Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Laws of Definite and Multiple Proportions
The Laws of Definite and Multiple Proportions
Uploaded by
kiki0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesThe document discusses the laws of definite and multiple proportions. The law of definite proportions states that the masses of elements in a compound are always in the same proportion. The law of multiple proportions states that when two elements form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other are in small whole number ratios. The document also provides guidelines for naming chemical compounds from their formulas.
Original Description:
Chemistry
Original Title
9.55
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the laws of definite and multiple proportions. The law of definite proportions states that the masses of elements in a compound are always in the same proportion. The law of multiple proportions states that when two elements form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other are in small whole number ratios. The document also provides guidelines for naming chemical compounds from their formulas.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesThe Laws of Definite and Multiple Proportions
The Laws of Definite and Multiple Proportions
Uploaded by
kikiThe document discusses the laws of definite and multiple proportions. The law of definite proportions states that the masses of elements in a compound are always in the same proportion. The law of multiple proportions states that when two elements form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other are in small whole number ratios. The document also provides guidelines for naming chemical compounds from their formulas.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
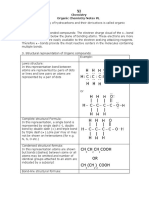
The Laws of Definite and Multiple Proportions
The rules for naming and writing formulas for compounds are
possible only because compounds form from the elements in
predictable ways.
These ways are summed up in two laws: the law of definite
proportions and the law of multiple proportions.
The Law of Definite Proportions
The law of definite proportions states that in samples of any
chemical compound, the masses of the elements are always in the
same proportions.
The Law of Multiple Proportions
The law of multiple proportions: Whenever the same two elements form
more than one compound, the different masses of one element that combine
with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole
numbers.
The Laws of Definite and Multiple Proportions
A Diagram of the Law of Multiple Proportions
9.1
9.1
9.1
Practicing Skills: Naming Chemical Compounds
In writing a chemical formula from a chemical name, it is helpful to
remember the following guidelines.
An -ide ending generally indicates a binary compound.
An -ite or -ate ending means a polyatomic ion that includes
oxygen is in the formula.
Practicing Skills: Naming Chemical Compounds
Prefixes in a name generally indicate that the compound is
molecular.
A Roman numeral after the name of a cation shows the
ionic charge of the cation.
You might also like
- Chemistry 1211K Test 1 Study GuideDocument2 pagesChemistry 1211K Test 1 Study GuidemeeeenonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basics of Process Engineers PDFDocument23 pagesChapter 1 Basics of Process Engineers PDFThiruThirunavukkarasu100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Concepts and Applications for Medicinal ChemistryFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Concepts and Applications for Medicinal ChemistryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Culminating: April 30, 2013Document5 pagesCulminating: April 30, 2013dance12345678No ratings yet
- Laws of Chemical CombinationDocument8 pagesLaws of Chemical CombinationYogendra VarmaNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chem Notes Class 11Document8 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chem Notes Class 11Jennika Jaison100% (1)
- Local Media7414347650560095855Document95 pagesLocal Media7414347650560095855katNo ratings yet
- Local Media4634812561624703664Document41 pagesLocal Media4634812561624703664katNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1MayankNo ratings yet
- What Is Chemical FormulaDocument6 pagesWhat Is Chemical FormulaVikrant DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- PDF 20231005 195926 0000Document20 pagesPDF 20231005 195926 0000UnKnOwn 0No ratings yet
- GC Outline 3rd PeriodicalDocument2 pagesGC Outline 3rd PeriodicalBejiNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry NotesDocument7 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry NotesEvelyn RiderNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Equations OclaritDocument10 pagesBalancing Chemical Equations OclaritChristian OclaritNo ratings yet
- Skills Iit Jee ChemistryDocument22 pagesSkills Iit Jee Chemistrysiddharth95480% (1)
