Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ERouting OSPF PT Practice SBA
ERouting OSPF PT Practice SBA
Uploaded by
JoseSalasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ERouting OSPF PT Practice SBA
ERouting OSPF PT Practice SBA
Uploaded by
JoseSalasCopyright:
Available Formats
ERouting OSPF PT Practice SBA : 88 % (22-05-2012)
A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity:
1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the
exam.
2. Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done. It will close automatically.
3. Click the Submit Assessment button to submit your work.
Introduction
In this practice Packet Tracer Skills Exam, you will:
finish the configuration of a partially configured network
establish connectivity to the UK and the Internet through the use of static and
dynamic routing
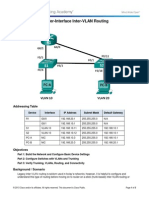
Addressing Table
Device
Interface
Address
Subnet Mask
S0/0/0
192.168.20.245
255.255.255.252
S0/0/1
192.168.20.241
255.255.255.252
S0/1/0
64 .100.50.2
S0/1/1
128.107.25.1
Lo0
172.16.0.4
Fa0/0
192.168.20.1
255.255.255.192
Fa0/1
192.168.20.118
255.255.255.248
S0/0/0
192.168.20.246
255.255.255.252
n/a
Lo0
172.16.0.1
255.255.255.255
n/a
Fa0/0
192.168.20.65
255.255.255.224
n/a
Fa0/1
192.168.20.113
255.255.255.248
n/a
S0/0/0
192.168.20.242
255.255.255.252
n/a
Lo0
172.16.0.2
255.255.255.255
n/a
Fa0/0
192.168.20.97
255.255.255.240
n/a
Fa0/1
192.168.20.114
255.255.255.248
n/a
Lo0
172.16.0.3
255.255.255.255
n/a
US-Admin
NIC
192.168.20.66
255.255.255.224
192.168.20.65
US-PC2
NIC
192.168.20.94
255.255.255.224
192.168.20.65
US-PC3
NIC
192.168.20.62
255.255.255.192
192.168.20.1
www.xyzcorp.com
NIC
192.168.20.98
255.255.255.240
192.168.20.97
US-HQ
Default Gateway
n/a
US-R1
US-R2
ServerLAN
Note: The password for user EXEC mode is cisco. The password for privileged EXEC
mode is class.
Step 1: Finish the IP Addressing.
Note: Initially, you can only access router US-R2 through the console connection on USAdmin.
a. Configure and verify interface addressing on US-R2.
Configure and activate all interfaces for US-R2 that are listed in the
addressing table.
b. Configure the correct IP addresses on US-PC2 and US-R1.
Configure US-PC2 with the last IP address in the subnet.
Configure the Fa0/1 interface on US-R1 with the last IP address in the
subnet.
c. Verify connectivity.
Step 2: Discover the Network.
Explore the network to determine the IP addressing of the serial interfaces that USHQ shares with US-R1 and US-R2.
Remotely access US-HQ. US-R1# telnet 192.168.20.245
Step 3: Configure Static and Default Routing.
a. Configure connectivity to the UK.
Using the next hop address 128.107.25.2, configure one summary static
route on US-HQ to include only the subnets used and reserved for the
UK. The UK subnets are listed in the following table:
HQ(config)# ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.255.252 128.107.25.2
UK Subnets
10.10.0.0/24
10.10.1.0/24
10.10.2.0/25
10.10.2.128/25
10.10.3.0/25
10.10.3.128/26
10.10.3.192/27
10.10.3.224/28
10.10.3.240/30
10.10.3.244/30
10.10.3.248/30
10.10.3.252/30
Configure a default route on US-HQ to send to the Internet all other
traffic for destinations that are not found in the US-HQ routing table. Use
the outbound interface argument.
HQ(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 S0/1/0
b. Verify static and default routing.
Step 4: Configure OSPF Routing.
a. Configure OSPF on US-HQ, US-R1, and US-R2.
Use OSPF process ID 3 and area 0.
Advertise each subnet individually with its corresponding wildcard mask.
On US-HQ, do not advertise the subnet to the Internet or the subnet to
UK.
