of the following is true concerning the
operation of a compound microscope?
A
B
C
The focal length of objective lens greater
than the focal length of eyepiece
Both objective lens and eyepiece has a high
power.
The characteristics of final image are
magnified, upright and virtual
virtual,upright,magnified,located at the focal
point
B real,inverted,magnified,located at infiniti
C virtual ,inverted,magnified,located at infiniti
11
0.05
100
500
12
17.5 cm
45.0 cm
B
D
The characteristics of the image is formed by a
camera are
A
B
C
D
virtual,upright ,enlarged
real,inverted,diminished
virtual,inverted,diminished
real,upright,enlarged
The image is formed by a slide projector is
A
B
C
D
Two convex lens of focal length 100 cm and 5
cm respectively is used in a telescope. What is the
linear magnification of the telescope?
A
C
E
Linear
Distance between the
magnification lens /cm
5
24.0
5
30.0
4
30.0
4
24.0
0.2
16.0
Two convex lens of power 2.5D and 20 D
respectively is used in a telescope. What is the
distance between the lens in normal adjustment?
B
D
A telescope has two convex lens of power 4.0 D
and 20.0D respectively.
Which of the following is true?
10 The characteristics of final image in a telescope
are
Which of the following statements about the
objective lens and eyepiece of a telescope?
Power of objective Power of
lens
eyepiece
low
high
A
high
low
B
low
low
C
high
high
D
8.0 cm
22.5 cm
50.0 cm
GCKL 2011
A
B
C
D
E
virtual,diminished,upright
real,magnified,inverted
virtual,magnified,inverted
real,magnified,upright
A
C
E
8
The characteristics of image is formed by the
objective lens of a microscope are
A
B
C
D
Chapter 5 - Light
enlarged,real,upright
enlarged,real,inverted
diminished,virtual,upright
diminished,real,inverted
13 Which of the following optical instrument
produced real image?
20
105
A Telescope
C Microscope
5-46
B Magnifying glass
D Slide projector
Physics Module Form 4
Answer:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Chapter 5 - Light
(c) State two differences between telescope and
microscope by completing the table below.
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Telescope
Section A
(Paper 2)
Structure Question:
1
GCKL 2011
The diagram shows the arrangement of the lenses
in a compound microscope.
Microscope
The diagram shows the arrangement of the lenses
in a telescope. The power of lens A and lens B are
0.5 D and 5D respectively.
(a) Why do the light rays PQ and RS are
parallel?
(1 mark)
(a) Complete the ray diagram in the diagram
above.
Answer:
.
(b) State the focal length of
(i) lens A
(2 marks)
..........................................................
(ii) lens B
(2 marks)
..........................................................
(b) State the characteristics of the final image
formed.
(1 mark)
(c) What is the distance between lens A and lens
B?
(2marks)
..................................................................
5-47
Physics Module Form 4
Chapter 5 - Light
(d) What is the linear magnification of the
telescope?
(2 marks)
(e) In the diagram above , complete the ray
diagram of the telescope.
(3 marks)
(f) State the characteristics of the final image
formed.
(2 marks)
...................................................................
The figure shows the lens and mirror arrangement
for a slide projector.
(a)
What is the function of
(i)
concave mirror (1 mark)
..........................................................
(ii)
condenser lens (1 mark)
.
..........................................................
(b) State two normal adjustment should be done
while using the slide projector.(2 marks)
..................................................................
(c) State the characteristics of the final image
formed..
(2 marks)
..................................................................
