Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eoc Algii Ref Page
Uploaded by
api-259852565Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eoc Algii Ref Page
Uploaded by
api-259852565Copyright:
Available Formats
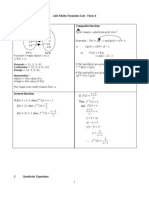
Algebra II Reference Page
Trigonometric Functions
y ,
r
csc =
r
y
r
x
cos = , sec =
x
r
y
x
tan = , cot =
y
x
sin =
Logarithm Properties
logb MN = logb M + logb N
M =
logb
logb M logb N
N
p
logb M = p logb M
x
r = x2 + y 2
logb x = y x = b
Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences and Series
a1
= 1st
r = common ratio
d = common difference
term
n = number of terms in series
an = nth term
Arithmetic Sequence: an = a1 + n 1 d
Geometric Sequence: an = a1 r n1
n a1+ an
or Sn = 1 n 2 a1+ n 1 d
2
2
n
a 1 r
Sn = 1
, r 1
1 r
a
S = 1 where r < 1
1 r
Sn =
Sum of a Finite Arithmetic Series:
Sum of a Finite Geometric Series:
Sum of an Infinite Geometric Series:
Combinations
nCr
Permutations
n!
r! n r !
n Pr
Binomial Theorem
a+b
n!
n r !
Quadratic Formula
b b2 4 ac
2a
2
y = ax + bx + c
x=
n n r r
=
a b
r
r =0
Interest Formulas
nt
r
n
Continuous compound interest: A = Pert
Compound interest: A = P 1 +
P = present value
A = future value
r = annual interest rate
t = time in years
n = frequency of compounding per year
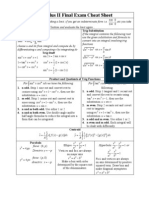
Algebra II Reference Page
Conic Sections Standard Equations
2
y =a xh
Parabola
y k
+k
x =a y k
or
= 4p x h
+h
x h = 4p y k
or
2
2
x h + y k = r2
Circle
x h
a2
Ellipse
xh
a2
Hyperbola
y k
b2
y k
=1
or
b2
=1
or
x h
y k
+
a2
b2
2
x h
y k
2
a
b2
=1
2
=1
Normal Curve Distribution
+ 2
+ 3
about 68%
about 95%
about 99.7%
Standard Deviation
Probability Formulas
Exclusive
P A or B = P A + P B
The standard deviation , , for values
x1, x 2 , x3 ,. . . , x n with mean is
determined by the following:
=
x1
+ x 2
+ . . . + xn
Inclusive
=
P A + P B P A and B
P A or B
2
Independent
P A and B = P A P B
Dependent
P A and B = P A P B A
Conditional
P A and B
P BA =
P A
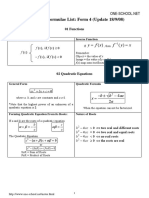
Algebra II Reference Page
Cramers Rule for Solving a System of Linear Equations
For a 2 2 System:
c1 b1
a1x + b1y = c1
a2 x + b2 y = c2
x=
c2 b2
a1 b1
a1 c1
y=
a2 c2
a1 b1
a2 b2
a2 b2
d1 b1 c1
a1 d1 c1
a1 b1 d1
d2 b2 c2
a2 d2 c2
a2 b2 d2
For a 3 3 System:
a1x + b1y + c1z = d1
a2 x + b2 y + c2 z = d2
a3 x + b3 y + c3 z = d3
x=
d3 b3 c3
a1 b1 c1
y=
a3 d3 c3
a1 b1 c1
z=
a3 b3 d3
a1 b1 c1
a2 b2 c2
a2 b2 c2
a2 b2 c2
a3 b3 c3
a3 b3 c3
a3 b3 c3
Converting Degrees to Radians
Converting Radians to Degrees
Multiply degree measure
by
180
Multiply radian measure
180
by
Definition of i
Absolute Value of a
Complex Number
i 2 = 1
i = 1
a + bi = a2 + b2
You might also like
- AMC Formulas PDFDocument17 pagesAMC Formulas PDFYounger Boxer MetalicNo ratings yet
- Maths Concepts and Formulae GuideDocument16 pagesMaths Concepts and Formulae GuideAt TanwiNo ratings yet
- Mathematical RelationshipsDocument5 pagesMathematical RelationshipsJuan A RaposoNo ratings yet
- Review of Trigonometric, Logarithmic, and Exponential FunctionsDocument5 pagesReview of Trigonometric, Logarithmic, and Exponential FunctionsArtist RecordingNo ratings yet
- HSC 3U Maths FormulaeDocument7 pagesHSC 3U Maths FormulaeHotz InatorNo ratings yet
- Eqworld: 34. + (A - 2Q Cos 2X) Y 0Document2 pagesEqworld: 34. + (A - 2Q Cos 2X) Y 0sijyvinodNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Algebra 2 TrigDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet Algebra 2 TrigfrancescoabcNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)Document4 pagesFormula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)naedkcinNo ratings yet
- QT Formulae ONLYDocument4 pagesQT Formulae ONLYSudhir PawarNo ratings yet
