Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Varnish: Amber Dammar Copal Rosin Sandarac Balsam Placename Libya Berenice
Uploaded by
tintinchanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Varnish: Amber Dammar Copal Rosin Sandarac Balsam Placename Libya Berenice
Uploaded by
tintinchanCopyright:
Available Formats
VARNISH
a transparent, hard, protective finish or film used to protect wood, metal & other
materials from air & moisture & to improve their appearance.
Varnish is traditionally a combination of a drying oil, a resin, and a thinner or
solvent.
Varnish finishes are usually glossy but may be designed to produce satin or semigloss sheens by the addition of "flatting" agents.
Varnishes are also applied over wood stains as a final step to achieve a film for gloss
and protection.
Varnishes used on metals are sometimes called lacquers which help prevent corrosion
without dulling the metallic appearance.
After being applied, the film-forming substances in varnishes either harden directly,
as soon as the solvent has fully evaporated, or harden after evaporation of the solvent through
certain curing processes, primarily chemical reaction between oils and oxygen from the air
(autoxidation) and chemical reactions between components of the varnish.
Environmental factors such as heat and humidity play a very large role in the drying
and curing times of varnishes. In classic varnish the cure rate depends on the type of oil used
and, to some extent, on the ratio of oil to resin. The drying and curing time of all varnishes
may be speeded up by exposure to an energy source such as sunlight or heat.
Other than acrylic and waterborne types, all varnishes are highly flammable in their
liquid state due to the presence of flammable solvents and oils.
COMPONENTS OF CLASSIC VARNISH
Drying oil different types include linseed oil, tung oil, and walnut oil. These
contain high levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Resin - include amber, dammar, copal, rosin {pine resin}, sandarac, balsam, and
others. The word varnish probably derives ultimately via ancient Greek from a
placename of a city in ancient Libya where resins from the trees of once existing
forests were sold. In modern English the ancient city is referred to as Berenice;
otherwise the existing city in modern Libya is called Benghazi.
Turpentine or solvent - Traditionally, natural (organic) turpentine was used as the
thinner or solvent, but has been replaced by several mineral based turpentine
substitutes such as white spirit or "paint thinner".
TYPES
Violin
Resin
Alkyd
Shellac
Spar Varnish
Drying oils
Polyurethane
Lacquer
Acrylic
Two-part
You might also like
- Solve Construction MaterialsDocument18 pagesSolve Construction MaterialsPawan SainiNo ratings yet
- Varnish: Varnish Is A Clear Transparent Hard Protective Finish or Film. Varnish Has Little or NoDocument7 pagesVarnish: Varnish Is A Clear Transparent Hard Protective Finish or Film. Varnish Has Little or NoRadost Galonja KrtinićNo ratings yet
- Varnish - WikipediaDocument9 pagesVarnish - WikipediaRamakant KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Surface Coatings - Paints, Varnish and LacquersDocument30 pagesSurface Coatings - Paints, Varnish and LacquersIzuNo ratings yet
- Transparent Wood Finishing Drying Oil Resin Thinner Solvent Glossy Color Pigment Paints Wood Stains Opaque TranslucentDocument1 pageTransparent Wood Finishing Drying Oil Resin Thinner Solvent Glossy Color Pigment Paints Wood Stains Opaque TranslucentjuandaleNo ratings yet
- Wa0014.Document16 pagesWa0014.Fatinha HernandesNo ratings yet
- Types of PaintsDocument22 pagesTypes of Paintsssm_majeed82% (11)
- Chapter One: 1.1 BackgroundDocument56 pagesChapter One: 1.1 BackgroundGalata BaneNo ratings yet
- Varnish and LacquerDocument8 pagesVarnish and LacquerVõ Xuân LâmNo ratings yet
- Paints, Varnishes and DistempersDocument14 pagesPaints, Varnishes and Distempersktnatasha100% (2)
- Varnishes: 20 - 21 Isha Patel 20 - 1 Divya Chaudhari 20 - 14 Riya Gamit 20 - 13 Tarannum VajifdarDocument21 pagesVarnishes: 20 - 21 Isha Patel 20 - 1 Divya Chaudhari 20 - 14 Riya Gamit 20 - 13 Tarannum VajifdardivyaNo ratings yet
- Varnish - Chemistry 2Document4 pagesVarnish - Chemistry 2Akshat GoyalNo ratings yet
- Homo Sapiens: Paint Is AnyDocument12 pagesHomo Sapiens: Paint Is AnyArmel Vic Baguinaon CuradaNo ratings yet