HQ(config)# router ospf 3
HQ(config-router)# network 192.168.20.244 0.0.0.3 area 0
HQ(config-router)# network 192.168.20.240 0.0.0.3 area 0
US-R1 (config)# router ospf 3
US-R1 (config-router)# network 192.168.20.0 0.0.0.63 area 0
US-R1 (config-router)# network 192.168.20.112 0.0.0.7 area 0
US-R1 (config-router)# network 192.168.20.244 0.0.0.3 area 0
US-R2 (config)# router ospf 3
US-R2 (config-router)# network 192.168.20.64 0.0.0.31 area 0
US-R2 (config-router)# network 192.168.20.112 0.0.0.7 area 0
US-R2 (config-router)# network 192.168.20.240 0.0.0.3 area 0
Disable OSPF updates out interfaces where there are no OSPF
neighbors available.
HQ(config-router)# passive-interface s0/1/0
HQ(config-router)# passive-interface s0/1/1
US-R1 (config-router)# passive-interface fa0/0
US-R2 (config-router)# passive-interface fa0/0
Configure US-HQ to send the default route to US-R1 and US-R2 in
OSPF updates.
HQ(config-router)# default-information originate
b. Modify the default OSPF operation.
Configure US-R1 to always be the DR by using a priority of 150.
Pour Fa0/1 , S0/0
US-R1 (config-if)# ip ospf priority 150
Configure US-R2 to always be the BDR by using a priority of 75.
Pour Fa0/1 , S0/0
US-R2 (config-if)# ip ospf priority 75
Change the hello interval to 30 seconds on US-R1 and US-R2 for the
LAN that these two routers share with ServerLAN.
US-R1 (config-if)# ip ospf hello-interval 30
US-R2 (config-if)# ip ospf hello-interval 30
Verify OSPF neighbor status.
US-R1# show ip ospf neighbor
c. Verify that OSPF is fully operational.
Verify that the routing tables on US-R1, US-R2, and US-HQ contain all
the expected routes. It may be necessary to shutdown and then
reactivate interfaces to force OSPF to converge.
US-R1# show ip route
Step 5: Verify Full Connectivity.
Although these are not scored, the following connectivity tests should be successful.
To test the static route to UK, successfully ping between US-HQ and UK-PC1.
To test the OSPF neighbor establishment with ServerLAN, successfully ping between
US-Admin and www.xyzcorp.com.
To test end-to-end connectivity between the US and UK, successfully ping between
US-PC2 and UK-PC3.
To test the default route, successfully ping the Cisco Server from US-Admin.
Version 1.0
Created in Packet Tracer 5.3.2.0027 and Marvel 1.0.1
All contents are Copyright 1992 - 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
You might also like
- Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware / Software InterfaceFrom EverandComputer Organization and Design: The Hardware / Software InterfaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (12)
- PLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosFrom EverandPLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- Ospf Acl PT Practice Sba 100% (CCND Discovery 3 and 4)Document10 pagesOspf Acl PT Practice Sba 100% (CCND Discovery 3 and 4)Ranga Sanjeewa100% (1)
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPDocument7 pages4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPLeo Leo17% (6)
- Dispensing OpticianDocument4 pagesDispensing OpticianFernando Cortés de PazNo ratings yet
- ERouting OSPF PT Practice SBADocument3 pagesERouting OSPF PT Practice SBAChristopher PhillipsNo ratings yet
- PT Practice Sba OspfDocument4 pagesPT Practice Sba Ospfdepeters3183No ratings yet
- Lab 6.3.1 Configuring and Propagating An OSPF Default RouteDocument5 pagesLab 6.3.1 Configuring and Propagating An OSPF Default Routemohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- 4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocument11 pages4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessJesús EnriqueNo ratings yet
- 4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocument10 pages4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessHector De Jesus Tapia GorgonioNo ratings yet
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocument11 pages6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesntutaNo ratings yet
- Boson Ccna CourseDocument33 pagesBoson Ccna Courseedara1234No ratings yet
- Configure Admistrative RolesDocument20 pagesConfigure Admistrative RolesestebanNo ratings yet
