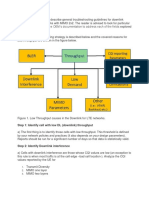
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HW 1
HW 1
Uploaded by
George PaceOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HW 1
HW 1
Uploaded by
George PaceCopyright:
Available Formats
HW #1: 10.
7, 8
Supplemental problems, Chap 1
Due: Jan 12, 2015
Prob. 10.8b: Use Matlab to calculate all spur frequencies to order 6 or less.
EE 440: Homework #1 Supplemental Problems
Supplemental Problem #1
Determine the number of US wireless subscriber connections in the year 2000 and the current
year. Compare to predictions made in the early 1980s by a marketing firm hired by AT&T (see
course textbook). Use CTIA (Cellular Telecommunications Industry Association) generated data.
Also determine the number of user minutes and text messages sent in the US between June of
last year and the current year.
Supplemental Problem #2
In reference to wireless user locations, identify the two primary wireless system types and
associated antenna gain values. Are high gain antennas always favored in wireless
communications? Why or why not? Also identify the three primary communication directionality
methods.
Supplemental Problem #3
Describe the GPS (Global Positioning System) method of triangulation for determining wireless
receiver location. What is the locus of points equidistant from one satellite? From two, three?
What is the minimum number of satellites required to identify a receiver located in space? Why?
Repeat for a receiver on the surface of the Earth.
Supplemental Problem #4
What is the optimum frequency range for wireless communications? Describe the disadvantages
of operating above and below this range.
Supplemental Problem #5
Wireless system configurations: Why is the message (voice or data) signal converted to a high
frequency (carrier) waveform for wireless transmission? Which hardware components are
necessary for this conversion? Describe the primary message (baseband) to carrier frequency
signal conversion methods and the advantages and disadvantages of each.
Supplemental Problem #6
Explain the FCC, RCC, FVC, and RVC procedure in cell phone connection establishment.
Explain the term cell in cell phones. Also describe the hand-off procedure.
You might also like
- ISDS 409 Exam 1 Study Guide - SolvedDocument10 pagesISDS 409 Exam 1 Study Guide - Solvedjay baoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Interference in Wireless Networks Application NoteDocument16 pagesFundamentals of Interference in Wireless Networks Application NotePuput Adi SaputroNo ratings yet
- Indoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GFrom EverandIndoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- LTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and OptimizationFrom EverandLTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and OptimizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Drive Test QuestionsDocument9 pagesDrive Test Questionsmoses50% (2)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Wireless Communication SystemsDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Wireless Communication SystemsPuja Kusuma50% (2)
- Exam 2013 - MarkingDocument6 pagesExam 2013 - MarkingMoses KaswaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Question Paper For JntuDocument4 pagesMobile Computing Question Paper For JntuBonam SandeepNo ratings yet
- 4g Lte ThesisDocument7 pages4g Lte ThesisFindSomeoneToWriteMyPaperUK100% (2)
- TSM 610-HW4Document3 pagesTSM 610-HW4Anonymous axHgedNo ratings yet
- 0517 Global System For Mobile Communication GSMDocument19 pages0517 Global System For Mobile Communication GSMkelvin ambazaNo ratings yet
- Ece Viii Wireless Communication (06ec81) NotesDocument108 pagesEce Viii Wireless Communication (06ec81) NotesAnupa Chandan100% (1)
- CTU BER White Paper v2Document31 pagesCTU BER White Paper v2Thuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- DL Throughput Troubleshooting - LteDocument6 pagesDL Throughput Troubleshooting - LteMahesh PratapNo ratings yet
- Downlink Throughput Troubleshooting - Lauro - Expert Opinion - LTE UniversityDocument4 pagesDownlink Throughput Troubleshooting - Lauro - Expert Opinion - LTE Universityalimola1248No ratings yet
- 3G Interview Questions and Answers ListDocument9 pages3G Interview Questions and Answers ListEngr AliNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Technical Report Series: 1x EV-DO Forward Link Physical and MAC LayerDocument12 pagesComputer Science Technical Report Series: 1x EV-DO Forward Link Physical and MAC LayerJoyal H L MenezesNo ratings yet
- CDMA Drive TestDocument16 pagesCDMA Drive Testhamed_hashim2001No ratings yet
- MC (SampleDocument11 pagesMC (SampleCabdi XuseenNo ratings yet