5-48
GCKL 2011
You might also like
- Physic Chapter 5 - LightDocument37 pagesPhysic Chapter 5 - LighteffahaziraNo ratings yet
- 9TH - Icse - Physics - Worksheet - Reflection of Light 2Document5 pages9TH - Icse - Physics - Worksheet - Reflection of Light 2manojboa100% (3)
- Answer Scheme-Physics LightDocument38 pagesAnswer Scheme-Physics LightSelva RajNo ratings yet
- Class Test 1 (Light) - AnswersDocument7 pagesClass Test 1 (Light) - Answerskeyur.gala0% (1)
- Welder'S Qualification Test Certificate: (As Per Asme Sec Ix)Document2 pagesWelder'S Qualification Test Certificate: (As Per Asme Sec Ix)vijay100% (1)
- Exercise MATTERDocument8 pagesExercise MATTERShu85No ratings yet
- SPM Physics Form 4 Chapter 5 Light NotesDocument26 pagesSPM Physics Form 4 Chapter 5 Light NotesManisha Sekaran Muniandy100% (3)
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 5Document48 pagesForm 4 Physics Chapter 5Misratul A'la Mahyuddin100% (4)
- Chapter 5, Form 4Document9 pagesChapter 5, Form 4Teoh MilayNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 25Document24 pagesPhysics Chapter 25aznmusikianNo ratings yet
- Eclipse Technical DescriptionDocument1,156 pagesEclipse Technical DescriptionKarar AL-Dahlki100% (1)
- Light and Geometric OpticsDocument53 pagesLight and Geometric OpticsLeah May Tamayo ManayonNo ratings yet
- Particle Size AnalysisDocument36 pagesParticle Size AnalysisAayush Jha SauravNo ratings yet
- Part UhxDocument51 pagesPart UhxSaif Eddine MJNo ratings yet
- SSW - April 2020 - Lowres Pages 42 45 PDFDocument4 pagesSSW - April 2020 - Lowres Pages 42 45 PDFBaher ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- Heckroodt, R. O Guide To The Deterioration and Failure of Building MaterialsDocument169 pagesHeckroodt, R. O Guide To The Deterioration and Failure of Building MaterialsAlfredo Landaverde GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Introduction To ScienceDocument17 pagesExercise Introduction To ScienceShu85No ratings yet
- Learncbse - In-Light Reflection and Refraction Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 ScienceDocument37 pagesLearncbse - In-Light Reflection and Refraction Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 SciencetummalaajaybabuNo ratings yet
- Hapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument29 pagesHapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeShu85No ratings yet
- 23.ray OpticsDocument50 pages23.ray OpticsRakesh Ranjan Mishra100% (1)
- SGL PT Brochure Graphite Block Heat ExchangersDocument16 pagesSGL PT Brochure Graphite Block Heat ExchangersdardocapoNo ratings yet
- Optimization Using TOSCADocument16 pagesOptimization Using TOSCAJunyan GuoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Light: Normal Reflected Angle Incident AngleDocument13 pagesChapter 5: Light: Normal Reflected Angle Incident AngleChristopher AuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Light Teacher's GuideDocument38 pagesChapter 5 Light Teacher's GuideFahmi AmiNo ratings yet
- Light ModuleDocument38 pagesLight ModuleZulhisyam NordinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Light - Teacher'sDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Light - Teacher'sSuadrifRunDamahumNo ratings yet
- Documents - MX Chapter 5 Light Teachers Guide 558445afb6f9eDocument38 pagesDocuments - MX Chapter 5 Light Teachers Guide 558445afb6f9eMK Joey ThamNo ratings yet
- Topic: Light: Chapter Highlight: 5.4 Lenses Image Form by Convex Lenses Object Distance Ray Diagram Image Distance Image Characte Ristics UsesDocument14 pagesTopic: Light: Chapter Highlight: 5.4 Lenses Image Form by Convex Lenses Object Distance Ray Diagram Image Distance Image Characte Ristics UsesNorhisham Mohamed SobriNo ratings yet
- Homework 1: Chinese New Years BreakDocument11 pagesHomework 1: Chinese New Years BreakgamahimeNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument13 pagesReflectionRajesh kuamrNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light TestDocument2 pagesReflection of Light TestVaishnavi RajgopalNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Light (Reflection) C-XDocument2 pagesWorksheet Light (Reflection) C-Xpratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - QWADocument58 pagesChapter 10 - QWADr.K E Reby RoyNo ratings yet