- 6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocument11 pages6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesCesar Lazo DiazNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktik Lab 2 - Securing The Router For Administrative Access - CompressedDocument57 pagesLaporan Praktik Lab 2 - Securing The Router For Administrative Access - CompressedRizky RismadhantiNo ratings yet
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocument11 pages6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesHani GoytomNo ratings yet
- 6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF Authentication - ILMDocument11 pages6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF Authentication - ILMRony Schäfer JaraNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 3-Vlan Dan Vlan TrunkingDocument11 pagesPertemuan 3-Vlan Dan Vlan TrunkingAgustianto PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document8 pagesLab 4pzydf6wjxvNo ratings yet
- 4.2.2.13 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs - ILMDocument16 pages4.2.2.13 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs - ILMCte eduNo ratings yet
- 6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationDocument7 pages6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationGISTSalehuddinNo ratings yet
- HRRPDocument7 pagesHRRPJavier CastilloNo ratings yet
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRP - ILMDocument18 pages4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRP - ILMjanakp2004No ratings yet
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPDocument7 pages4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPjb100% (1)
- ERouting OSPF PT Practice SBADocument4 pagesERouting OSPF PT Practice SBAiAndry50% (2)
- 5.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN RoutingDocument5 pages5.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN RoutingNery Cifuentes0% (1)
- Lab 7 - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLsDocument6 pagesLab 7 - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLsmeerasNo ratings yet
- Lab 6.2.2 Configuring OSPF Authentication: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The EnterpriseDocument4 pagesLab 6.2.2 Configuring OSPF Authentication: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The Enterprisemohammad_shahzad_iiuiNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Static RoutingDocument5 pagesLab 4 - Static RoutingdaveNo ratings yet
- Lab 3: Configuring RIP V2 Routing: ObjectiveDocument8 pagesLab 3: Configuring RIP V2 Routing: ObjectiveRon PriceNo ratings yet
- 11 Cisco Device Functions - Lab ExercisesDocument7 pages11 Cisco Device Functions - Lab ExercisesTent DorinNo ratings yet
- ERouting OSPF PT Practice SBADocument4 pagesERouting OSPF PT Practice SBAwilsonmadridNo ratings yet
- 2675 Test12Document11 pages2675 Test12kinabapaul49No ratings yet
- 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLsDocument9 pages9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLsDaniel Sandoval CaizatoaNo ratings yet
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- IP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsFrom EverandIP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsNo ratings yet
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- Multicore DSP: From Algorithms to Real-time Implementation on the TMS320C66x SoCFrom EverandMulticore DSP: From Algorithms to Real-time Implementation on the TMS320C66x SoCNo ratings yet
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.From EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.No ratings yet
- Cisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1From EverandCisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1No ratings yet
- CCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamFrom EverandCCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamNo ratings yet
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONFrom EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Worksheet PDFDocument73 pagesCapital Budgeting Worksheet PDFProvakar DebNo ratings yet
- Presentation PfizerDocument13 pagesPresentation PfizerProvakar DebNo ratings yet
- Why Aircraft Industry Goes For Horizontal Rather Then AutonomousDocument10 pagesWhy Aircraft Industry Goes For Horizontal Rather Then AutonomousProvakar DebNo ratings yet