- Types of Paints With GlossaryDocument22 pagesTypes of Paints With Glossarylaniejane bedesNo ratings yet
- Paints and VarnishesDocument7 pagesPaints and Varnishesvikasmeerut100% (1)
- Types of PaintsDocument5 pagesTypes of PaintsSatyamTiwariNo ratings yet
- Paints: Building Technology 1Document26 pagesPaints: Building Technology 1KC PanerNo ratings yet
- Satish Varnish PDFDocument20 pagesSatish Varnish PDFCRAZY ARCHINo ratings yet
- Paint - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesPaint - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadidodido_67No ratings yet
- Material Portfolio LakshmiDocument33 pagesMaterial Portfolio Lakshmilakshmi achayathNo ratings yet
- The Carpenters, Joiners, Cabinet Makers and Gilders' Companion: Containing Rules and Instructions in the Art of Carpentry, Joinery, Cabinet Making, and Gilding - Veneering, Inlaying, Varnishing and Polishing, Dying and Staining Wood, & IvoryFrom EverandThe Carpenters, Joiners, Cabinet Makers and Gilders' Companion: Containing Rules and Instructions in the Art of Carpentry, Joinery, Cabinet Making, and Gilding - Veneering, Inlaying, Varnishing and Polishing, Dying and Staining Wood, & IvoryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chap 10. Paint N VarnishesDocument42 pagesChap 10. Paint N VarnishesRiwaj PhuyalNo ratings yet
- PaintDocument10 pagesPaintTú NgọcNo ratings yet
- PaintsDocument14 pagesPaintsBarshat KhakurelNo ratings yet
- Black MagicDocument32 pagesBlack MagicjananeyNo ratings yet
- Varnishes Bodu and DemoDocument15 pagesVarnishes Bodu and DemoKD DavidNo ratings yet
- Uv AbsorberDocument3 pagesUv AbsorberMohammad Doost MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Some Thing More About PaintDocument8 pagesSome Thing More About Paintsaurabh maneNo ratings yet
- French Polishing and Wood Surface Finishing for Amateurs - The Do It Yourself SeriesFrom EverandFrench Polishing and Wood Surface Finishing for Amateurs - The Do It Yourself SeriesNo ratings yet
- Paint IndustryDocument44 pagesPaint IndustryAyesha KhanNo ratings yet
- Liquid LubricantsDocument17 pagesLiquid LubricantsAkankshaMahajanNo ratings yet
- Woodworking Finishes - How To Choose and Use Them - You Can Make Stuff!!!Document16 pagesWoodworking Finishes - How To Choose and Use Them - You Can Make Stuff!!!Homayoon GeramifarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PAINTSDocument33 pagesChapter 6 PAINTSnabilahNo ratings yet
- Paint: Prof - DR/ Mostafa KhafagyDocument16 pagesPaint: Prof - DR/ Mostafa Khafagysic 20162085No ratings yet
- Rosin: Rosin, Also Called Colophony or Greek Pitch (Pix Græca), Is A Solid Form ofDocument3 pagesRosin: Rosin, Also Called Colophony or Greek Pitch (Pix Græca), Is A Solid Form ofMashudi FikriNo ratings yet
- Paints & VarnishesDocument6 pagesPaints & VarnishesmdnahidulhoquenhNo ratings yet
- Paints and CoatingsDocument29 pagesPaints and CoatingsRai JeanNo ratings yet
- PAINTDocument2 pagesPAINTKIM PAULO DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- PaintsDocument24 pagesPaintsanique_senior100% (1)
- BLDGTC11-Paints & CoatingsDocument32 pagesBLDGTC11-Paints & CoatingsArtsome Barbie G100% (1)
- Paint: Paint Is Any Liquid, Liquifiable, or Mastic Composition Which AfterDocument8 pagesPaint: Paint Is Any Liquid, Liquifiable, or Mastic Composition Which Aftersanthoshmarch9920No ratings yet
- Types of Furniture FinishesDocument7 pagesTypes of Furniture FinishesCara LiudmilaNo ratings yet
- Painter's MaterialsDocument14 pagesPainter's Materialsmickyraycon45No ratings yet
- Paint, Wood and Weather: Colin Mitchell-RoseDocument7 pagesPaint, Wood and Weather: Colin Mitchell-RoseJohn Anand KNo ratings yet
- Hwno.7 - Bsa1c - Saylon - Efraine AndreaDocument69 pagesHwno.7 - Bsa1c - Saylon - Efraine Andreaefraineandrea.saylonNo ratings yet
- Paints and VarnishesDocument10 pagesPaints and VarnishesKalyan Ramavath100% (1)
- Paints and VarnishesDocument24 pagesPaints and VarnishesEmina HuseinovicNo ratings yet
- Paints and Varnishes AssignmentDocument10 pagesPaints and Varnishes AssignmentKalyan Ramavath0% (1)
- PaintsDocument4 pagesPaintsShuvanjan DahalNo ratings yet
- Solvents and DiluentsDocument5 pagesSolvents and DiluentsChris FordNo ratings yet
- 4th Year-PaintsDocument60 pages4th Year-PaintsMd Mehrab Alam Shayikh100% (1)