- Important Question For Class 10 Science Light Reflection and RefractionDocument1 pageImportant Question For Class 10 Science Light Reflection and RefractionAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ch.10 - Light (Reflection)Document35 pagesCh.10 - Light (Reflection)Urmila GNo ratings yet
- Chapter22 2014 15Document23 pagesChapter22 2014 15Puteri Nur Shaheerah100% (1)
- Mac Test F5 2009Document6 pagesMac Test F5 2009NURUL AIN TAY BT ABDULLAH100% (1)
- 10 Science Imp ch10 1Document10 pages10 Science Imp ch10 1Satyansh SinghNo ratings yet
- s5 Physics Holiday Homework WorksheetDocument1 pages5 Physics Holiday Homework WorksheetA.P.SNo ratings yet
- SET 4 MODUL CEMERLANG FIZIK F4B5 2018 SkemaDocument41 pagesSET 4 MODUL CEMERLANG FIZIK F4B5 2018 SkemaJeemion JealiNo ratings yet
- Light ReflectionDocument37 pagesLight Reflectionimraan smNo ratings yet
- Competency-Based Questions - As Per NEP RecommendationsDocument5 pagesCompetency-Based Questions - As Per NEP RecommendationsWolf2No ratings yet
- Light Form 4 (Phsics)Document24 pagesLight Form 4 (Phsics)saffiya imanNo ratings yet
- Reqelford International Schoo: Light - Worksheet 1Document2 pagesReqelford International Schoo: Light - Worksheet 1shivaNo ratings yet
- G-10 Physics Important Questions FinalDocument29 pagesG-10 Physics Important Questions FinalRohan SenapathiNo ratings yet
- Extra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Document5 pagesExtra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Zoha AzizNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Reflection and Refraction of Light Study Notes 2015-16Document15 pagesClass 10 Reflection and Refraction of Light Study Notes 2015-16dvrao_chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Modul Kelas Bimbingan Fasa 2 Chapter 5: Light SPM 2003, Section A, No. 4 (7Document9 pagesModul Kelas Bimbingan Fasa 2 Chapter 5: Light SPM 2003, Section A, No. 4 (7Teoh MilayNo ratings yet
- Physics QB1 Class 10Document2 pagesPhysics QB1 Class 10Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction Selected Question With Answer 2Document28 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Selected Question With Answer 2SHEETAL GOLANo ratings yet
- 23 Ray OpticsDocument50 pages23 Ray Opticsanirudh100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document46 pagesChapter 3Moin KhanNo ratings yet
- 5 Physics Light Test Name: For The Multiple Choice Questions CIRCLE The Letter of The BEST Answer 1Document11 pages5 Physics Light Test Name: For The Multiple Choice Questions CIRCLE The Letter of The BEST Answer 1Rafael Marco ManubayNo ratings yet
- Latihan Light f1Document19 pagesLatihan Light f1igori76No ratings yet
- 10 THDocument3 pages10 THRohitNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Light RevDocument24 pagesGrade 10 Light RevDanny BlessyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 Class 10 Notes.Document9 pagesWorksheet 3 Class 10 Notes.John WickNo ratings yet
- G10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Document10 pagesG10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Urmila GNo ratings yet
- DPP (4-5) 12th Physics - AN Batch - Eng - WADocument3 pagesDPP (4-5) 12th Physics - AN Batch - Eng - WAYoutuber RSNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection Extra QuestionsDocument7 pagesLight Reflection Extra Questionskrishna priyaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-test Electric Potential, Current Electricity-A, Ray Optics-A 1mark Questions: (ANSWER ALL)Document4 pagesPHYSICS-test Electric Potential, Current Electricity-A, Ray Optics-A 1mark Questions: (ANSWER ALL)shylaNo ratings yet
- 5+mark+questions +CBSE+X +light +25 12 2019 PDFDocument45 pages5+mark+questions +CBSE+X +light +25 12 2019 PDFPiyushNo ratings yet
- Ch-9 Light Reflection & RefractionDocument25 pagesCh-9 Light Reflection & RefractionBasit RasoolNo ratings yet