- Notes 2 Class - XI A & B Subject-Chemistry Ch. 1 - Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument6 pagesNotes 2 Class - XI A & B Subject-Chemistry Ch. 1 - Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- STEM 3 (Chem) Definition of TermsDocument1 pageSTEM 3 (Chem) Definition of TermsBilly JamesNo ratings yet
- 4.2. Formulas, Equations, and Stoichiometry NotesDocument9 pages4.2. Formulas, Equations, and Stoichiometry Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- Clarisa Unit 2Document10 pagesClarisa Unit 2Noviana TevaNo ratings yet
- LAS Week 2 GenChem1 Q3Document6 pagesLAS Week 2 GenChem1 Q3Leonor LlavanesNo ratings yet
- Basic Scope of ChemistryDocument6 pagesBasic Scope of ChemistryMarie Dianne LimosNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 9th Notes Chapter 2Document4 pagesChemistry Class 9th Notes Chapter 2scribdexpressNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Balancing EquationsDocument14 pagesLesson 8 - Balancing Equations27kauasNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept & StoichiometryDocument8 pagesMole Concept & StoichiometryNareshNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument1 pageChempam tubigNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesChemistry NotesTanishq KapoorNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 OrganizerDocument1 pageUnit 4 Organizerapi-331028317No ratings yet
- Section B-Arc Tutors Chemistry Crash Course Sources of Hydrocarbon CompoundsDocument38 pagesSection B-Arc Tutors Chemistry Crash Course Sources of Hydrocarbon CompoundsakeemNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules: Laws of Chemical CombinationsDocument3 pagesAtoms and Molecules: Laws of Chemical CombinationsAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- 309 Havemeyer: Have You Seen This Hall in The Movies??? But Before We Start The ShowDocument28 pages309 Havemeyer: Have You Seen This Hall in The Movies??? But Before We Start The ShowPrince SanjiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Molecules and CompoundsDocument19 pagesChapter 5 Molecules and CompoundsChristian JamesNo ratings yet
- Vicky Chahar Vicky Chahar: HomoaromaticityDocument20 pagesVicky Chahar Vicky Chahar: HomoaromaticityVicky ChaharNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Definitions Term 3Document4 pagesSTPM Chemistry Definitions Term 3ChooNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument7 pagesChemistry ReviewerAlthea ElaineNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Q4 MODULE 6-NotesDocument18 pagesSCIENCE 10 Q4 MODULE 6-Notesluhh bhieNo ratings yet
- Beige Elegant Minimal Business Plan Executive Summary DocumentDocument1 pageBeige Elegant Minimal Business Plan Executive Summary DocumentDestrok27No ratings yet
- Laws of Chemical CombinationDocument9 pagesLaws of Chemical CombinationMexico EnglishNo ratings yet
- GenChem1 Activtiy4Document1 pageGenChem1 Activtiy4Crystal SnowNo ratings yet
- The Language of ChemistryDocument7 pagesThe Language of Chemistrydivya raghavNo ratings yet
- STOICHIOMETRYDocument49 pagesSTOICHIOMETRYanggiNo ratings yet
- 11chemistry - Organic chemistry-Notes&VLDocument14 pages11chemistry - Organic chemistry-Notes&VLPrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Print Sillabus TSSCDocument5 pagesPrint Sillabus TSSCsiscapeweNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM CHEMICAL FORMULA and NAMING OF COMPOUNDSDocument35 pagesGEN CHEM CHEMICAL FORMULA and NAMING OF COMPOUNDSKC KayeNo ratings yet
- Geometry Chapterwise PYQs-By-Galaxy-of-MathsDocument29 pagesGeometry Chapterwise PYQs-By-Galaxy-of-MathsDinkar YeoleNo ratings yet
- Compounds and Chemical FormulasDocument35 pagesCompounds and Chemical Formulasjolina OctaNo ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument2 pagesChem ReviewerJean Rene DiegoNo ratings yet
- Get To Know About Huckel's Rule & Its Use in Determining The Aromatic - Non-Aromatic Character of A CompoundDocument3 pagesGet To Know About Huckel's Rule & Its Use in Determining The Aromatic - Non-Aromatic Character of A CompoundFrank GomesNo ratings yet
- Chem 101Document10 pagesChem 101Jonar MarieNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Class 11 Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques PDFDocument32 pagesChemistry Notes Class 11 Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques PDFAnonymous j4ScL7Jp71% (7)
- Chemical Equations: Before You ReadDocument7 pagesChemical Equations: Before You ReadafhNo ratings yet
- (CHEMISTRYDocument6 pages(CHEMISTRYcponnusamy411No ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Chemical Reactions and Equation: EO: DefineDocument6 pagesLesson 3: Chemical Reactions and Equation: EO: DefineEdgardo VILLASEÑORNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChemical BondingBangtan ArmyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Module Notes and LinksDocument14 pagesOrganic Chemistry Module Notes and Linkshernys NietoNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesOrganic Chemistrysamhi96No ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)