- Waxes Are A Diverse Class of Organic Compounds That Are Hydrophobic, MalleableDocument5 pagesWaxes Are A Diverse Class of Organic Compounds That Are Hydrophobic, MalleableAmmar SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- PaintDocument11 pagesPaintMyo Win TheinNo ratings yet
- Composition of PaintsDocument4 pagesComposition of PaintsAleem Ahmed100% (1)
- Salicylic Acid in Flexible CollodionDocument6 pagesSalicylic Acid in Flexible CollodionOsamaAliMoussaNo ratings yet
- WaxDocument6 pagesWaxSuiko22No ratings yet
- Hardwax Oil: Oils Waxes IngredientsDocument11 pagesHardwax Oil: Oils Waxes IngredientsRajpal Singh KochharNo ratings yet
- Paints: Consists of 3 Components: Pigment:-Binder, Vehicle or Resin: - SolventDocument5 pagesPaints: Consists of 3 Components: Pigment:-Binder, Vehicle or Resin: - SolventAshitNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Finishing Furniture - Including Chapters on, Spraying, Opaque and Transparent FinishesFrom EverandA Guide to Finishing Furniture - Including Chapters on, Spraying, Opaque and Transparent FinishesNo ratings yet
- Staining and Polishing - Including Varnishing & Other Methods of Finishing Wood, with Appendix of RecipesFrom EverandStaining and Polishing - Including Varnishing & Other Methods of Finishing Wood, with Appendix of RecipesNo ratings yet
- Tokyo Animation CollegeDocument1 pageTokyo Animation CollegetintinchanNo ratings yet
- Getting A Sense of ThemeDocument27 pagesGetting A Sense of ThemetintinchanNo ratings yet
- Marina Bay SandsDocument13 pagesMarina Bay SandstintinchanNo ratings yet
- Leaning Tower of PisaDocument13 pagesLeaning Tower of PisatintinchanNo ratings yet
- Planning Guide For Escalators and Moving Walks - enDocument40 pagesPlanning Guide For Escalators and Moving Walks - entintinchanNo ratings yet
- Economic Assesment in Building Disney Land in HongkongDocument27 pagesEconomic Assesment in Building Disney Land in HongkongtintinchanNo ratings yet
- Santiago CalatravaDocument26 pagesSantiago CalatravatintinchanNo ratings yet
- Planning Guide For Escalators and Moving Walks - enDocument40 pagesPlanning Guide For Escalators and Moving Walks - entintinchanNo ratings yet
- Manuscript Accomplishment ReportDocument2 pagesManuscript Accomplishment ReporttintinchanNo ratings yet
- Theme Parks and AtrractionsDocument90 pagesTheme Parks and AtrractionstintinchanNo ratings yet
- 1636213602!Document15 pages1636213602!tintinchanNo ratings yet
- Amusement Park...Document18 pagesAmusement Park...tintinchanNo ratings yet
- Two Way SlabDocument27 pagesTwo Way SlabtintinchanNo ratings yet
- TO Construction Management: Specialization IiDocument14 pagesTO Construction Management: Specialization IitintinchanNo ratings yet
- Japanese AnimationDocument7 pagesJapanese AnimationtintinchanNo ratings yet
- Turning TorsoDocument7 pagesTurning TorsotintinchanNo ratings yet
- Raphael's :the Manual of AstrologyDocument276 pagesRaphael's :the Manual of AstrologyANTHONY WRITER100% (2)
- Building Utilities REVIEWERDocument10 pagesBuilding Utilities REVIEWERtintinchanNo ratings yet
- PD 957 Slides PedrosantosjrDocument34 pagesPD 957 Slides Pedrosantosjrtintinchan100% (1)
- ZodiacsDocument293 pagesZodiacsjoselito69100% (1)
- History of Animation PrinciplesDocument78 pagesHistory of Animation Principlestintinchan100% (7)
- Housing NHMFCDocument5 pagesHousing NHMFCtintinchanNo ratings yet
- Architectural StructuresDocument1 pageArchitectural StructurestintinchanNo ratings yet
- Walt Disney Studios: Animation Research TaskDocument14 pagesWalt Disney Studios: Animation Research TasktintinchanNo ratings yet
- Philippine Animation Industry Landscape - TholonsDocument11 pagesPhilippine Animation Industry Landscape - TholonstintinchanNo ratings yet
- Philippine Creative IndustryDocument164 pagesPhilippine Creative IndustrytintinchanNo ratings yet
- Animation Industry 2011 by BOI PDFDocument14 pagesAnimation Industry 2011 by BOI PDFshenyang28No ratings yet
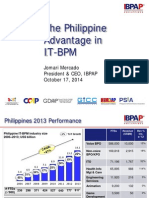
- Philippine Advantage in IT-BPMDocument17 pagesPhilippine Advantage in IT-BPMtintinchanNo ratings yet
- Walt Disney Organizational StructureDocument2 pagesWalt Disney Organizational StructuretintinchanNo ratings yet
- Animation History in AmericaDocument8 pagesAnimation History in AmericatintinchanNo ratings yet