- Marketing ManagementDocument3 pagesMarketing ManagementProvakar DebNo ratings yet
- ProvakarDocument4 pagesProvakarProvakar DebNo ratings yet
- Birmingham Airport Case StudyDocument4 pagesBirmingham Airport Case StudyMelisa KhawNo ratings yet
- Pfizer Question Case Report MOBDocument3 pagesPfizer Question Case Report MOBProvakar DebNo ratings yet
- Introduction To VLSI Circuits and Systems Solution Manual by John P Uyemura PDFDocument77 pagesIntroduction To VLSI Circuits and Systems Solution Manual by John P Uyemura PDFSatish Bollam88% (8)
- Hello World! The Beginning of The Programing LanguageDocument1 pageHello World! The Beginning of The Programing LanguageProvakar DebNo ratings yet
- Incident Command System (Ics)Document8 pagesIncident Command System (Ics)ghhj erorNo ratings yet
- Kerala Ayurveda Kendra-MenuDocument6 pagesKerala Ayurveda Kendra-MenuPartheebanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03-Analysis and Design For Axial CompressionDocument46 pagesChapter 03-Analysis and Design For Axial Compressionyolo louoNo ratings yet
- 6419B ENU Trainer Handbook Part2Document142 pages6419B ENU Trainer Handbook Part2kaminetaNo ratings yet
- Pterosaurs Flying Contemporaries of The Dinosaur-Andre J Veldmeijer Mark Witton Ilja Nieuwland PDFDocument137 pagesPterosaurs Flying Contemporaries of The Dinosaur-Andre J Veldmeijer Mark Witton Ilja Nieuwland PDFManu Adri100% (7)
- Narrative Report v.1Document4 pagesNarrative Report v.1Crisyl Lipawen100% (1)
- Facilitating Learning ActivityDocument7 pagesFacilitating Learning ActivityKaren Lao67% (3)
- TM 1 TemplatesDocument80 pagesTM 1 Templatesflorence baliwang100% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S2212827116002080 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S2212827116002080 MainRio KatamusNo ratings yet
- Social Anxiety: How It's Different From ShynessDocument16 pagesSocial Anxiety: How It's Different From Shynessapi-318157111No ratings yet
- Traits & TypesDocument19 pagesTraits & TypesmehmoodanwerNo ratings yet
- Bi Tonic SortDocument20 pagesBi Tonic SortPragati VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Steps To Christ SummaryDocument3 pagesSteps To Christ SummaryFarai ManjoNo ratings yet
- Using ODBC XML Data With Crystal ReportsDocument30 pagesUsing ODBC XML Data With Crystal ReportsMenelaosNo ratings yet
- Viollet Le DucDocument9 pagesViollet Le Duc1SI17AT040 SREESHA K LNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Healing Effect of Honey On Infected Open Fracture WoundsDocument3 pagesA Study On The Healing Effect of Honey On Infected Open Fracture WoundsMuhammad AlamzebNo ratings yet
- Brahma SamhitaDocument120 pagesBrahma Samhitasubhobrata1No ratings yet
- The Emerald Tablet of Hermes TrimegistusDocument1 pageThe Emerald Tablet of Hermes TrimegistusTarik H. HindicNo ratings yet
- By Hank Friedman, USA: IntroductoryDocument9 pagesBy Hank Friedman, USA: IntroductoryShivarubhanNo ratings yet
- Islam and Prophet MuhammadDocument8 pagesIslam and Prophet MuhammadAmora MaxineNo ratings yet
- EE-480 Wireless Communications Week 2: Dr. Sajjad Shami Eed SST UMT LahoreDocument36 pagesEE-480 Wireless Communications Week 2: Dr. Sajjad Shami Eed SST UMT LahoreM Usman RiazNo ratings yet
- Intercultural Pragmatics in The Speech of American L2 Learners of Russian: Apologies Offered by Americans in RussianDocument30 pagesIntercultural Pragmatics in The Speech of American L2 Learners of Russian: Apologies Offered by Americans in RussianSaood KhanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Part ListDocument11 pagesElectrical Part ListLucky GodsNo ratings yet
- EM-C - 63×E1-AH SPO1460 Product DescriptionDocument15 pagesEM-C - 63×E1-AH SPO1460 Product Descriptionphuongnt1710100% (1)
- Your Wellness IntelligenceDocument1 pageYour Wellness Intelligencelackua100% (1)
- BFM Project FinalDocument76 pagesBFM Project FinalChirag LakhotiaNo ratings yet
- Criterion Based Automatic Generation of Question PaperDocument5 pagesCriterion Based Automatic Generation of Question PaperVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- FM&HM ManualDocument67 pagesFM&HM ManualAdabala Kumar Sanjay GIERMININGNo ratings yet
- Russuff SSM BeverlyDocument4 pagesRussuff SSM Beverlyazila taibNo ratings yet