Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IE111 Tut 02
IE111 Tut 02
Uploaded by
swvo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pages1. The position vector of object B relative to object A is rBA = rB - rA = 50 m - 30 m = 20 m.
2. The vectors A = 35i N and B = 45j N. Their resultant vector is R = A + B = 35i + 45j N, with coordinate angles α = arctan(45/35), β = 0, γ = arctan(35/√(35^2+45^2)).
3. Given vectors A = 45 N and B = 65 N, with desired resultant R = 70 N at [105°, 5°, 98°], the vector C is calculated to have a magnitude and direction that produces this
Original Description:
IE111
Original Title
IE111 tut 02
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The position vector of object B relative to object A is rBA = rB - rA = 50 m - 30 m = 20 m.
2. The vectors A = 35i N and B = 45j N. Their resultant vector is R = A + B = 35i + 45j N, with coordinate angles α = arctan(45/35), β = 0, γ = arctan(35/√(35^2+45^2)).
3. Given vectors A = 45 N and B = 65 N, with desired resultant R = 70 N at [105°, 5°, 98°], the vector C is calculated to have a magnitude and direction that produces this
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesIE111 Tut 02
IE111 Tut 02
Uploaded by
swvo1. The position vector of object B relative to object A is rBA = rB - rA = 50 m - 30 m = 20 m.
2. The vectors A = 35i N and B = 45j N. Their resultant vector is R = A + B = 35i + 45j N, with coordinate angles α = arctan(45/35), β = 0, γ = arctan(35/√(35^2+45^2)).
3. Given vectors A = 45 N and B = 65 N, with desired resultant R = 70 N at [105°, 5°, 98°], the vector C is calculated to have a magnitude and direction that produces this
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
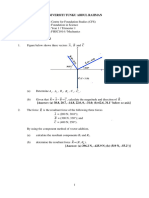
IE 111 Statics, Tutorial Sheet 02
1. Object A is defined below by a position vector rA = 30 m. Object B is at position
vector rB = 50 m. Calculate the position of B relative to A, ie rBA = rB - rA.
2. Vector A below is a force acting at the origin whose magnitude is 35 N. B is 45
N.
a. Express vectors A and B in vector form, ie A = Axi + Ayj + Azk.
b. Calculate the resultant force at the origin and express it in vector form.
c. Calculate the coordinate angles of the resultant force, ie , , and .
3. Vector A is 45 N and B is 65 N. A third vector C will be added to the system so
that the resultant vector, R = A + B + C, has a magnitude of 70 N and coordinate
angles [, , ] = [105, 5, 98]. Calculate the magnitude and direction of C.
You might also like
- VectorsDocument26 pagesVectorsAditya Bansal0% (1)
- HW 2 Solutions PDFDocument23 pagesHW 2 Solutions PDFJovani Perez100% (1)
- A282 Chapter 1 - Vector AnalysisDocument36 pagesA282 Chapter 1 - Vector AnalysisSisyloen Oirasor100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Vector AlgebraDocument28 pagesChapter 3 Vector AlgebraJosamy Martinez100% (1)
- 1 Methods Standards and Work DesignDocument19 pages1 Methods Standards and Work Designswvo0% (2)
- Microsoft PowerPoint - 2. ELMAG - 1 - Vector AlgebraDocument43 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - 2. ELMAG - 1 - Vector AlgebraDeni Ristianto100% (1)
- Physics Chapter 2Document13 pagesPhysics Chapter 2RaheEl Mukhtar0% (1)
- VectorsDocument9 pagesVectorsImash MinokaNo ratings yet
- Addition and SubtractionDocument3 pagesAddition and SubtractionbruktawitNo ratings yet
- Solutions For Take Home Quiz 1Document6 pagesSolutions For Take Home Quiz 1Nexty GamingNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Vector and ScalarDocument5 pagesTopic 2 - Vector and ScalarRomel TugadeNo ratings yet
- Forces in 3DDocument11 pagesForces in 3DAdeboye BusayoNo ratings yet
- BAB 3 BA501 Vector Dan ScalarDocument29 pagesBAB 3 BA501 Vector Dan ScalarAriez AriantoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document4 pagesTutorial 2Cheryl LowNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Revision Notes Vector AlgebraDocument8 pagesClass 12 Revision Notes Vector Algebrashubham upadhyayNo ratings yet
- ME 121: Engineering MechanicsDocument26 pagesME 121: Engineering MechanicsMuhammad FahadNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - Scalars and Vectors - 2023 - 2024Document3 pagesTutorial 2 - Scalars and Vectors - 2023 - 2024rachaelkalima11No ratings yet
- VectorsDocument46 pagesVectorsLeonidas RocksNo ratings yet
- ScalarsDocument11 pagesScalarsbisratbirhanu52No ratings yet