- Light, Colour and SightDocument61 pagesLight, Colour and SightDayah D DebabNo ratings yet
- Sainik School Goalpara: Extra Homework Subject: Science (Physics) Class: XDocument4 pagesSainik School Goalpara: Extra Homework Subject: Science (Physics) Class: XBornil Bikash BhuyanNo ratings yet
- FAQ PhysicsDocument30 pagesFAQ Physicsamit21oct2005No ratings yet
- Cylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandCylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Etr Kualiti Fizik SPM 2013Document3 pagesEtr Kualiti Fizik SPM 2013Shu85No ratings yet
- Fric FricDocument1 pageFric FricShu85No ratings yet
- Integrated Curriculum For Secondary Schools: Ministry of Education MalaysiaDocument3 pagesIntegrated Curriculum For Secondary Schools: Ministry of Education MalaysiaShu85No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher GuideDocument20 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher GuideShu85No ratings yet
- Exercise Cell As The Basic Unit of Living ThingsDocument16 pagesExercise Cell As The Basic Unit of Living ThingsShu85100% (1)
- For Form 3Document1 pageFor Form 3Shu85No ratings yet
- ADocument20 pagesAShu85No ratings yet
- Final - Constitutive Behaviour of Bond in RC Structures Based On Pull Out Strength PDFDocument25 pagesFinal - Constitutive Behaviour of Bond in RC Structures Based On Pull Out Strength PDFRakesh SiempuNo ratings yet
- Physics Double Slit ExperimentDocument16 pagesPhysics Double Slit Experimentvikas vermaNo ratings yet
- Stain Test For Finishes: 1. DefinitionDocument4 pagesStain Test For Finishes: 1. DefinitionSoo SeoNo ratings yet
- Magic MilkDocument3 pagesMagic Milklahsivlahsiv684No ratings yet
- Physics Final Project PresentationDocument17 pagesPhysics Final Project Presentationapi-295869449No ratings yet
- Critical Review On Design of Shaft With Multiple Discontinuities and Combined Loadings ICCIET - 2014Document9 pagesCritical Review On Design of Shaft With Multiple Discontinuities and Combined Loadings ICCIET - 2014Harry Eduardo CuartasNo ratings yet
- Retrofit Plastics GBM März 2022Document23 pagesRetrofit Plastics GBM März 2022Sanel TucakovicNo ratings yet
- Molecular Drag Pumps: MDP SeriesDocument12 pagesMolecular Drag Pumps: MDP SeriesSupriya ManojNo ratings yet
- 9-GC HoodDesignandEntryEffects PDFDocument57 pages9-GC HoodDesignandEntryEffects PDFKyaw San OoNo ratings yet
- MG-880 Specification PDFDocument3 pagesMG-880 Specification PDFMartin HasskelNo ratings yet
- Effect of Structure On Properties of A Polymer.Document2 pagesEffect of Structure On Properties of A Polymer.Mohana Sandhya GorleNo ratings yet
- FE-Analysis of An Integrated Plate Connection Between Jacket Structure and Skirt-Pile Sleeve - (3) - MMC Oil & Gas EngineeringDocument3 pagesFE-Analysis of An Integrated Plate Connection Between Jacket Structure and Skirt-Pile Sleeve - (3) - MMC Oil & Gas EngineeringherisiswantogoNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document4 pagesLab 3vroody555No ratings yet
- Chap 3 MechanicsDocument45 pagesChap 3 MechanicsAngelo Luigi Yasay100% (2)
- Thermal Barrier CoatingDocument18 pagesThermal Barrier CoatingVishal VsNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - Chemistry and Physics - Oceanography 2021Document2 pagesLab 7 - Chemistry and Physics - Oceanography 2021juanNo ratings yet
- BSC Petroleum Engineering HandBook 2023Document43 pagesBSC Petroleum Engineering HandBook 2023rayyanibrahimkansangbata2005No ratings yet
- Rigaku BioSAXS Webinar 093009Document49 pagesRigaku BioSAXS Webinar 093009squirellNo ratings yet
- Watertite SP 2000Document2 pagesWatertite SP 2000Alexi ALfred H. TagoNo ratings yet
- Optimizacion de Sistemas de DistribucionDocument2 pagesOptimizacion de Sistemas de DistribucionJesus RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Laser Lamp Kit: Instruction ManualDocument18 pagesLaser Lamp Kit: Instruction ManualpowerdaggerNo ratings yet
- Structure Design Manual - Mar2018Document13 pagesStructure Design Manual - Mar2018aapennsylvaniaNo ratings yet