- Essential formulae for Number and AlgebraDocument16 pagesEssential formulae for Number and AlgebraMaruthappan Sundaram100% (1)
- EquationsDocument17 pagesEquationshasanmt23100% (1)
- Essential FormulasDocument7 pagesEssential FormulasShinigami01001No ratings yet
- HSN Course SummaryDocument26 pagesHSN Course SummaryQwaAlmanlawiNo ratings yet
- Math FormulasDocument22 pagesMath FormulasRushab ShahNo ratings yet
- Notes MathDocument4 pagesNotes MathNaveed Atta UllahNo ratings yet
- Ah FormulaeDocument5 pagesAh FormulaeVijay RajuNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Sets: IGCSE Mathematics Colegio Monte VIDocument7 pages1.1. Sets: IGCSE Mathematics Colegio Monte VIsrgonchiNo ratings yet
- Maths Revision Formulas ResultsDocument5 pagesMaths Revision Formulas ResultsDarrenPurtillWrightNo ratings yet
- List of Formulae in StatisticsDocument3 pagesList of Formulae in Statisticssawantdt100% (1)
- Quantum Mechanics - Homework Assignment 3: Alejandro G Omez Espinosa October 8, 2012Document7 pagesQuantum Mechanics - Homework Assignment 3: Alejandro G Omez Espinosa October 8, 2012Ale GomezNo ratings yet
- Calculus FormulaDocument2 pagesCalculus FormulaleeshiNo ratings yet
- MATH-FORMULAE1 mEquation of normal: y − y1 = − 1 ( x − x1 ) mmDocument16 pagesMATH-FORMULAE1 mEquation of normal: y − y1 = − 1 ( x − x1 ) mmNicholas Rogers80% (5)
- Calculus FormulasDocument19 pagesCalculus FormulasSherry MengNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Formulae ListDocument8 pagesAdd Maths Formulae ListWong Hui SeanNo ratings yet
- Formulasheetalgebra 2 TrigDocument4 pagesFormulasheetalgebra 2 Trigapi-265200443No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet: Graphs, Quartiles, Relative Frequency & MoreDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet: Graphs, Quartiles, Relative Frequency & MoreKathlynGraceNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Calculus 2 Formula Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Word - Calculus 2 Formula Cheat SheetHunterKing199375% (4)
- Calculus FormulasDocument19 pagesCalculus Formulaspjf004No ratings yet
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form4Document16 pagesSPM Add Maths Formula List Form4Alvin HonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document33 pagesLesson 2strom89No ratings yet
- MF9 Formula Sheet - List of FormulasDocument9 pagesMF9 Formula Sheet - List of FormulasBrendon Nyabinde75% (4)
- TRIGONOMETRIC RELATIONSDocument1 pageTRIGONOMETRIC RELATIONSVesna Suvala100% (1)
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 pagesMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Higher Maths: Formulae: Essential Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument5 pagesAdvanced Higher Maths: Formulae: Essential Trigonometric IdentitiesknoxmathsNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"From EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- AP Calculus Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Calculus Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- 25 Dividing Complex NumbersDocument8 pages25 Dividing Complex Numbersapi-259852565No ratings yet
- Make Up ProjectDocument1 pageMake Up Projectapi-259852565No ratings yet
- Review Sheet AnswersDocument1 pageReview Sheet Answersapi-259852565No ratings yet
- Inverse of A 2 X 2Document17 pagesInverse of A 2 X 2api-259852565No ratings yet
- Review SheetDocument1 pageReview Sheetapi-259852565No ratings yet
- August 6 - SubstitutionDocument34 pagesAugust 6 - Substitutionapi-259852565No ratings yet
- Multiplying Matrices Day 1Document31 pagesMultiplying Matrices Day 1api-259852565No ratings yet
- August 5 - EliminationDocument31 pagesAugust 5 - Eliminationapi-259852565No ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument4 pagesSyllabusapi-259852565No ratings yet