- EC8551 CN Question BankDocument43 pagesEC8551 CN Question BankRaja Pirian100% (3)
- Review Questions Test 1 AnswerDocument81 pagesReview Questions Test 1 AnswerhgghkjNo ratings yet
- Review Questions For Test-1 (With Answers) : Chapter 1: Introduction To Data CommunicationsDocument81 pagesReview Questions For Test-1 (With Answers) : Chapter 1: Introduction To Data CommunicationshgghkjNo ratings yet
- Downlink Throughput TroubleshootingDocument4 pagesDownlink Throughput TroubleshootingAbel MumaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Interference PDFDocument15 pagesFundamental of Interference PDFfarrukhmohammedNo ratings yet
- Communication System and Digital Network 2 City and Guilds Syllabus T3Document13 pagesCommunication System and Digital Network 2 City and Guilds Syllabus T3tchadza100% (1)
- Mobile Computing: Sixth Semester Diploma Examination in Engineering/Technology-MARCH, 2014Document17 pagesMobile Computing: Sixth Semester Diploma Examination in Engineering/Technology-MARCH, 2014Midhun CMNo ratings yet
- Chapter V FinalDocument16 pagesChapter V FinalhariNo ratings yet
- Jntuworld: R07 Set No. 2Document6 pagesJntuworld: R07 Set No. 29010469071No ratings yet
- Experiment No.1: 1. AIM: 2. EquipmentDocument7 pagesExperiment No.1: 1. AIM: 2. EquipmentNilesh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Chapte Rwise Content DocxDocument18 pagesChapte Rwise Content DocxwexidaNo ratings yet
- Teletraffic Engineering and Network PlanningDocument14 pagesTeletraffic Engineering and Network PlanningMuhammad RidlonNo ratings yet
- LTE Field Testing RCR Feature ReportDocument24 pagesLTE Field Testing RCR Feature ReportDaniel RoureNo ratings yet
- Downlink Throughput TroubleshootingDocument4 pagesDownlink Throughput TroubleshootingcspkerNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks Seminar Report and TopicDocument32 pagesWireless Networks Seminar Report and TopicAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Mimo Antenna Selection ThesisDocument8 pagesMimo Antenna Selection ThesisPaySomeoneToDoMyPaperCanada100% (1)
- Mobile Computing Previous Papers by JNTUKDocument4 pagesMobile Computing Previous Papers by JNTUKKumara Raja Jetti100% (1)
- Downlink Throughput Troubleshooting: LauroDocument5 pagesDownlink Throughput Troubleshooting: LauroImran KhanNo ratings yet
- Answer Q2 NIITDocument21 pagesAnswer Q2 NIITvannhuy100% (1)
- Lte Advanced Zahidghadialy 121117090131 Phpapp01Document11 pagesLte Advanced Zahidghadialy 121117090131 Phpapp01Jordan RashevNo ratings yet
- 05 - LTE KPI OverviewDocument52 pages05 - LTE KPI Overviewmazen100% (3)
- Definiti o 1Document2 pagesDefiniti o 1Abdul HameedNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Network Chapter 1Document7 pagesData Communication and Network Chapter 1Alia NadzirahNo ratings yet
- Wireless Measurement System For CDMA Base Station Transmit PowerDocument4 pagesWireless Measurement System For CDMA Base Station Transmit PowerMohit PatelNo ratings yet
- Cs9251 Mobile ComputingDocument13 pagesCs9251 Mobile ComputingSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Downlink Throughput TroubleshootingDocument4 pagesDownlink Throughput TroubleshootingfarhanhhhNo ratings yet
- LTE Uplink Throughput TroubleshootingDocument4 pagesLTE Uplink Throughput TroubleshootingsumantabhuinNo ratings yet
- Chaitanya Dabke EETS 8392: Wireless Internet: Ans. TrueDocument4 pagesChaitanya Dabke EETS 8392: Wireless Internet: Ans. TrueShantamNo ratings yet
- CN 3Document8 pagesCN 3Yalamanchili PavanNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Exam Paper by JNTUKDocument4 pagesMobile Computing Exam Paper by JNTUKKumara Raja JettiNo ratings yet
- Jimma University: Jimma Institute of TechnologyDocument5 pagesJimma University: Jimma Institute of TechnologyGenene GebreNo ratings yet
- 2.2.4.3 Lab - Researching WAN TechnologiesDocument5 pages2.2.4.3 Lab - Researching WAN TechnologiesSeptimanjaniNo ratings yet
- ITN 100 - Quiz 1Document6 pagesITN 100 - Quiz 1ahlam1707No ratings yet
- Academic 52813 3025753 72022 PDFDocument5 pagesAcademic 52813 3025753 72022 PDFfkkgđkjkNo ratings yet
- Lte LectureDocument106 pagesLte LectureJunior Diaz100% (1)
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesFrom EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- OQAM/FBMC for Future Wireless Communications: Principles, Technologies and ApplicationsFrom EverandOQAM/FBMC for Future Wireless Communications: Principles, Technologies and ApplicationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The International Telecommunications Regime: Domestic Preferences And Regime ChangeFrom EverandThe International Telecommunications Regime: Domestic Preferences And Regime ChangeNo ratings yet