- Scientific Reasons / Short Questions: Chapter # 1 Scope of PhysicsDocument22 pagesScientific Reasons / Short Questions: Chapter # 1 Scope of PhysicsKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Teaching Notes - (Xiii) : VectorsDocument10 pagesTeaching Notes - (Xiii) : VectorsSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Vector AlgebraDocument2 pagesChapter 10 Vector AlgebraggNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 LM General Physics 1 Module3Document16 pagesGrade 12 LM General Physics 1 Module3Josue NaldaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Practice Problems, Module 2: Engineering MechanicsDocument16 pagesSolutions To Practice Problems, Module 2: Engineering MechanicsShaun Patrick AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Vector AdditionDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Vector Additionmeia quiderNo ratings yet
- Appendix A - AdditionandSubtractionofVectors - FinalDocument12 pagesAppendix A - AdditionandSubtractionofVectors - FinalPresley AbrauNo ratings yet
- Statics 2Document7 pagesStatics 2Allen ChristianNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document74 pagesSession 2Syed Shahzad AliNo ratings yet
- MechanicsDocument104 pagesMechanicsMerawi TilahunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Vector Algebra: 3.1 Introduction To Vector AnalysisDocument20 pagesChapter 3: Vector Algebra: 3.1 Introduction To Vector AnalysisGolden ChanNo ratings yet
- Physics1 ProblemSheet 2Document3 pagesPhysics1 ProblemSheet 2Sanie HeeseungNo ratings yet
- A Some Basic Rules of Tensor Calculus PDFDocument26 pagesA Some Basic Rules of Tensor Calculus PDFrenatotorresa2905No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Scalars and VectorsDocument14 pagesChapter 1 Scalars and VectorsSolomon G.No ratings yet
- Vector Calculations in KinematicsDocument36 pagesVector Calculations in KinematicsKarthikeyanRamanujamNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem: SolutionDocument3 pagesSample Problem: SolutionSagheer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 CutnellDocument26 pagesChap 1 Cutnellbl9nkverseNo ratings yet
- Review Notes in PhysicsDocument36 pagesReview Notes in Physicsroxy8marie8chanNo ratings yet
- Vectors and ScalarsDocument26 pagesVectors and ScalarsYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 03 Vectors ObjetivesDocument2 pagesActivity No. 03 Vectors ObjetivesJhonatan RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Vector Algebra: Complete Study Guide & Notes OnDocument8 pagesVector Algebra: Complete Study Guide & Notes Onsharan1281No ratings yet
- CH 3 8Document19 pagesCH 3 8Shaivalini SharmaNo ratings yet
- Motion in PlaneDocument20 pagesMotion in PlanekartikthedashingNo ratings yet
- Advanced Math 1 Principles and Sample ProblemsDocument5 pagesAdvanced Math 1 Principles and Sample ProblemsKrisha Jean MacalinoNo ratings yet
- Vector AlgebraDocument0 pagesVector Algebramothi26_pcmNo ratings yet
- Vektor: Mathematics For EngineeringDocument17 pagesVektor: Mathematics For EngineeringSyeihan S SyahNo ratings yet
- 02 Chapter 2 - Force VectorDocument20 pages02 Chapter 2 - Force VectorShaun KerouacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Vector Cross and Dot ProductDocument19 pagesChapter 4 Vector Cross and Dot ProductRyan Philip CatapangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.7-2.8Document32 pagesChapter 2.7-2.8haloNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Vectors Questions With Answers @moeremedialprojectDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Vectors Questions With Answers @moeremedialprojectsemiramisbah69No ratings yet
- C2 MatlabDocument22 pagesC2 MatlabDiana Carolina LeonNo ratings yet
- Vector Theory EDocument26 pagesVector Theory EthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Phy10 Wk01 Vector 1Document69 pagesPhy10 Wk01 Vector 1Jed Efraim EspanilloNo ratings yet
- Assessmnet 02Document16 pagesAssessmnet 02Lekhani DasanayakeNo ratings yet
- Vector Analysis: Multivector Review and Training CenterDocument10 pagesVector Analysis: Multivector Review and Training CenterMark FrancisNo ratings yet
- Ch. 3 SolutionsDocument41 pagesCh. 3 SolutionsLucas Merritt50% (2)
- Vectors EngDocument20 pagesVectors EngRusmila DewiNo ratings yet
- Vectors: Iit-Physics - Set - IDocument24 pagesVectors: Iit-Physics - Set - IHemant Kumar100% (1)
- Grade 9 Unit 7Document3 pagesGrade 9 Unit 7NatayNo ratings yet
- LN 4 - ME 1227 Engineering MechanicsDocument14 pagesLN 4 - ME 1227 Engineering MechanicsSakibNo ratings yet
- Ie 111 Statics Tutorial Sheet 15 Problem 1 Calculate The Centroid (X, Y) of The Shaded Figure BelowDocument1 pageIe 111 Statics Tutorial Sheet 15 Problem 1 Calculate The Centroid (X, Y) of The Shaded Figure BelowswvoNo ratings yet
- IE111 Tut 11Document2 pagesIE111 Tut 11swvoNo ratings yet
- Ie 111 Statics Tutorial Sheet 06 1. If F (300i - 200j + 150k) N, Calculate M, M and MDocument1 pageIe 111 Statics Tutorial Sheet 06 1. If F (300i - 200j + 150k) N, Calculate M, M and MswvoNo ratings yet